TOPIC 8 CARBON - A LEVEL GEOGRAPHY - EDEXCEL
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Acidification
The gradual reduction of pH of the oceans, due to dissolving carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Afforestation
Planting trees and vegetation in the aim of increasing forest cover.
Biofuel
Burning crops and vegetation for electricity and heat
Carbon Capture & Storage (CCS)
The capture of carbon dioxide emissions directly from the factory, pumped into disused mines rather than being released into the atmosphere. - pumped underground
Carbon Fluxes
The movement of carbon between stores.
Carbon Neutral
A process that has no net addition of carbon dioxide to the environment.
Carbon Stores
Places where carbon accumulates for a period of time such as rocks and plant matter.
Choke Points
Points in the logistics of energy and fuel that are prone to restriction.
Combustion
The process of burning a substance, in the presence of oxygen, to release energy.
Decomposition
The break down of matter, often by a decomposer which releases carbon dioxide through their own respiration.
Energy Mix
The composition of a country's energy sources.
Energy Pathway
The movement of energy from its extraction or source, through pipes, freight logistics or cabling.
Energy Players
Key companies and individuals who own, distribute and sell energy and energy sources.
Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
The build-up of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, reducing the amount of solar radiation reflected into space.
Inorganic Carbon
Carbon stored in carbonated rocks.
Non-Renewable
A source of energy that can only be used once to generate electricity or takes thousands of years to replace e.g. Fossil Fuels.
Nuclear Fusion
The process of joining atomic nuclei together, to produce energy.
OPEC
Oil and Petroleum exporting countries. An organisation that supports and coordinates fossil fuel exporting countries.
Organic Carbon
Carbon stored in plant material and living organisms
Outgassing
The release of dissolved carbon dioxide (e.g. at plate boundaries, warming the oceans).
Photosynthesis
The process of converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. All plants and some organisms rely on this process to survive.
Primary Energy
The initial source of energy, as it is naturally found. This could be natural ores, water, crops or radioactive material.
Renewable
Primary energy that can be re-used to produce electricity or has a short lifetime, therefore any used can be replaced quickly e.g. Hydroelectric, biomass, solar.
Respiration
The process of converting glucose and oxygen into carbon dioxide and energy. Some organisms rely on respiration to survive.
Secondary Energy
The product of primary energy, mostly electricity.
Sequestration
The transfer of carbon from the atmosphere to stores elsewhere - living biosphere, inorganic rocks, etc.
Thermohaline Circulation
The movement of volumes of seawater from cold deep water to warm water surface water
Tipping Point
A critical threshold where any changes to a system after the tipping point are irreversible.
Urbanisation
The growth of populations in towns and cities.
Carbon Pump
The processes that operate in the oceans to store and circulate carbon - it is a natural energy force resulting in carbon flux - both gravity and descending cold currents transfer plankton remains from the ocean surfaces to seafloors.
Thermohaline circulation
The global system of surface water and deep ocean currents driven by differences in temperature (thermo-) and salinity (-haline).
Greenhouse effect
The natural process whereby outgoing thermal radiation is trapped by the atmospheric gases: water vapour, CO2 and methane.
Fossil fuels
Coal, oil and natural gas - they contain high proportion of carbon.
Energy mix
The proportions of different sources of energy used by households and industry, together with those used in electricity generation in a country.
Energy security
Where there is an uninterrupted availability of reliable energy at a national level and at an affordable price.
Fracking
The process by which shale oil and gases can be extracted using water, sand and chemicals at high pressure to crack open rocks.
Photovoltaic cells
The main method by which solar power is generated - they convert energy from the sun into an electric current.
Insolation
incoming solar energy
Biomass
Organic matter that is used as a fuel.
Biochar
The name for charcoal when it is used for the purpose of being added to the soil.
ocean acidification
A decrease in the pH of the oceans caused by the uptake of CO2 (from fossil fuel combustion) from the atmosphere.
