College Biology - Biochemistry Unit
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Test 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
Elements
Substances that can no longer be broken down into other substances and keep their characteristic properties
CHNOPS - what is it
An acronym for the 6 essential elements to life (99%)
CHNOPS - what they stand for
C - Carbon
H - Hydrogen
N - Nitrogen
O - Oxygen
P - Phosphorus
S - Sulfer
Valance Electron - what is it
Electrons found only on the outside layer
Valance Electron - how to find
# of electrons - 10
Lewis Dot Structure
The amount of electrons in an element
Focus on Valence Electrons in drawing
Go around until all sides have 1 before moving to doubling up
Subatomic Particles
Neutron (0), Electron (-), and Proton (+)
Atomic Number - where it is found
Top right corner of element
Atomic Mass - where it is found
Bottom of the element
Proton
Atomic #
Electron
Atomic #
Neutron
Atomic Mass - Atomic #
Isotope
Element with a different atomic mass
Orbitals
The undefined path an electron travels in
How Orbitals Work
Move to lowest energy level possible (close to nucleus)
If energy is added, electrons move/jump to higher levels
Energy is given off when electrons move back to lower levels
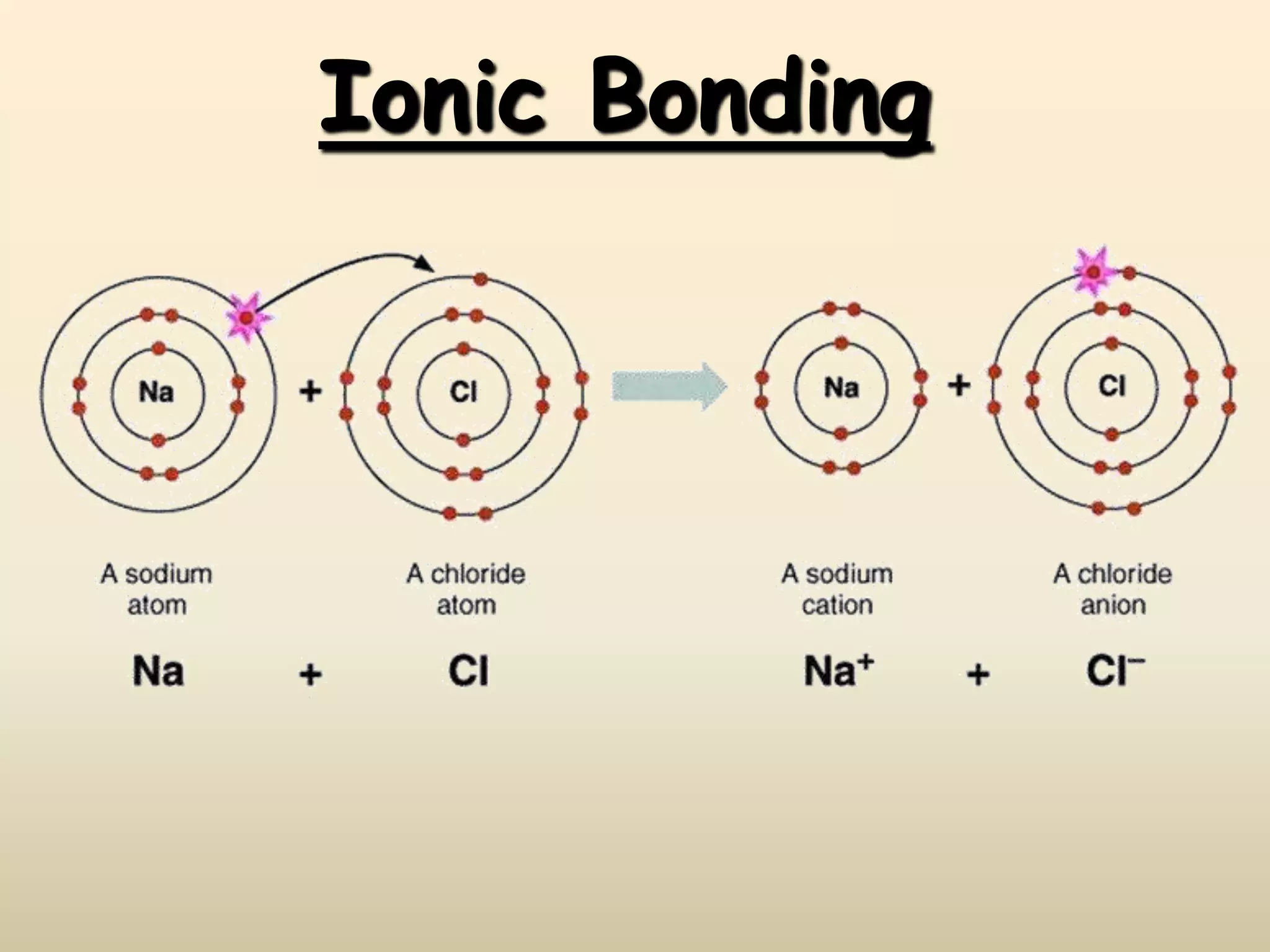
Ionic Bonds - weak
One atom gains electrons & one atom loses electrons
The two atoms become charged and are called ions
Ionic Bond Example
Make sure to draw arrows
The + and - are opposite of what you think
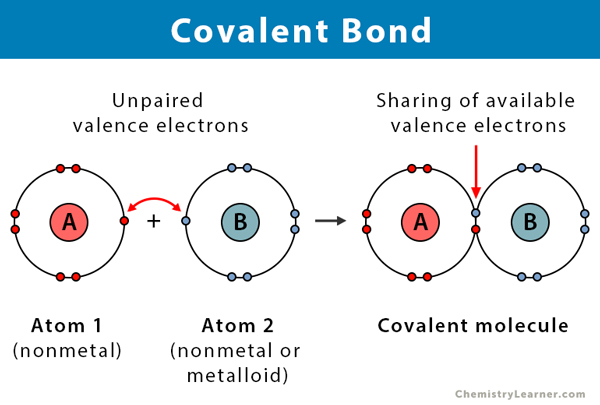
Covalent Bonds - strong
The sharing of electrons
Can be polar or non-polar
