AP Pysch
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:01 PM on 5/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
1
New cards
Structuralism
a historic perspective…not in use today…introspection.
2
New cards
introspection
observing one’s own mental state
3
New cards
Functionalism
focused on the purpose of consciousness and behavior…individual differences…has influenced the educational system.
4
New cards
Structuralism vs Functionalism
\
Structuralism studied the contents of the mind through the use of lab experiments and introspection. Functionalism was more interested in using direct observation and fieldwork in order to better understand the adaptive function of behavior.
Structuralism studied the contents of the mind through the use of lab experiments and introspection. Functionalism was more interested in using direct observation and fieldwork in order to better understand the adaptive function of behavior.
5
New cards
Psychoanalysis
the perspective that human behavior is driven by the unconscious mind…
6
New cards
Behaviorism
all behaviors are learned
7
New cards
Humanism
Looking at how the whole human achieve his/her potential (self-actualization)
8
New cards
Biopsychology
everything psychological is also biological
9
New cards
Evolutionary Psychology
natural selection over generations also applies to thoughts and behaviors
10
New cards
Cognitive Psychology
Our thought processes control our behaviors.
11
New cards
Sociocultural
\
\
Thoughts and behaviors vary based on cultural context.
12
New cards
Gestalt Psychology
The whole is different than the sum of its parts
13
New cards
Wilhelm Wundt
regarded as the first modern psychologist because he gathered data about human thinking in a laboratory setting (empirical analysis). ….
also came up with the structuralism perspective …examining the structures that made up the mind
also came up with the structuralism perspective …examining the structures that made up the mind
14
New cards
William James
came up with the functionalism perspective which sought to causal relationships between internal states and external behaviors.
15
New cards
Sigmund Freud
came up with the Psychoanalysis + Structuralism perspectives…also the psychoanalysis stages +psychoanalytic theory
16
New cards
John Watson
one of the people that came up with the Behaviorism perspective and Operant Conditioning
17
New cards
B.F Skinner
one of the people that came up with the Behaviorism perspective and Operant Conditioning
18
New cards
Ivan Pavlov
one of the people that came up with the Behaviorism perspective
19
New cards
Abraham Maslow
one of the people that came up with the humanist perspective
20
New cards
Jean Piaget
came up with the cognitive psychology perspective…cognitive development stages
21
New cards
Erik Erikson
came up with the psychosocial stages…
22
New cards
Phineas Gage
Gage's accident helped teach us that different parts of the brain play a role in different functions….survived severe damage to the brain.
23
New cards
Albert Bandura
came up with Observational Learning ..or modeling
24
New cards
Lev Vygotsky
came up with one of the stage theories…..humans continuously develop throughout their lives….
25
New cards
Lawrence Kohlberg
came up with the moral development stages
26
New cards
Howard Gardner
came up with the multiple intelligence within the theories of intelligence
27
New cards
Alfred Binet
wanted to design a test to identify which children needed special attention in school….Stanford Binet IQ test
28
New cards
Charles Darwin
came up with the Evolutionary Perspective
29
New cards
Ivan Pavlov’s Dogs
Learning technique classical conditioning….is the association between a neutral stimulus and a stimulus that produces a reflexive, involuntary response
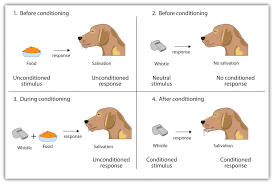
30
New cards
Albert Bandura’s Bobo Doll
Observational learning …also known as modeling..
1. Observation
2. Imitation
1. Observation
2. Imitation