Ecosystem service
A way of valuing natural systems - it attempts to measure 'what an ecosystem does for society', e.g - trees taking up co2 as they grow are providing a service.
Tipping point
A point in time when change becomes irreversible and moves from one stable state to another.
Kuznets curve
A graph that shows a theoretical relationship between environmental quality and economic development (often shown as rising personal income).
Albedo
Refers to the reflectiveness of surfaces that redirects shortwaves solar radiation back into space with limited heat absorption - it is rated between 0 and 1.
- Light colours - 0.1 - high albedo
-Dark colours - 0.7
Aquaculture
The management of water environments for the purpose of increasing the harvesting of fish stocks (fish farming).
carbon fixation
The initial incorporation of carbon into organic compounds.
carbon sink
A natural environment that absorbs and stores more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than it releases, which offsets greenhouse gas emissions.
Carbon pools
Places where carbon accumulates in ecosystems
Biogeochemical
relating to or denoting the cycle in which chemical elements are transferred between living systems and the environment
OPEC
Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries
Ocean carbon store
Carbon dioxide is dissolved by oceans from the atmosphere
Atmospheric carbon stores
Carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere through volcanic activity, respiration, wildfires and outgassing etc.
Terrestrial carbon stores
Carbon stored in the ground - specifically within sedimentary rocks.
volcanic outgassing
the release of gases into the atmosphere during volcanic eruptions
Chemical weathering of rocks
Atmospheric CO2 dissolves in water and becomes acid to weather rocks on land
Sedimentary carbonate rocks
60,000-100,000,000 billion tonnes
carbon capture and storage (CCS)
The process of capturing waste CO2, transporting it to a storage site, and depositing it where it will not enter the atmosphere, normally underground.
Hydrogen fuel cells
A device that uses hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity
Electric vehicles
Benefits = carbon neutral, cheap and minimal noise
Costs = only 340 mile range, 4903 charging locations to 110,000 EVs 2017, cost, energy source
Peatlands
Areas of peat soil in wetland habitats formed by the accumulation of partially decayed organic matter. Peat is commonly used as a garden compost. - they release methane.
Forest dieback
tropical rainforests could become drier and change to less productive grasslands
absorb less carbon
lower NPP
Carbon taxation (mitigation)
Governments impose taxes on carbon emissions - encouraging low carbon alternatives.
energy effiency
a measurement of usable energy after an energy conversion
Water conservation and management
smart irrigation, recycling sewage water for agriculture, developing stringent conservation techniques
+ can be effective in reducing consumption
- difficult for people to adapt to
Land-use planning
a set of policies and activities related to potential uses of land that is put in place before an area is developed
Flood risk management
- Strengthening the embankments of streams and rivers
- Putting in place flood emergency procedures
- Steering urban development away from high-risk areas such as floodplains
solar radiation management
a type of climate engineering which seek to reflect sunlight and thus reduce global warming.
Resilient agricultural systems
conservation cropping with no ploughing which retains stubble and grows over crops
+ increased yields
+ increased incomes for farmers
business as usual
Emissions continue rising at current rates, RCP 8.5 - up to 4 degree exceed
Some mitigation
Emission rise to 2080 then fall, RCP 6 - likely to exceed 2 degrees.
Strong mitigation - carbon neutral
Emissions stabilise at half todays level by 2080, RCP 4.5 - not as likely to exceed 2 degree increase.
Aggressive mitigation - go green
Emissions halved by 2059, RCP 2.6 - not likely to exceed 2 degree increase.
Biosphere
Is made up of the parts of the Earth where life exists. (All (known) life is carbon. - It extends from the deepest roots systems of trees, to the dark environment of ocean trenches, to lush rainforests and highest mountain tops.
Why is carbon important?
- It is needed by all plants and animals in order to survive.
- The recycling of carbon is essential for life on Earth.
- It enables plants to provide their own energy (producers), which consumers ultimately derive their energy from.
