Unit 4 Communication and Coordination (Sensory and Endocrine Systems)
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Mechanoreceptors
– stimulated by changes in pressure or movement
– Found in skin and muscles
Thermoreceptors
– stimulated by changes in temperature
– Found in skin
Pain receptors
– stimulated by tissue damage
– Found in skin and viscera
Chemoreceptors
– stimulated by changes in chemical concentration of substances
– Used for taste and smell
Photoreceptors
– stimulated by light
– Found only in the eye
cause of pain
chemicals released by inflamed tissues
referred pain
inside the body’s organs, pain is often felt in another area.
ex: pain from the heart is felt in the left shoulder and arm
papillae
(bumps) on the tongue that contain many receptors
sweet, sour, salty, bitter, umami
taste receptors can distinguish between these tastes…
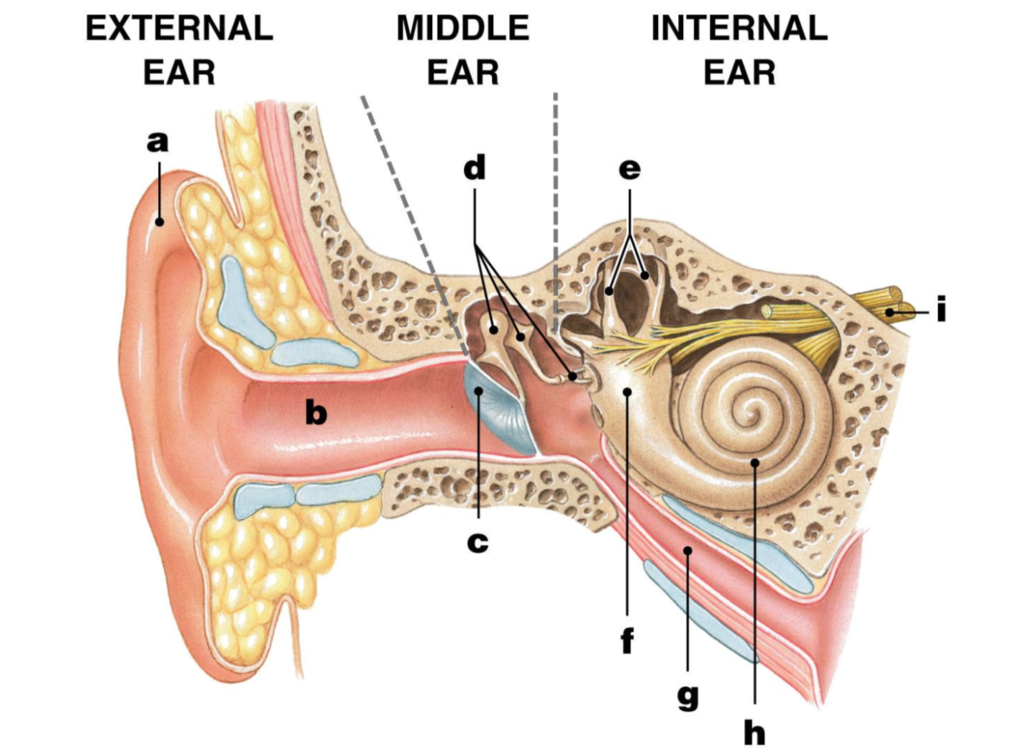
pinna/auricle
label A
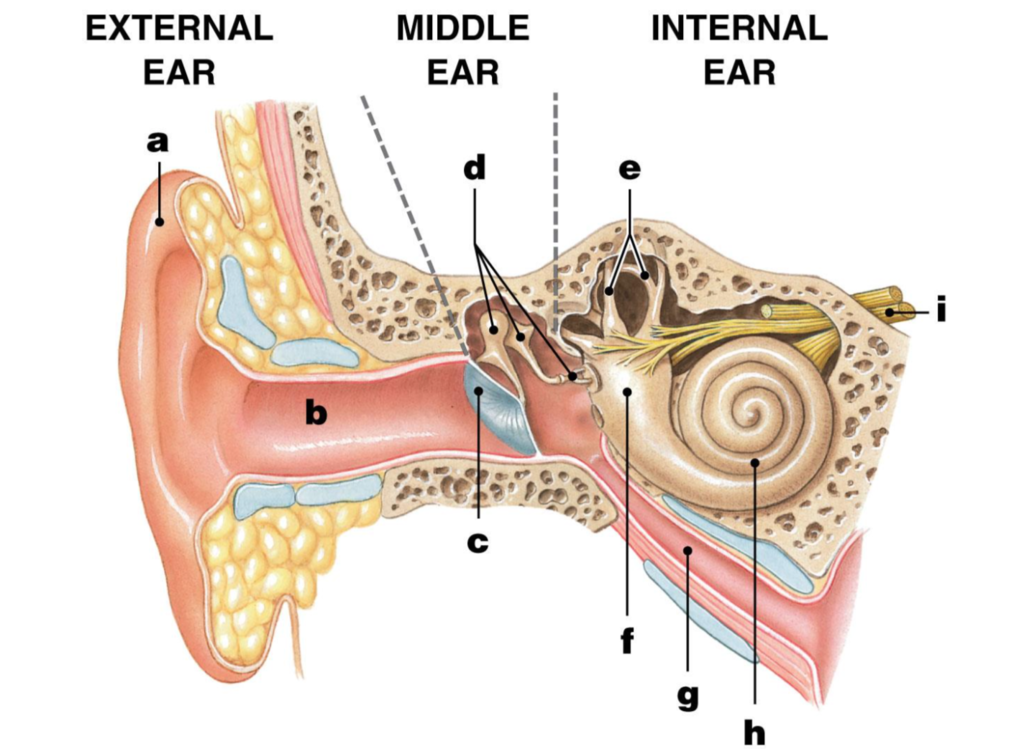
ear/auditory canal
label B
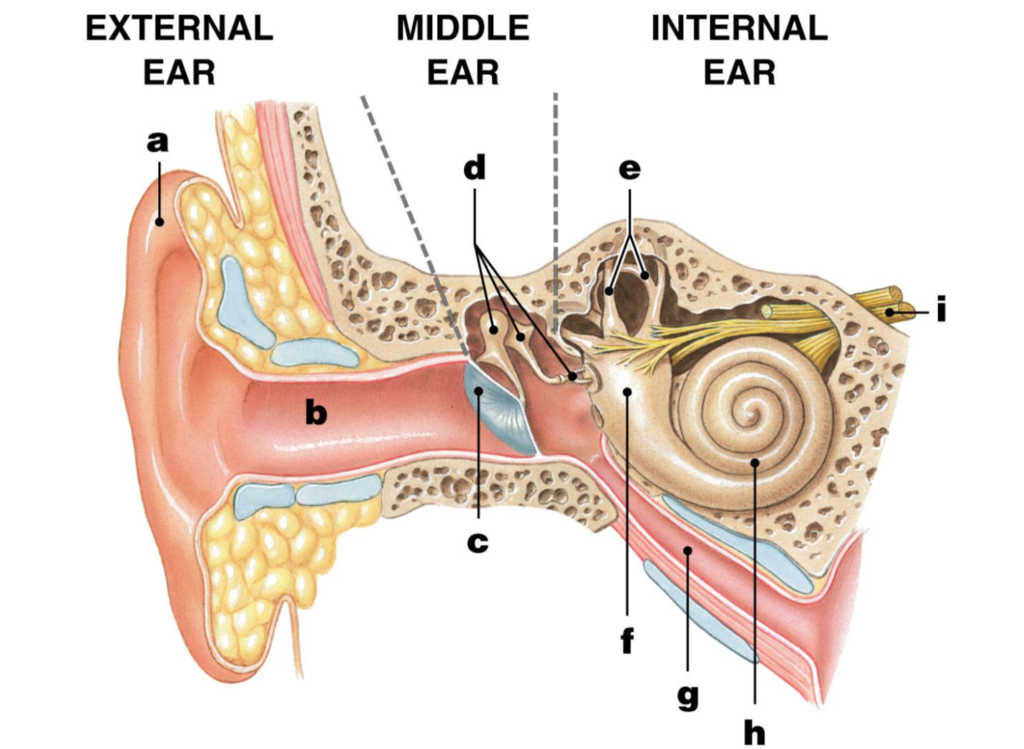
eardrum/tympanic membrane
label C
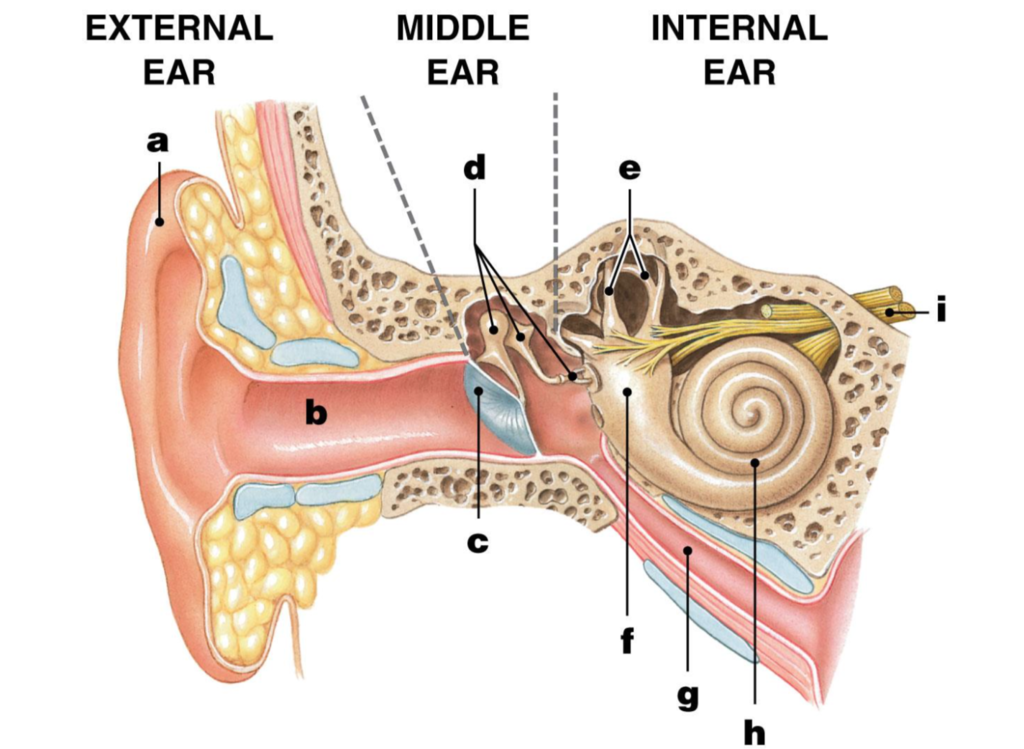
ossicles
label D
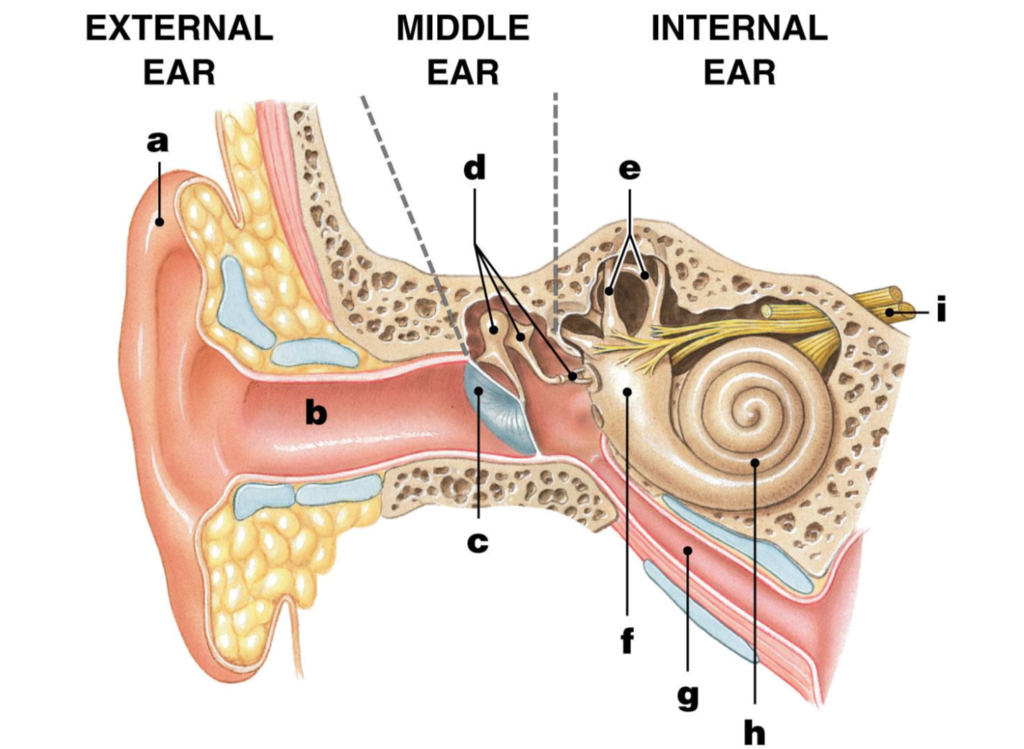
