06.G BIO Mutations (PART G)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Mutagen
A chemical or physical agent that interacts with DNA and causes a mutation
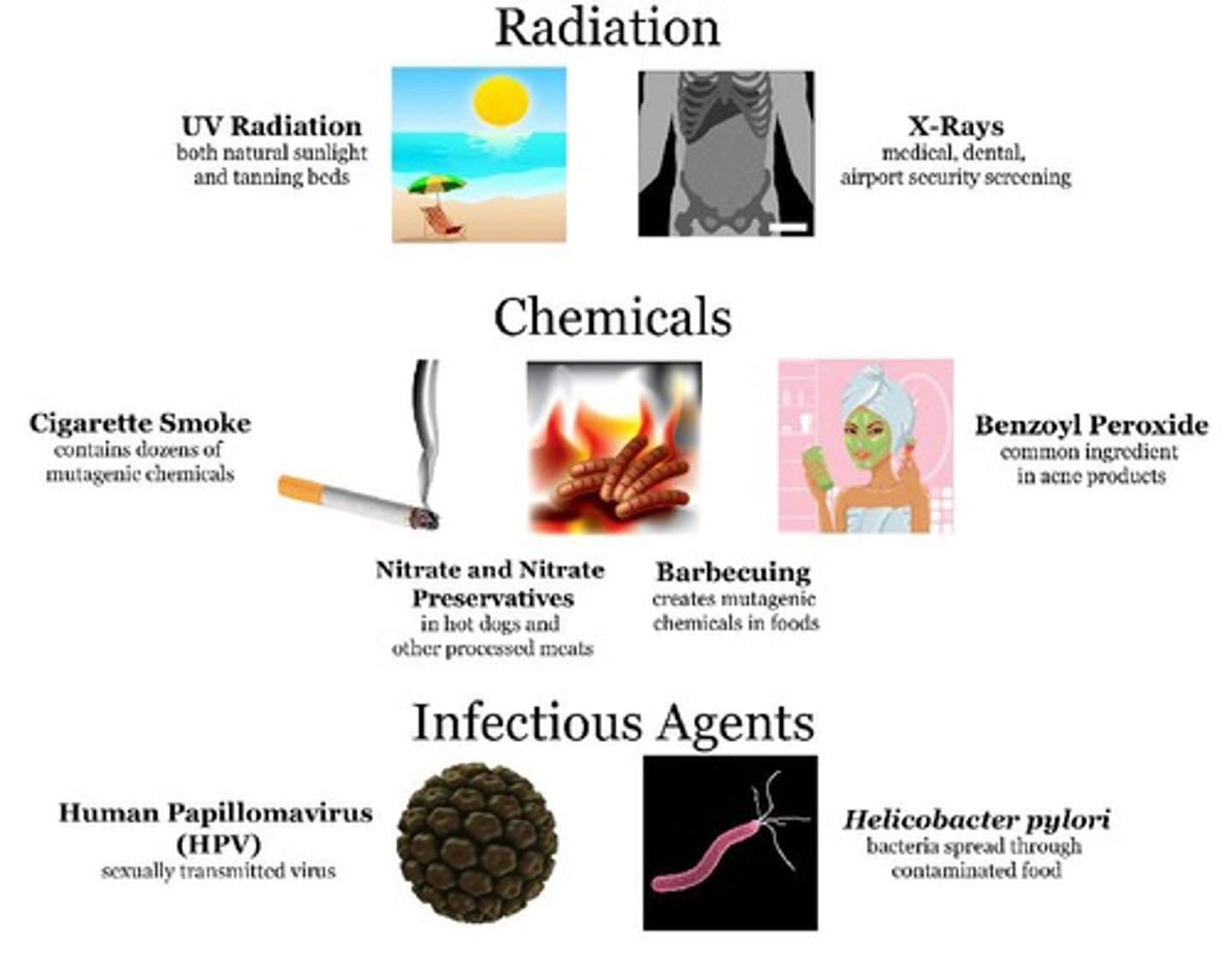
Mutagens (Examples)
Radiation (UV light, X-rays)
Chemicals (pesticides, tobacco)
