attention and transformers
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
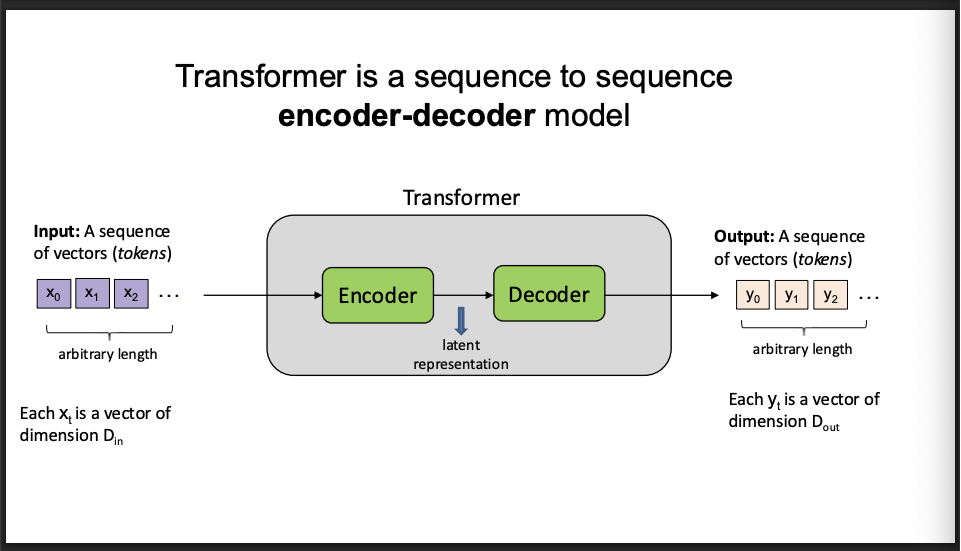
transformer is a
sequnce to sequence
encoder decoder model
Transformer is based on
"Attention"
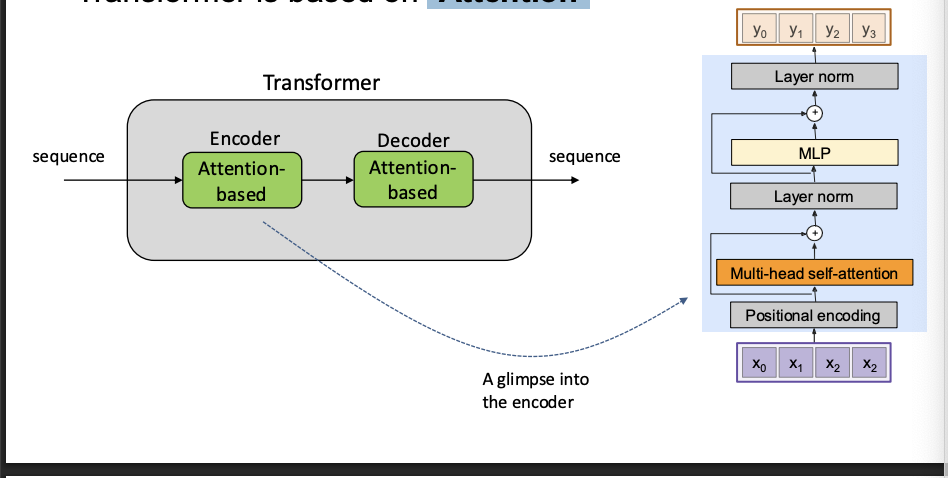
What’s so cool with "Attention"?