malleus/hammer
label D1
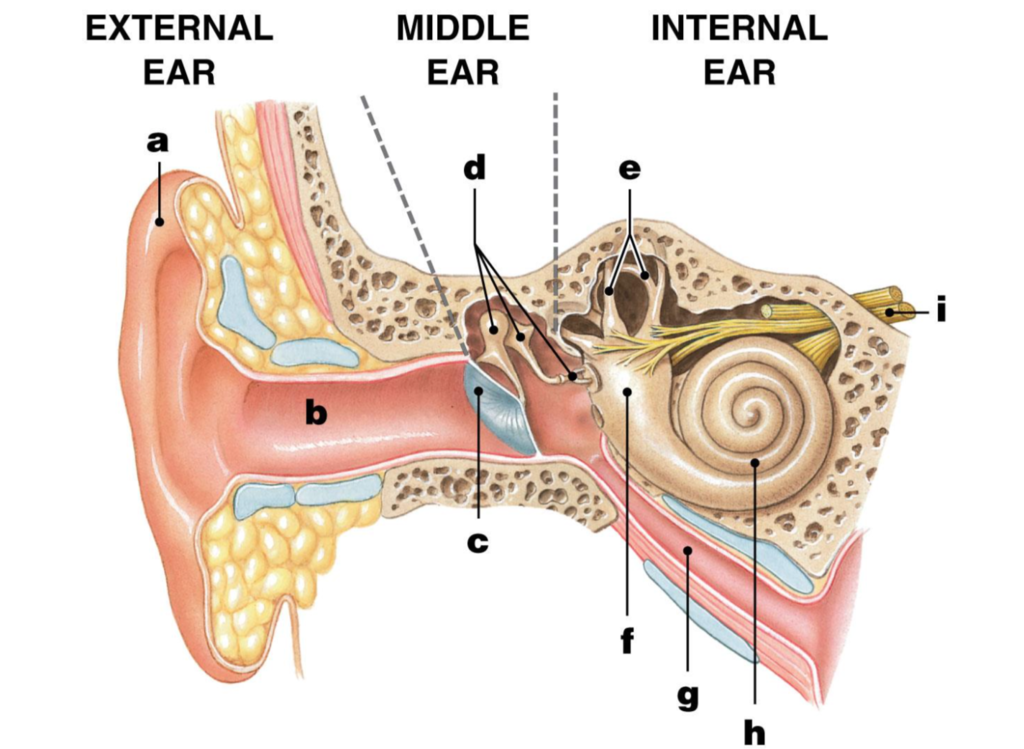
incus/anvil
label D2
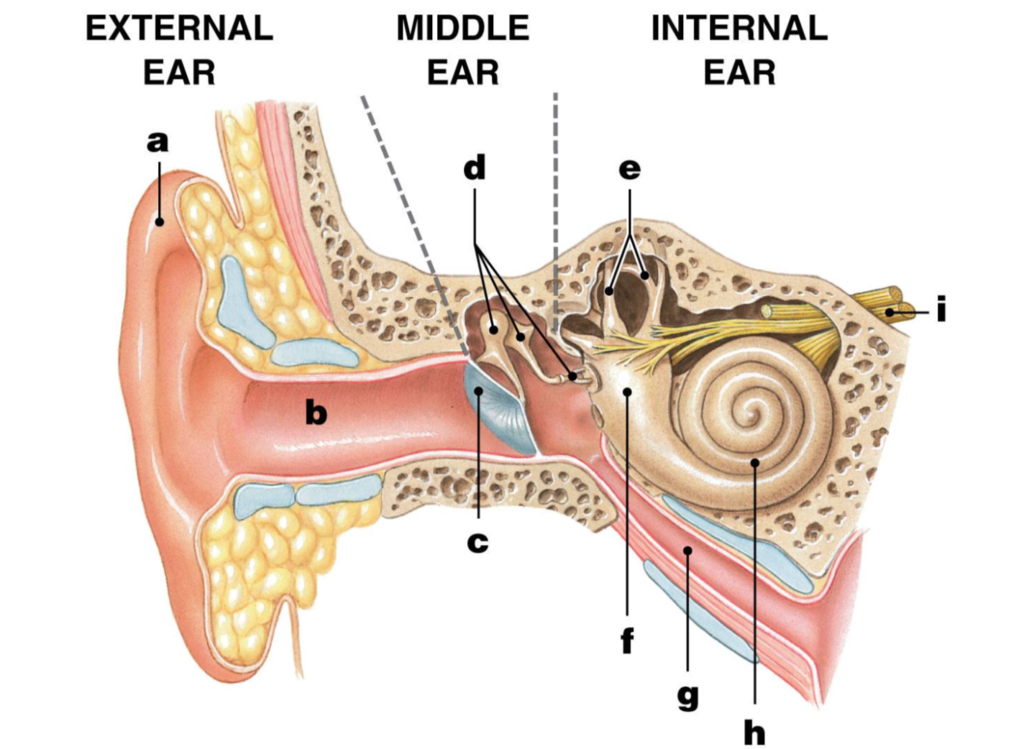
stapes/stirrup
label D3
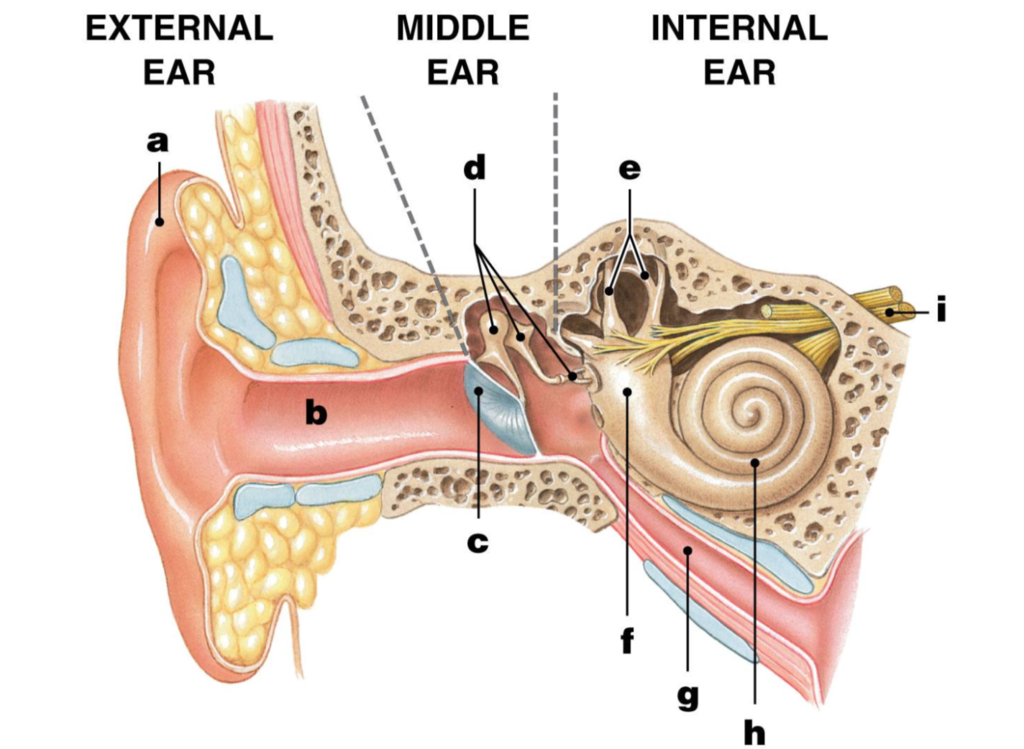
semicircular canals
label E
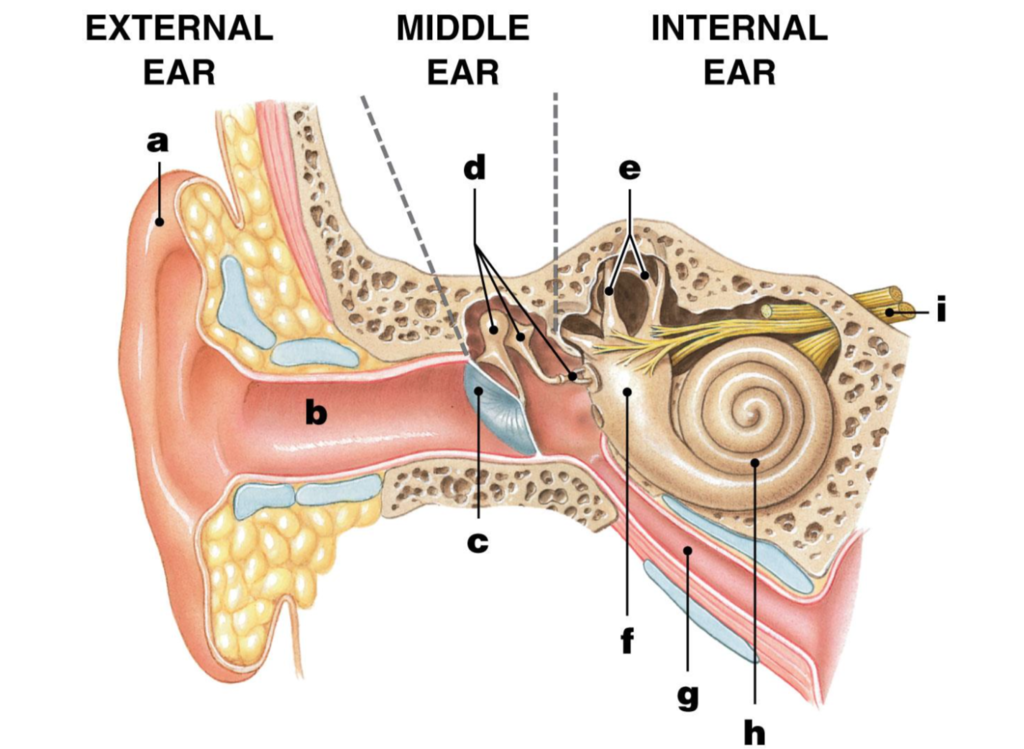
vestibule
label F
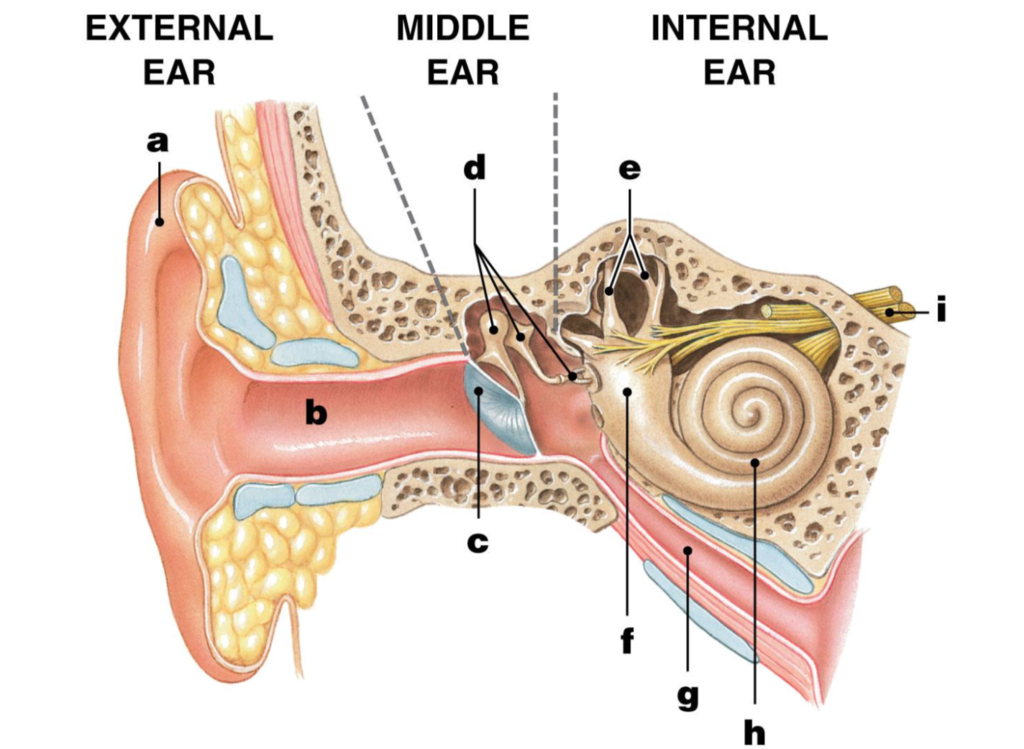
eustachian tube
label G
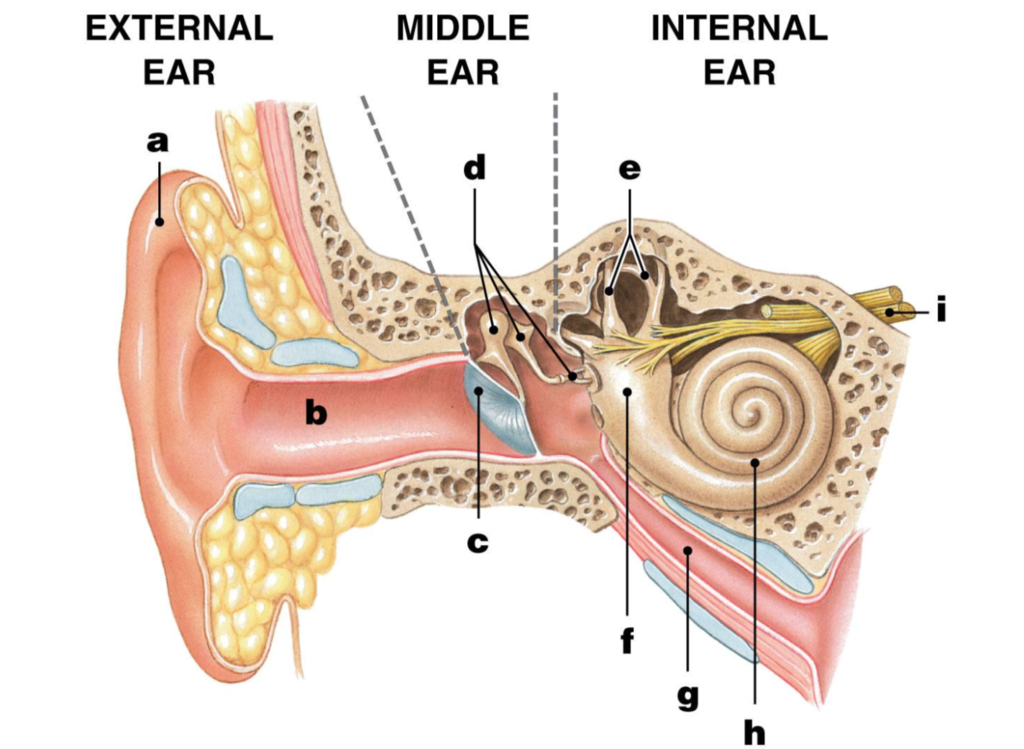
