Male and Female Pelvis (copy)
1/131
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
What organs are in the true pelvis?
bladder, distal ureters, bowel, female reproductive organs
What is the linea terminalis?
the border between the true and false pelvis. true pelvis
What muscles make up the false pelvis?
Posas major and the iliacus
Where does the psoas major originate?
lateral spine, distal thoracic and first 4 lumbar vertebrae
Where does the iliacus muscle originate?
superior iliac fossa and iliac crest
What is the iliopsoas?
distal posas combines with iliacus
Where does the iliopsoas attach?
lesser trochanter of femur
What is the lateral landmark of the true pelvis?
the iliopsoas
What muscle may be seen in a sonographic image at the lateral borders of the bladder?
the iliopsoas
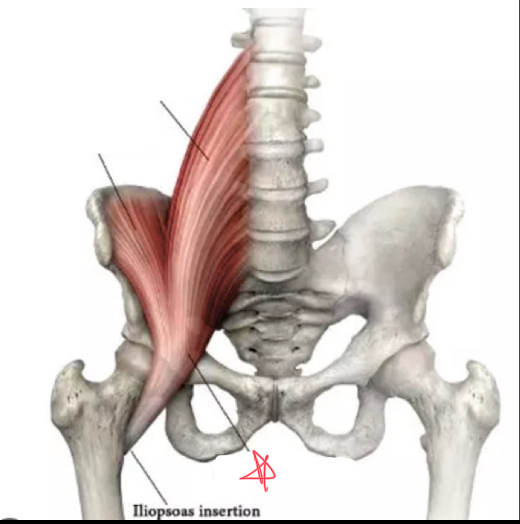
What is the origin of the piriformis?