Infectious agents (viruses, bacteria)
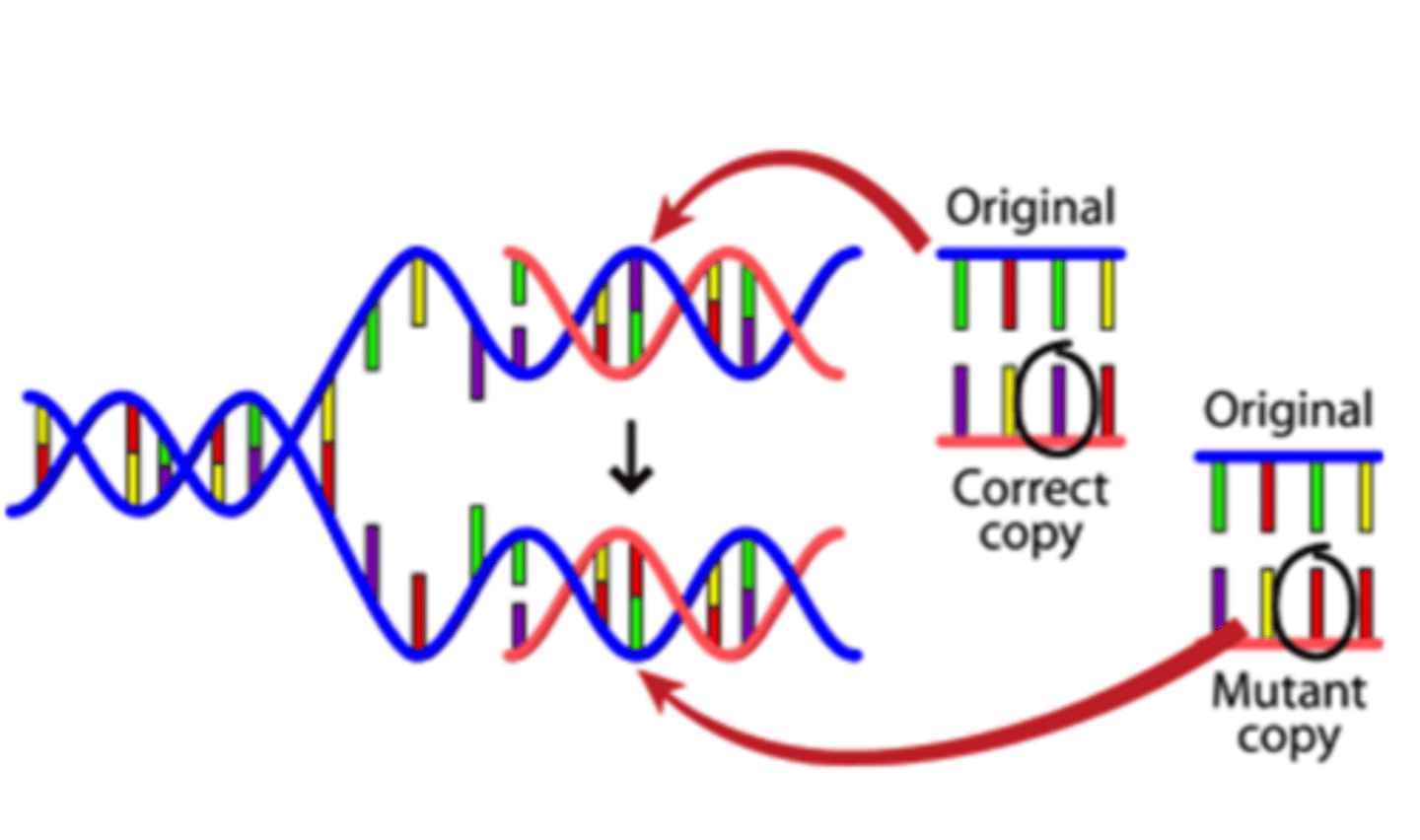
Mutation (Description)
Random changes to DNA that can occur when DNA fails to copy properly or when exposed to mutagens like specific chemicals or radiation; can be beneficial, neutral, or harmful to the organism