cochlea
label H
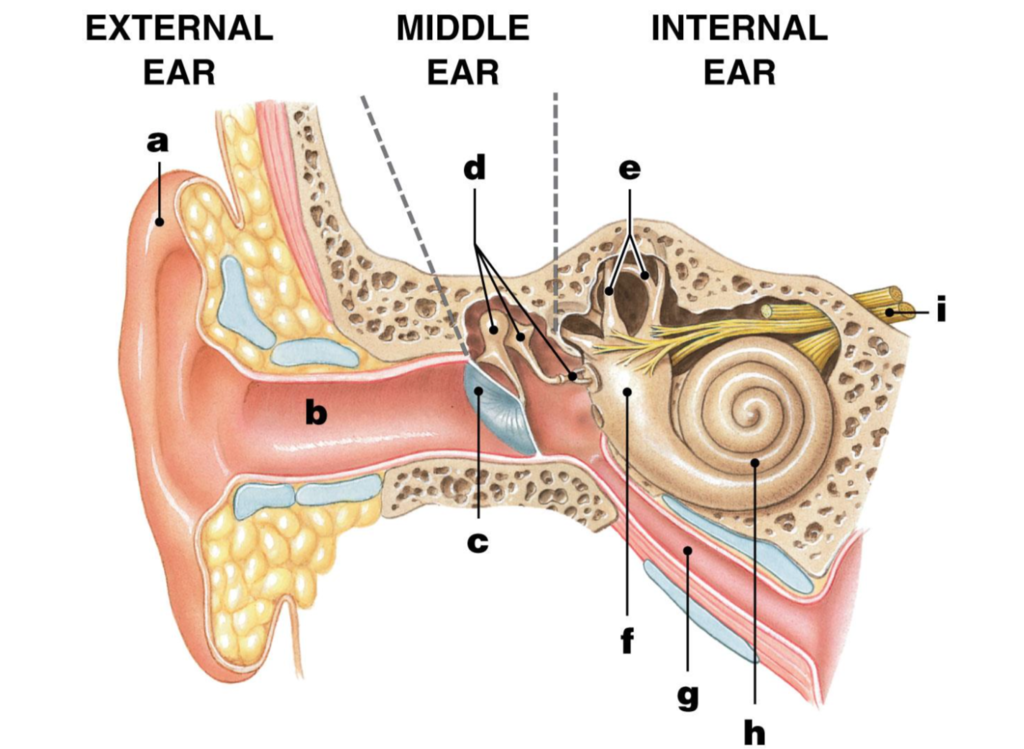
Auditory nerve
label I
how we hear
– 1. Sound waves travel through the auditory canal to the eardrum.
– 2. The sound waves cause the eardrum to vibrate.
– 3. The vibration causes the malleus (hammer) to hit the incus (anvil) and then the stapes (stirrup).
– 4. The vibration passes to the fluid in the cochlea of the inner ear.
– 5. Each part of the spiral cochlea is sensitive to different frequencies of sound.
– 6. The auditory nerve takes impulses to the brain.
equilibrium
– Mechanoreceptors in the semicircular canals detect rotation and movement of the head
– Little hair cells send information to the brain to cause appropriate motor output so as to correct position when it is unbalanced.