Polar
Electrons are pulled more towards one nuclei than another, the molecule is charged
Non-polar
Electrons are pulled equally towards nuclei and there is no charge
Covalent Bond Example
Remember to add charges (+) and (-)
Circle covalent bonds
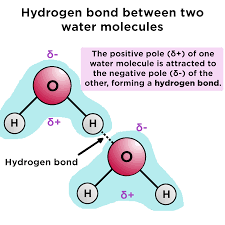
Hydrogen Bond - weakest
Form between compounds, these bonds break and reform easy
Hydrogen Bond Example
Covalent bonds that connect in a larger form
Super Solvent - Importance of Water
Dissolves more compounds in greater amounts than any other liquid
Example of Super Solvent
Breaks things down in the body
Solute
Getting dissolved
Solvent
Doing the dissolving
Solid is less dense than liquid - Importance of Water
Solid has more H bonds (water molecules spread out)
Liquid is moving and H bonds are breaking and reforming quickly
Example of Solid is less dense than liquid
Only top of lake freezes
High Specific Heat - Importance of Water
It takes a lot of energy to raise water temp
Water absorbs heat
When the environment around water cools off, water releases heat
High Specific Heat
The amount of energy it takes to raise the temp 1 degree C
Example of High Specific Heat
Stable environments and bodies
Cohesion - Importance of Water
Water is attracted to water
Adhesion
Water is attracted to another substance
Surface Tension
Molecules are not attracted to the air above, pulled towards water below
Example of Cohesion
Trees get water into roots
Hydrophobic
Doesn’t mix well with water
Hydrophilic
Does mix well with water
pH Scale
Membranes and Enzymes require a specific pH
0 - very acidic
7 - neutral
14 - not acidic
0 - 7: acid
