Ch. 11 & 12 of mechanical ventilation
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
The total respiratory cycle time
What is TCT
Inspiration time (Ti) + Expiratory time (Te)
Total cycle time (TCT)
4 seconds
How often will the patient get a breath from Total respiratory cycle time
1 second
How much will patient get a breath from inspiratory time (T1)?
3 seconds
How much will patient get a breath from expiratory time (Te)?
Time period from beginning inspiration to the beginning of next inspiration
What is total cycle time
Encourage work of breathing
Oxygen consumption
Minute ventilation
Myocardial work
What can happen if your patient is having dyssychrony?
With the assisted (Patient triggered) or Controlled (Time triggered) Breath
When can dyssynchrony can occur?
Both pressure-time Waveforms depict the step ascending ramp pattern
What does the waveforms look like if the patient triggers their own breath?
Patient is taking their own breath. Pressure-time waveform
What is this waveform?
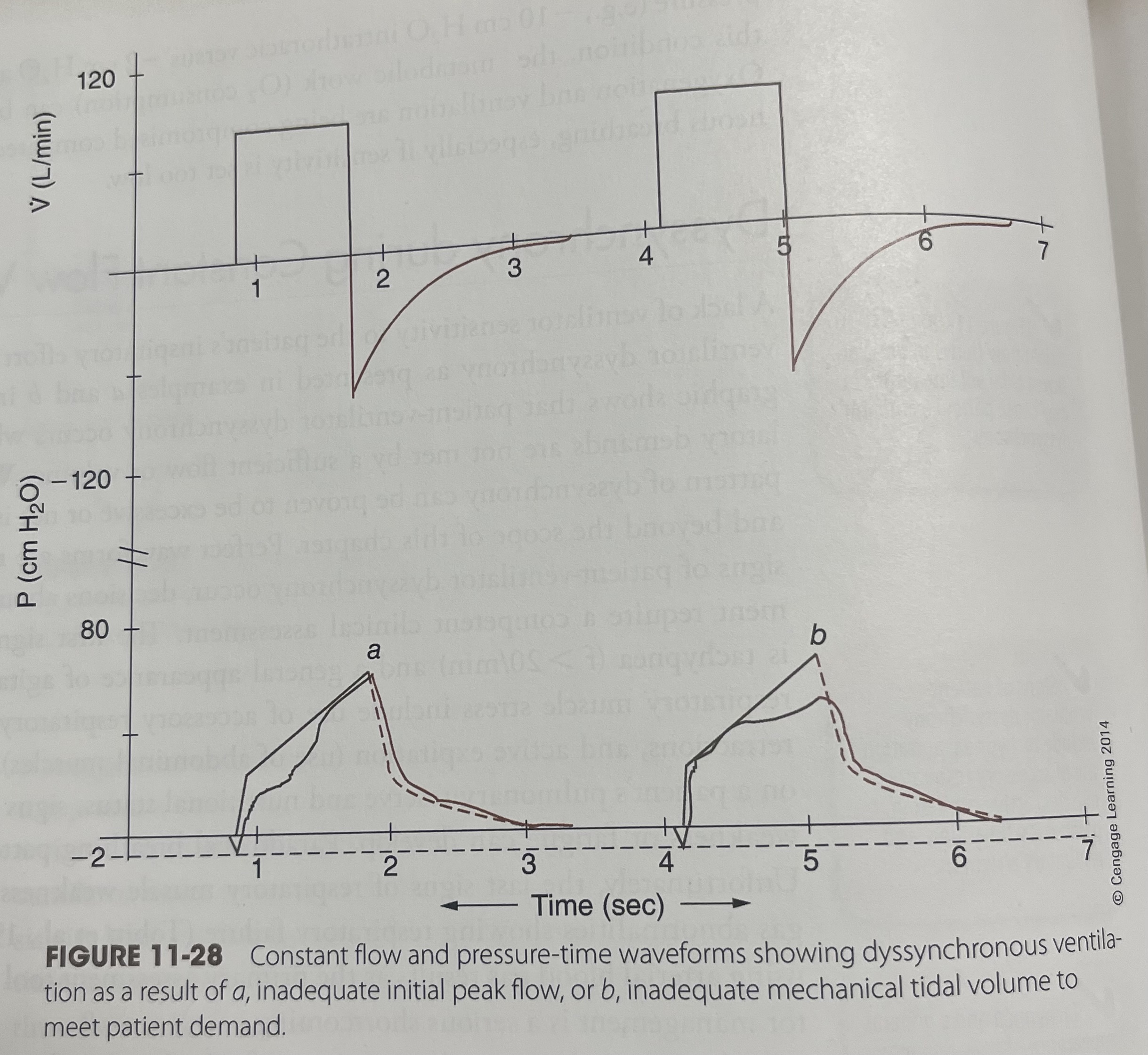
Constant flow and pressure-time
What is this waveforms?