– Vertigo (dizziness)
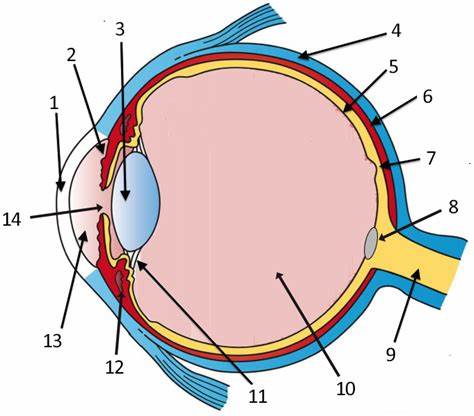
cornea
label 1
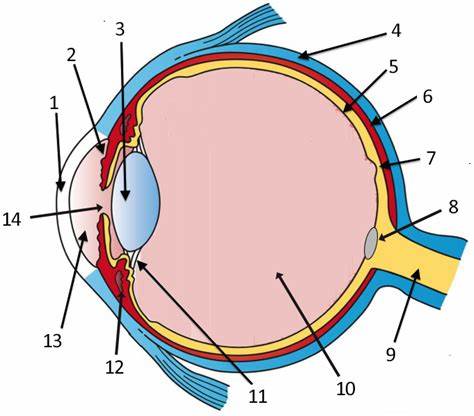
Lens
label 3
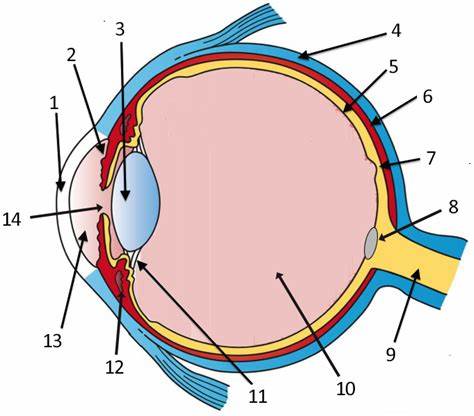
sclera
label 4
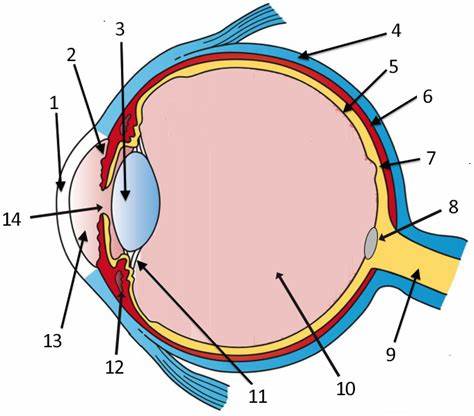
pupil
label 14
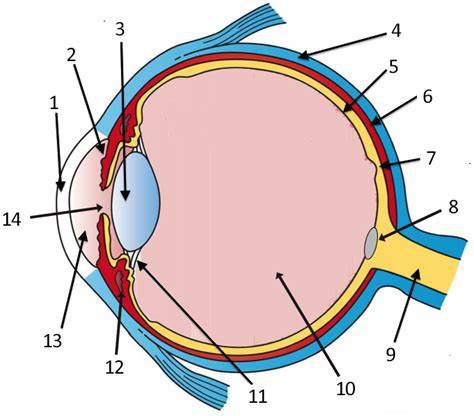
optic disc
label 8
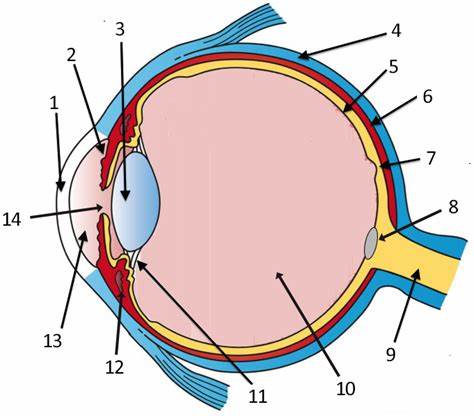
aqueous humor
label 13
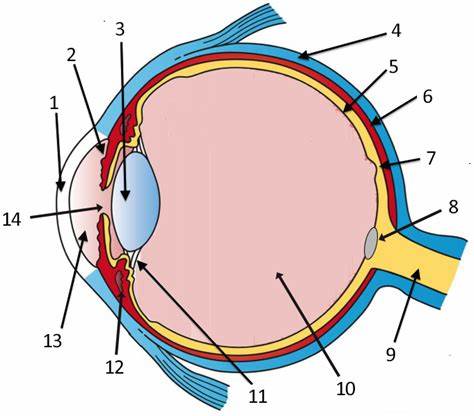
optic nerve
label 9
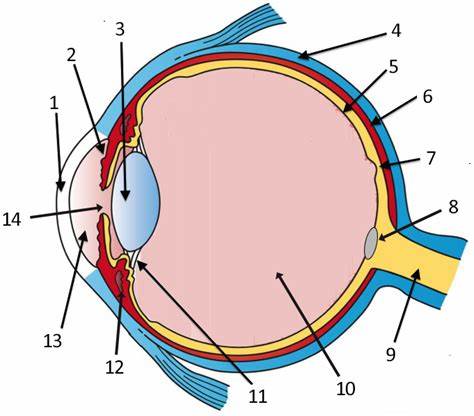
iris
label 2
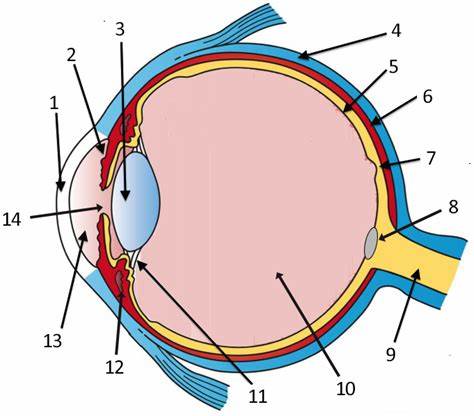
ciliary body
label 11
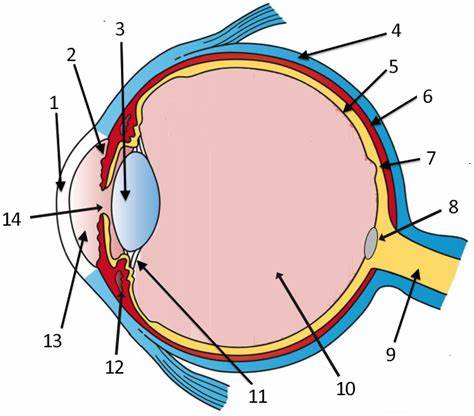
choroid
label 6
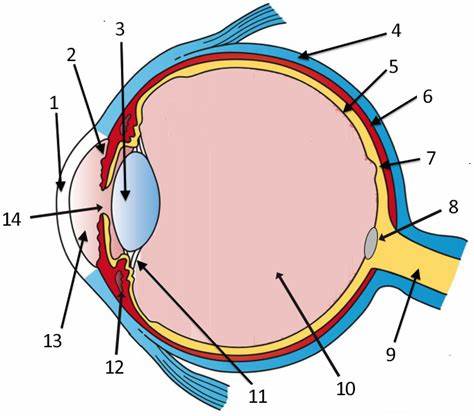
vitreous humor
label 10
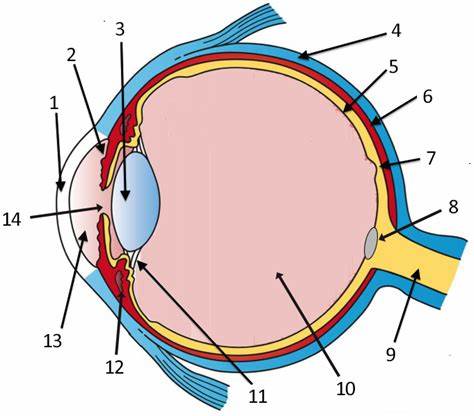
retina
label 5
sclera
protection (white of eye)
cornea
refracts light (allows for it to pass through), transparent (window of the eye), only human tissue that can be transplanted w/o fear of rejection
vitreous humor
maintains eyeball shape (gel-like substance)
Retina
has photoreceptor cells that detect light and send impulses to the brain; contains rods and cones; 2 layers
Glaucoma
Damage to the optic nerve occurs due to increased eye pressure
– Can lead to blindness
Cataracts
– Clouding of the lens that affects vision
– Very common in older people
lens
focuses light; divides the eye into 2 chambers (aqueous and vitreous)
ciliary body
holds lens in place, accommodation
iris
regulates light entrance (muscle); colored part of the eye
pupil
rounded opening in the iris that admits light
hormonal stimuli
•Glands are encouraged by hormones secreted by other glands.
•Ex: Hypothalamus stimulates pituitary
humoral stimuli
•Levels of nutrients and ions in the blood can cause glands to secrete hormones.
•Ex: Blood calcium levels stimulate parathyroid glands
neural stimuli
•Nerve impulses cause glands to secrete hormones.
•Ex: Sympathetic nervous system during stress causes release of epinephrine from adrenal glands.
anterior pituitary gland
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) → Causes thyroid to produce thyroxine