- Stored carbon, eg, fossil fuels, are used to provide energy that derives industry and our economies.
The carbon cycle
- Plants make carbon compound from carbon dioxide they take from air (photosynthesis).
- Animals obtain carbon compounds by eating plants or other animals, or both.
- Animals and plants return carbon back to the atmosphere when they respire.
- When animals and plants die, microbes digest them and obtain carbon compounds from their bodies.
- Microbes respire, this releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
- Burning of wood and fossil fuels releases large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere - Human activities have caused an imbalance in the natural carbon cycle = more co2 in the atmosphere now than before.
Hydrocarbons
Are a wide range of chemical compounds based on carbon and hydrogen - eg, coal, oil, gas etc.
Carbon units of measurements
Gtc = a gigatonne of co2 is used to measure the amount of carbon in stores
The main carbon stores
- Lithosphere (rock) = 100 million Gtc
- Hydrosphere (oceans) = 38,000 Gtc
- Biosphere = 3,000 Gtc
- Pedosphere (soil) = 1,500 Gtc
- Atmosphere (GHGs) = 750 Gtc
- Cryosphere (snow, ice, permafrost) - CH4 (Methane)
IPCC
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
- Independent climatologists that produce climate actions
Marine snow
In the deep ocean, marine snow is a continuous shower of mostly organic detritus falling from the upper layers of the water column. It is a significant means of exporting energy from the light-rich photic zone to the aphotic zone below.
Plankton bloom
Is a phytoplankton population explosion - they occur when sunlight and nutrients are readily available to the plants, and they grow and reproduce to a point where they are so dense that their presence changes the colour of the water in which they live.
Ocean gyre
Large system of circular ocean currents formed by global wind patterns and forces created by Earth's rotation. - The ocean conveyor belt = movement of water around the world.
Lithification
The process by which sedimentary rocks become compressed into solid rock (lithology) due to pressure - turns sediment into rock.
Diffusion
Is the exchange of carbon gases between the surface layers of two or more spheres. - The net movement of carbon from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. -
Carbon source
A store that emits more carbon than it absorbs
Carbon sink
A store that absorbs more carbon than it emits
Cryosphere
Means the place on Earth where water is in its solid form - eg, snow.
Where does carbon originate?
- Carbon and CO2 originates from the Earth's interior.
- Most CO2 is formed when carbonate rocks undergo metamorphosis
- The CO2 formed is released into the atmosphere through volcanic activity at plate boundaries and hot spots.
- Once released carbon doesn't just stay in the atmosphere but ends up in other stores.
Carbon cycling
Is the movement of carbon
- Organic = refers to matter derived from living things both plants and animal residues.
- Non-organic = refers ti compounds that derive from non-living matter.
- Gaseous = found as co2, cH4 and carbon monoxide.
What are the carbon flows?
- Respiration
- Erupting volcanoes
- Decomposition
- Weathering
- Erosion
- Combustion
- Photosynthesis
- Carbon Sequestration
What are the carbon stores?
- Atmosphere
- Sedimentary rocks
- Lithosphere
- Fossil fuels
- Ocean surfaces
- Biosphere
- Cryosphere
- Deep oceans
The geological cycle
The creation and modification by numerous physical, chemical, and biological processes of the materials on or near the earths surface.