types of ways to model attention mathematically
Cross Attention
• Self Attention
• Multi-head Attention
• Masked Attention
cross attention layer
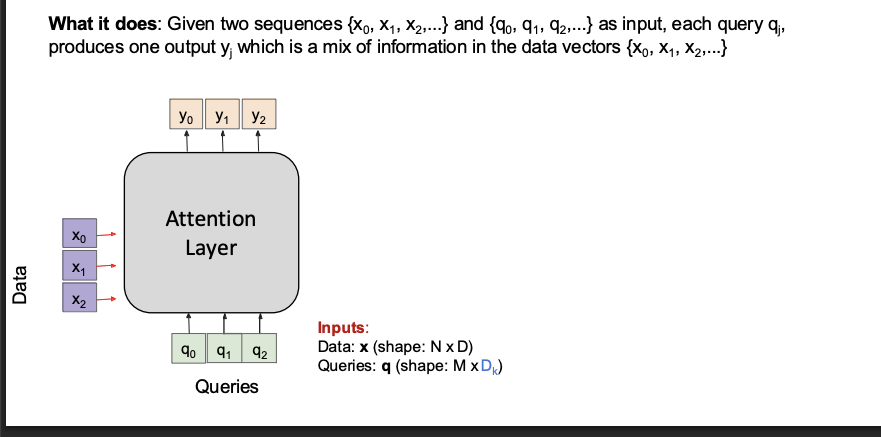
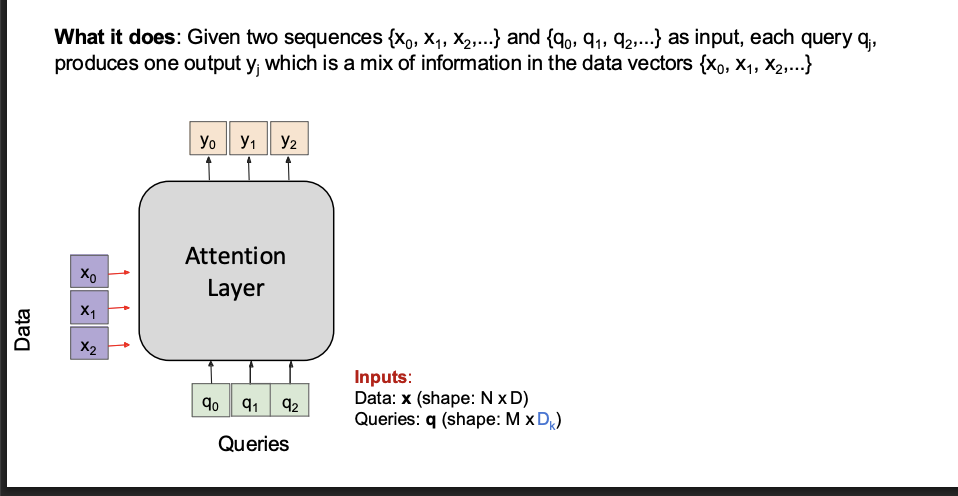
In attention, instead of only looking at the last hidden state, the model can:
“Look at all relevant parts of another sequence and decide what matters most right now.”
what is cross attention
Cross-attention = attention between TWO DIFFERENT sequences.
Example:
Source sequence = English sentence
Target sequence = French sentence being generated
When generating each target word, the model:
looks at all source words and decides which ones are important.
That is cross-attention.
Type | Attends to |
|---|
Self-attention | Same sequence |
Cross-attention | Another sequence |
intutiion of cross attention using rnn language
3. Intuition Using RNN Language
Think of this like:
Instead of the decoder using only:
h_t = RNN(h_{t-1}, x_t)
It also gets a context vector:
h_t = RNN(h_{t-1}, x_t, context_t)And that context_t is computed by attention over the encoder states.
the core idea of cross attention in one sentence
Cross-attention computes a weighted sum of another sequence’s representations, where the weights are decided by similarity.