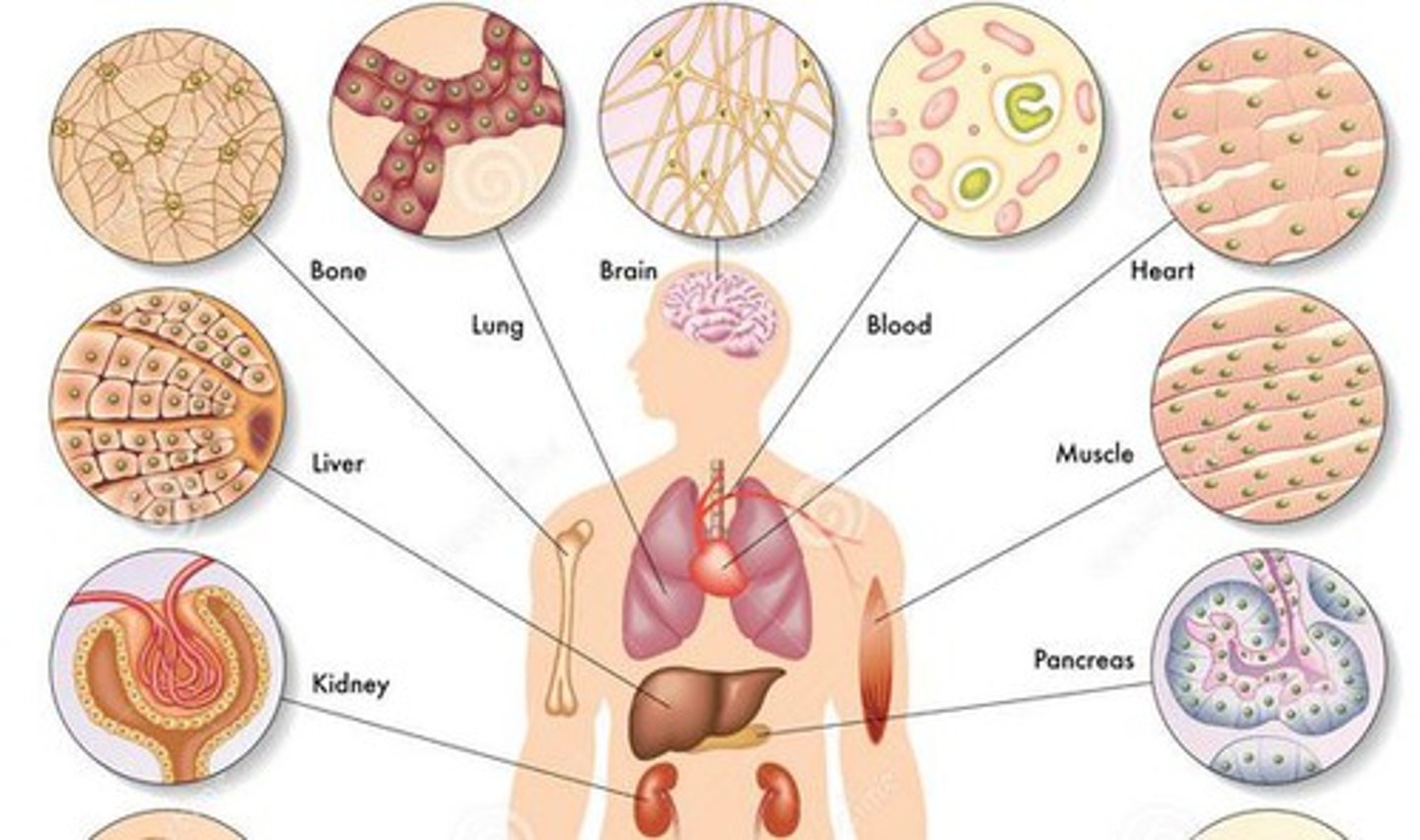
Somatic cells
Any cell in multicellular organism except an egg or sperm
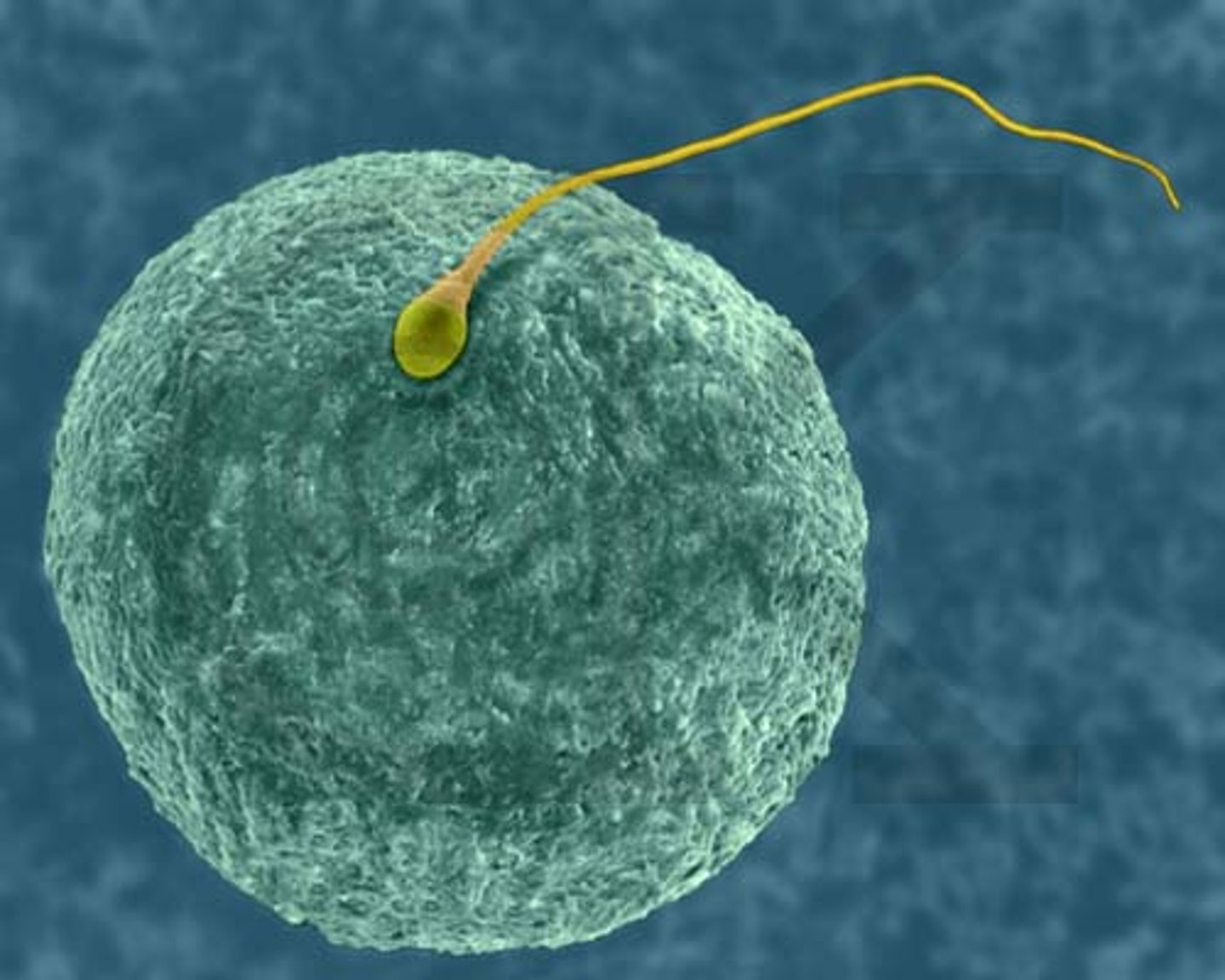
Germ Cells (Gametes)
Reproductive cells that give rise to sperm and ; also known as gametes
Mutations (Types)