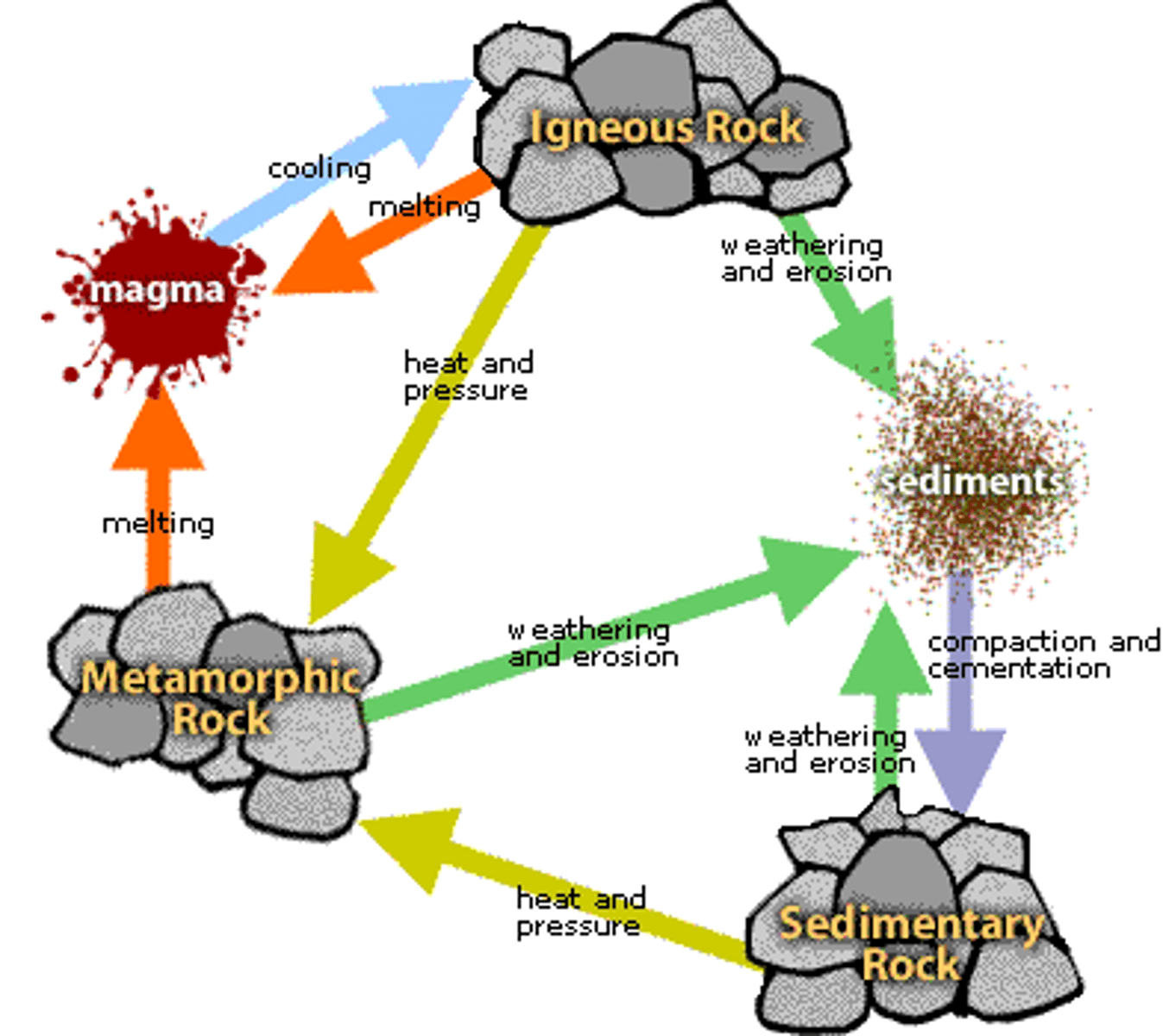
Igneous rock
Forms when magma cools and crystallises, either at volcanoes on the surface of the Earth (extrusive, eg, granite) or while melted rock is still inside one crust (intrusive, eg, basalt)
Subduction
Is the melting of the Earth.
Erosion
Is the breakdown of rocks into material that is transported away by wind or water.
Weathering
Is the breakdown of rocks in situ, the sediment stays in the same area. - mechanical, chemical, and biological
Sedimentary rock
Formed by large layers of sediment that were deposited under water.
Metamorphic rock
Formed through the transformation of other rocks by heat and pressure.
Geological carbon
Results from the formation of sedimentary carbonate rocks (limestone and chalk in the oceans)