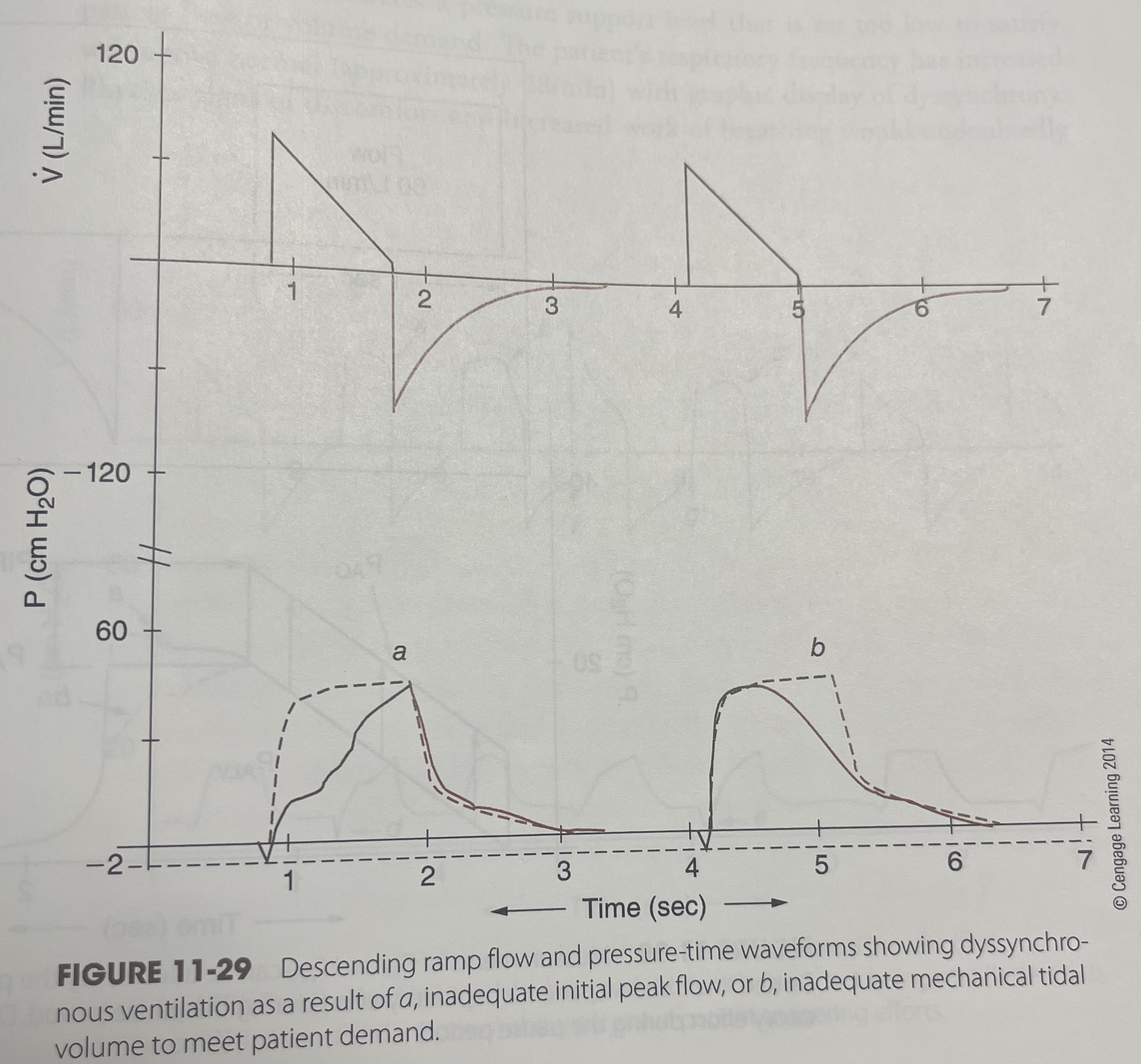
Descending ramp flow and pressure-time waveform
What is this waveform?