Gene mutations
Chromosomal mutations
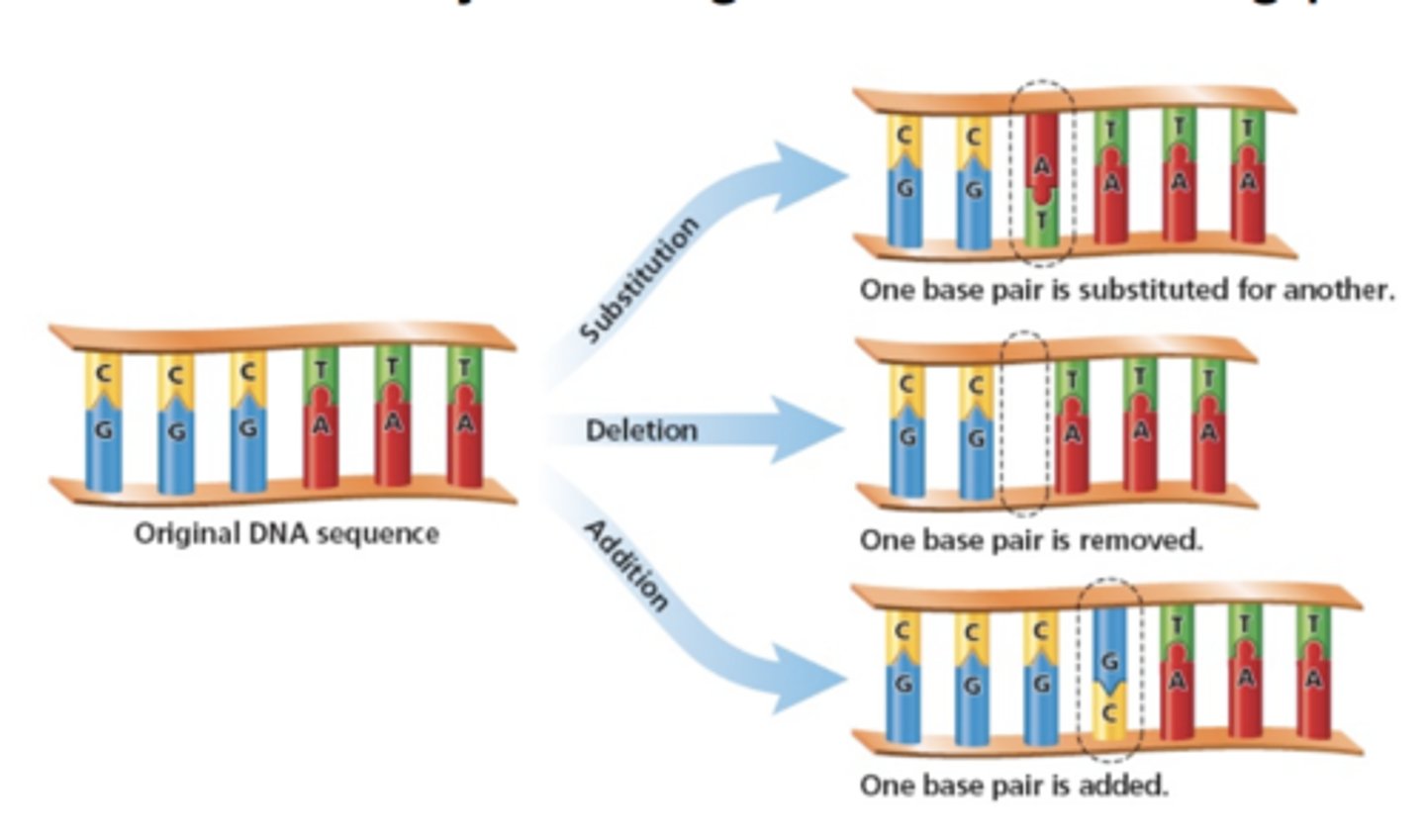
Gene Mutation (Description)
Mutations that result from changes in one or a few nucleotides and are called point mutations
Occurs when nucleotides are substituted, inserted or deleted
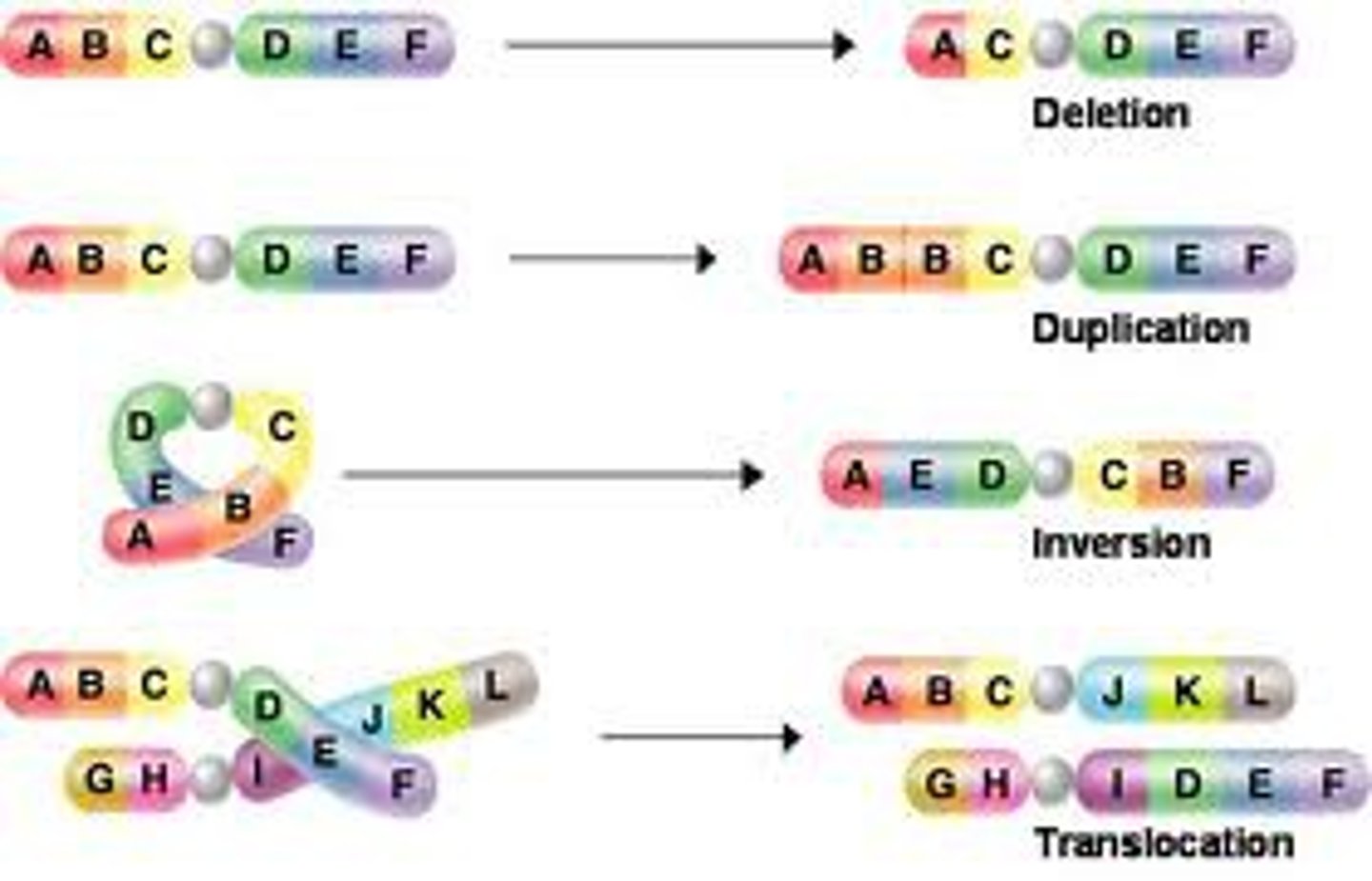
Chromosomal Mutation (Description)
Mutations that result from changes in the number or structure of chromosomes; occurs when section of the chromosome are deleted, duplicated, inverted (flipped) or translocated (moved) to different locations during mitosis or meiosis.
