Cytoskeleton
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is dynamic instability
sudden conversion from growth to shrinkage and vice verse as long as there is a uniform free subunit concentration
What is keratin
in hair/nails
Made of intermediate filaments (most common type)
Anchor to desmosomes/hemidesmosomes
Alterations lead to unusual blistering diseases
What is intermediate filament (simple)
ropelike fibers made of intermediate filament proteins
Several types:
Provides mechanical strength
Extend across the cytoplasm, giving cells mechanical strength and distributing the mechanical stresses in an epithelial tissue by spanning the cytoplasm from one cell-cell junction to another
What is the minus end in actin filament
Minus end = slower growing (pointed) end on actin filament
What is a neurofilament
type of intermediate filament that contribute to axonal diameter which is then important for the speed of action potential
Important in axons, especially during development
Alteration and accumulation of these in neurons lead to ALS
What is the plus end in actin filament
Plus end = faster growing (barbed) end on actin filament
What are some general basics of the cytoskeleton
Cytoskeleton:
Spatial & mechanical functions depend on it
Made of protein filaments and tubules in an organized structure
Important in cell shape, cell movement, internal structure, intracellular transport, intercellular communication, organelle, & cell anchoring
Is dynamic and adaptable because of the constant changes the cell undergoes during development, cell cycle, phagocytosis, and other functions
Multiple filaments are needed at a time because single filaments are prone to easily breaking but the strong bonds won’t allow them to disassemble quickly