anterior surface of sacrum
What is the insertion of the piriformis?
greater trochanter of femur
Where is the piriformis?
posterior to uterus, ovaries, vagina, and rectum
What muscle might be mistaken for ovaries on an ultrasound?
the piriformis
What is the largest nerve in the body?
the sciatic nerve
Where does the sciatic nerve originate?
lower lumbar and upper sacral nerves
Where does the sciatic nerve run?
most commonly under the piriformis, but it varies per patient
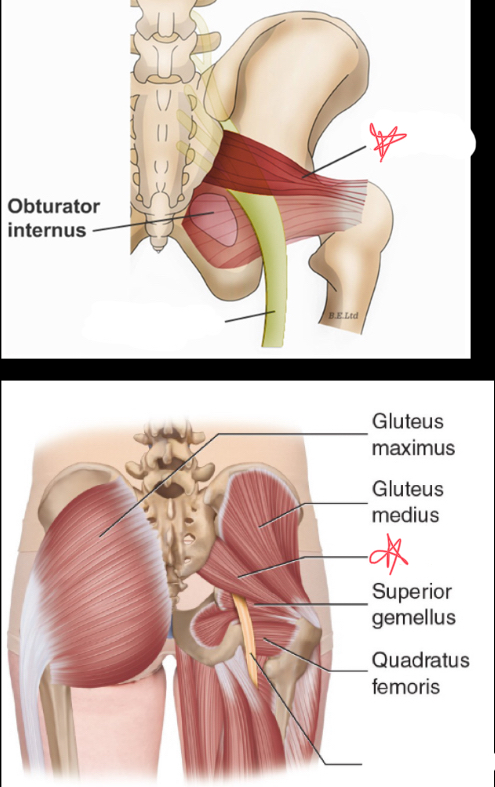
Where does the obturator internus originate?
the anterior lateral margins of true pelvis
Where does the obturator internus insert?
greater trochanter of femur
Where does the obturator internus lie?
posterior and medial to the iliopsoas muscle at the vaginal level
What muscles make up the levator ani?
Puborectalis
iliococcygeus
pubococcygeus