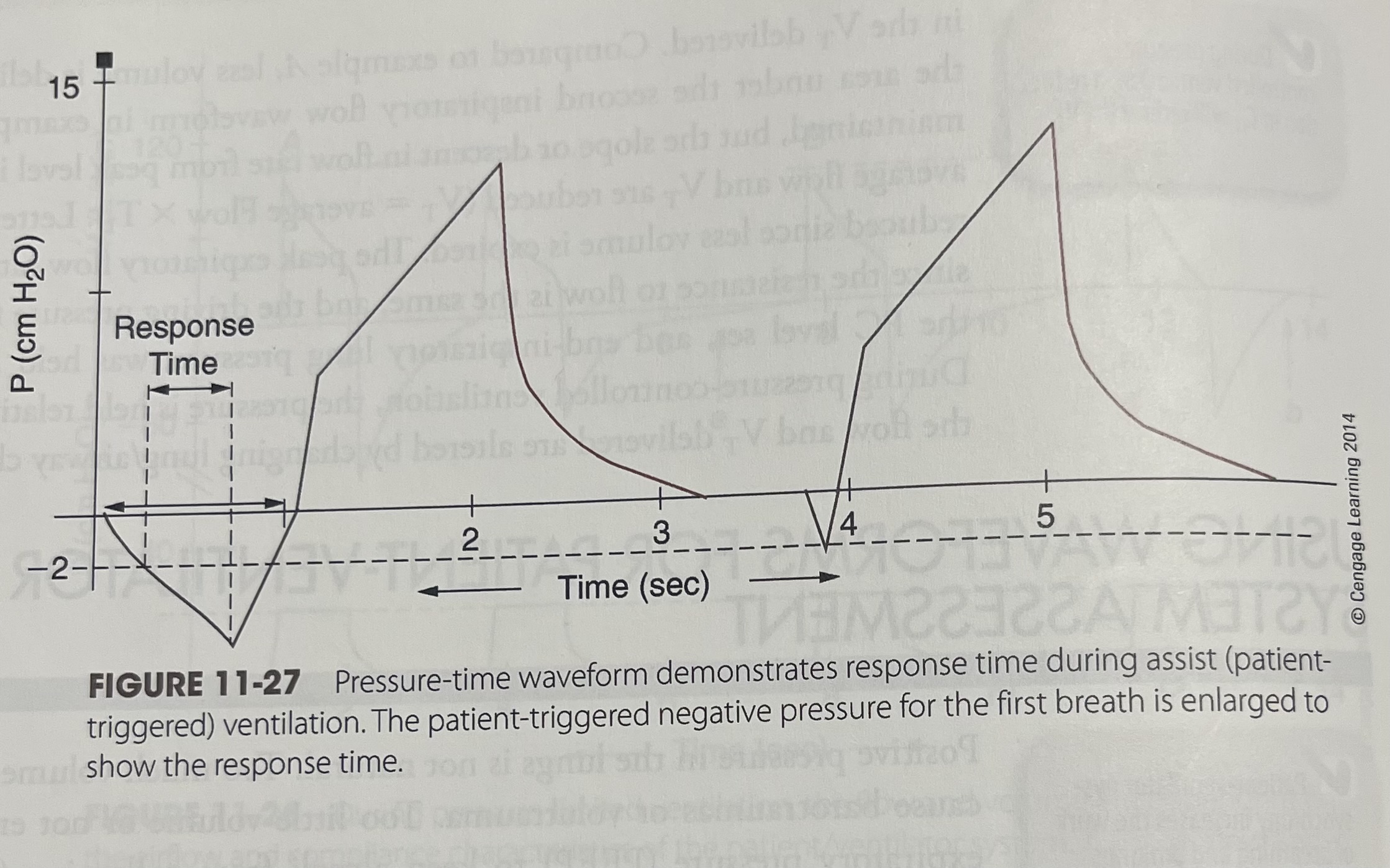
The patient triggered negative pressure for the first breath is enlarged to show the response time
What does pressure-time waveform shows
Dyssynchoronous ventilation as a result of a, inadequate initial peak flow, or b, inadequate mechanical tidal volume to meet patient demand
What does constant flow and pressure-time waveform shows