Specialized cells use cytoskeletal elements to perform their functions (ex: myofibrils)
Accessory proteins: help position cells next to each other
Motor proteins (dynein, kinesin) with microtubules
“walk” across MT with ATP hydrolysis
Tubulins, myosin, actinin, cadherin, vinculin, vimentin, desmin
What is actin
Actin = microfilaments/thin filaments
Protein that links transmembrane proteins to cytosolic proteins
pinches cell shut after division
Whole cell locomotion
Cell surface shape
Interacts with microtubules during cell division
Very dynamic/moves around
Part of the cortex (@ the periphery and extends to the microvilli)
Makes up the contractile ring
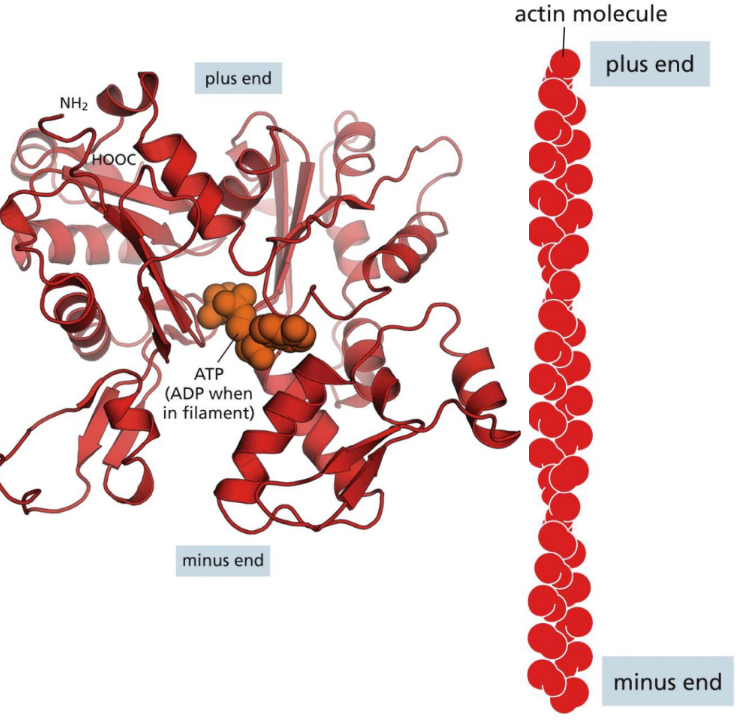
What is the actin structure
Structure = 2 types (F or alpha actin)
G-actin = each subunit carrying an ATP/ADP (polar)
Alpha actin = found in muscle, beta and gamma in all non-muscle cells
F-actin = formed from actin subunits assembling head-to-tail (plus to minus end)
Have structurally different ends
Minus end = slower growing (pointed)
Plus end = faster growing (barbed) *SUBUNITS ADDED TO PLUS END during elongation
Complex between actin filaments and the motor protein myosin
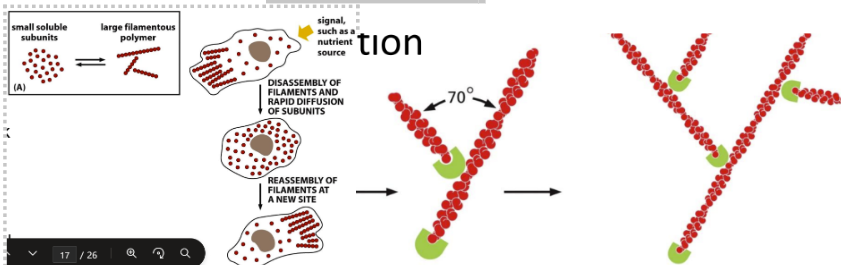
How is actin assembled
Assembly = subunit assembly and disassembly occurs rapidly because of weak non-covalent linkages
Filament nucleation is process of initial aggregation
Branching nucleation & actin web
Arp2 & Arp3 serve as nucleation hubs
Bind to preexisting actin filaments to form a web and act as a plus end for monomer addition
New actin subunits added on the plus end
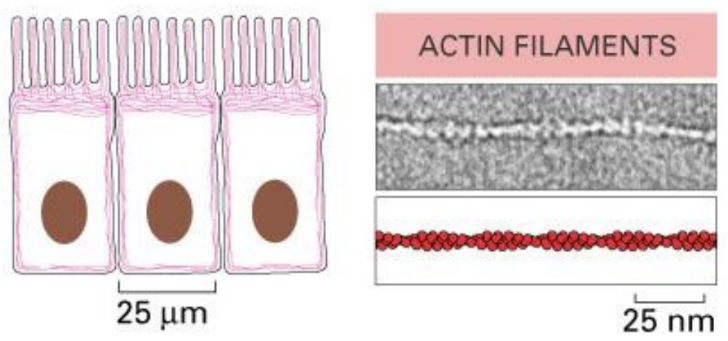