What is the function of the levator ani?
form the pelvic foor, supports and positions pelvic organs
testicle
egg shaped organ within scrotum, produces sperm and male hormones
epididymis
duct posterior to testicle that transports sperm to vas deferens
EJ duct
formed where the vas deferens meets seminal vesicle, pass through prostate and open to urethra
seminal vesicles
paired glands at posterior to bladder and superior to prostate
prostate
gland surrounding neck of urinary bladder and male urethra
bulbourtheal gland
pea shaped glands inferior to prostate and just proximal to penile tissue
corpus cavernosum
two masses of erectile tissue (anterior) forming most of the penis
corpus spongiosum
single smaller mass of erectile tissue surrounding urethra (posterior)
In a transverse transabdominal bladder and prostate image, where are the organs located?
bladder: anterior
prostate: posterior
In a sagittal transabdominal bladder and prostate image, where are the organs located?
prostate is seen posterior and inferior to bladder
What is the broad ligament?
double fold of peritoneum covering the fallopian tubes, ovaries, uterus, & blood vessels
Where does the broad ligament attach?
extends from lateral walls of uterus to sidewalls of pelvis
What is the cardinal ligament?
thickening at base of the broad ligament
Where does the cardinal ligament attach?
lateral cervix and vagina to pelvic wall
Where does the ovarian ligament attach?
extends from cornua to medial aspect of ovary
Where does the round ligament attach?
arises from the cornua anterior to fallopian tubes and extends to pelvic sidewalls
Where does the suspensory/infundibulopelvic ligament attach?
extends from lateral ovary to pelvic sidewall
Internal iliac arteries
