PSYCH 101 - Week 1, Intro to Psych
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What Is Psychology
Psychology is the science of behaviour and mental processes
Who Are These People Called Psychologists?
Study all aspects of life
Diverse areas of focus (e.g., research, teaching, clinical work)
How Did Psychology Begin?
Origins in philosophy:
Socrates: “Know thyself”
Plato and Aristotle: body, mind, and soul
Descartes: “I think therefore I am”
Empiricists (e.g., Locke and Hume): all knowledge is linked to experience and comes from our senses
How Did Psychology Begin? (cont’d)
Young science: Began a little more than a century ago
Different schools of psychological thought emerged…
Structuralism – focused on basic elements of the mind (or structure)
Edward Titchener
Functionalism – focused on how (and why) the mind functions
William James: “Consciousness, he argued, consists of a continuous flow of thoughts. In analyzing consciousness
into its “elements,” the structuralists were looking at static points in that flow
Wilhelm Wundt is considered the founder of psychology
established the first formal laboratory for research in psychology
established the first journal devoted to publishing research on psychology
Psychology’s Roots in Canada
1891: First experimental laboratory in the British Empire established by James Baldwin at the University of Toronto
1892: Baldwin helped found the American Psychological Association
1939: Canadian Psychological Association founded
Important Canadian contributions by Brenda Milner and Donald Hebb (both of McGill University)
What’s the difference between a psychologist and a psychiatrist?
Many psychologists have professional training and clinical skills to evaluate and treat your mental health using psychotherapy (talk therapy), psychological evaluations and testing.
Psychologists work in many different settings, for example, schools
They also do a lot of research
Psychiatrists are concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of psychological problems and disorders
Medical doctor who specialize in brain
Sometimes counsel?
7 Key Themes in Psychology
Psychology is empirical
a) Empiricism is the premise that knowledge should be acquired
through observation
Psychology is theoretically diverse
a) A theory is a system of interrelated ideas used to explain a set of observations
b) Lots of different theories to explain human behaviour and human mental processes
Psychology evolves in a sociohistorical context
a) Interconnections exist between what happens in psychology and what happens in society at large
b) When we think of diversity, we must think about what’s going on in the world at the time that influences human behaviour
Behaviour is determined by multiple causes
a) Leads us to rational idea that lots of different things can impact behaviour
Behaviour is shaped by cultural heritage
Heredity and environment jointly influence behaviour
a) Heredity: the passing on of physical or mental characteristics genetically from one generation to another. Looking at how both influence behaviour at once
People’s experience of the world is highly subjective

What Makes Psychology A Science?
Use of scientific principles, methods and procedures for:
Knowledge development
Prediction
(Social sciences are a bit limited in ability to predict)
Psychology is Based on 2 Premises: #1?
Empiricism: knowledge through careful observation, not ‘logic,’ ‘common sense,’ or ‘intuition’
Common sense: subjective based on life experience. Yes, its based in “intuition” however is still based in culture, experiences etc. you cannot say there is something everybody knows
Psychology is Based on 2 Premises: #2?
Theory development: collection of interrelated ideas & observations that describe, explain and predict behaviour or mental processes
Research needs to be grounded in theory. Theory is important!