the math of cross attention simple and clean
We have:
Query (Q): comes from decoder
Keys (K): come from encoder
Values (V): come from encoder
Q ∈ R^{n × d}
K ∈ R^{m × d}
V ∈ R^{m × d}
n = target length
m = source length
d = vector size
Step 1: Compute similarity scores
Scores = Q K^T
This gives:
Scores ∈ R^{n × m}Step 2: Normalize with softmax
Weights = softmax(Q K^T / sqrt(d))Step 3: Weighted sum of values
Output = Weights × V
Result:
Output ∈ R^{n × d}cross attention layer slides
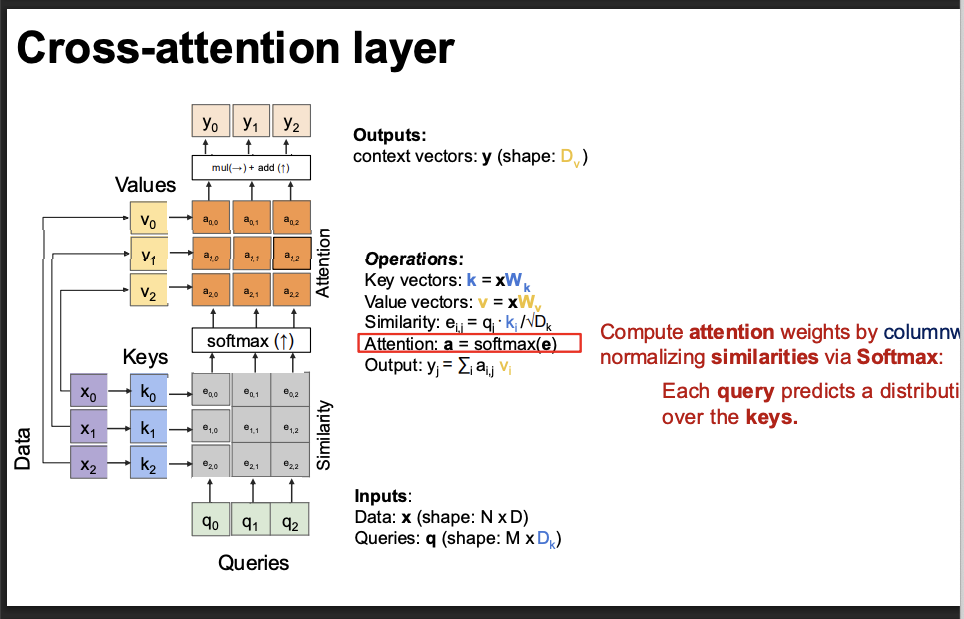
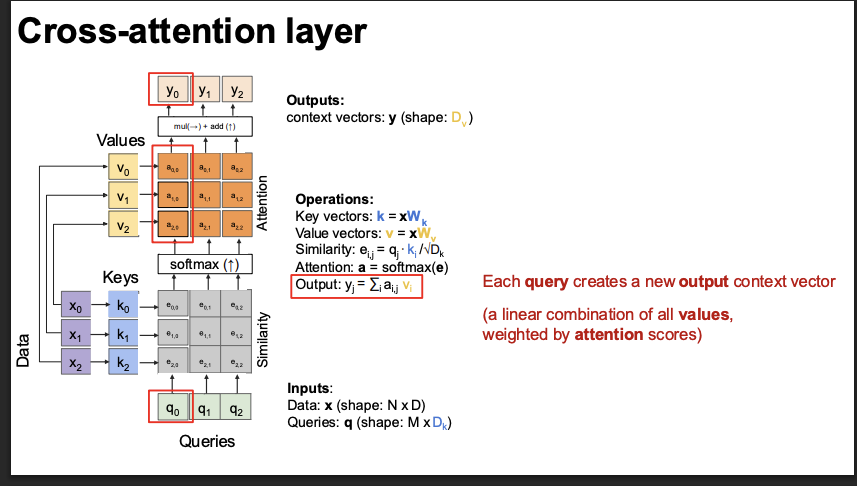
notice that its a scaled dot product.
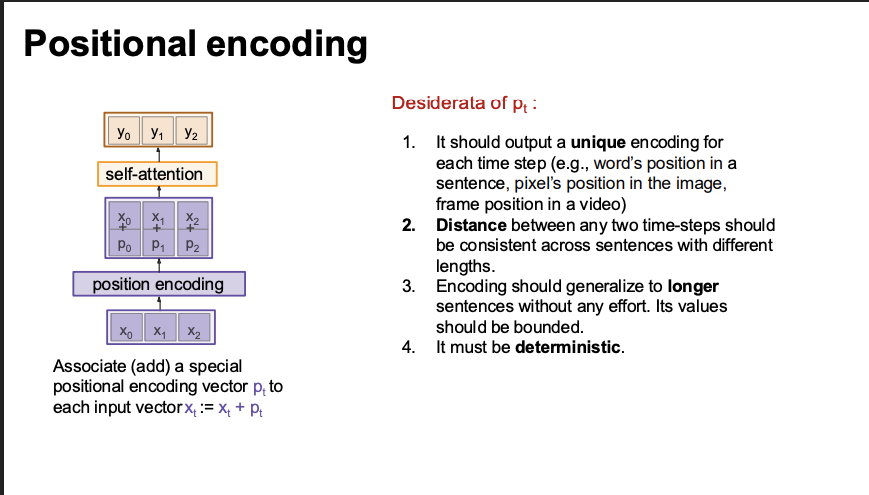
permutation equivariance
Self-attention doesn’t care about the order of the input vectors!