branch of the common iliac
posterior to uterus and ovaries
uterine arteries
branch of internal iliac arteries, supplies vagina, uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, and ovaries
arcuate arteries
branch of uterine arteries
prominent vessels in outer 1/3 of myometriumi
ovarian arteries
branch off aorta just inferior to the renal arteries
supply ovaries
Where does the right ovarian vein empty into?
The IVC
Where does the left ovarian vein empty into?
left renal vein
What are the spaces in the female pelvis?
retrouterine
anterior cul de sac
space of retzius
What is the retrouterine pouch?
anterior to rectum and posterior to uterus
What is the most inferior space in the female pelvic cavity?
retrouterine pouch
What are the other names for the retrouterine pouch?
pouch of Douglas
posterior cul de sac
Which pelvic space is the most likely to accumulate fluid?
retrouterine
Where is the anterior cul de sac?
anterior to uterus and posterior to bladder
What is the other name for the anterior cul de sac?
the vesicouterine pouch
Where is the Space of Retzius?
anterior to bladder and posterior to symphysis pubis
What are the other names for the Space of Retzius?
retropubic space
prevesical space
iliac crest
pubic symphysis
sacrum
iliac crest
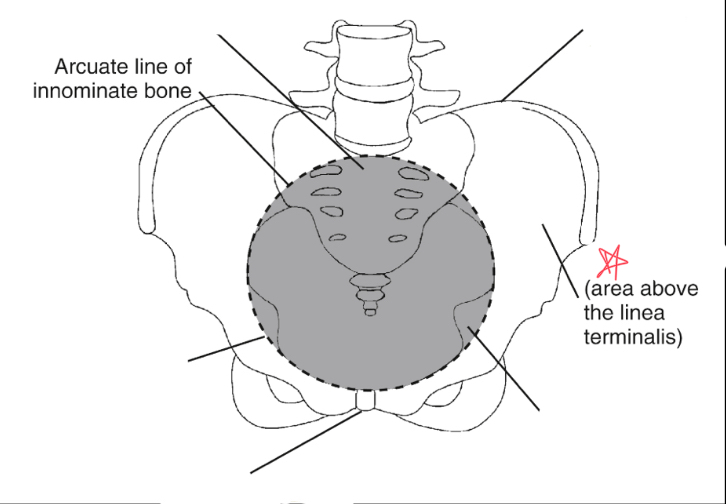
false pelvis
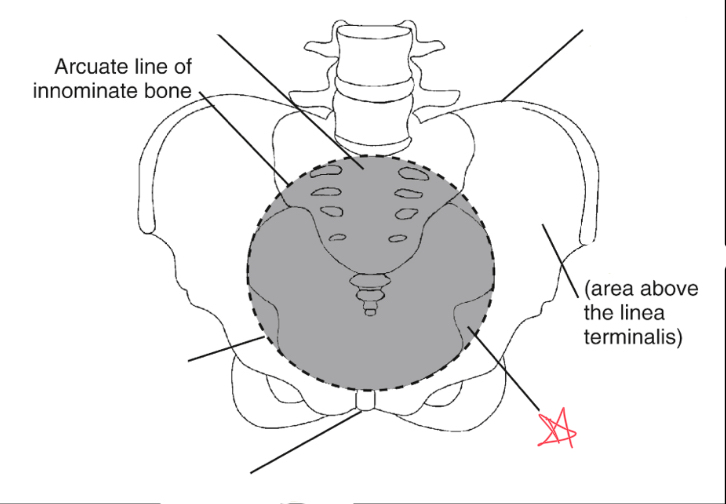
true pelvis
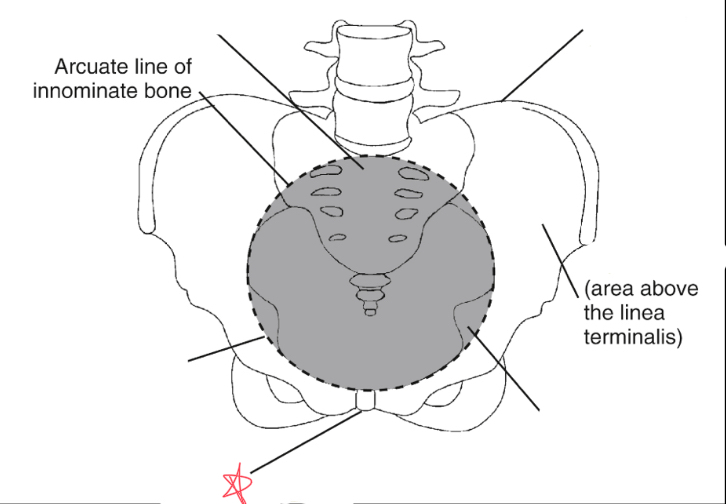
pubic symphysis
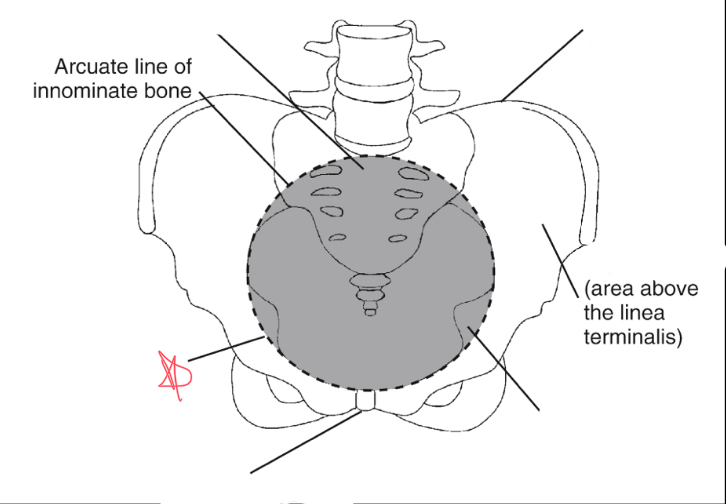
linea terminalis
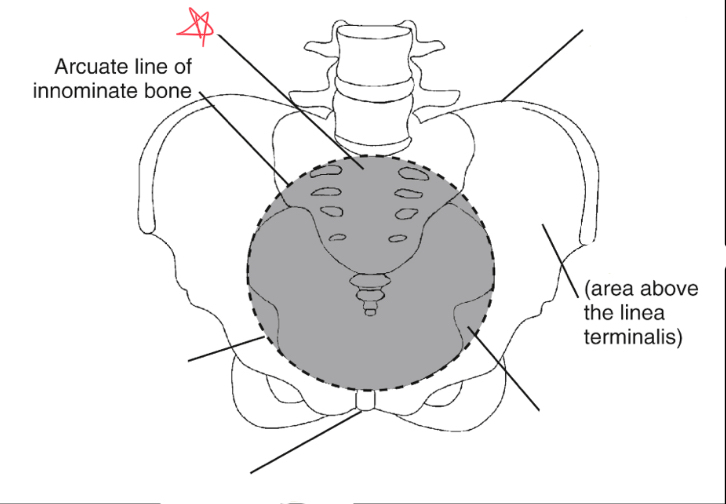
sacral promontory
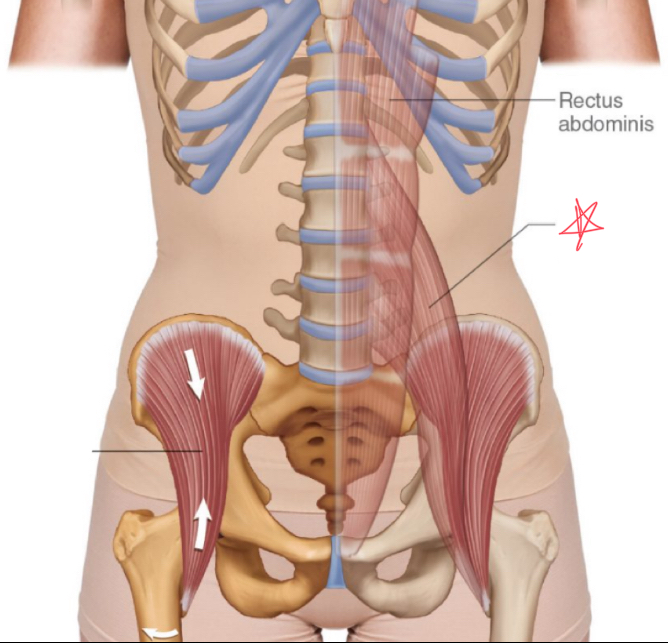
psoas major
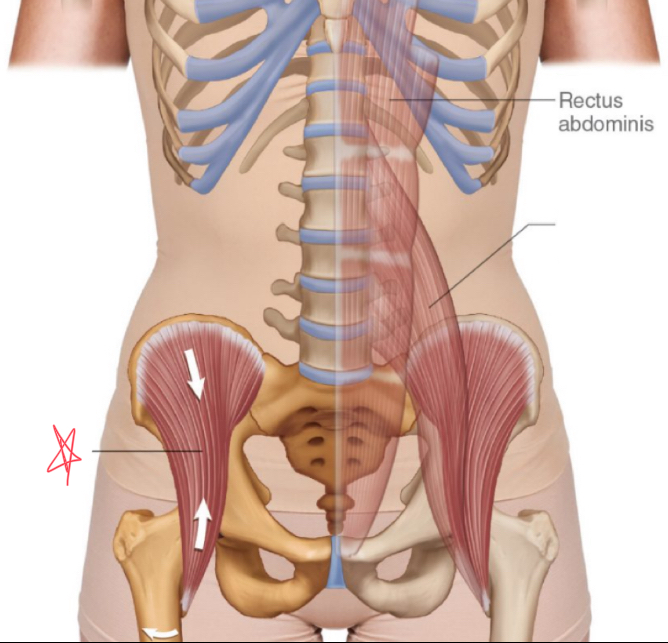
iliacus
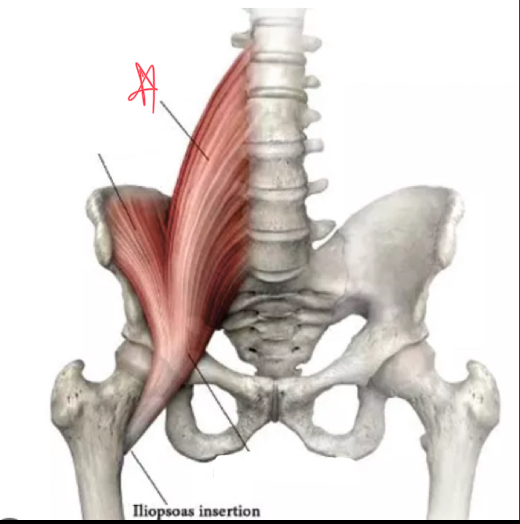
psoas
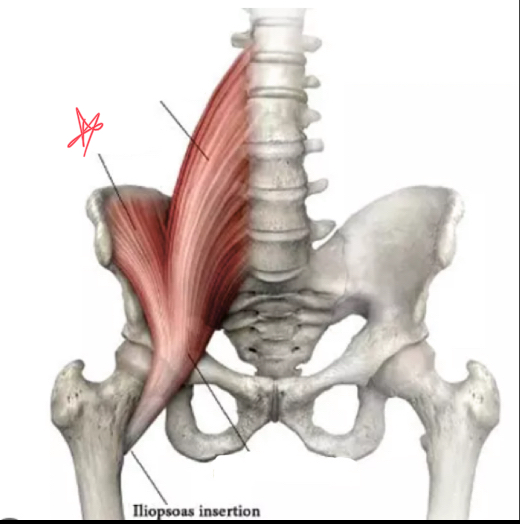
