Lab Evaluation of Hemostasis (Exam 2)
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
To analyze coagulation components, blood must be drawn in a ______ tube.
sodium citrate (light blue)
What is the ratio needed of blood to anticoagulant?
9:1
What are some reasons for coagulation specimen rejection?
- Ratio is off
- Clotted
- Gross hemolysis
- Hematocrit >55%
What conditions warrant caution or alternative measurement?
- Icteria or lipemia
- Patient is on heparin
- Lupus anticoagulant
How is platelet rich plasma (PRP) made?
Centrifuging at a low speed for a long time (30 min)
How is platelet poor plasma (PPP) made?
Centrifuging at a high speed for a short time (10 min)
Platelet counts for PRP and PPP?
PRP: 200,000-300,000/uL
PPP: <10,000/uL
PRP is used for platelet ______.
aggregometry
PPP is used for ______ assays.
clot-based
Bleeding time (BT) is used to evaluate platelet ______ and ______.
adhesion, aggregation
BT normal range
2-9 minutes
The Platelet Function Analyzer (PFA)-100 measures the time (seconds) required for whole blood to occlude holes in a membrane coated with ______ plus ______.
collagen, EPI or ADP
The PFA-100 is used instead of bleeding time to measure platelet ______.
adhesion/aggregation
The PFA-100 can't be used for differentiating ______ vs. ______.
vWD, platelet function disorder
Thromboelastography (TEG) assesses the patient's overall ______ status.
coagulation
TEG is used to rapidly evaluate ______.
bleeding aptients
TEG procedure
A cup of whole blood rotates around a pin that detects resistance as clotting occurs
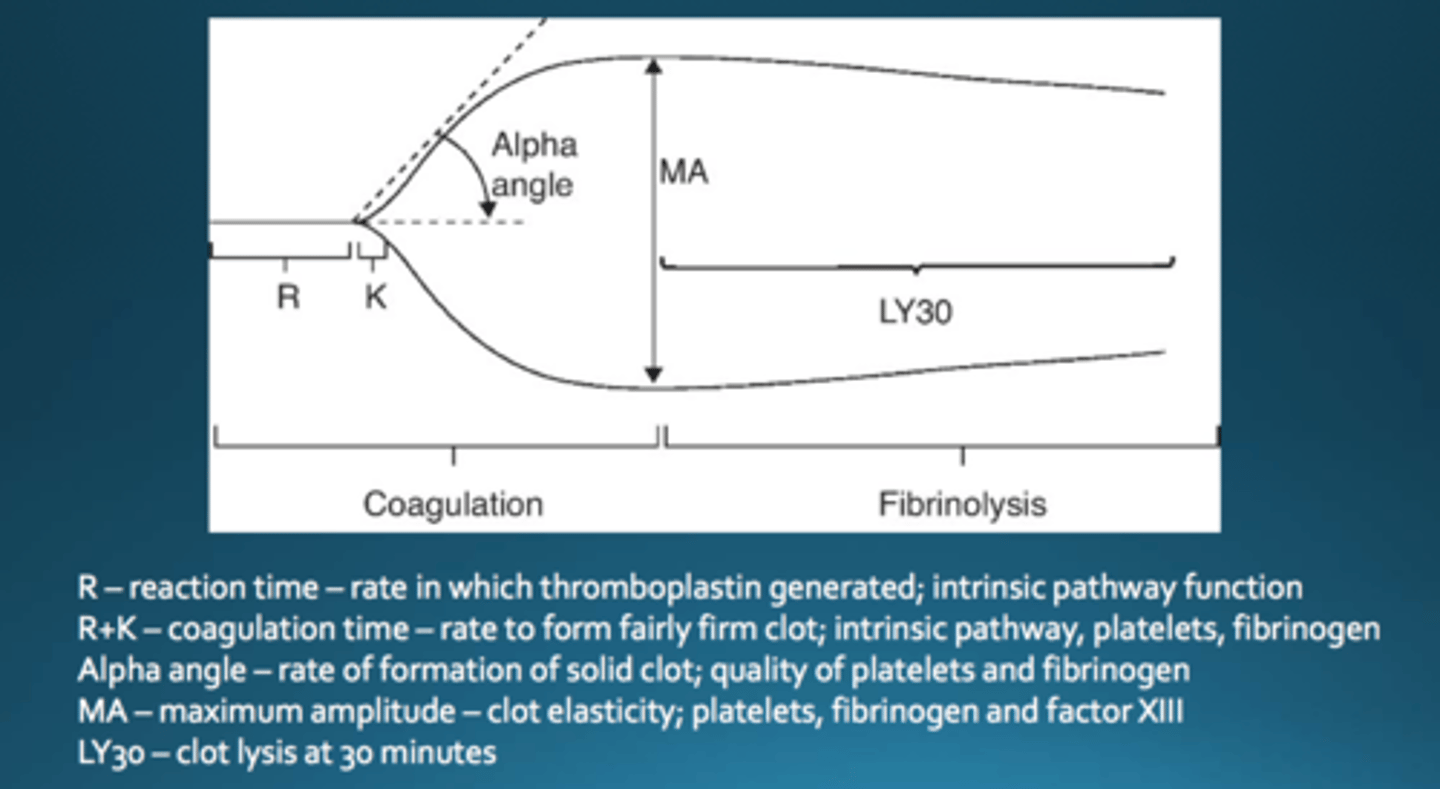
Rotational Thromboelastography (ROTEM) is a variation of TEG that involves the rotation of the ______.