What are actin filaments
Actin filament = helical polymers of the protein actin
Flexible structures that are organized into a variety of linear bundles
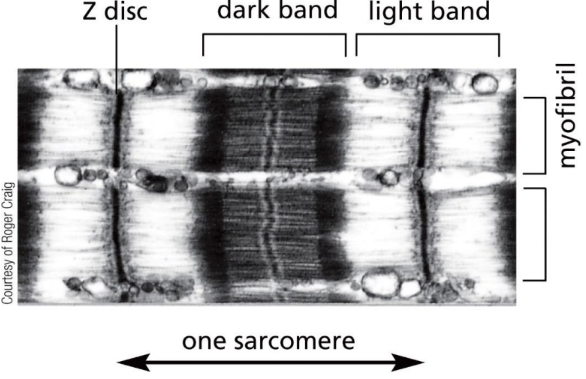
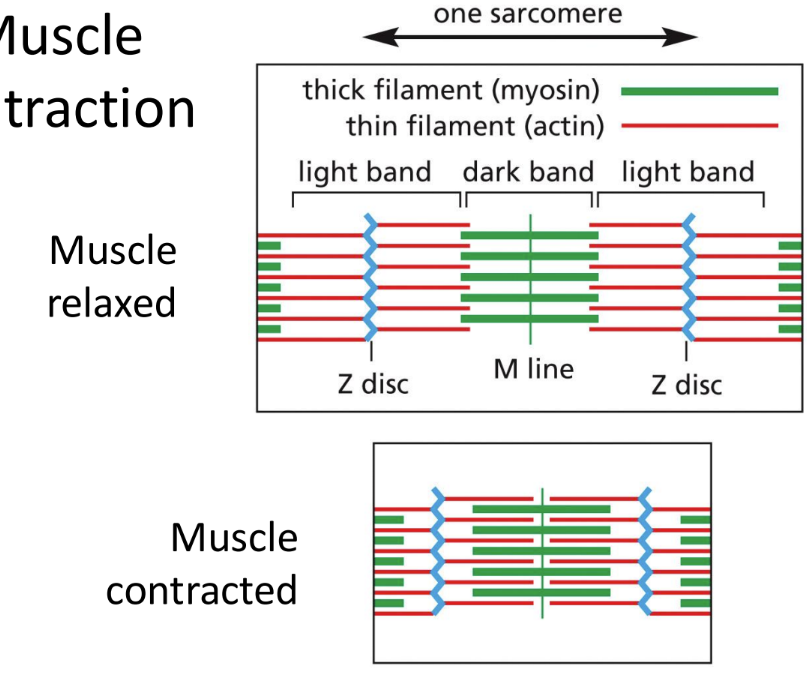
What are myofibrils
Myofibrils (in striated skeletal muscle cytoplasm) consist of sarcomeres
Actin & myosin (motor protein) interact here
Light band – actin only
Dark band – actin and myosin
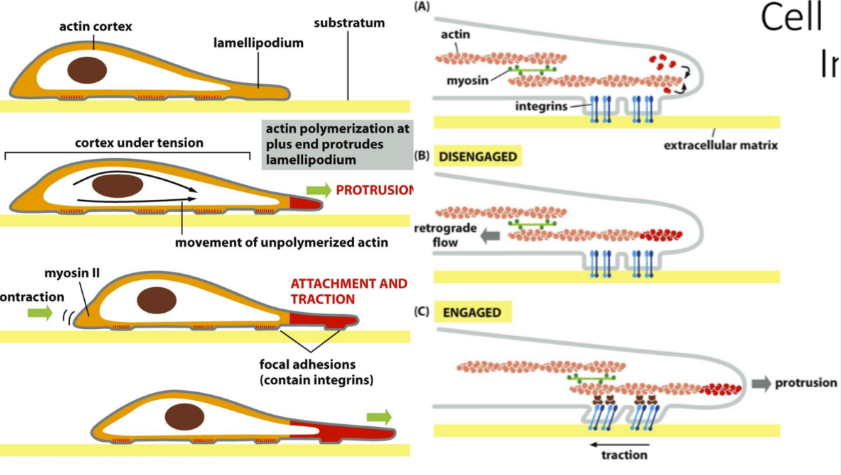
How does cell movement occur with actin
Cell movement with actin:
Protrusion = protruding lamellipodium by polymerizing plus end of actin
Engaged = integrins help move cell forward (protrusion)
Attachment and traction = Moves cell in direction if “signal” is worth it
Disengaged = retrograde flow backwards
What are microtubules
Microtubules = made of proteins that position organelles, involved in intracellular transport, and are needed for cell division
Long hollow cylinders made of protein tubulin
More rigid than actin filaments or intermediate filaments
Long & straight and have one end attached to a centrosome
Interacts with microtubules during cell division
Binds to chromatid via kinetochore
Formed from subunits of tubulin
Alpha & beta subunits bind to GTP but ONLY beta uses it (alpha keeps it in the structure)
Grow out from centrosome
Microtubule organizing center with embedded centrioles and nucleation sites (important during mitosis)
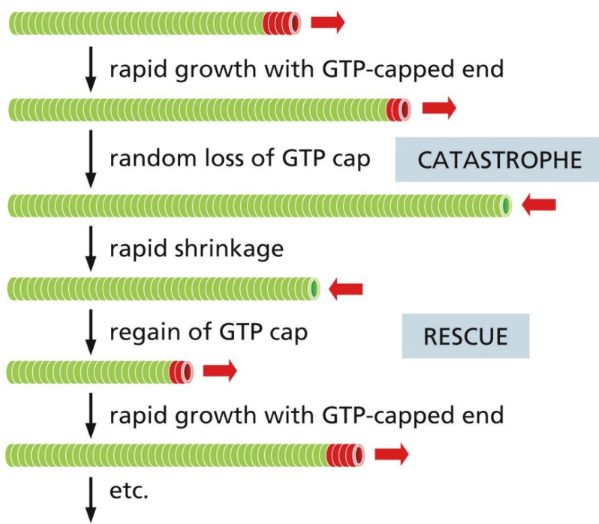
How are microtubules formed
Formation = growth occurs at beta end of tubule only
Have dynamic instability = sudden conversion from growth to shrinkage and vice verse as long as there is a uniform free subunit concentration