Gene Mutations (Types)
Substitution
Deletion
Insertion
Chromosomal Mutations (Types)
Deletion
Duplication
Inversion
Translocation
Point mutations
Gene mutations involving changes in one or a few nucleotides, include substitution, deletion and insertion of nucleotides
Frameshift mutations
Gene mutations that shifts the "reading frame" of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a nucleotide; include insertion an deletion
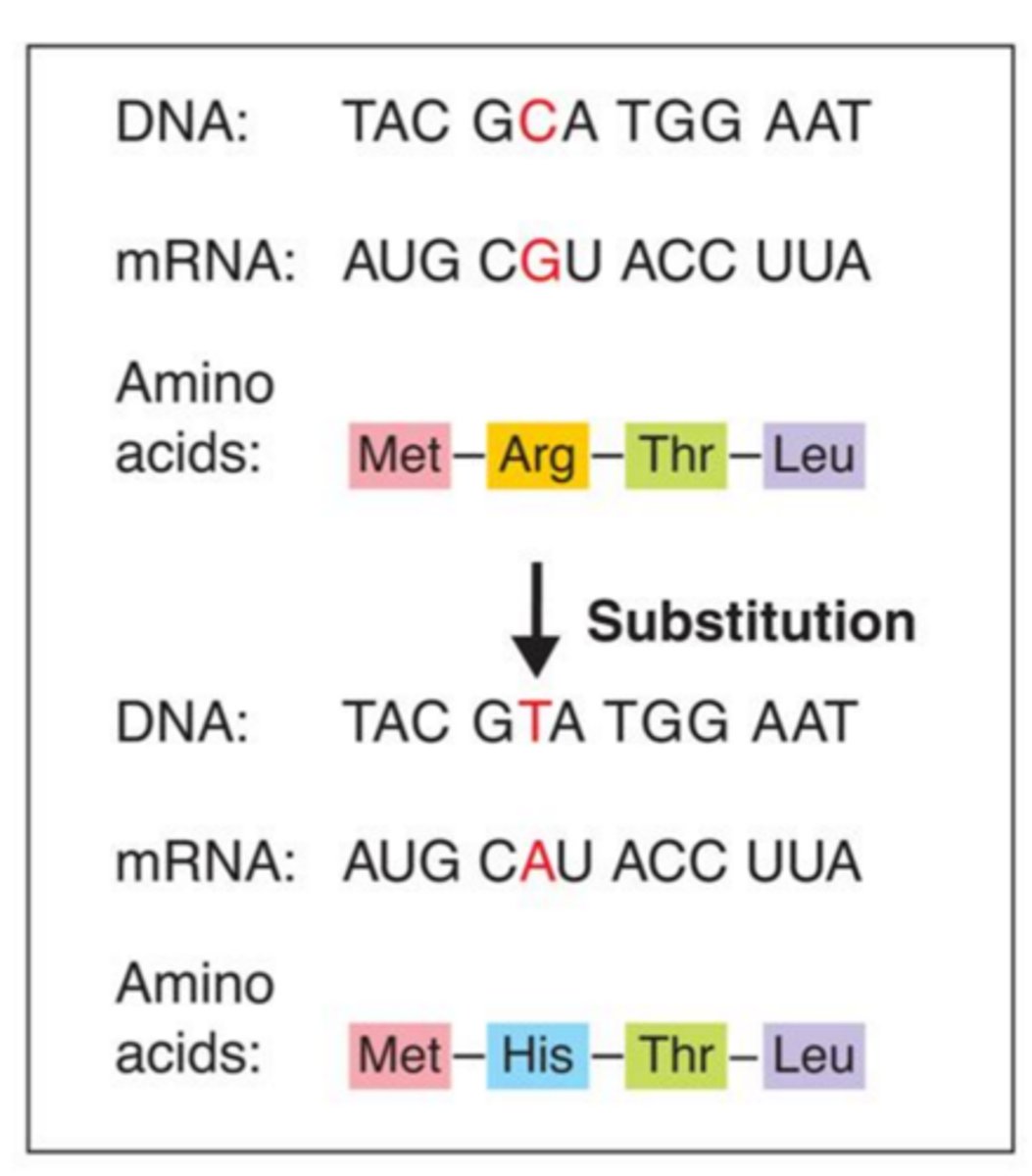
Gene mutation (Substitution)