positional encoding
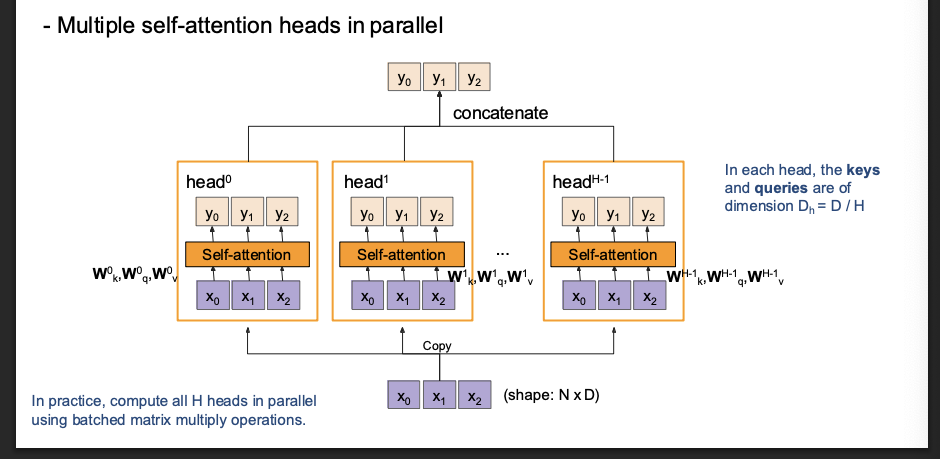
multi head self attention layer
semantic segmentation idea fully convolution
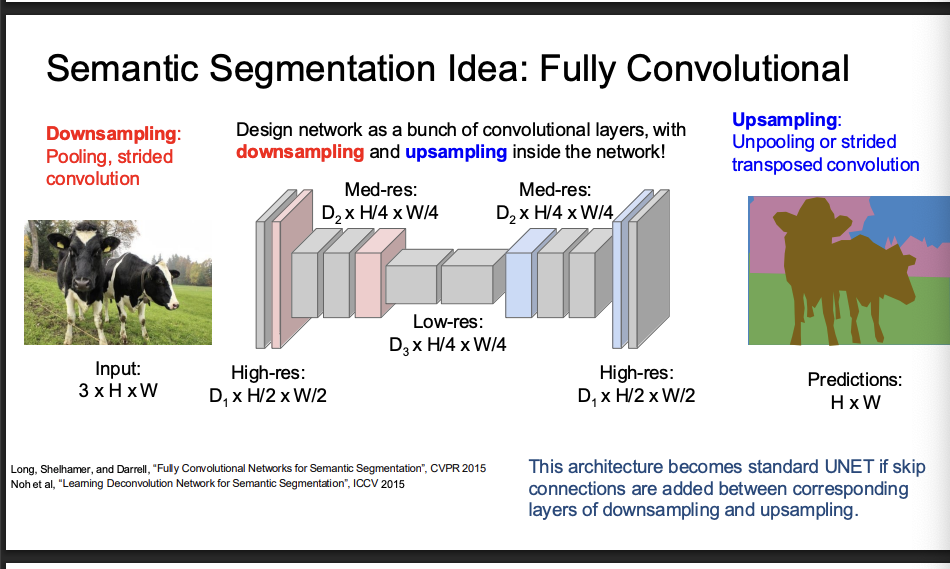
unet
downsample, upsample, but also have skip connections
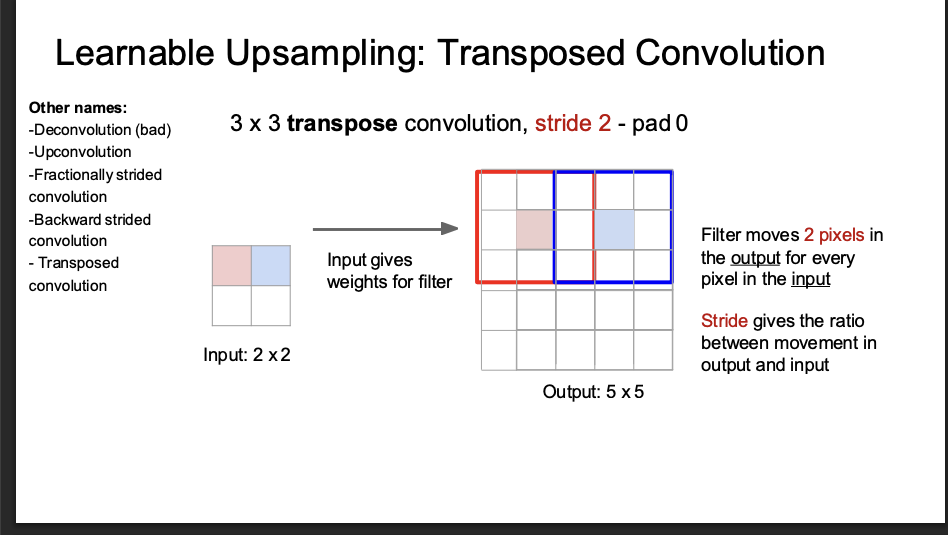