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) → Stimulates adrenal glands
Growth Hormone (GH) → Stimulates growth in bones and muscles
Melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH) → Stimulates melanocytes to produce melanin
Prolactin (PRL) → Stimulates production of breast milk
Gonadotropins → Luteinizing hormone → Stimulates release of sex hormones
Gonadotropins → Follicle stimulating hormone → Stimulates egg or sperm production
posterior pituitary gland
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or vasopressin → Increases water retention in kidneys, decreasing urine production
Oxytocin (OT) → Stimulates contraction of uterus during
childbirth and promotes release of breast milk
hypothalamus
Its main function is to control the pituitary gland by hormonal and neural stimulation.
This allows for functions like:
•Control of brain stem & spinal cord
•Center of emotional response
•Body temperature regulation
•Regulation of food intake
•Controls thirst
•Regulates sleep & wake cycles
pineal gland
Melatonin → Rise and fall during day and night causing sleep and wake cycles.
thyroid gland
Calcitonin → Reduces the calcium levels in the blood
Thyroid Hormones (TH) → Thyroxine (T4) & Triiodothyronine (T3) → Regulate metabolism and body heat production, controls cellular oxygen usage, and maintains blood pressure
parathyroid gland
parathyroid hormone (PTH) → brings calcium out of the main regulator of body mineral metabolism through parathormone (PTH) actions on bone and kidney
adrenal glands
Epinephrine & Norepinephrine → Regulate the “fight or flight”
response to emergency situations. Increases heart rate, blood
pressure, blood flow, intake of oxygen for immediate
energy.
Glucocorticoids (ex: cortisol & aldosterone) → Regulate ion levels for quick energy
Pancreas
Insulin → Lower blood glucose levels
Glucagon → Raise blood glucose levels
thymus
thymopoietin, thymosin → involved in the development of the immune system.
hyposecretion
not enough hormone is released
hypersecretion
too much hormone is released
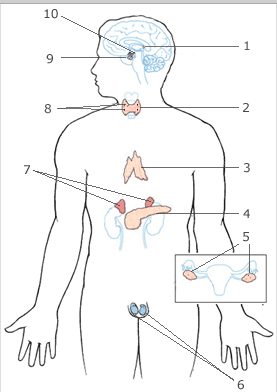
pineal gland
label 1