7 - 14: base
pH scale - H accepter
Base
pH scale - H yielder
Acid
Carbon (life is based on)
4 valence electrons
Great bonding
Covalent bonds (strong)
Atoms attach to a carbon compound, giving it a special property / shape
Most are polar (+) (-)
General composition of any carbohydrate
CxH2xOx
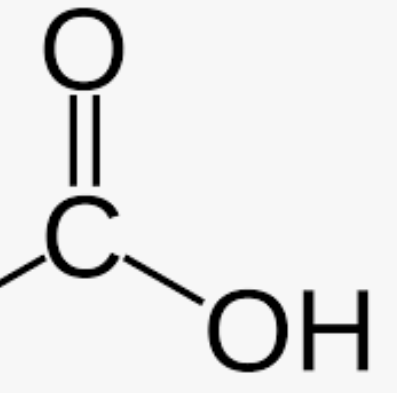
Carboxyl (COOH)
Found in fatty acids / amino acids
Remember to have constant at the beginning (C with 3 H bonds)
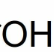
Hydroxyl (OH)
Found in alcohol / carbohydrates
Remember to have constant at the beginning (C with 3 H bonds)
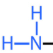
Amino (NH2)
Found in amino acids
Remember to have constant at the beginning (C with 3 H bonds)
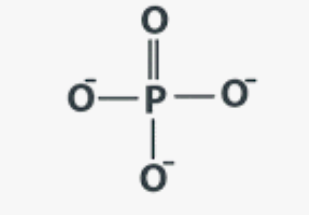
Phosphates (PO4)
Found in DNA / ATP
Remember to have constant at the beginning (C with 3 H bonds)
Monomer
Small molecule that can be combined w/ others to make a polymer
Polymer
Large molecule made up of similar sub units (monomers)
Monosaccharides - Carbohydrates
One carbohydrate - monomers: glucose, fructose, deoxyribose
Disaccharides - Carbohydrates
Two carbohydrates - maltose, sucrose, lactose, dehydration / condensation reactions, glycosidic bonds
Glycosidic
The bond between 2 glucose molecules
Represented with an O between molecules (only in carbohydrates)
Polysaccharides - Carbohydrates
Complex carbs
Starch - polysaccharides
Carb storage in plants
Gycogen - polysaccharides
Carb storage in animals (muscle and liver cells)
Cellulose - polysaccharides
Structure to plants — insoluble fiber for animals (Dense and rigid)