Growth to shrinkage = “catastrophe”
Shrinkage to growth = “rescue”
Nucleation occurs in the MTOC (microtubule-organizing center) using gamma tubulin and other proteins that serve as a template that serve as a template for the 13 protofilament structure
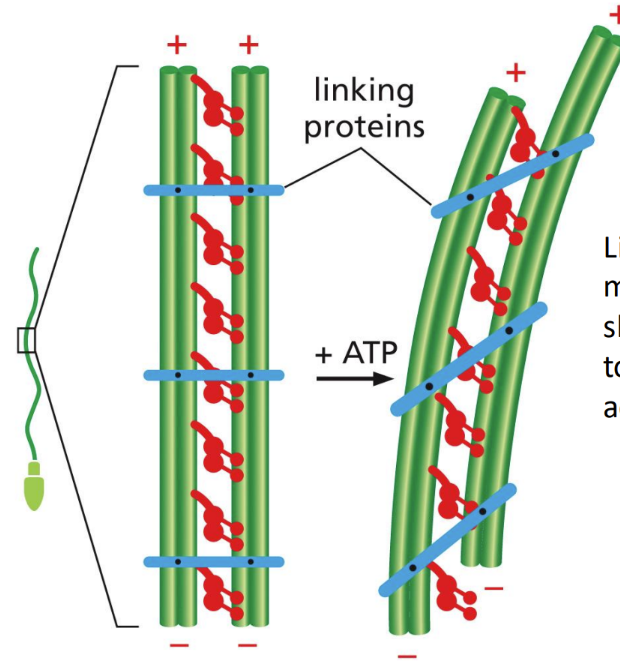
What is MT bending
Bending = linker proteins stop microtubules from sliding and allow them to bend instead
Motor action causes bending (bending and NO skiing motion)
How do motor proteins relate to MT
Motor proteins attach to microtubules & walk using repeated ATP hydrolysis
Done by tubulin
Motor proteins important
Dynein walks toward the negative end of the microtubule
Kinesin walks towards the positive end of the microtubule
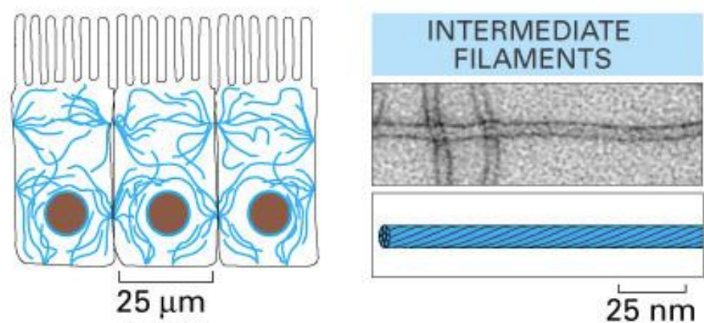
What are intermediate filaments (descriptive)
Intermediate filaments = several proteins that provide mechanical strength & line the inside of the nuclear envelope
Ropelike fibers made of intermediate filament proteins (non-polarized)
Form the nuclear lamina
Found in vertebrate cells that are required to deal with mechanical stress
Nuclear lamina (inner lining of nuclear envelope), keratins (hair/nails), neurons
Do NOT contain a nucleotide binding site (not ATPase)
Nonpolar because both ends of the protein are the same
Unclear how it assembles/disassembles - likely through phosphorylation
Keratins is the most common type (therefore bind to desmosomes/hemidesmosomes)
Make up neurofilaments -> which contribute to rigidity and formation of neurons (contribute to axonal diameter which is important for the speed of the action potential)
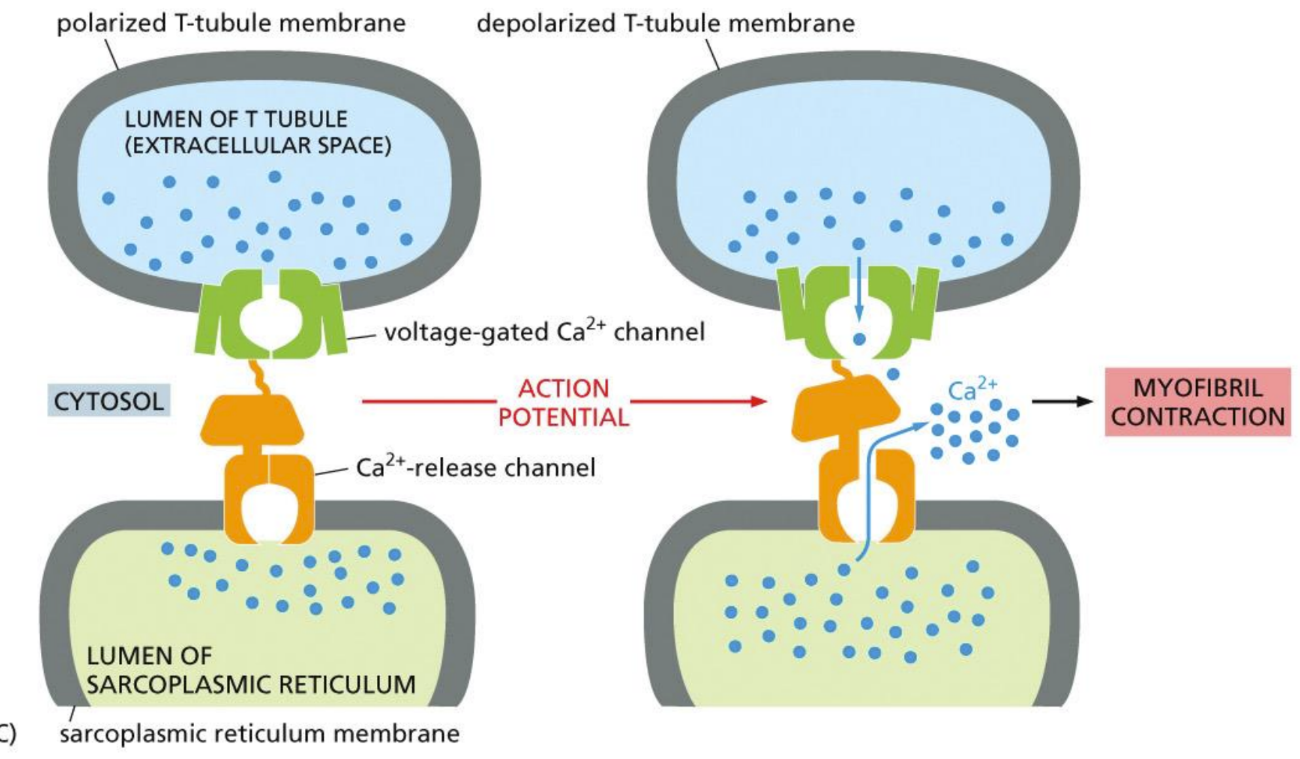
What role does the Sarcoplasmic reticulum play in muscle cells