pin
ROTEM gives information on ...
- Clotting time
- Clot formation
- Clot stability
- Lysis
- Activity of coagulation factors
- Platelet function
- Fibrinolysis
Platelet aggregometry procedure
PRP in a cuvette + agonist --> light transmission aggregometry (LTA)
Normally, after the addition of the agonist, platelets will change shape from ______ to ______.
discoid, spherical
As aggregates form, there is an increase in ______.
% Transmission
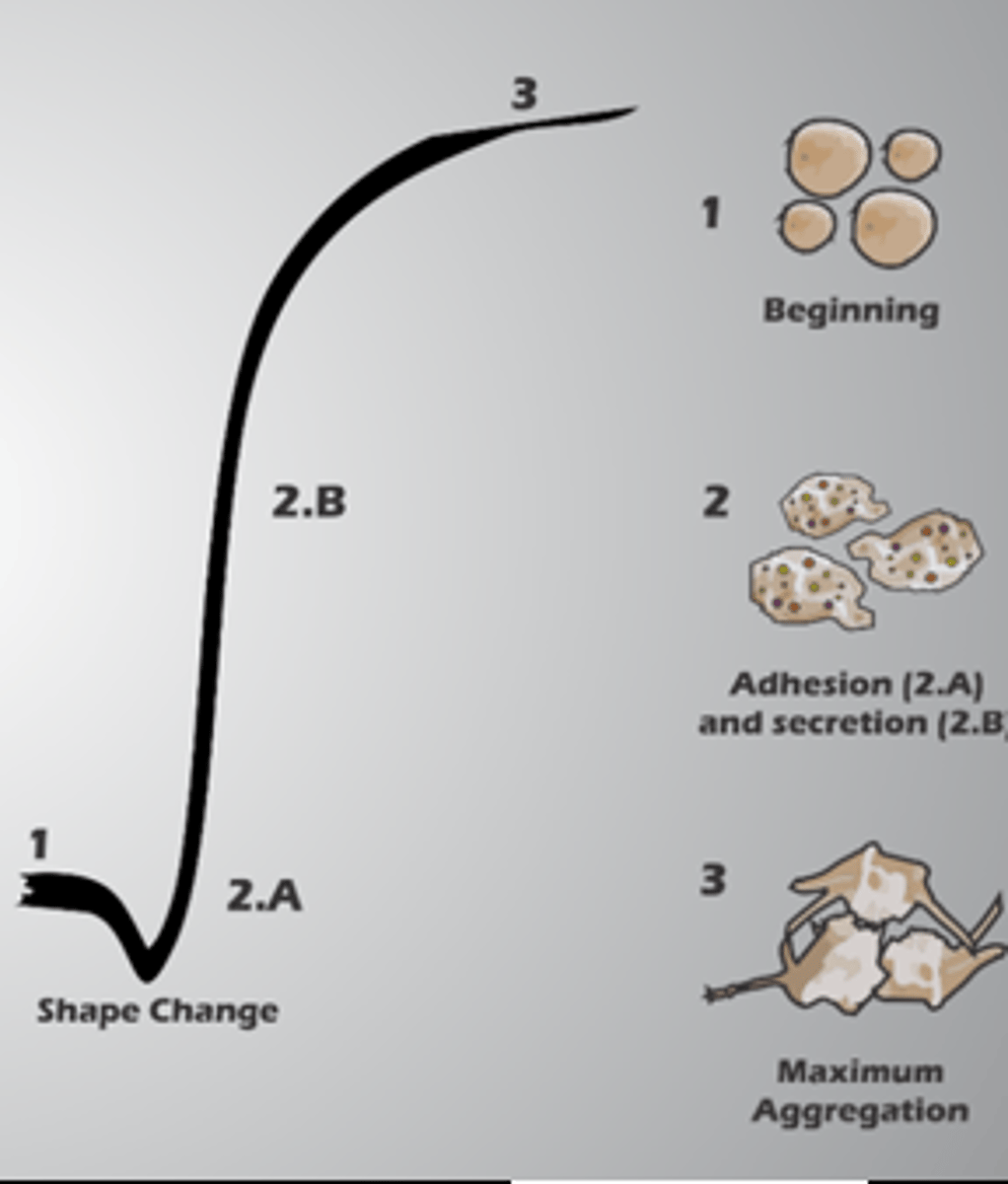
What agonists are used in platelet aggregometry?