Showing dyssynchronous ventilation as a result of a, inadequate initial peak flow or b, inadequate mechanical title volume to meet patient demand
What descending ramp flow and pressure-time waveforms show
Increase in airflow resistance (Obstructive lung disease) Prolongs to expiatory time
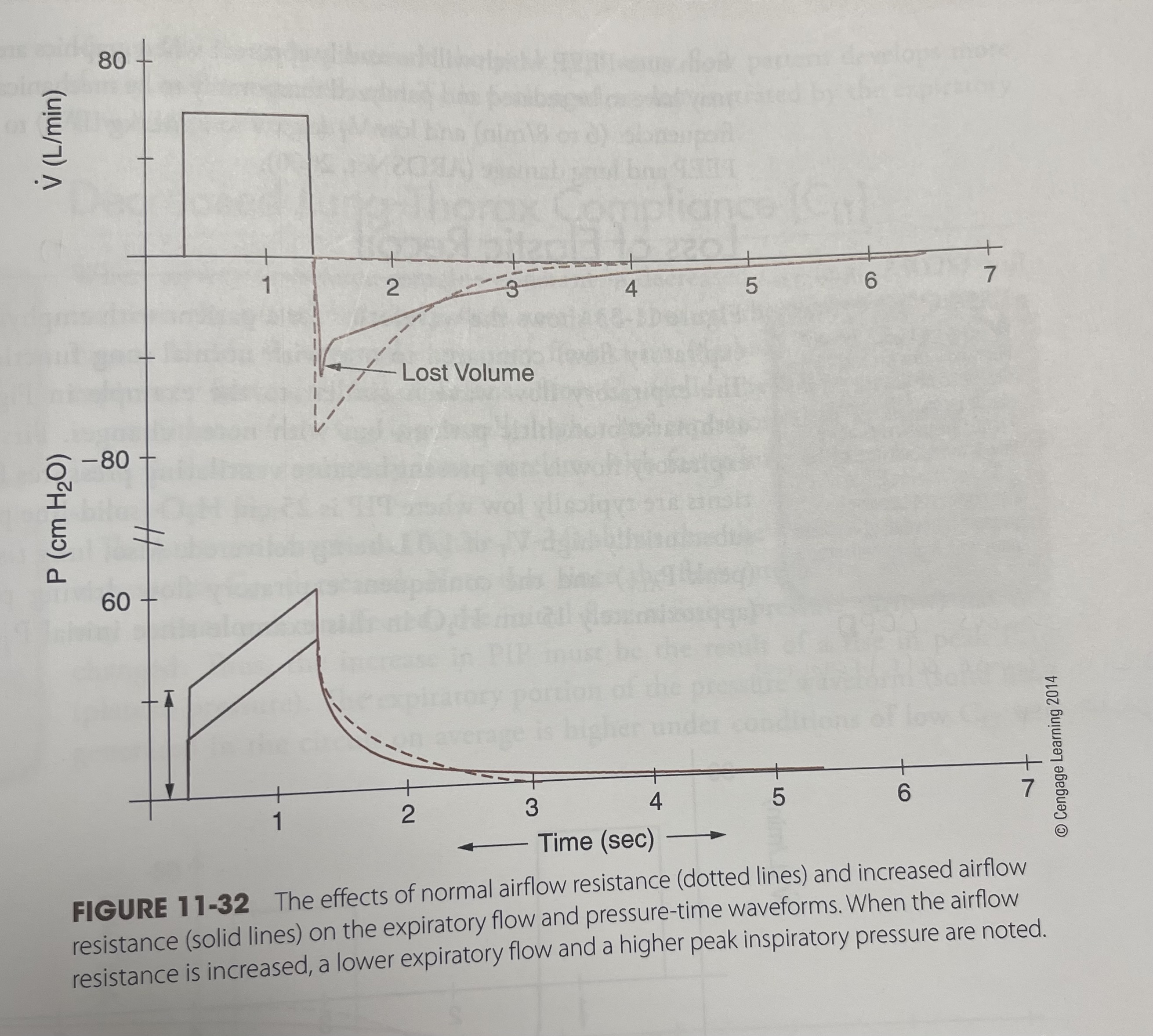
The expiratory flow solid line in the flow-time waveform show
Air trapping, Auto-PEEP, and volutrauma.
When airflow resistant increase what can happen?