Holds Ca2+ until it receives signal to release it (used for muscle contraction)
P-type ATPase calcium pump = best characterized is Ca pump in sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) of skeletal muscle cells
SR serves as intracellular store of Ca in muscle
Ca pump moves Ca from the cytosol back into the SR (because need Ca for muscle contraction)
Calcium pumping cycle = hydrolysis of ATP, phosphate event, antiport
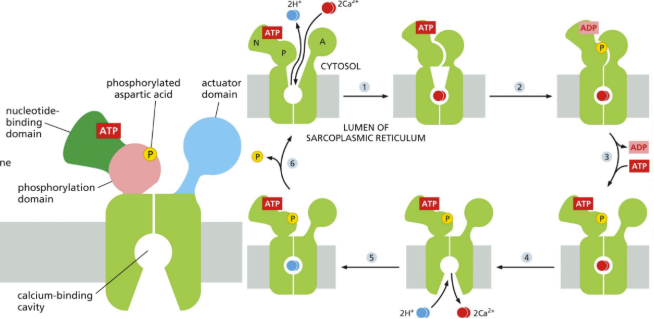
What is the myosin-actin system
Myosin-actin systems =
Myosin = motor protein that slides along actin polymers for muscle contraction using ATP hydrolysis
Muscle contraction = require calcium & troponin
Calcium binds troponin, causing tropomyosin to move away from actin so it can bind to myosin to shorten sarcomere and contract muscle
Troponin is measured clinically to determine whether an acute heart attack has occurred (stress indicator)
What is tubulin
Tubulin = The protein subunit of microtubules
Alpha & beta subunits bind to GTP but ONLY beta uses it (alpha keeps it in the structure)
What is a microtubule (simple)
Microtubule = formed from subunits of tubulin
Grow out from the centrosome
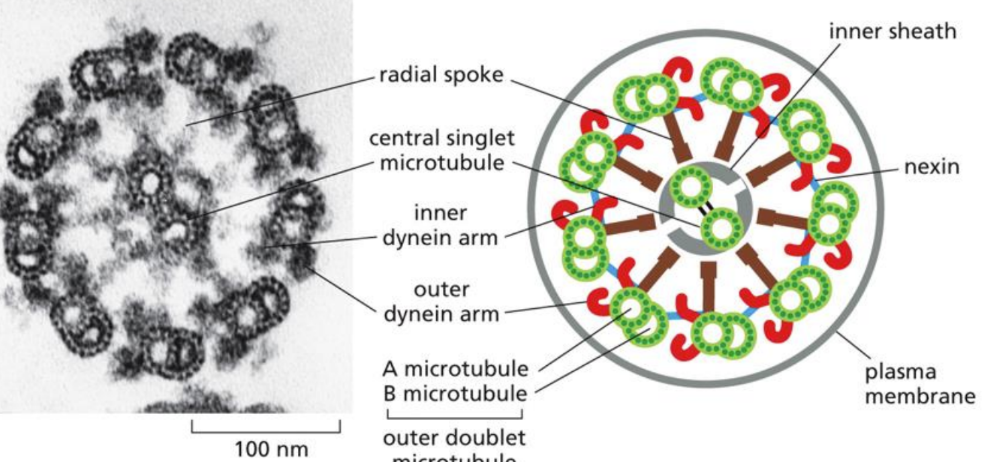
What is cilia
Cilia = shorter (than flagella) but beat rhythmically and move fluid over cell surfaces
made from microtubules & motor proteins
Do NOT move cells
Produced by axoneme (core) - image
Made of microtubules and associated proteins in a special pattern
Found in the respiratory tract, gut epithelium & inner ear hair cells (move sound)
Primary cilia = serves as a cell signaler or receptor on certain cells (like nasal epithelial cells)
Found in call cells (call have a nonmotile cilia = primary cilium)