- ADP
- Thrombin
- Collagen
- EPI
- Arachidonic Acid
- Ristocetin
ADP binds to P2Y1 and P2Y12 to suppress membrane-associated ______ activity. What is the effect of this?
adenylate cyclase
Platelet aggregation occurs
ADP is inhibited by ______ and ______.
aspirin, NSAID's
Thrombin is the most potent physiological activator of ______.
platelets
Thrombin cleaves ______ and ______.
PAR-1, PAR-2
Cleavage of these proteins results in full secretion and ______.
aggregation
Thrombin receptor-activating peptide (TRAP) only triggers ______ and not coagulation.
aggregation
Collagen binds to GP Ia/IIa and GP VI on platelets inducing release of granules and ______ generation.
TXA2
TXA2 is a potent inducer of ______.
platelet aggregation
This causes a lag phase (30-60 seconds) and then starts ______.
secondary aggregation
EPI binds to alpha-2-adrenergic receptor and causes ______ secretion.
ADP
Whatever aggregates with ADP will also aggregate with ______.
EPI
Arachidonic acid assesses the viability of the ______ pathway.
cyclooxygenase (arachidonic acid to TXA2)
Arachidonic acid assesses aggregation independent of ______ integrity.
membrane
Ristocetin (RIPA test) normally induces a monophasic ______.
agglutination
RIPA requires ______ to be present in a patient's specimen and the platelets must possess an intact ______.
vWF, surface membrane
With ristocetin cofactor assay for vWF, ______ platelets are used in lieu of patient platelets.
reagent
Ristocetin cofactor assay for vWF procedure
Patient PPP + reagent platelets + ristocetin --> optical instrument
With this test, there is a direct relationship between ______ concentration and ______ response to platelets.
vWF, aggregometer
What causes absence of platelet aggregation due to ADP or EPI?
- Platelet membrane disorders
- Cyclooxygenase pathway enzyme deficiencies
- NSAID use
- Storage pool disease
What causes absence of platelet aggregation due to thrombin?
- Storage pool disorders (not membrane or CO related)
What causes absence of platelet aggregation due to collagen?
- Membrane abnormalities
- Storage pool defect
- Release defects
- NSAID/aspirin use
What causes absence of platelet aggregation due to arachidonic acid?
- NSAID/aspirin use
- Suppressed CO activity
- Deficiencies in eicosanoid pathway enzymes
What causes absence of platelet aggregation due to ristocetin?
- Bernard-Soulier syndrome
- vWD
PT sample storage requirements
Room temp or refrigerated for 24 hours
APTT sample storage requirements
Room temp or refrigerated for 4 hours (no heparin)
Room temp or refrigerated for 1 hour (heparin)
If a patient's hematocrit is over 55%, the amount of ______ must be adjusted using a specific formula.
anticoagulant
Polycythemia vera patients have more cells than normal, which decreases the amount of plasma and ______ available.
plasma factors
Prothrombin Time (PT) evaluates what pathways?
Extrinsic and common
PT is also used to monitor ______ therapy with INR.
Coumadin
PT procedure
- Warm a source of tissue extract (thromboplastin) + citrated plasma
- Incubate
- Measure time needed to clot
Prolonged PT could indicate a ______ deficiency.
factor
PT is most sensitive to ______ deficiencies.
Factor VII
PT is not sensitive to ______ or ______ deficiencies.