Normal airflow resistance (Dotted lines) And increase airflow resistance (Solid lines) On the expiratory, flow and pressure-time
What is this waveforms?
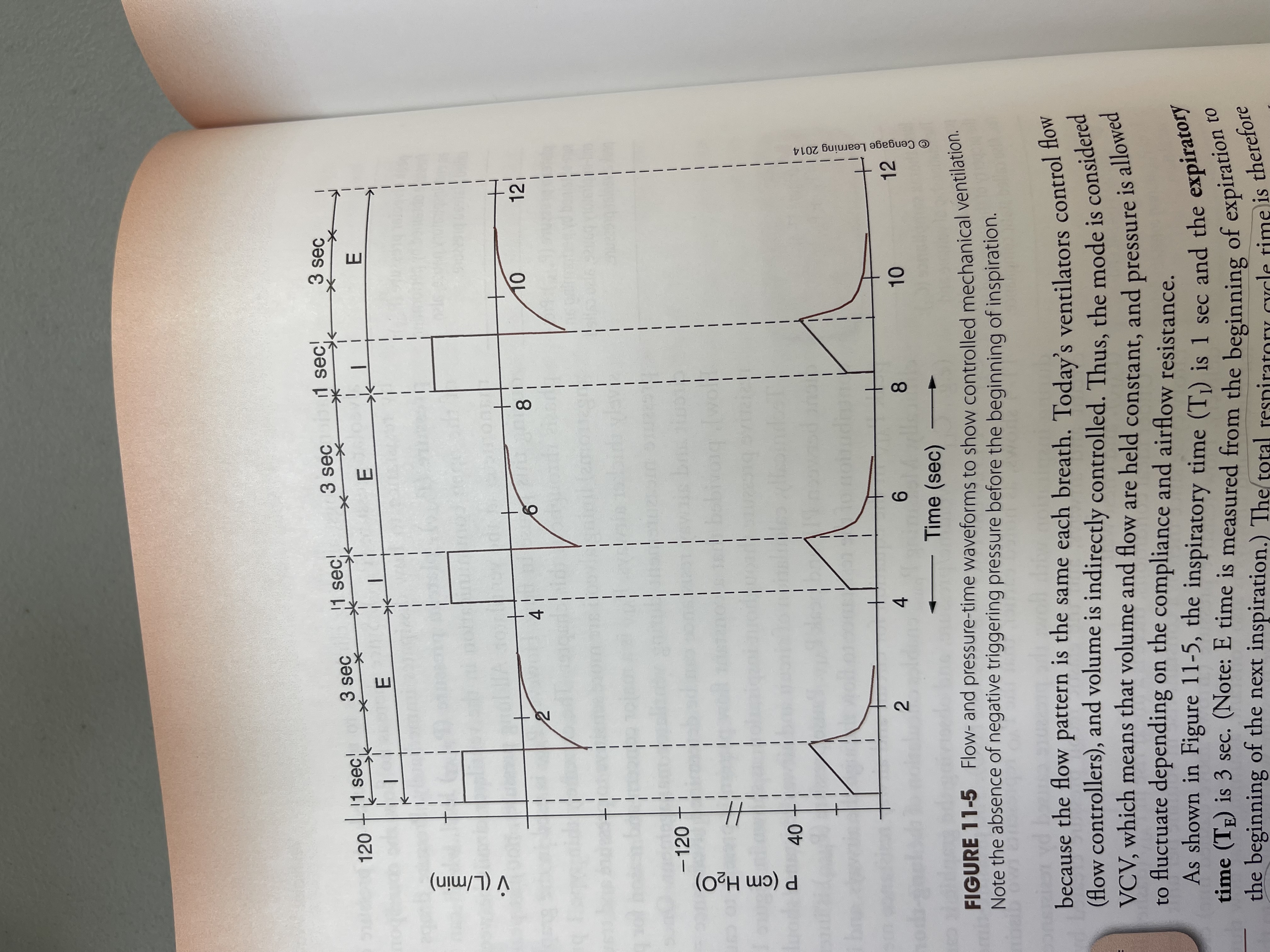
Flow and pressure time waveforms To show controlled mechanical ventilation.