Theory Overview
Theory is like a lens! They offer different perspectives and stuff. Theories also vary across time and sociohistorical periods
The “map” metaphor
The “map” is not the “territory”
They are organized based on the perspective you are focusing on. It is based on what u are highlighting
What one theory highlights, another obscures
And so:
Theories are:
Historically situated and variable
Reflect social and moral thinking of the day
Limited
8 out of Some Major Theoretical Perspectives in Psychology*
Psychodynamic
Behaviourism
Humanistic
Cognitive
Developmental
Social
Cultural
Evolutionary
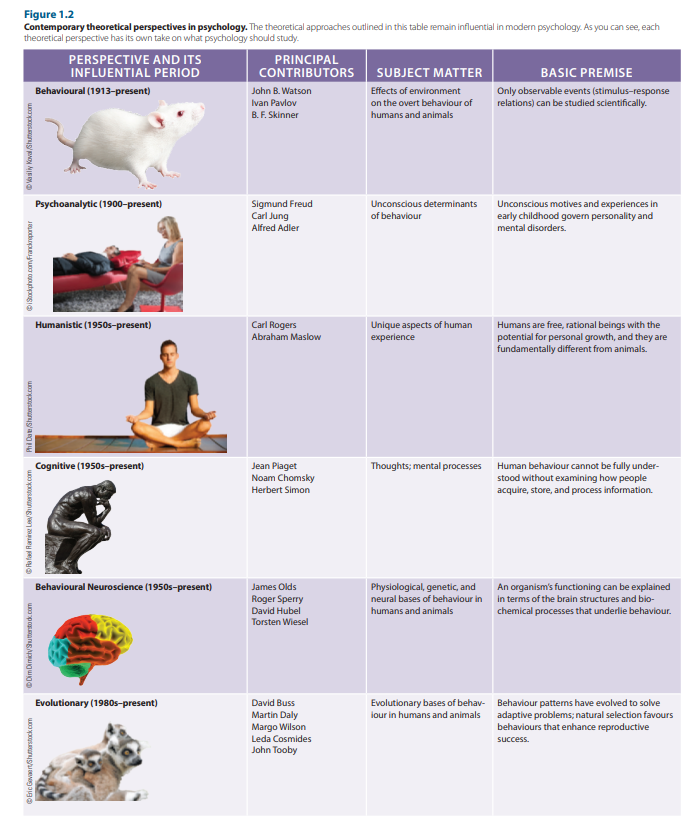
Psychodynamic (focus on)
Founder: Sigmund Freud
Proposed that unconscious mental processes direct behaviour
the unconscious: contains thoughts, memories, and desires that are well below the surface of conscious awareness but that nonetheless exert great influence on behaviour
Therapeutic technique: Psychoanalysis
Based on idea that on the conscious, mental processes direct our behaviour, focuses on the subcounsious/unconsiusness
Technique that came from theory is psychoanalysis
Behaviourism (focus on)
Founder: John Watson
believed psychology should be the study of behaviour since the conscious was a private matter and u could only technically observe its surroundings
Rejected study of the contents of consciousness
Focused on measuring only what is observable
There’s no one truth in psychology
Focus on interactions with the environment, that’s all lol
Humanistic (focus on)
Developed by Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow
Individuals motivated by need for self-actualization
Emphasizes person’s positive qualities, unique experiences
Self actualization: means being all u can be
People are unique and you should focus on their unique experiences
Contracts both psycho and behavioural. Those theories obscured people’s actual experiences
Cognitive
Focuses on such processes as perception, memory, and thinking
Mental processes involved in knowing
Ideas/Thoughts → Behaviour
Looks at how people think, what they think, what kind of mental process do we draw and and use
What happens inside our head impact our behaviours
Social
Focus on how social factors affect both behaviour and mental processes
Deals with social interactions, their origins, and how they impact individuals
How groups impact individuals
Nuanced environment discussions
How do people impact how you think and what you do
Evolutionary
Based on ideas of Charles Darwin
Assumes behaviours that help organisms adapt will be passed on to successive generations
Reproduction, adaptation, “survival of the fittest”
Multiple Theoretical Perspectives Inform the Research in Psychology - General Notes
Remember, theory and research work together!
Theory informs research questions
Research tests theory
When theory is tested and research is not supporting it, QUESTION THE THEORY :D
Psychology as a Science
What does “doing science” mean to you?
Participant observer
Can u be objective in observations if u are apart of group or by having values that have been socially ingrained in yourself?
Is Psychology a “real” science?
Psychology follows principles of “hard” sciences but has space for subjectivity/ different opinions because people don’t sit still, they are odd
Doing Research: Three Principles of the Scientific Endeavour
Objectivity
To be empirical u have to be objective
Systematic Observation
Replicability
Shows that your idea might actually be right
Operational definitions (clarity, measurability)
An operational definition describes the actions or operations that will be used to measure or control a variable.
To be testable, scientific hypotheses must be formulated precisely, and the variables under study
must be clearly defined. Researchers achieve these
clear formulations by providing operational definitions of the relevant variables.
they establish precisely what is meant by each variable in the context of a study