iliacus
iliopsoas
piriformis
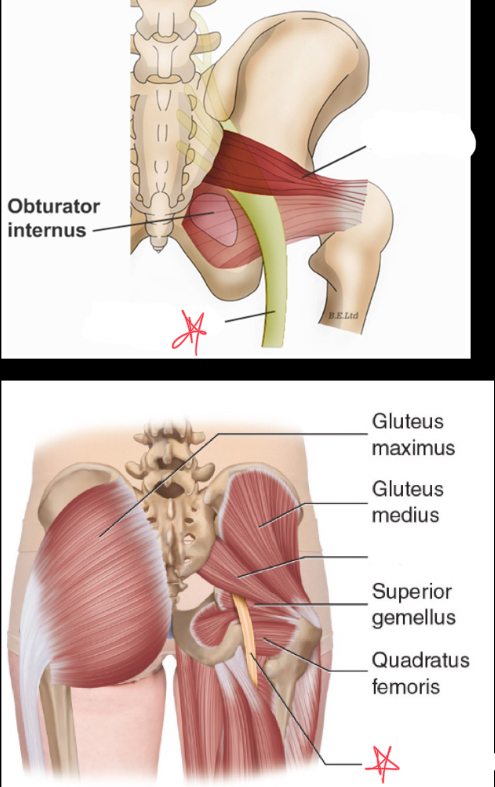
sciatic nerve
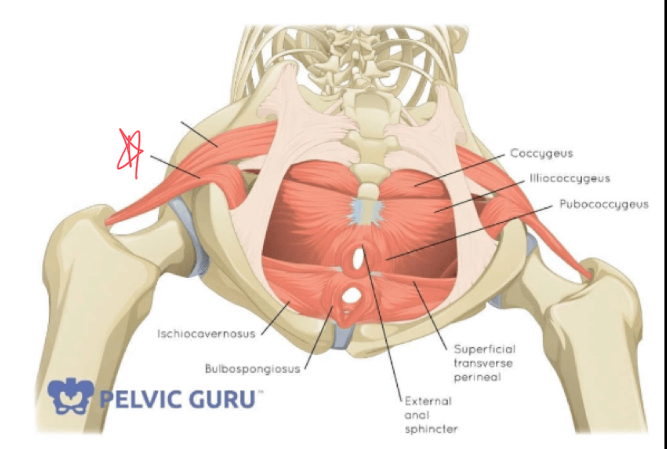
obturator internus
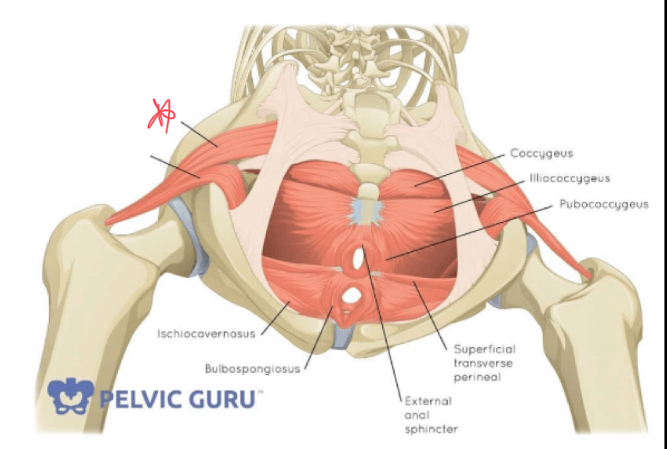
piriformis
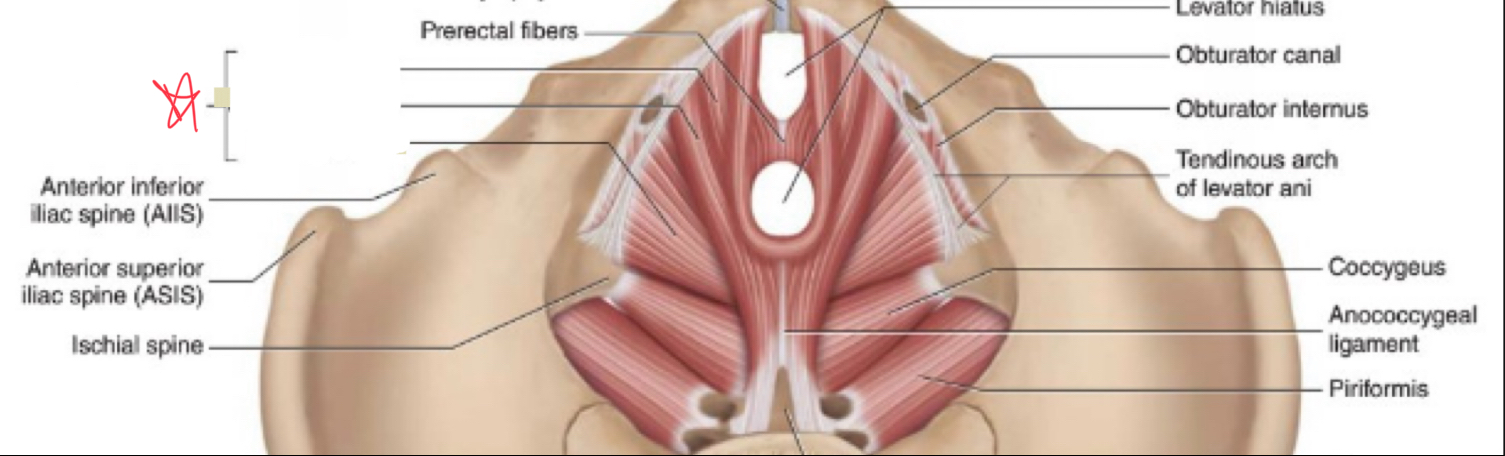
levator ani
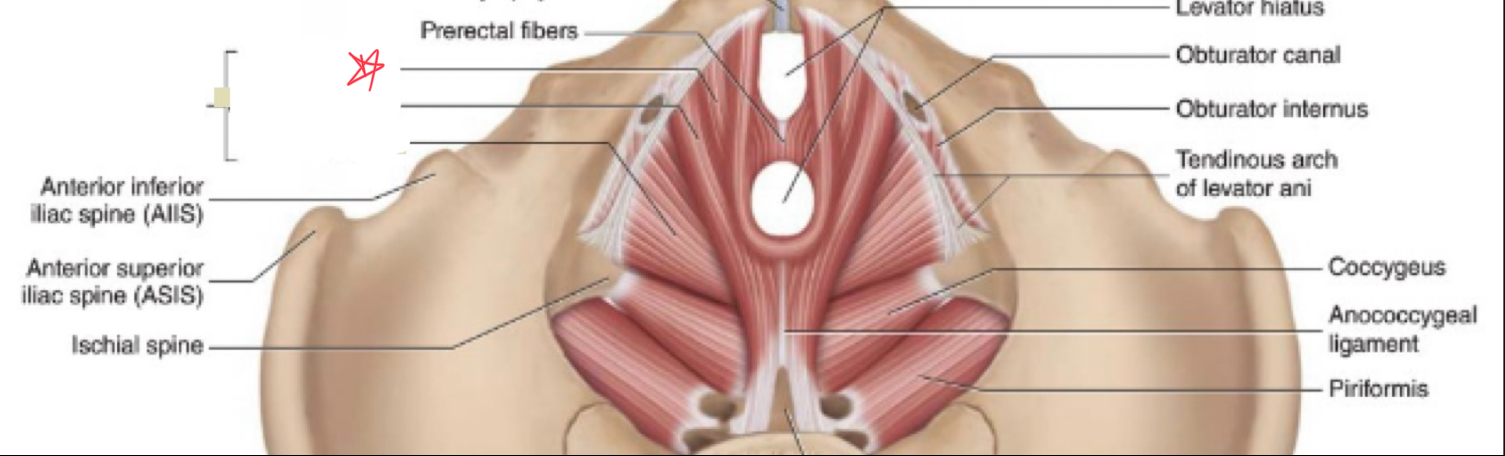
puborectalis
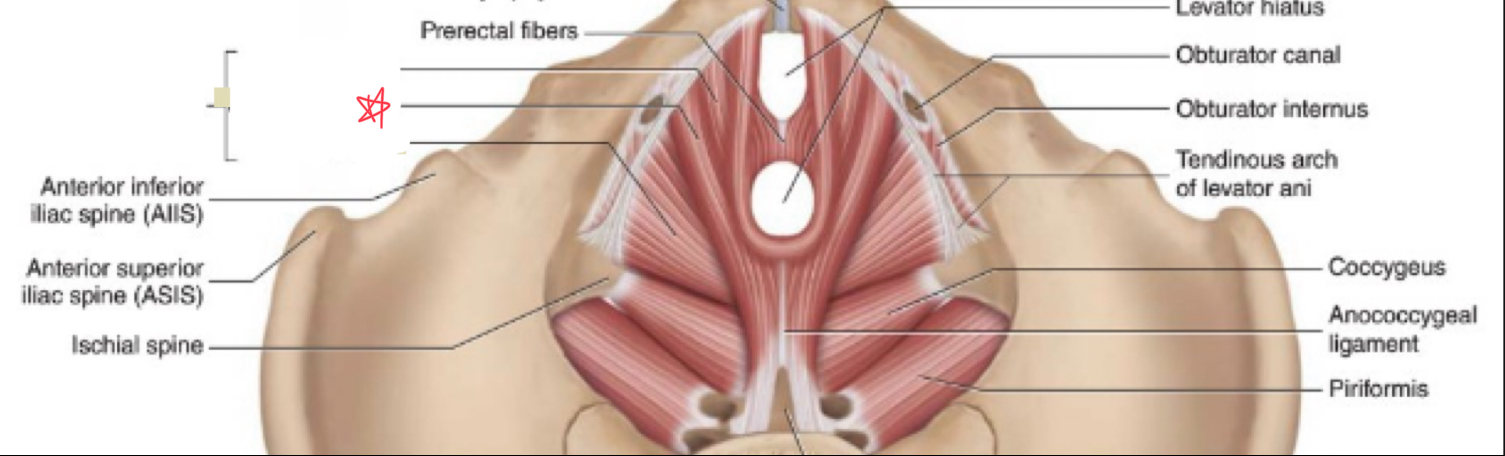
pubococcygeus
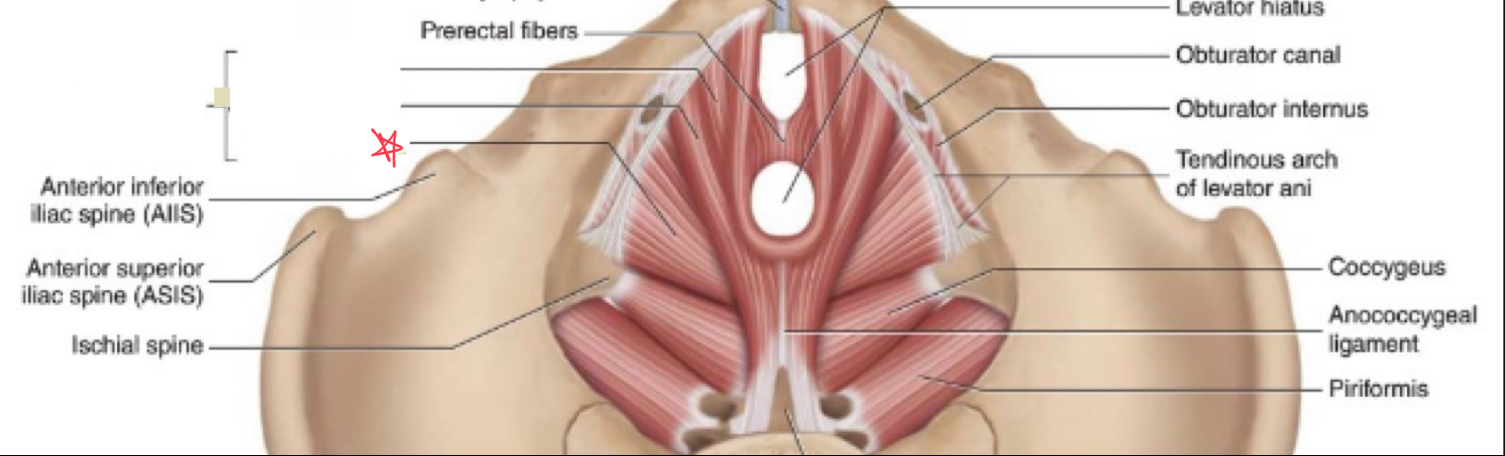
iliococcygeus
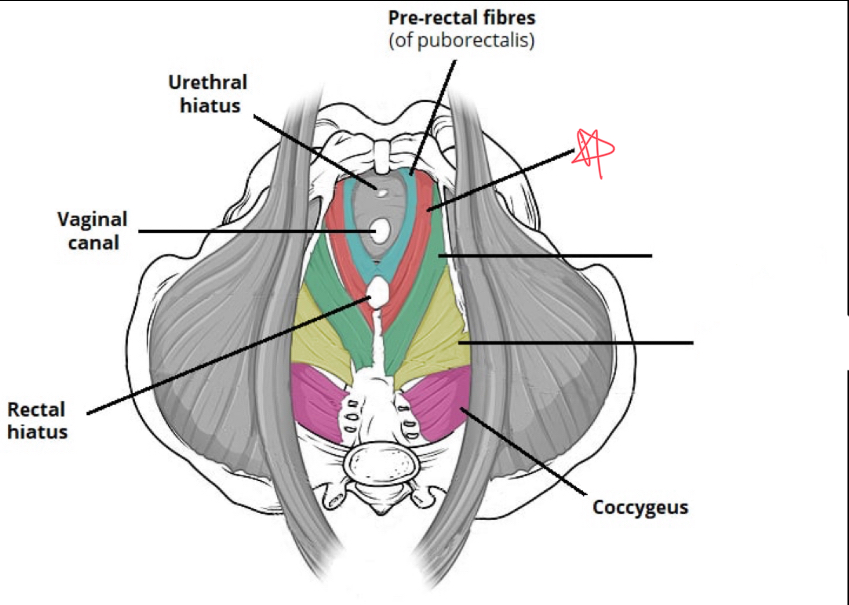
puborectalis
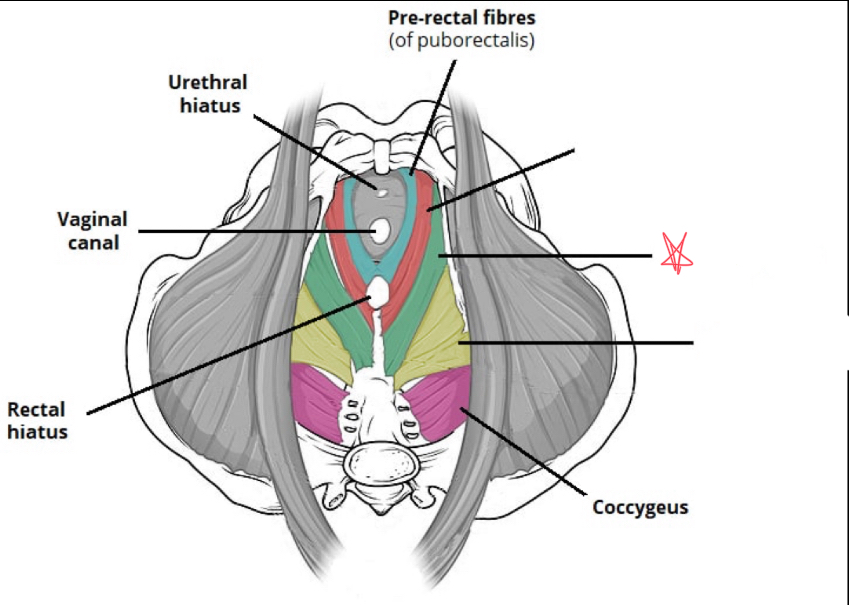
pubococcygeus
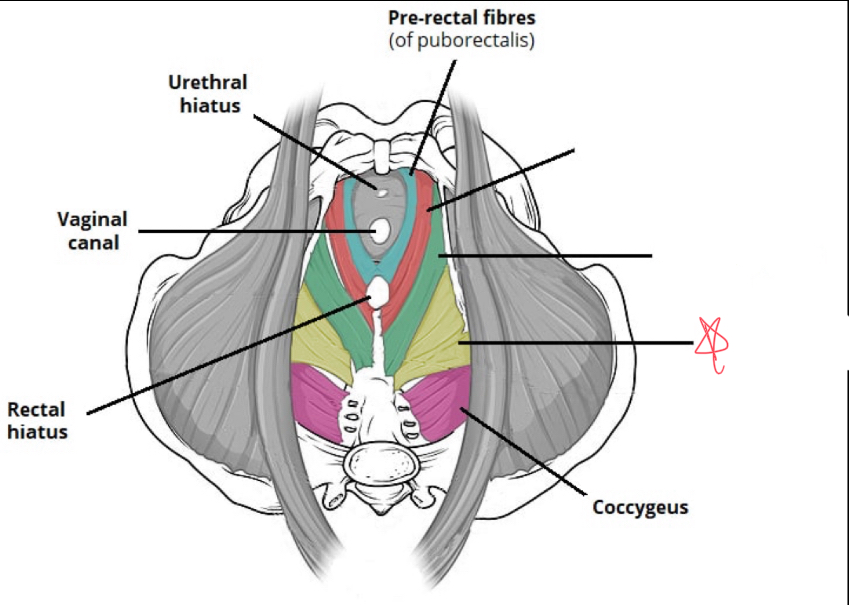
iliococcygeus
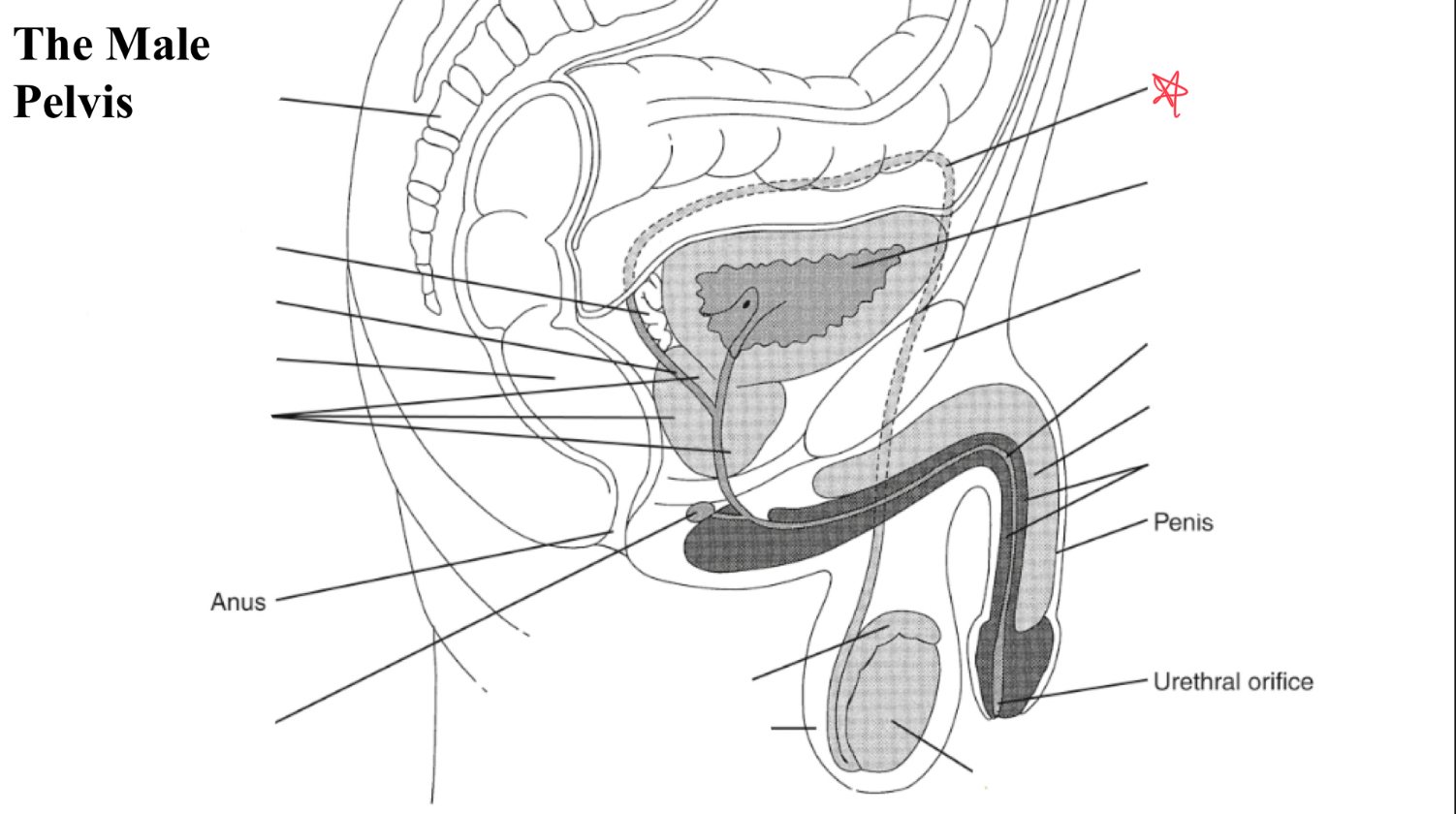
vas deferens
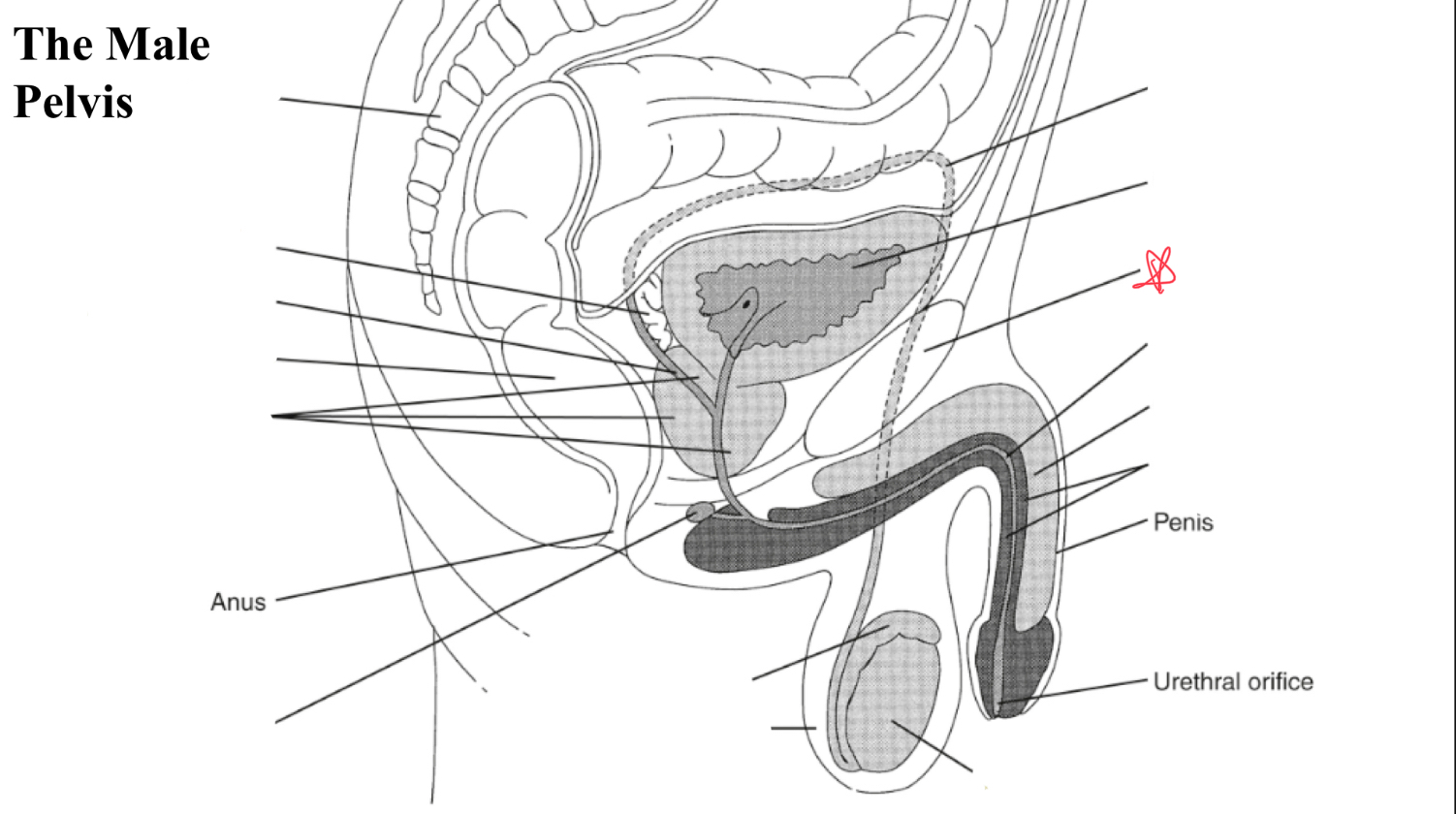
symphysis pubis
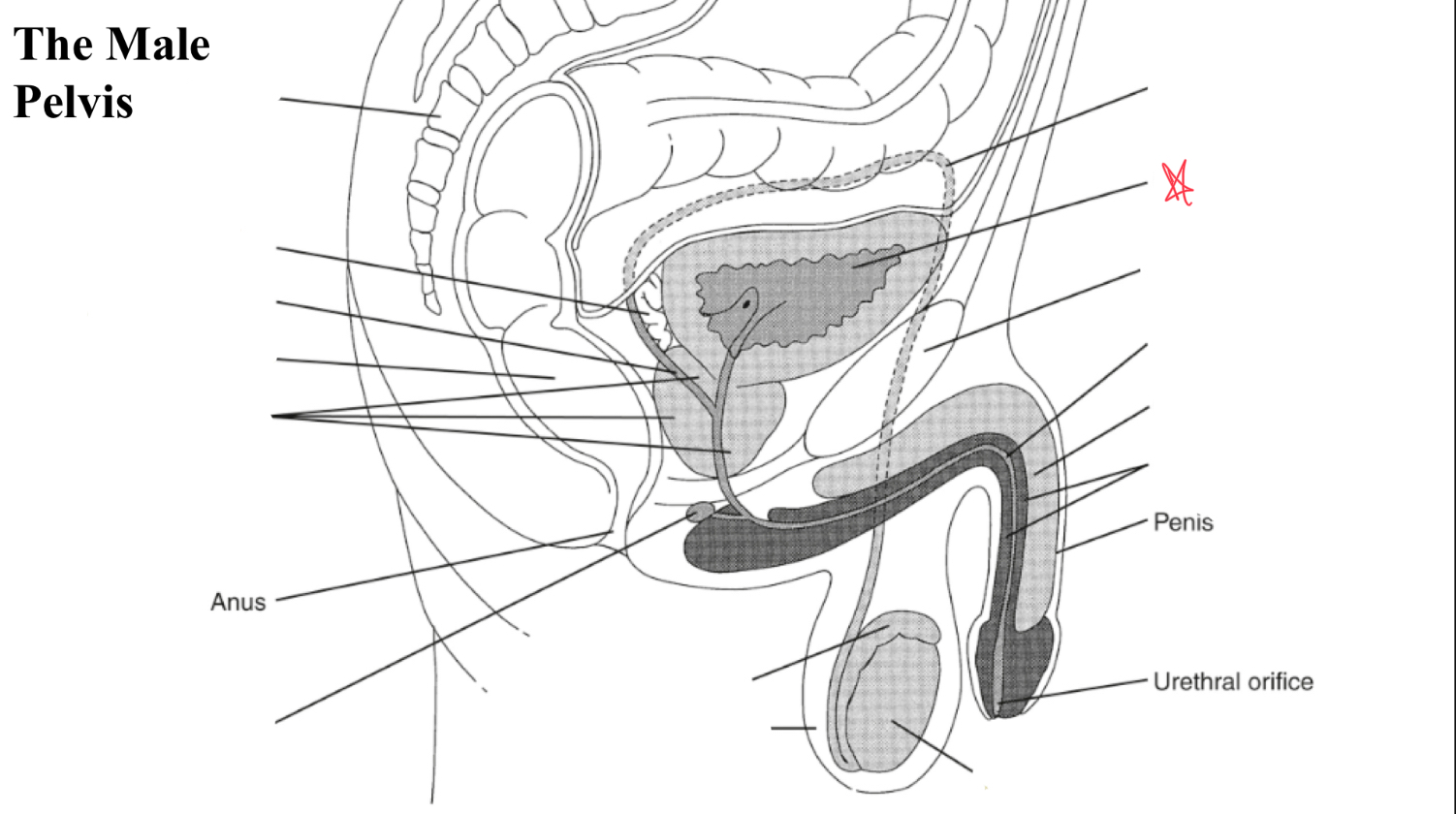
bladder
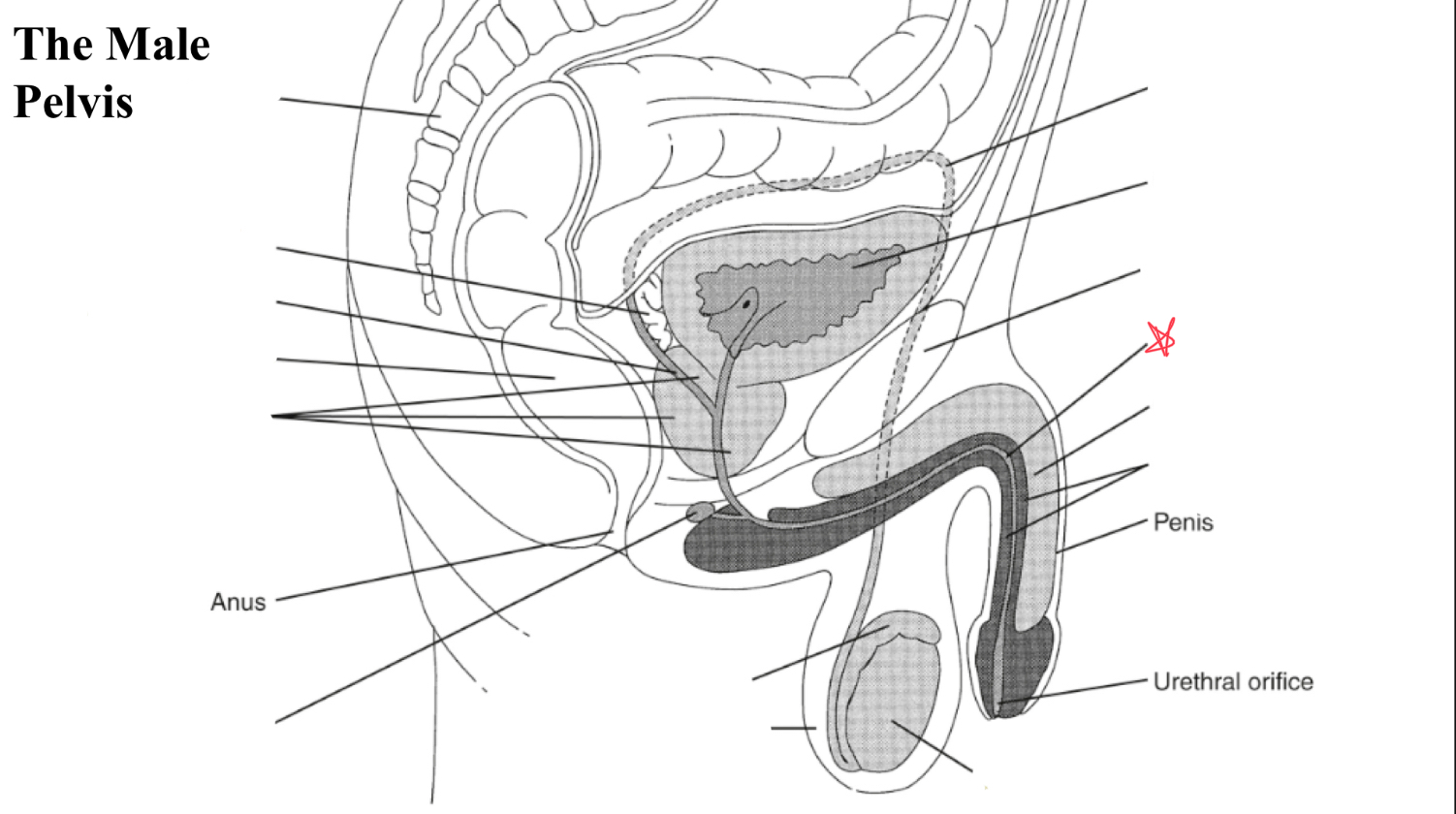
urethra
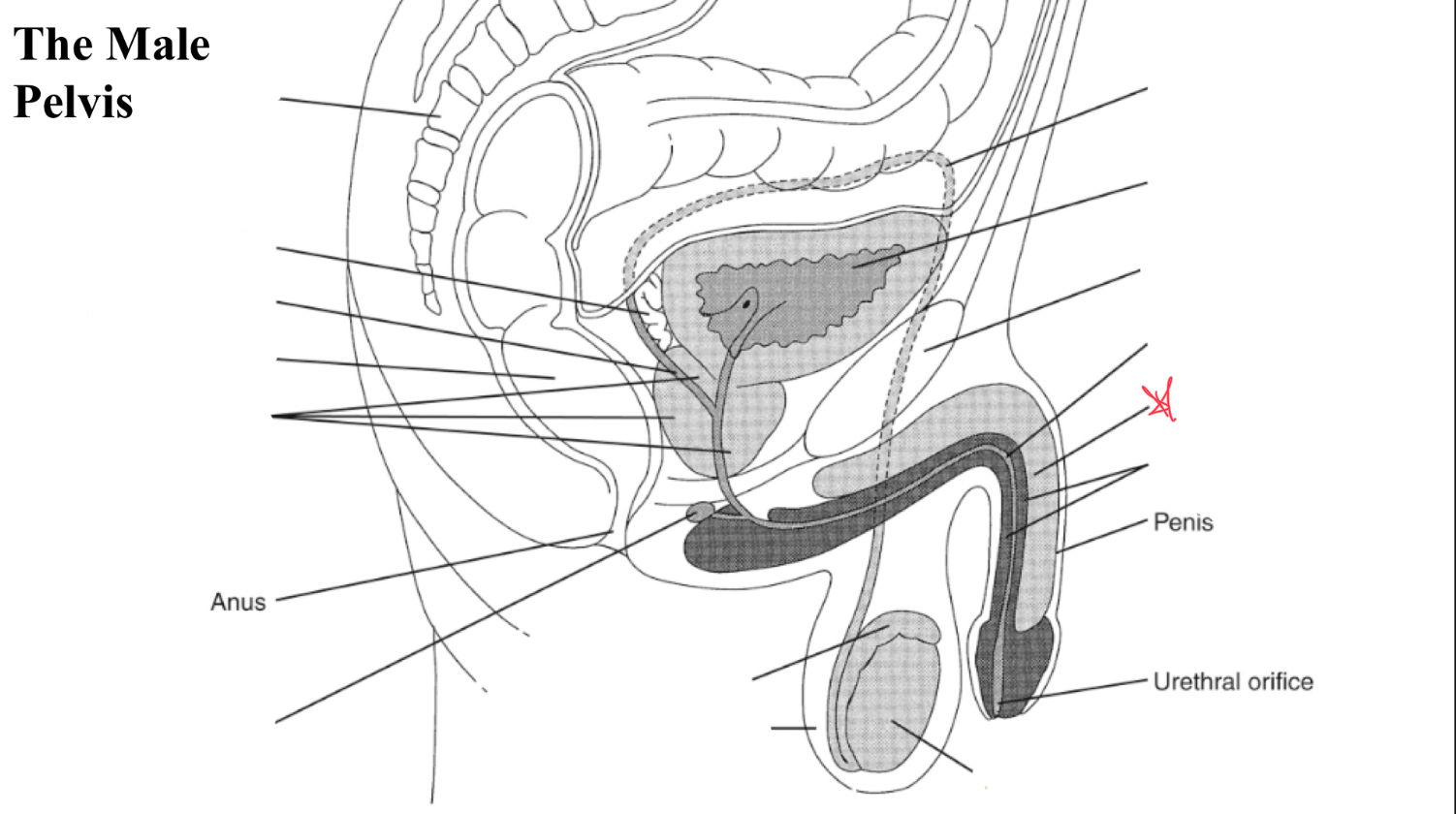
corpus cavernosum