Factor VIII, IX
Thromboplastin = ______ + ______
phospholipids + tissue factor
International Normalized Ratio (INR) is used to ______ prothrombin time.
standarize
The ______ is the numeric value found on every lot of tissue extract.
International Sensitivity Index (ISI)
Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT) evaluates what pathways?
Intrinsic and common
aPTT is used to monitor ______ therapy.
heparin
aPTT procedure
- Add citrated plasma + activators + phospholipid
- Incubate
- Add calcium
- Measure time to clot
Prolonged apTT could indicate ______ deficiency.
factor
Factor Assays are used to evaluate ______ levels.
specific factor
Factor Assay procedure
- Add dilutions of citrated plasma to citrate substrate plasma that is known to be deficient for the factor of interest
- Concentration of factor being tested is a % of the activity in normal plasma
Fibrinogen is measured by the ______ Assay.
Clauss Fibrinogen
This assay measures the amount of fibrinogen in ______.
PPP
Clauss Fibrinogen Assay procedure
- Standard curve of normal plasma by a modification of the thrombin time test
- Standard dilution of patient plasma made
- Clotting time measured via optical density, value determined from the graph
Causes of decreased fibrinogen
- DIC due to consumption
- Liver disease due to decreased synthesis
- Inherited deficiencies
Causes of increased fibrinogen
- Increased age
- Female, pregnancy, oral contraception
- Post-menopause
- Acute phase reaction
Thrombin Time (TT) evaluates the conversion of ...
Fibrinogen to fibrin (by thrombin)
TT procedure
- Incubate citrated PPP
- Add excess thrombin
- Measure clotting time
Prolonged TT could indicate presence of ______ or a deficiency in ______.
heparin, fibrinogen
Reptilase Time (RT) evaluates the presence of _______.
thrombin inhibitors
RT procedure
- Snake venom cleaves fibrinopeptide A from fibrinogen, initiating the polymerization of fibrin
- Plasma + viper snake venom
- Timed for presence of a clot vs. normal control
Prolonged RT indicates abnormal or no synthesis of ______.
fibrinogen
RT is not affected by ______.
heparin
D-Dimer is used to assess ______ activity.
fibrinolytic
D-Dimer is detectable in ...
- DIC
- Pulmonary embolism
- DVT
What can cause a false positive D-Dimer result?
- Pregnancy
- Malignancy
- Cigarette smoking
- Trauma
- Infection
- Sepsis
Factor XIII assays are used to detect Factor XIII ______.
deficiency
Factor XIII deficiency will cause a normal PT and aPTT but the patient will have ______.
bleeding/bruising
Factor XIII assay procedure
- Patient plasma + 5.0M urea
- Observe clot
A stable clot will remain intact in 5.0M urea after ______ hours.
24 (unstable clot dissolves)
Mixing studies are used to differentiate between a ______ deficiency and a circulating ______.
factor, inhibitor
Mixing studies procedure
- Patient PPP + normal pooled plasma (NPP) in varying dilutions
- Clotting time measured
Bethesda Assay is used to evaluate the presence of and quantify the amount of inhibitor against _______.
Factor VIII
Bethesda Assay procedure
- Patient PPP (serial dilutions) + NPP
- Incubate 2 hours
- Run as aPTT
The level of inhibitor in the specimen is expressed as a ______ of the control.
percentage
vWF antigen test uses ______.
ELISA (sandwich)
What are the components of the vWF antigen test?
Coating Ab: Specific rabbit anti-human vWF Ab
Antigen: In patient plasma
Enzyme: Peroxidase
Substrate: Ortho-phenylenediamine in hydrogen peroxide
What causes high levels of vWF antigen?
- Pregnancy
- Oral contraceptive use
- Physical exercise
- Stress
- Age
Decreased levels of vWF antigen are seen with ______.
vWD
vWF activity is done through ______
RIPA
vWF activity procedure
- Reconstituted platelets mixed with dilutions of patient plasma
- Ristocetin added
- Rate of aggregation measured
- Rate is proportional to the vWF activity
Normal vWF in plasma will show an extended ladder of ______ including high MW forms.
multimers
vWF multimer analysis is done via ______.
western blot
vWD is associated with the lack of all ______ MW forms.
intermediate and/or high
Chromogenic anti-Xa assay procedure
- Patient sample + known amounts of Xa and antithrombin
- LMWH or UFH (in patient sample) binds to antithrombin to inactivate Xa
- Xa measured by cleavage of chromophore-linked substrate
Xa activity and LMWH/UFH are ______ proportional.
inversely