Chitin - polysaccharides
Exoskeleton structure of arthopods / animals
Lipid Properties
Insolubility in water (hydrophobic)
Form internal containers for living things
Store energy
Insulation
Not a polymer - has blobs :)
Triglyceride
Make up most of the lipid weight in food
Glycerol plus three fatty acids
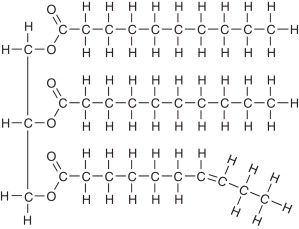
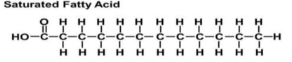
Saturated Fat
Fatty acids that have as many H atoms bonded to it as possible
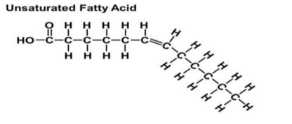
Unsaturated Fat
Fatty acids that have one or more double bonds (room for more H)
Trans Fat
In between Saturated and Unsaturated Fat
Eating trans fat increases blood cholesterol levels and the risk of heart disease
The worst type of fat
Saturated Fat Drawing
Molecule is flat, stack up close: forms solids
Remember carbon base in front
Unsaturated Fat Drawing
Molecule bends: forms liquids
Remember carbon base in front
Steroid Traits (reminder: it is also a lipid)
4 carbon rings: all points are considered carbon
Cholesterol
found in cell membrane of animals
Testosterone / Estrogen
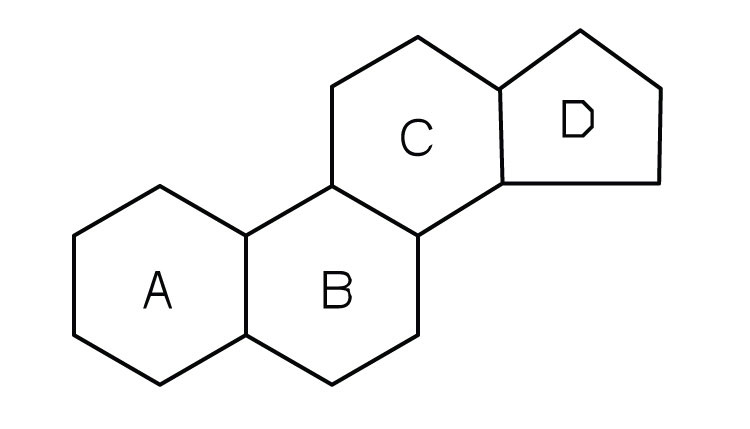
Cholesterol
HDL, LDL are 2 types of this molecule that is used to maintain membrane stability
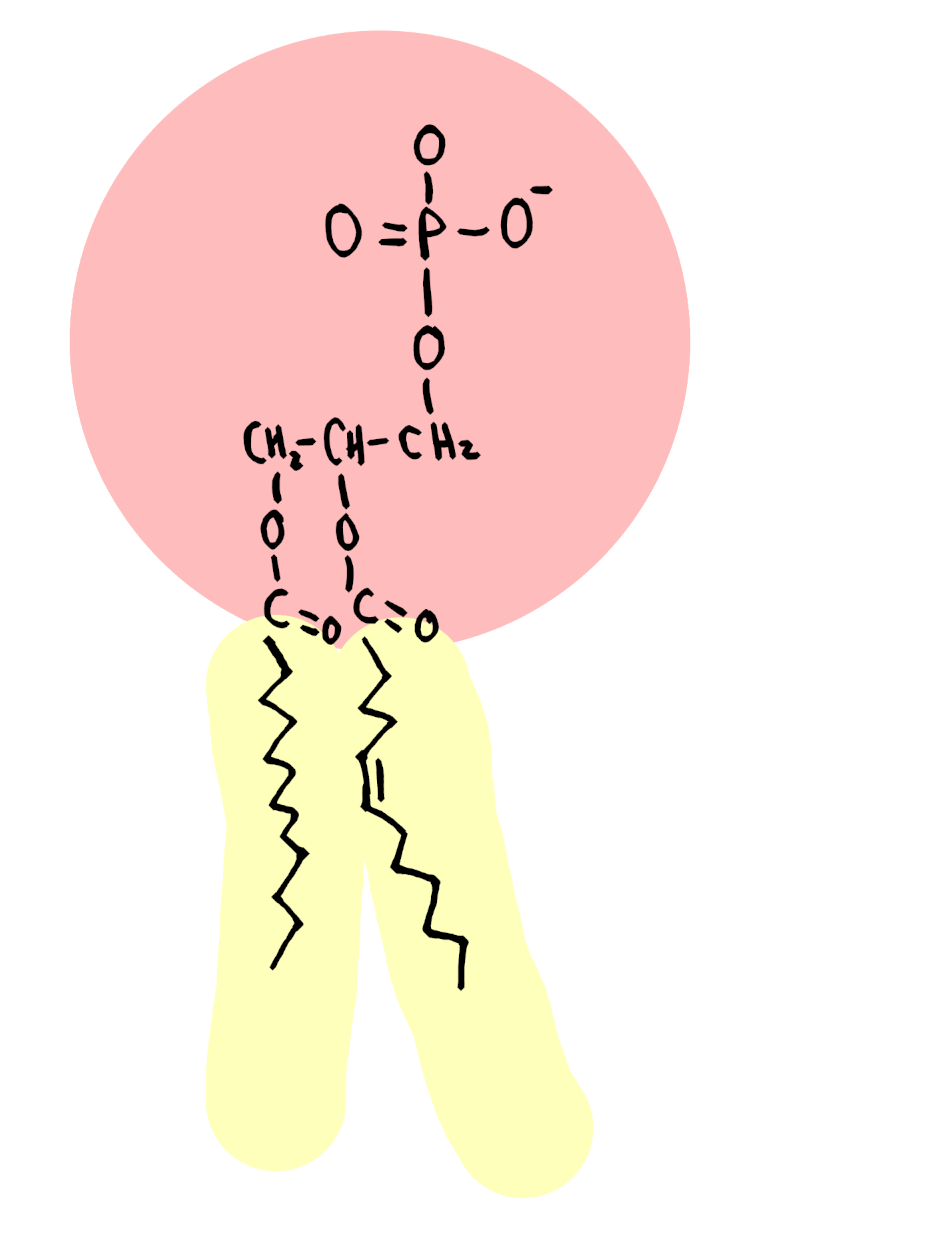
***Phospholipids (unique, do not follow pattern of lipids)
Glycerol, 2 fatty acids, phosphate group
Fatty acid tails are hydrophobic
Phosphate head is hydrophilic
Protein Monomer
Amino Acid
Polypeptide - protein
Linear chain of amino acids
When the polypeptide folds up 3-D, it is called a protein
What combines with an amino group to make a polypeptide chain?