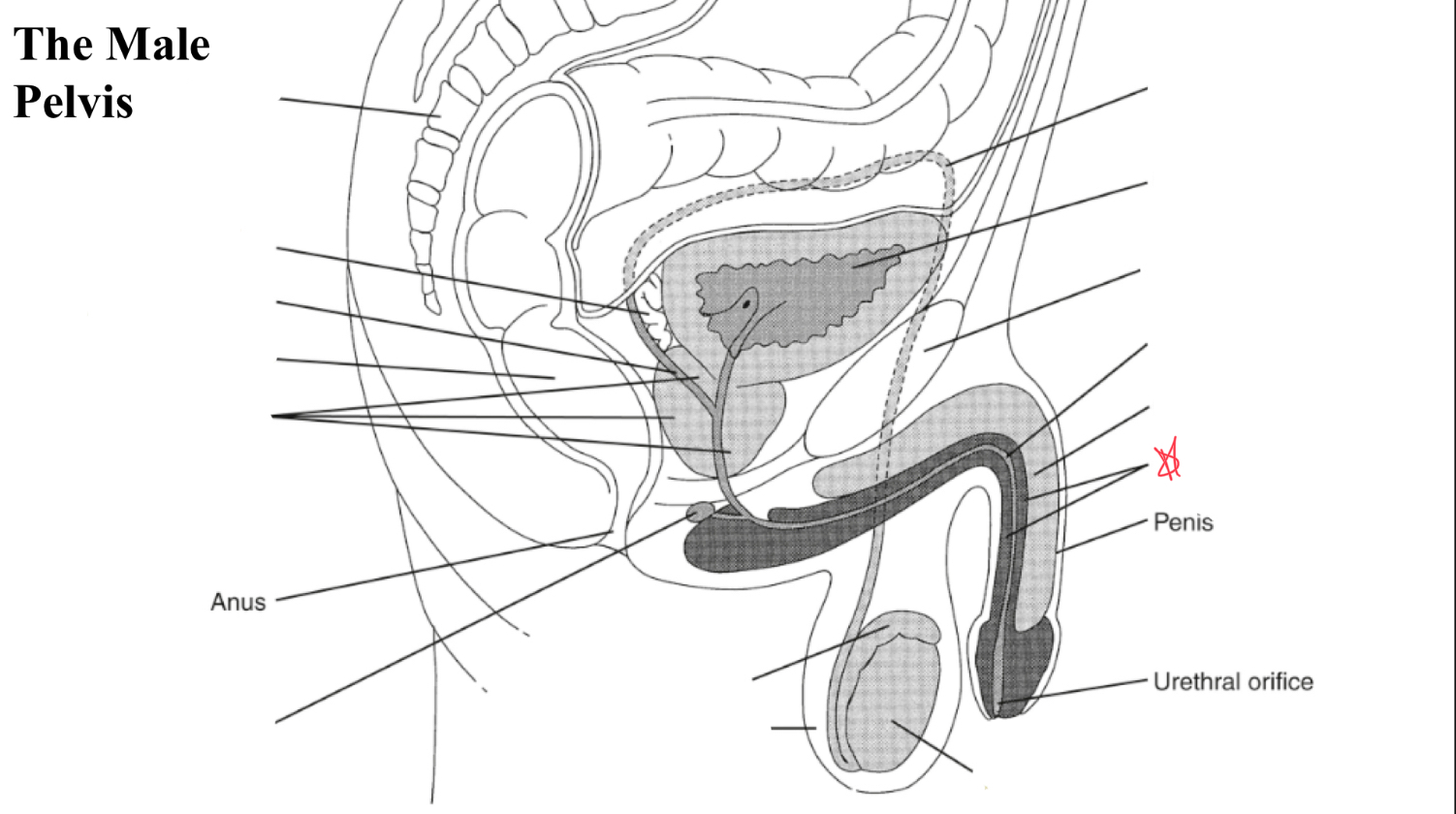
corpus spongiosum
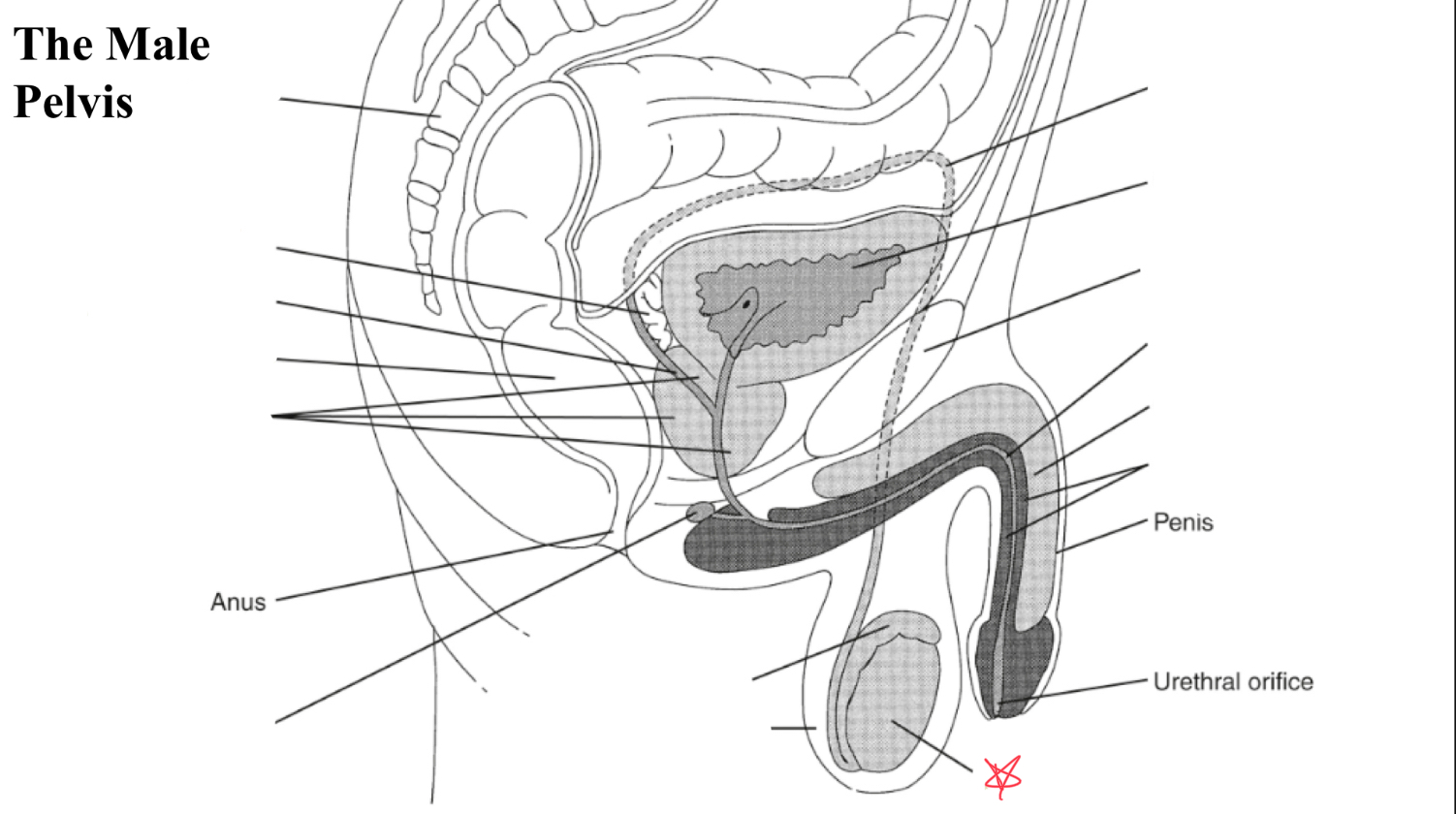
testis
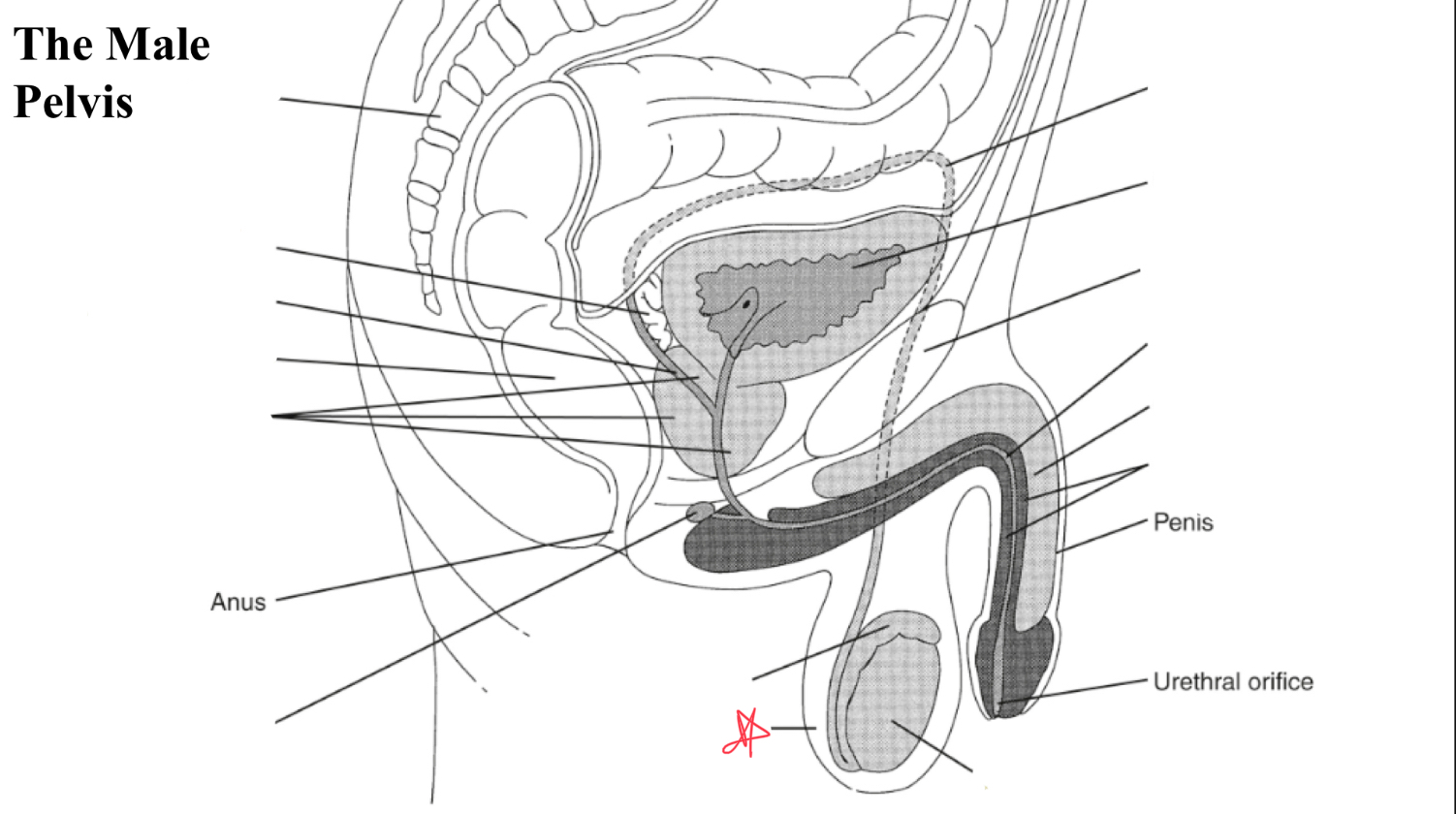
scrotum
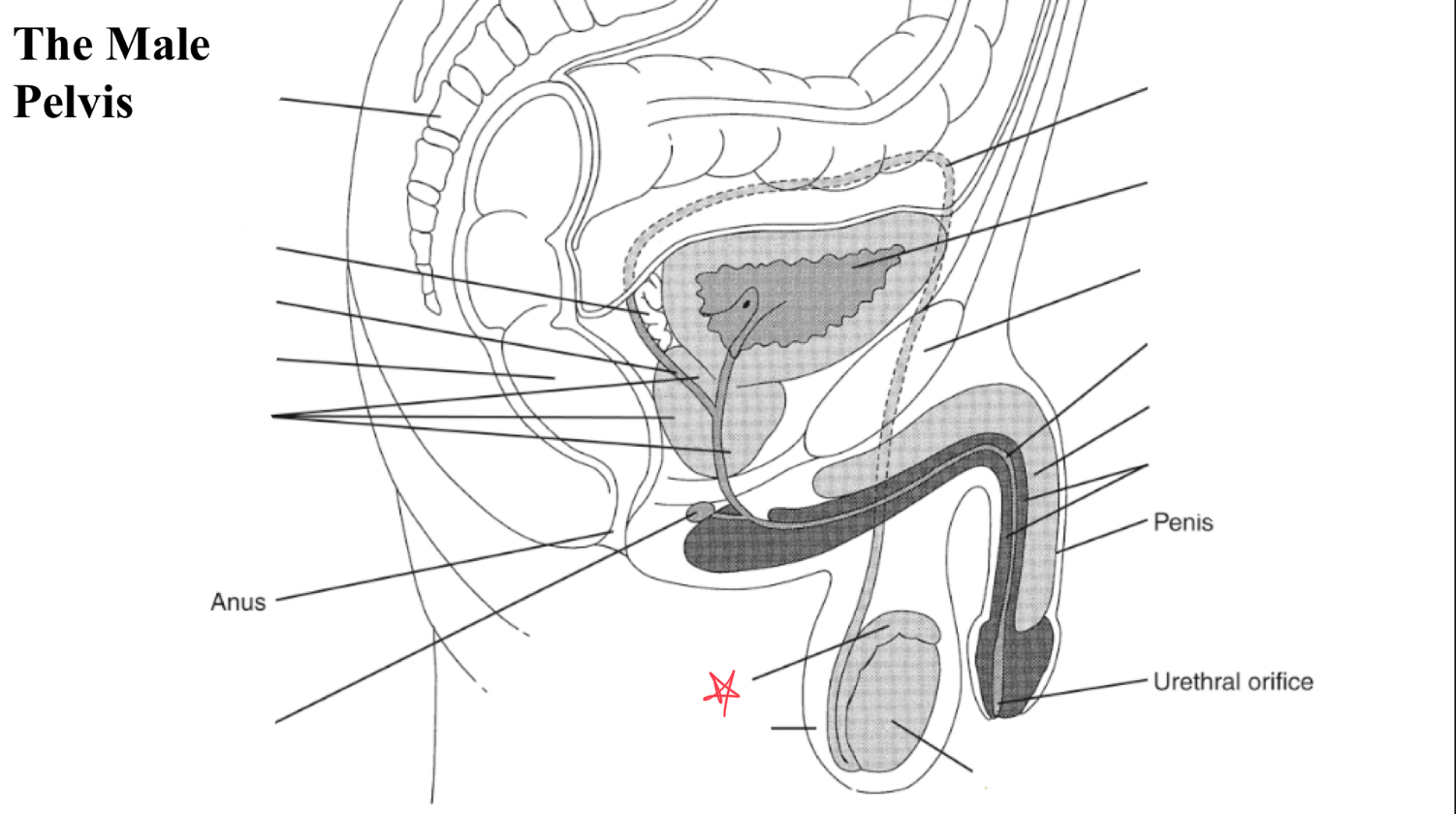
epididymis
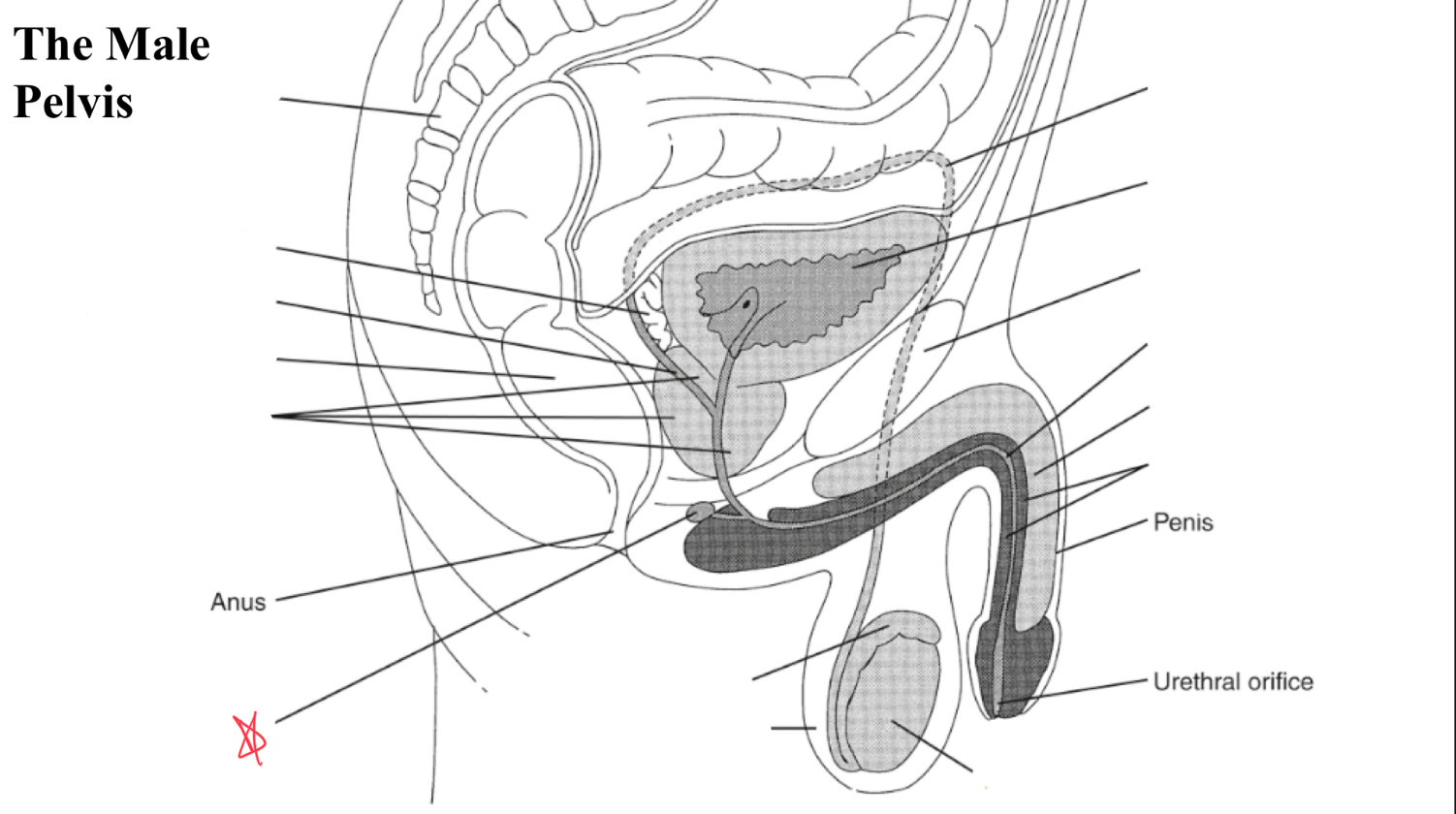
bulbourtheal gland
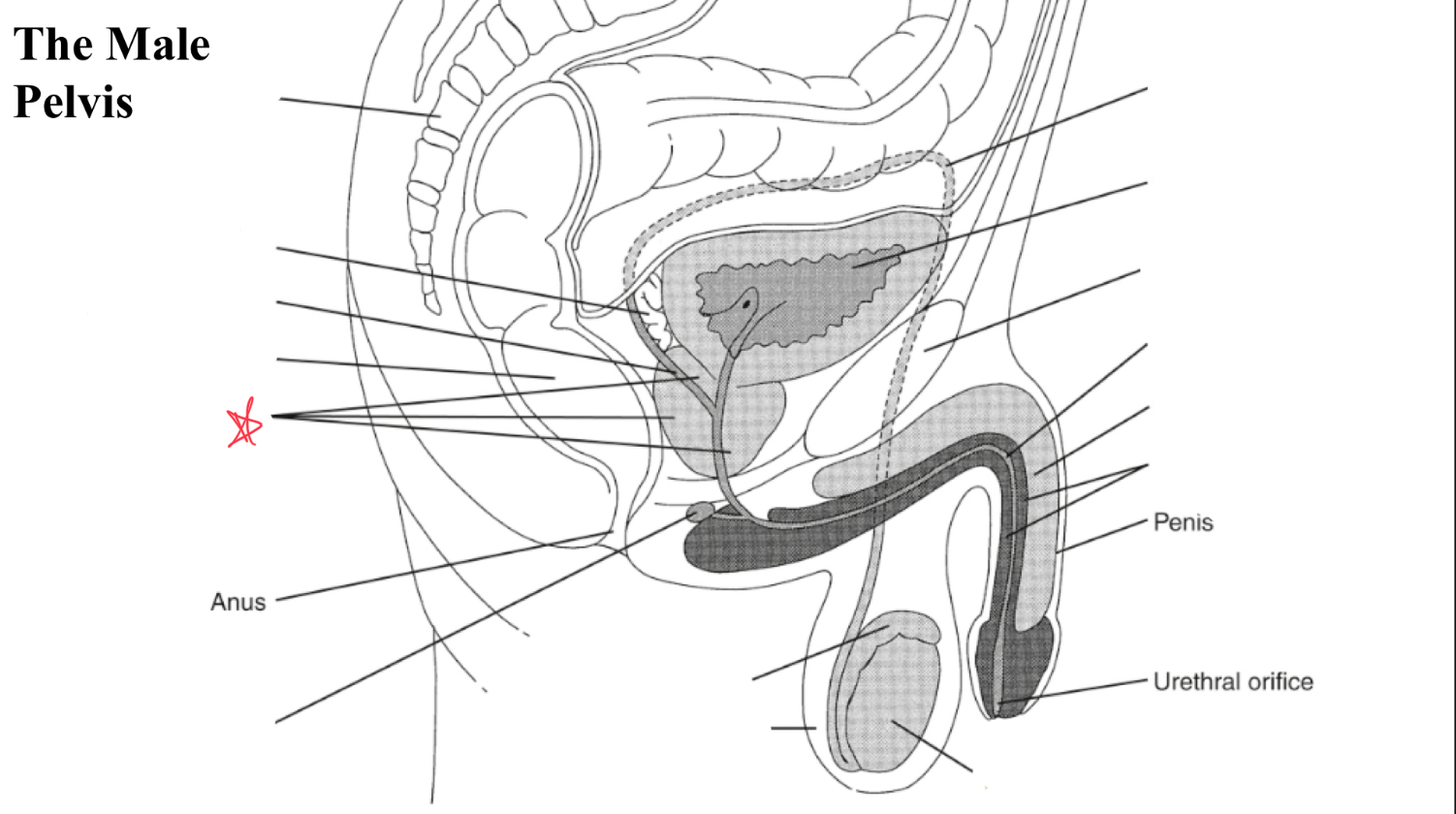
prostate
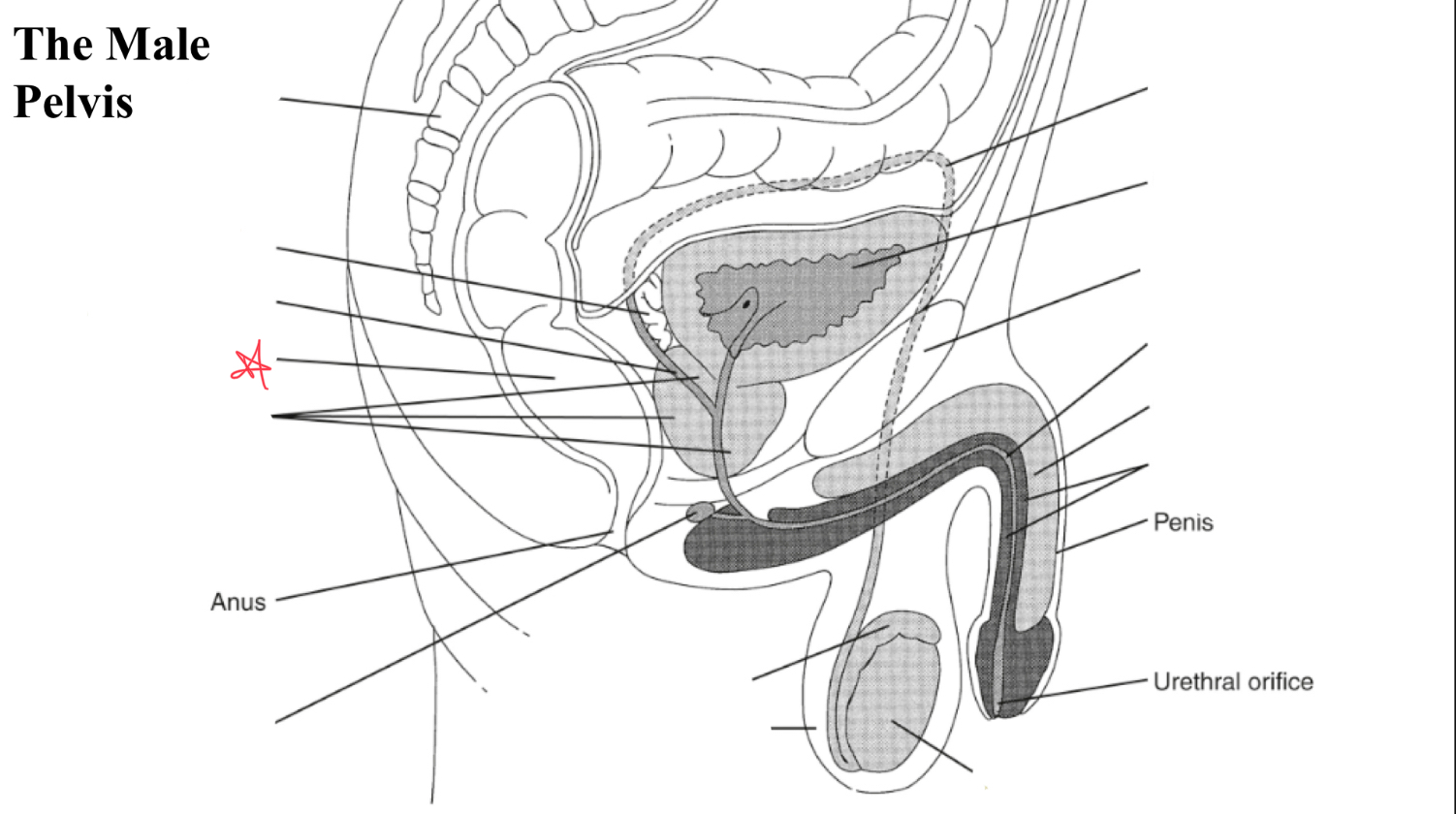
rectum
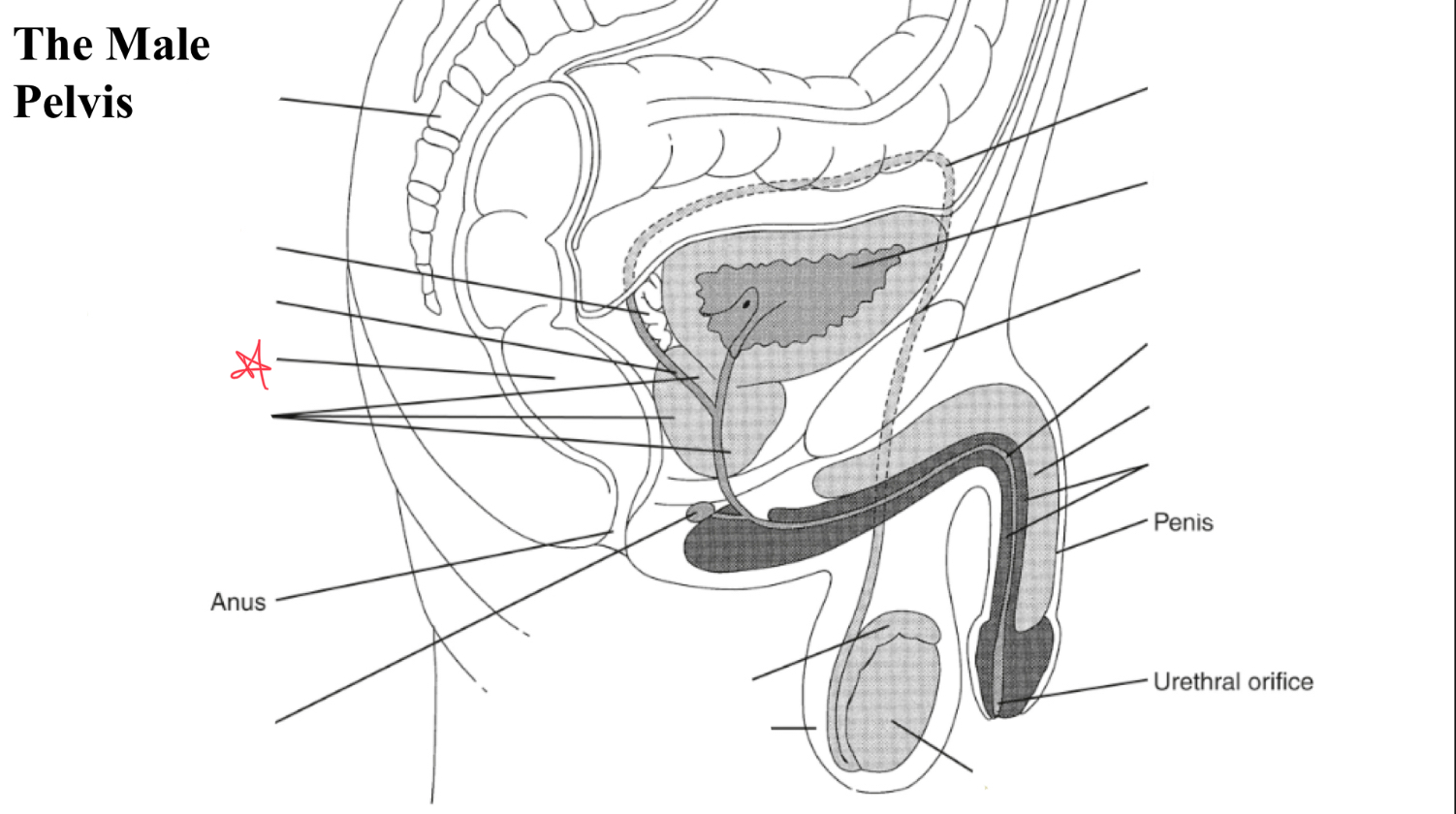
EJ duct
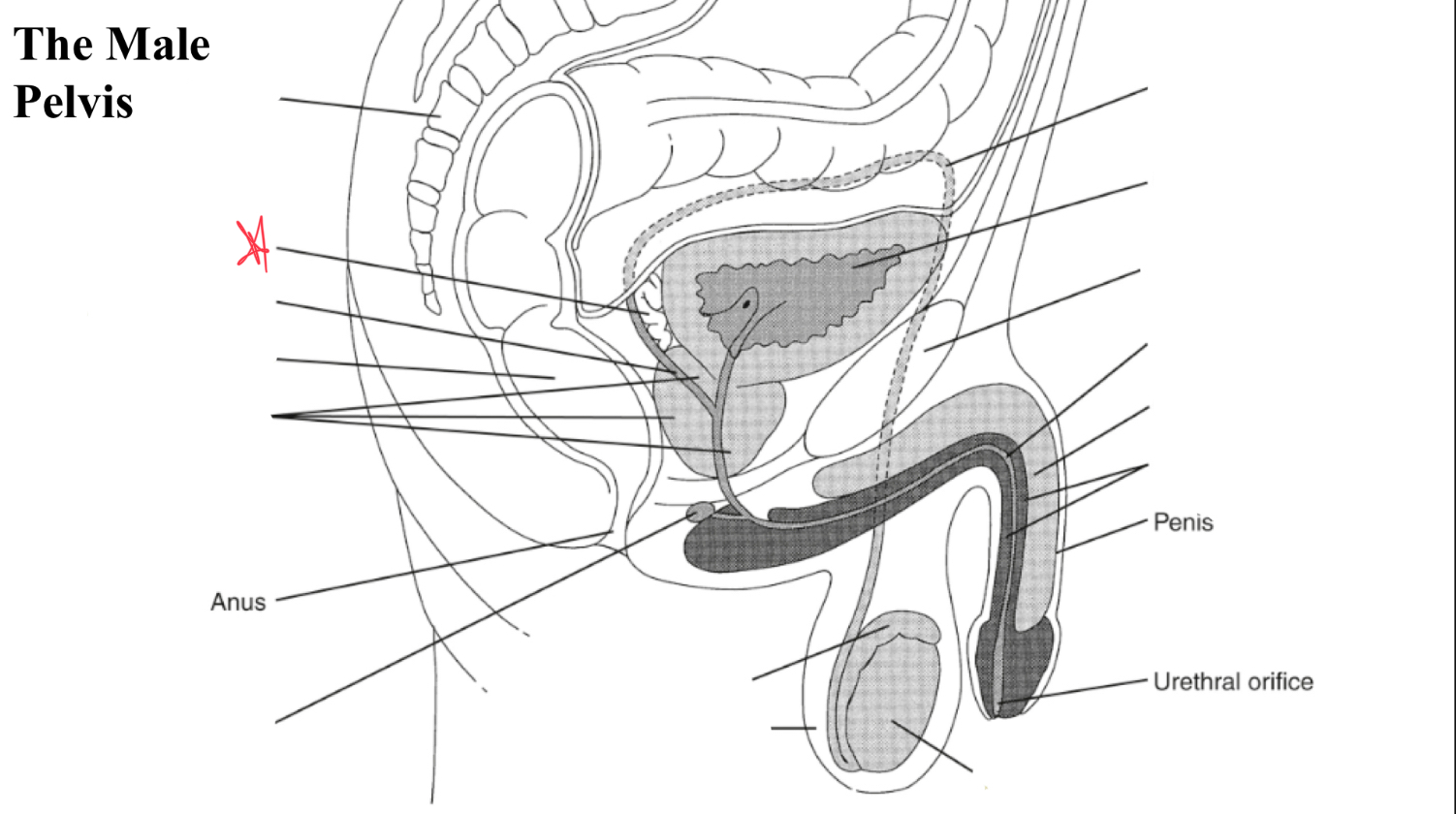
seminal vesicle
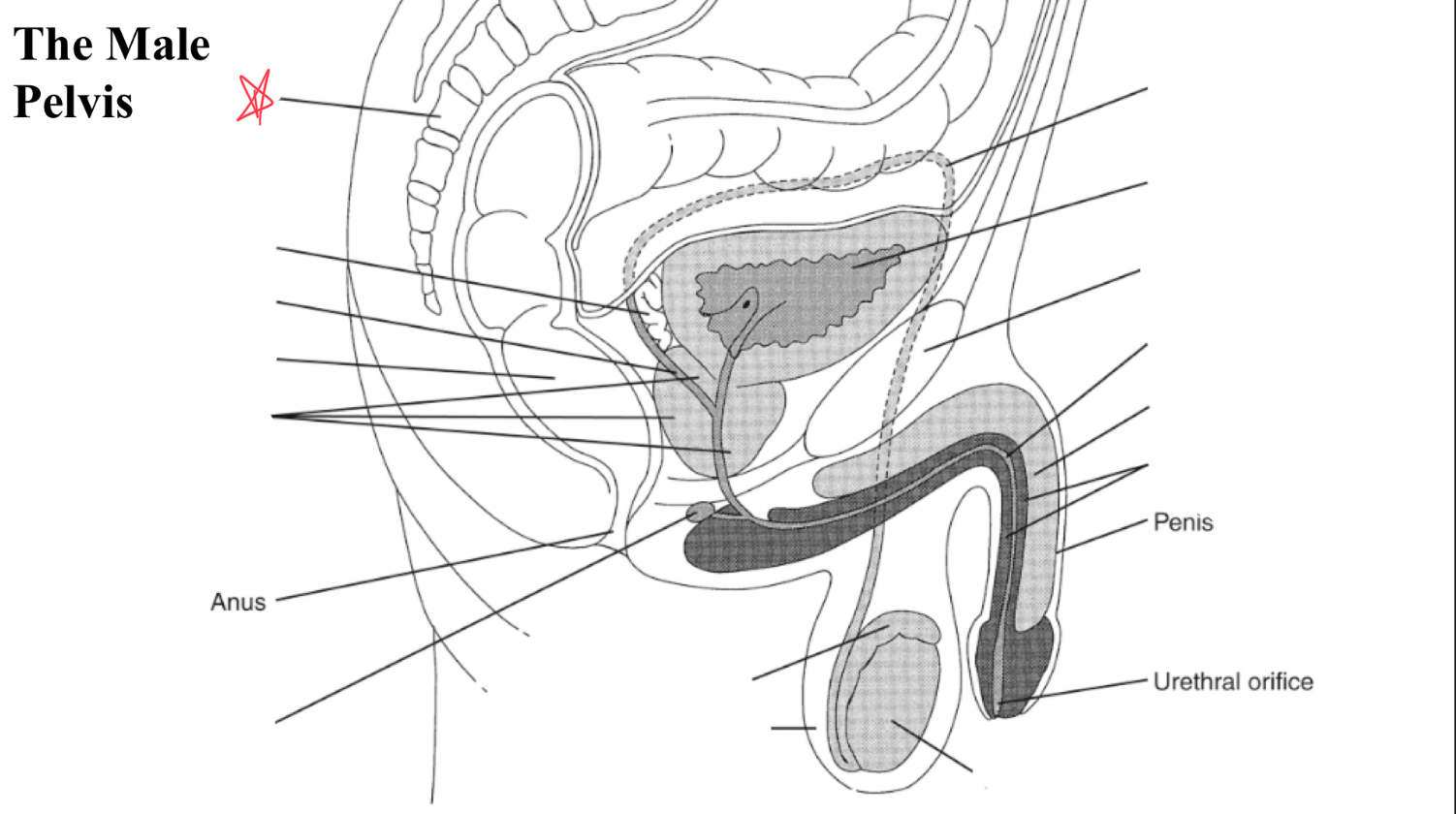
sacrum
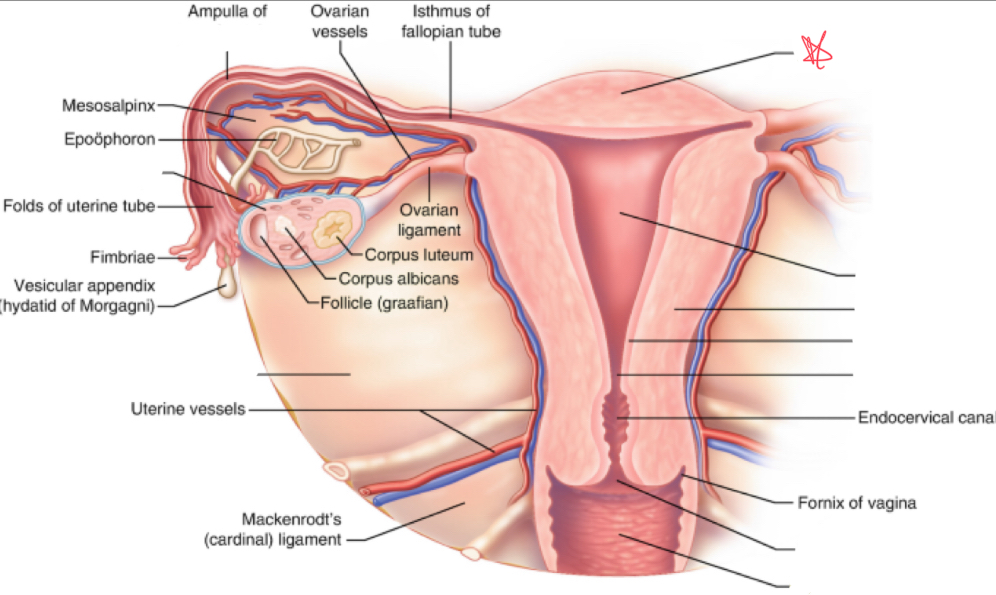
fundus
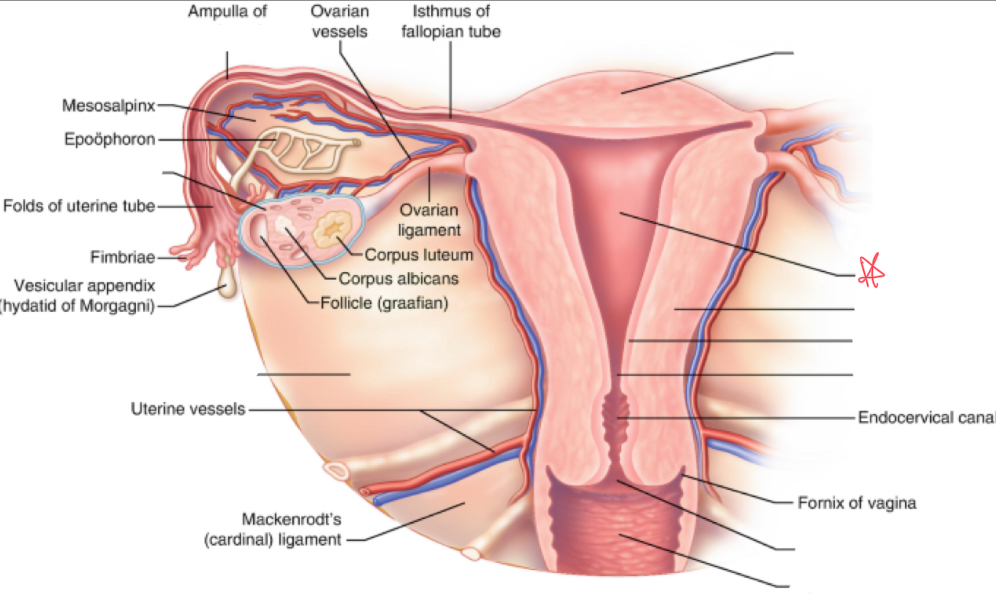
uterus (body)
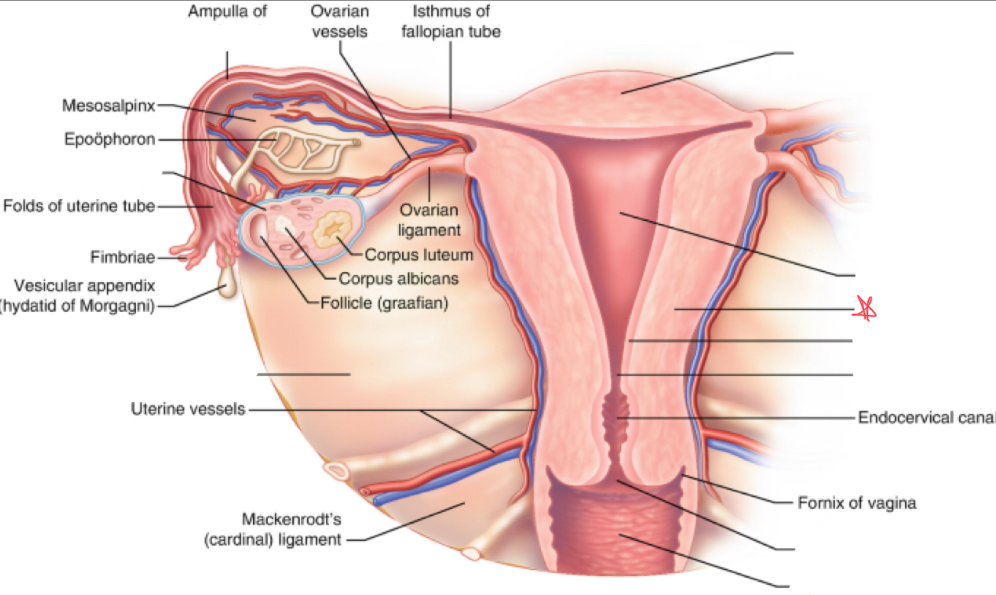
myometrium
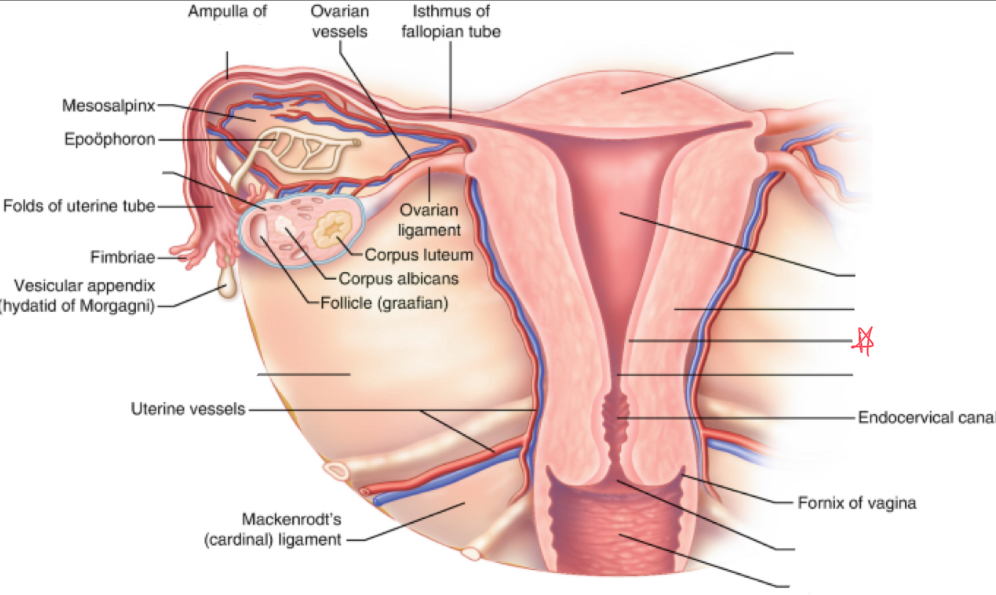
endometrium
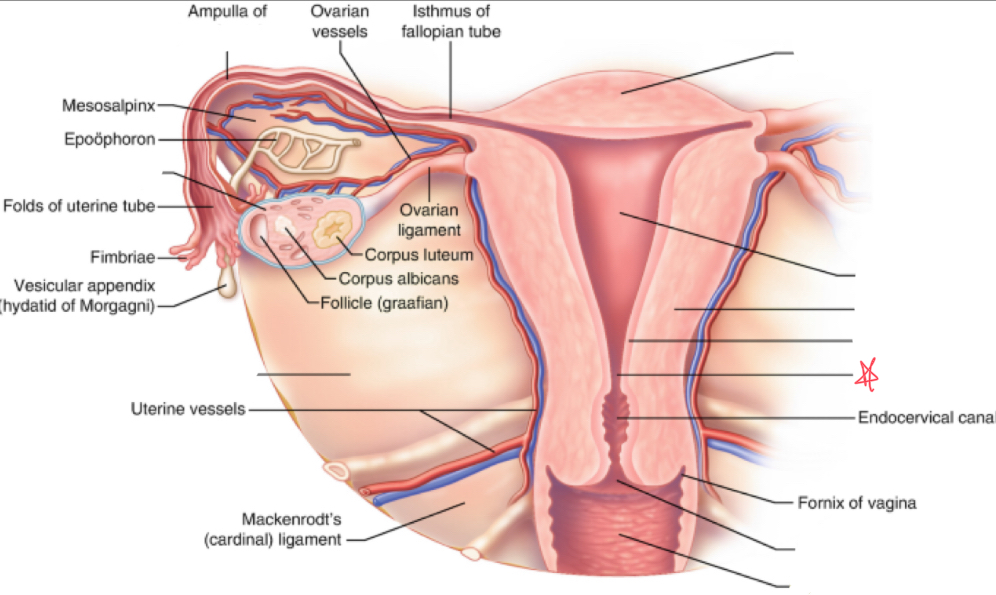
internal os
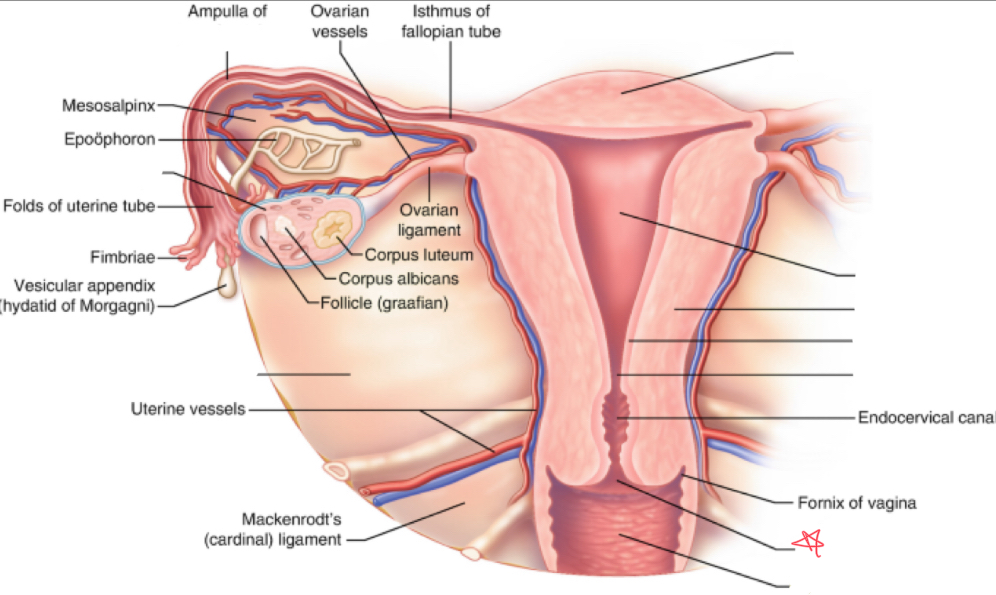
external os
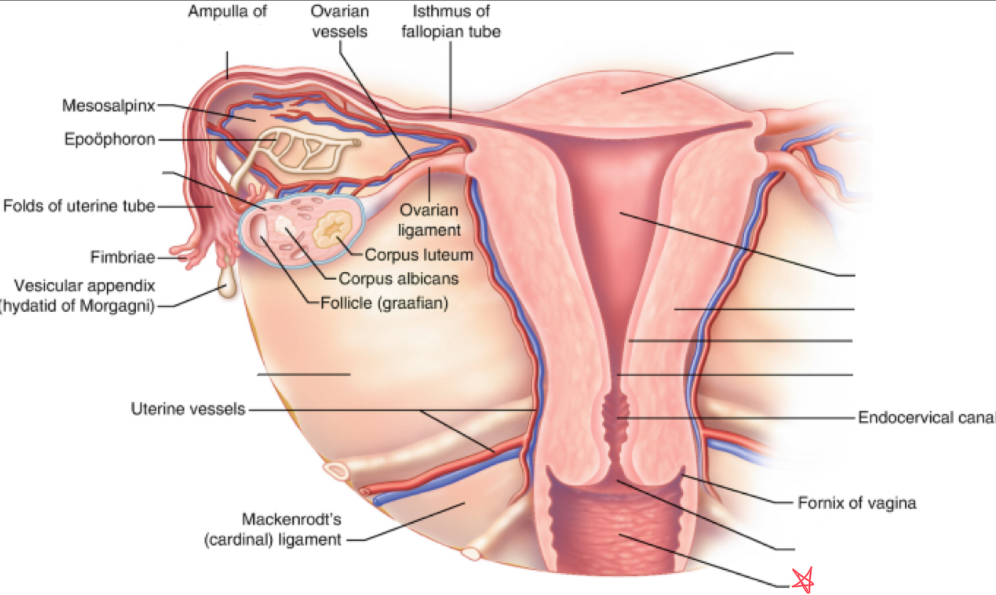
vagina