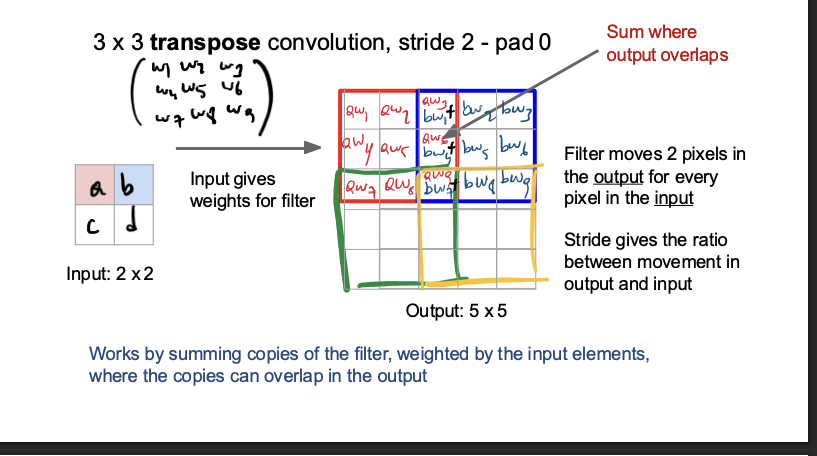
learnable upsampling - transposed convolution
pretty much like reverse lmao?
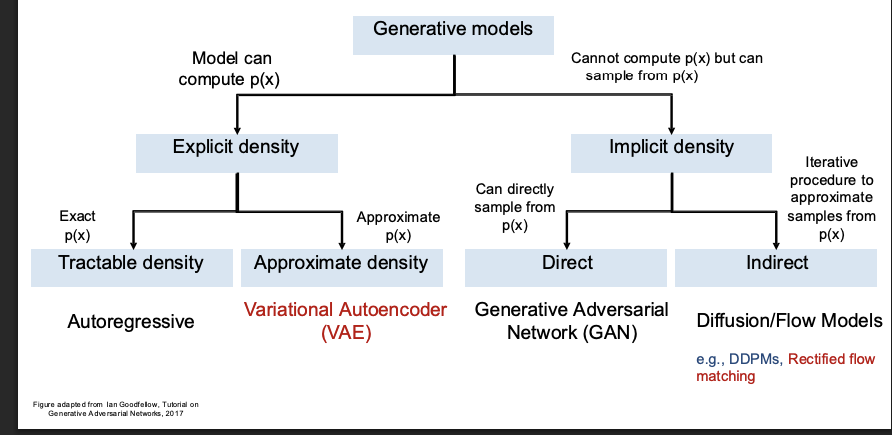
taxonomy of generative models
general idea rectified flow matching

auteoeconders