Carboxyl
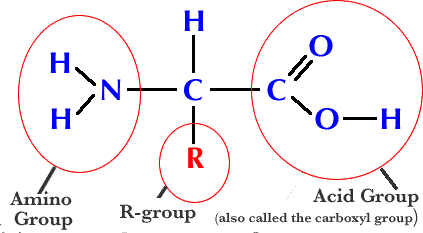
Amino Acid & Protein Traits
All have carboxyl, amino, and H on top
Order of amino acids determines the protein
All amino acids have 1 carboxyl and 1 amino group
Carboxyl group of one amino acid bonds with the amino group of another
Protein Drawing
Called a peptide bond between proteins
R - The variant group in protein that ultimately determines the shape
Protein Structure - how it works
THE SHAPE IS CRUCIAL
Puzzle / Lock & Key
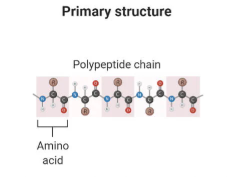
Primary Structure - protein
Sequence of amino acids
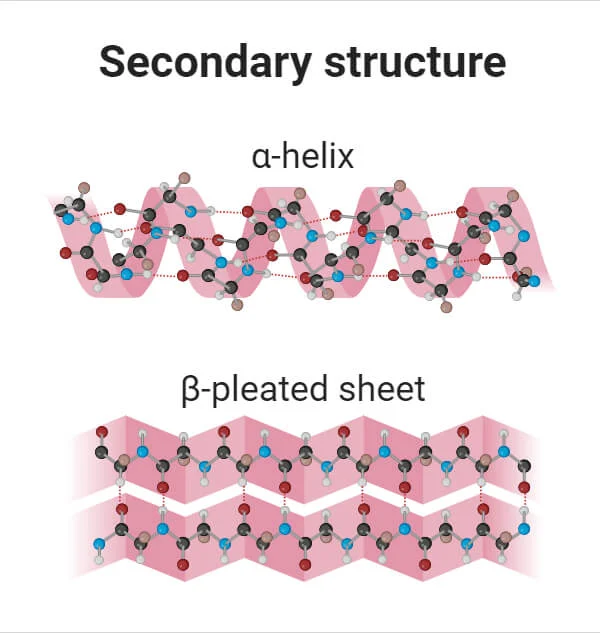
Secondary Structure - protein
Coils created by bonds between amino acids
Helix or B Pleated Sheet
Tertiary Structure - protein
Larger 3-D shapes
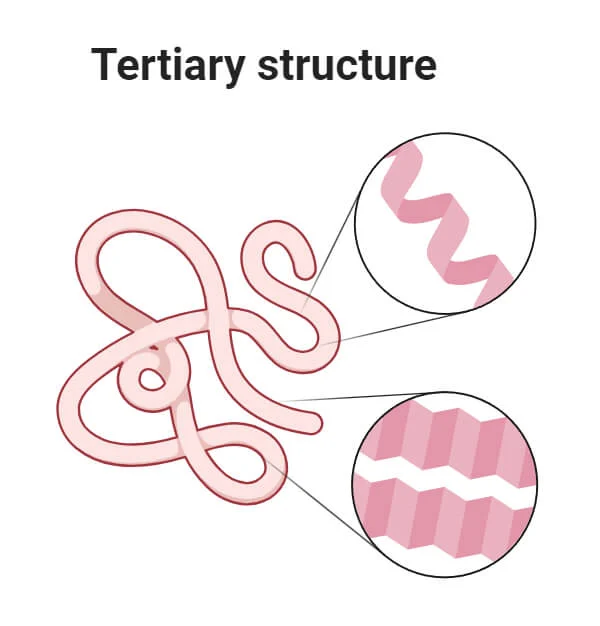
Quaternary Structure - protein
Several polypeptides linked

Nucleic Acid Examples
DNA
RNA
ATP
Nucleotide
The basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA)
Dehydration
A water molecule is lost or removed from the reacting molecules
Type of reaction that is used in forming carbohydrates, lipids and proteins
Protein Molecule Diagram Characteristics
Begins with NH2
Has a Carboxyl
Amino Acid
R group
Carbohydrates Molecule Diagram Characteristics
ONLY carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen throughout
Nucleic Acids Molecule Diagram Characteristics
Have nitrogen or N in the rings ONLY (no other N in any chains)