Note the absence of negative triggering pressure before the beginning of inspiration
What is this Wave form
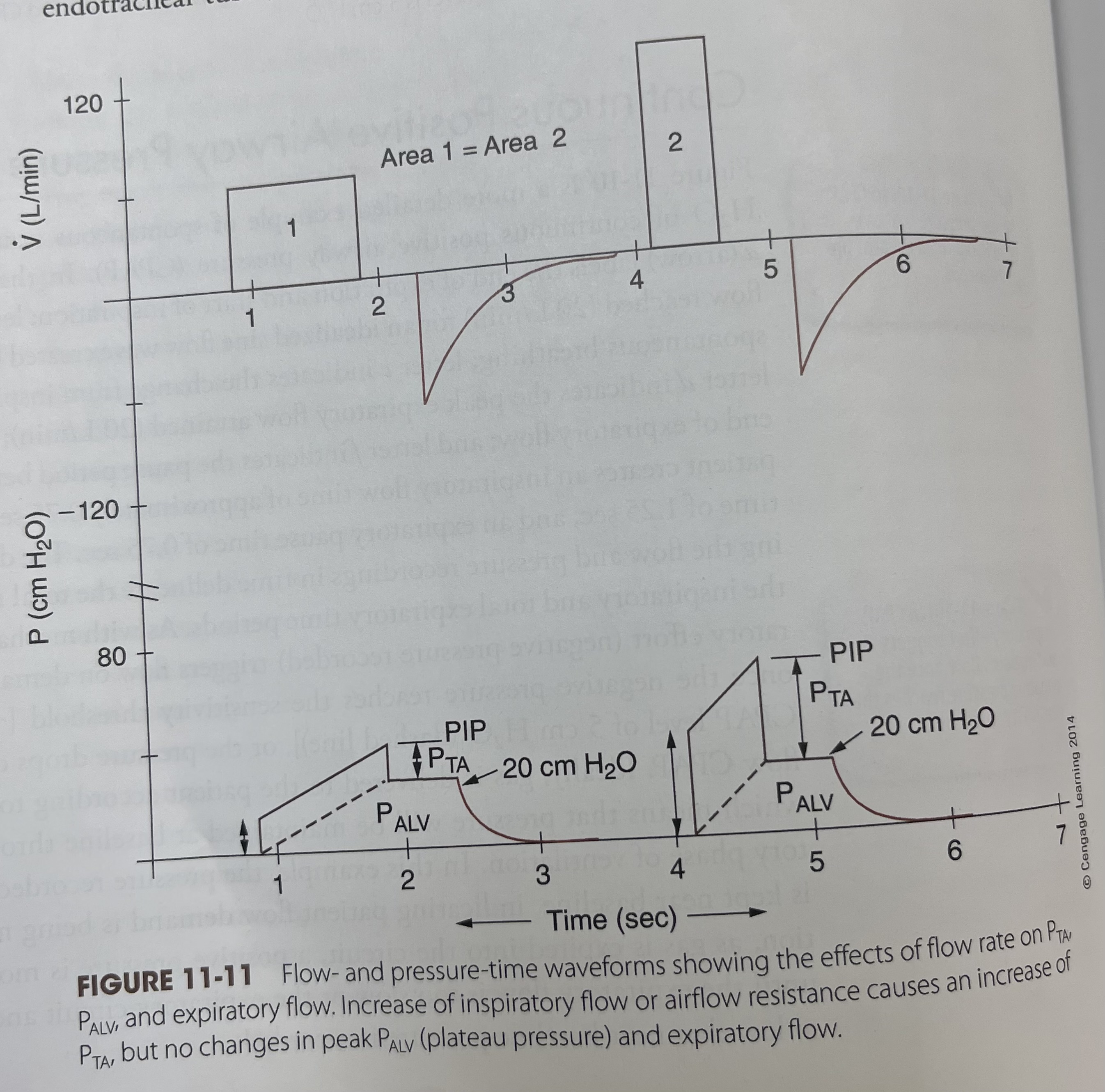
Flow and pressure time waveforms showing the affects of flow rate on PTA, PALV, And expiratory flow.
Increase of inspiratory flow or airflow resistance causes an increase of PTA, but no changes in peak PALV (Plateau pressure) and expiratory flow
What is this waveform?
Increase,higher
____ in flow rate cause as a ___ Airflow resistance, and thus corresponding responding increase in PIP and PTA
No
Does peak alveolar pressure Affected by changes in flow rate?
Increase
Decrease in lung thorax Compliance causes an ___ Increase in PALV and PIP
True
True or False Trans airway pressure (PTA) It’s not affected by changes in compliance