A gene mutation that occurs when a single nucleotide is substituted for another; typically results in the the change to just one amino acid
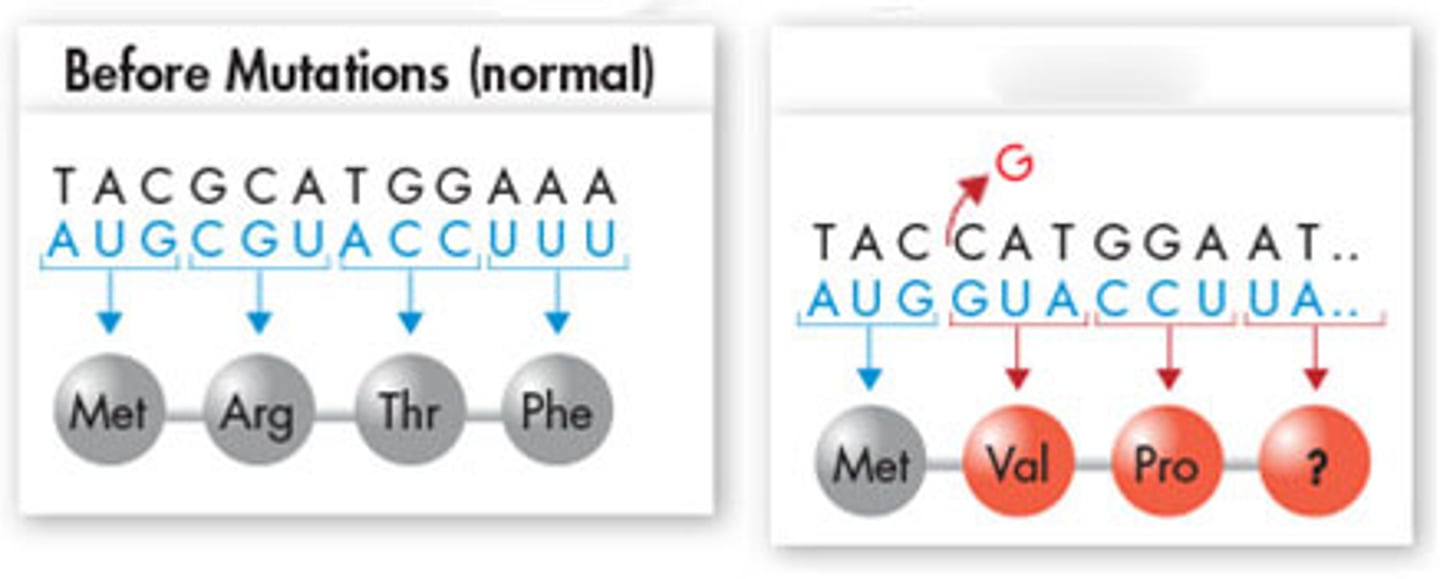
Gene mutation (Deletion)
A gene mutation that occurs when a nucleotide base is deleted; results a frameshift mutation in which every amino acid that occurs after the deletion is impacted
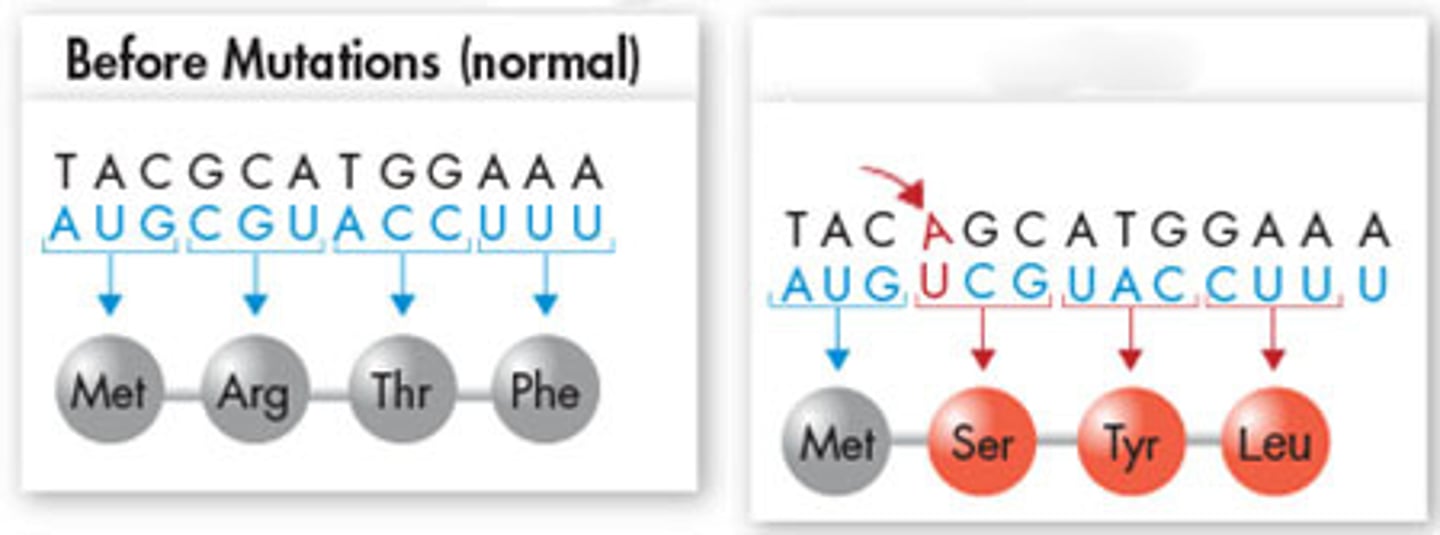
Gene mutation (Insertion)
A gene mutation that occurs when a nucleotide base is inserted; results a frameshift mutation in which every amino acid that occurs after the insertion is impacted