Lipids Molecule Diagram Characteristics
Have carbon and hydrogen BUT very few oxygens
CAN HAVE ester bonds: The bond formed between both organic molecules
Most likely one at the beginning or a couple throughout
Enzyme
A protein that speeds up chemical reactions
Example of an enzyme
Lactase
-ASE = enzyme
How do enzymes work?
Either split OR combine molecules (build OR break down)
Substrate
The substance an enzyme works on
Enzyme Shape
Stays the same
Substrate Shape
Changes shape
Metabolic Pathway (simple terms)
Most large scale activities involve multiple enzymes
Set of enzyme steps
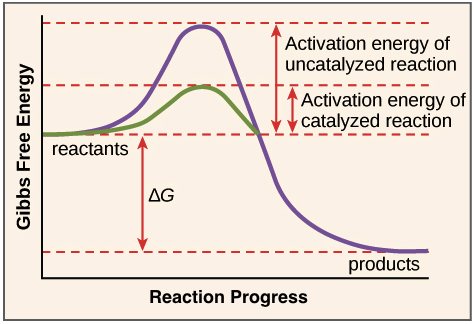
Enzymes lower what?
Enzymes lower the activation energy
Enzyme Characteristics
Proteins with a Tertiary and Quaternary structure
Only a few of the amino acids are involved in binding the substrate
Active Site
Active Site
Where the substrate binds
Reactant
A substance that takes part in and undergoes change during a reaction
Product
Substances generated by living organisms during metabolic or biochemical processes
What affects the amount of product?
Amount of substrate
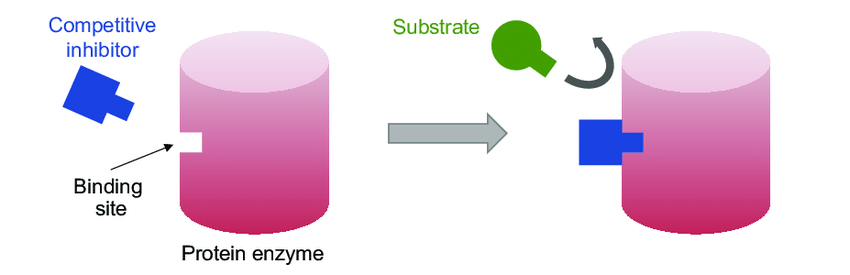
If the active site is occupied by a molecule that is not a substrate
Competitive Inhibition
Competitive Inhibition
Blocked off
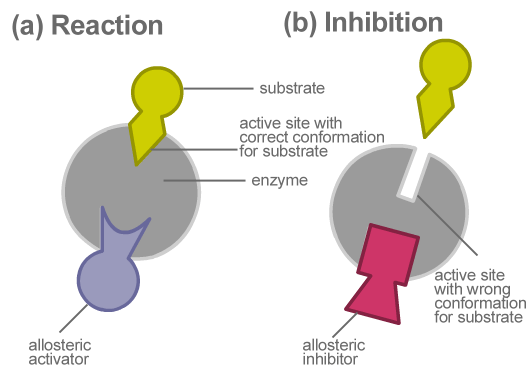
Negative Allosteric Regulation
On/Off Enzyme
Enzyme Lab - Ezyme
Catalase