Act as responder to external environment
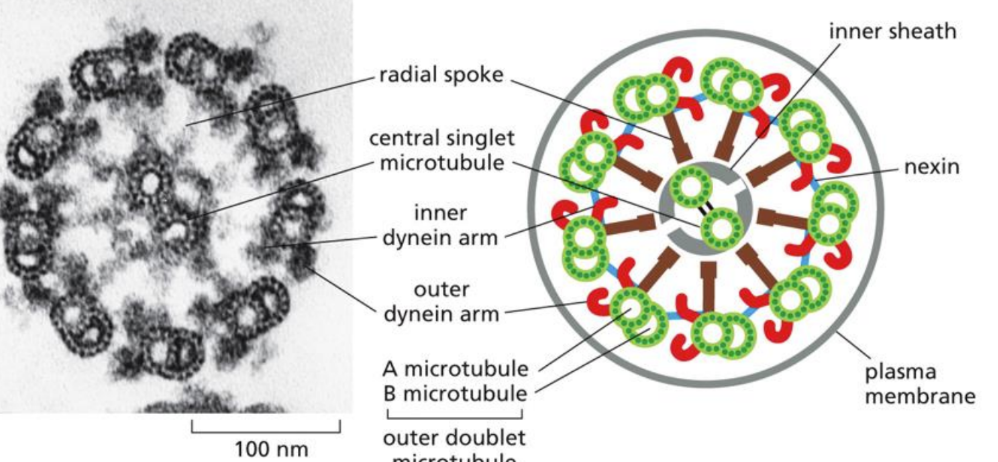
What is the flagella
allow cells to swim through liquid media
made from microtubules & motor proteins
Produced by axoneme (core) - image
Made of microtubules and associated proteins in a special patter
What is troponin
Required for muscle contraction (with calcium)
Calcium binds troponin, causing tropomyosin to move away from actin so it can bind to myosin to shorten sarcomere and contract muscle
Measured clinically to determine whether an acute heart attack has occurred (stress indicator)
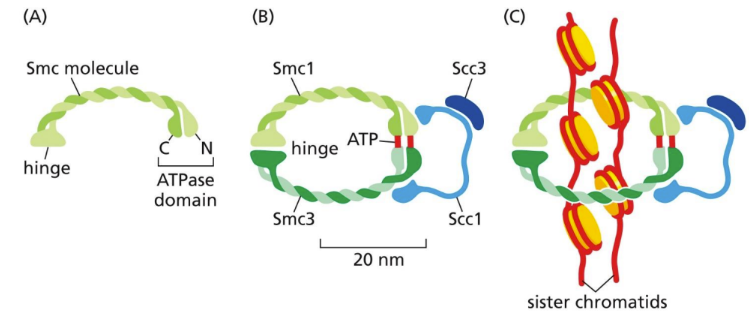
What is cohesin
involved at the end of S phase to hold sister chromatids together (bracelet)
Located at many locations along sister chromatids (keep sister chromatids together)
Must be destroyed during metaphase to anaphase transition
S-Cdk also stimulates increase in histone protein synthesis for nucleosome synthesis
How does the cytoskeleton relate to development
ytoskeleton and development:
Timing of gene expression for normal protein presence is critical
Growth cones = find and form connections with other cells
Tips of growth cones = lamellipodia (filled with actin)
Myosin required to contract the cell
Growth cones grow because of tropic factors (hormones/stimulants/signals) and other substances on/in a substratum
Respond to cues
Growth cones are essential for early development of structures
Embryonic development requires extensive cell movement
Actin and tubulin are essential
PIP5Kly plays a role in actin dynamics and focal adhesion formations, therefore, when defective, there are myocardial developmental defects
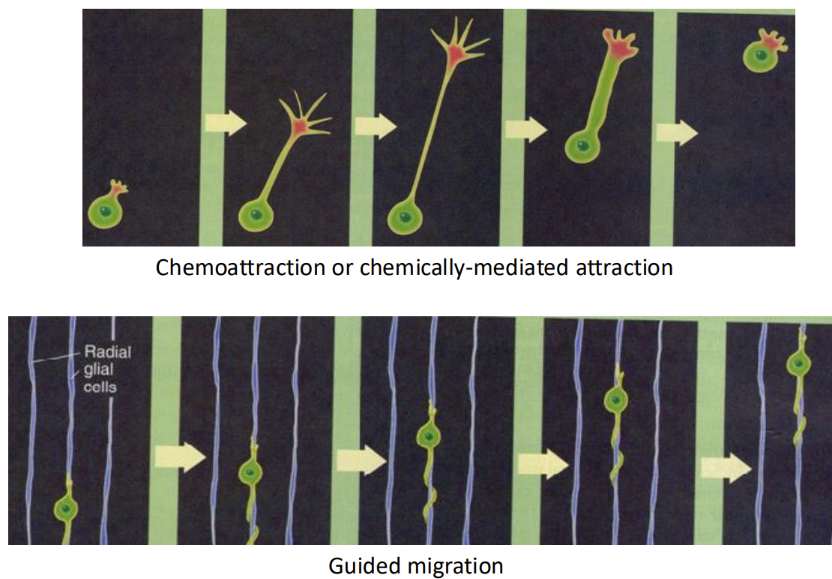
