Concept 8.2: The free-energy change of a reaction tells us whether or not the reaction occurs spontaneously
1/9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Free energy (G)
The portion of a system’s energy that can do work when temperature and pressure are uniform throughout the system, as in a living cell

Delta G
The change in free energy, related to changes in temperature, total energy, and entropy
Represents the difference between the free energy of the final state and free energy of the initial state
Lower levels signify more stability after spontaneous expenditure

Spotaneous processes
Processes that use energy and increase total entropy
Causes a negative change in free energy (negative delta G)
Creates more stability in a system to work towards equilibrium

Nonspontaneous processes
Processes that build up or maintain total levels of energy or entropy
Causes a zero or positive change in free energy (positive delta G)
Used by the cell to perform work

Unstable systems
Systems with higher levels of free energy (G)
Seen with a diver on a platform being less stable than in the water
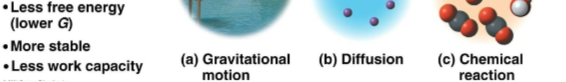
Stable systems
Systems with lower levels of free energy
Seen with a diver in the water after jumping off a platform, thus using energy
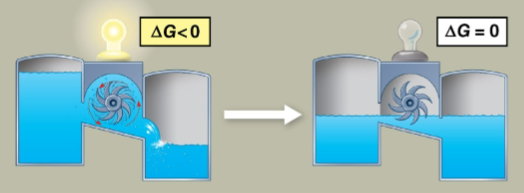
Equilibrium
The point at which forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate, creating maximum stability
Systems must nonspontaneously work to move away from equilibrium
Eventually reached by closed or isolated systems, but never reached in an open living cell with flowing materials enabling work
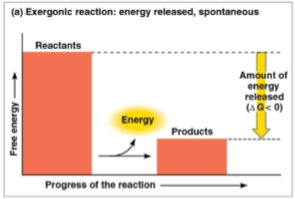
Exergonic reaction
A reaction that creates a net release of free energy to the surroundings, causing energy to be expended outward
Products store less free energy than reactants, creating a negative delta G and thus signifying a spontaneous reaction towards equilibrium
This releases potential energy
G determines how much work a reaction can perform
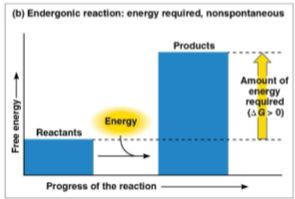
Endergonic reaction
A reaction that absorbs free energy from the surroundings, causing energy to be drawn inward
Products store more free energy than the reactants, creating a positive delta G and thus signifying a nonspontaneous reaction away from equilibrium
Higher delta G amounts require more initial energy input
Catabolic pathway
A chain of reactions as seen in cellular respiration’s individual products becoming reactants for the next steps
Steady glucose and waste progression ensure that equilibrium is never reached