Chromosomal mutation (Deletion)
A chromosomal mutation that occurs when all or part of a chromosome is lost

Chromosomal mutation (Duplication)
A chromosomal mutation that occurs when extra copies are found on a single chromosome

Chromosomal mutation (Inversion)
A chromosomal mutation that reverses the direction of parts of a single chromosome
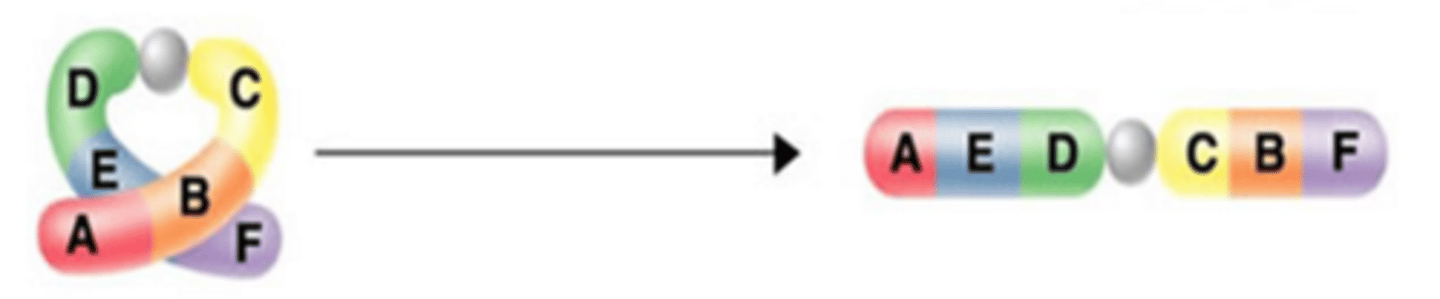
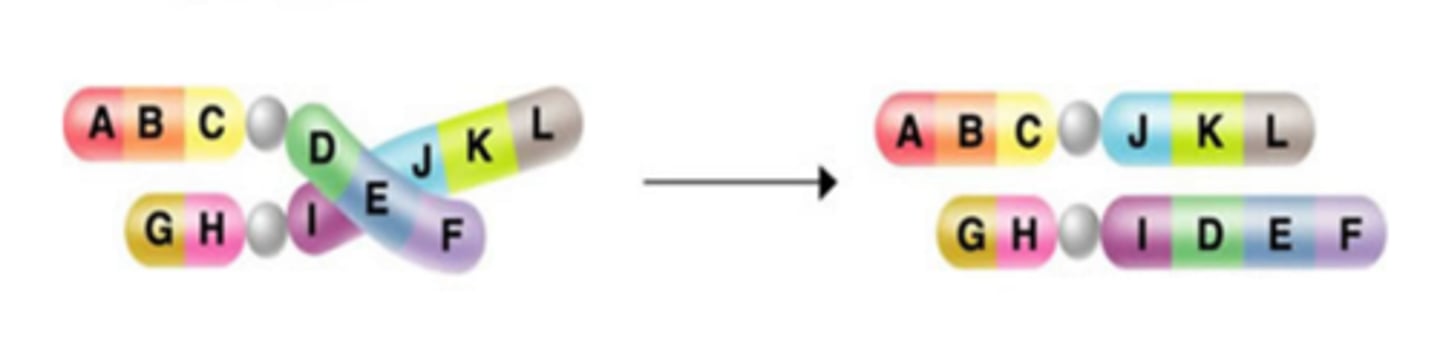
Chromosomal mutation (Translocation)
A chromosomal mutation that occurs when parts of a chromosome move to another chromosome