How is the cytoskeleton cued to move
Cues to move
Growth cones “grow” or “shrink” based on environmental cues
Contact-mediated attraction/repulsion = contact with an adhesion protein in the substrate
Chemoattraction/chemorepulsion = attraction to an emitted chemical cue
Some cells “climb” on filaments/tubules formed by other cells to their appropriate positions during development
What is Kartagener syndrome
hereditary dynein deficits
Paralyzed cilia so chronic lung disease due to insufficient movement of cilia from defect in dynein arms
Embryonic developmental issues
Mutations on 2 genes on chr. 9
Both code for proteins found in the ciliary outer dynein arm lea to this syndrome
What is epidermolysis bullosa
Blistering diseases caused by alterations in keratins (int. Filament)
Genetic defect in keratins
Because keratins bind to hemi/desmosomes (therefore, basal lamina is not held down)
Skin ruptures or blisters with any mechanical stress
What is ALS
ALS = alterations and accumulation in neurofilaments (int. Filaments) in the neuron
What is spina bifida
Spina bifida = neural tube closure requires numerous cellular events based on cell migration BUT doesn’t happen
Caused by vitamin deficiency during pregnancy (aspartic acid?)
What is Kennedy disease
Kennedy disease = sertoli cells (make sperm) have altered cytoskeleton and lack androgen receptors on nucleus
Alterations causes infertility & jaw dropped
What are myocardial developmental defects
Myocardial developmental defects = associated with impaired intracellular junctions that lead to heart failure and extensive prenatal lethality at embryonic day 11.5 of development
Actin disorganized and cadherin missing