31
New cards
Edward Tolman’s Rats
Latent learning….is learning that becomes obvious only once a reinforcement is given for demonstrating it…..Tolman’s rats in a maze
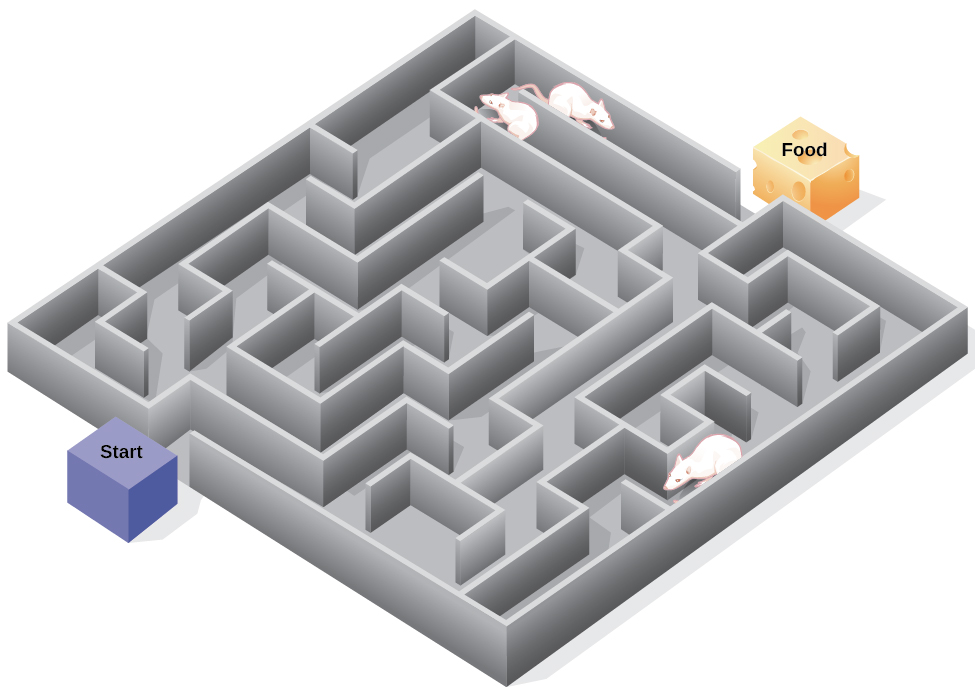
32
New cards
Wolfgang Kӧhler’s chimps
Insight learning….occurs when one suddenly realizes how to solve a problem…..

33
New cards
Harry Harlow’s wire mother
\
one was a simple construction of wire and wood, and the second was covered in foam rubber and soft terry cloth.
one was a simple construction of wire and wood, and the second was covered in foam rubber and soft terry cloth.

34
New cards
David Rosenhan’s Psychiatric experiments
pioneer in applying psychological methods to the practice of law, including the examination of expert witnesses, jury selection, and jury deliberation
35
New cards
Asch conformity study
people conform for two main reasons: they want to fit in with the group (normative influence) and because they believe the group is more informed than they are (informational influence)…Asch measured the number of times each participant conformed to the majority view.
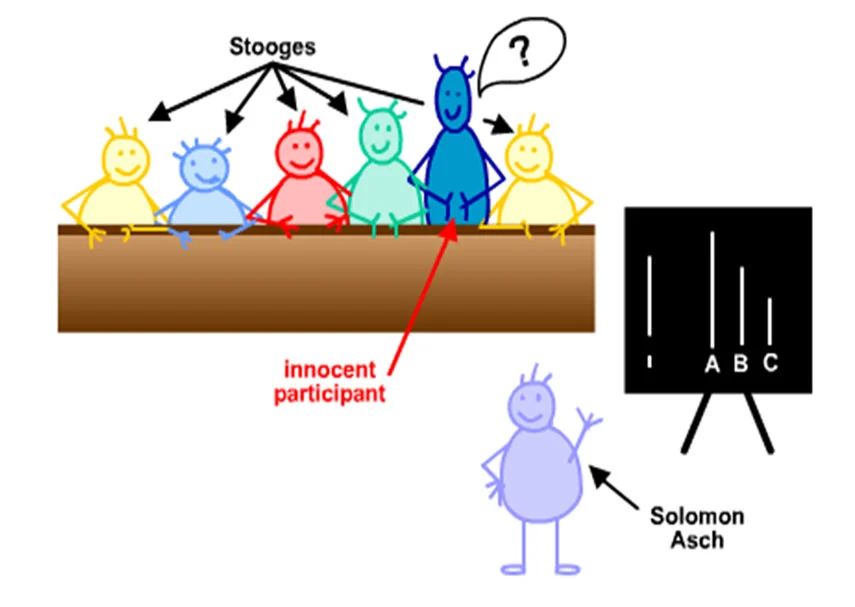
36
New cards
Milgram obedience experiment
\
The experiment was controversial because it revealed people's willingness to obey authority figures even when causing harm to others, raising ethical concerns about the psychological distress inflicted upon participants and the deception involved in the study.
The experiment was controversial because it revealed people's willingness to obey authority figures even when causing harm to others, raising ethical concerns about the psychological distress inflicted upon participants and the deception involved in the study.
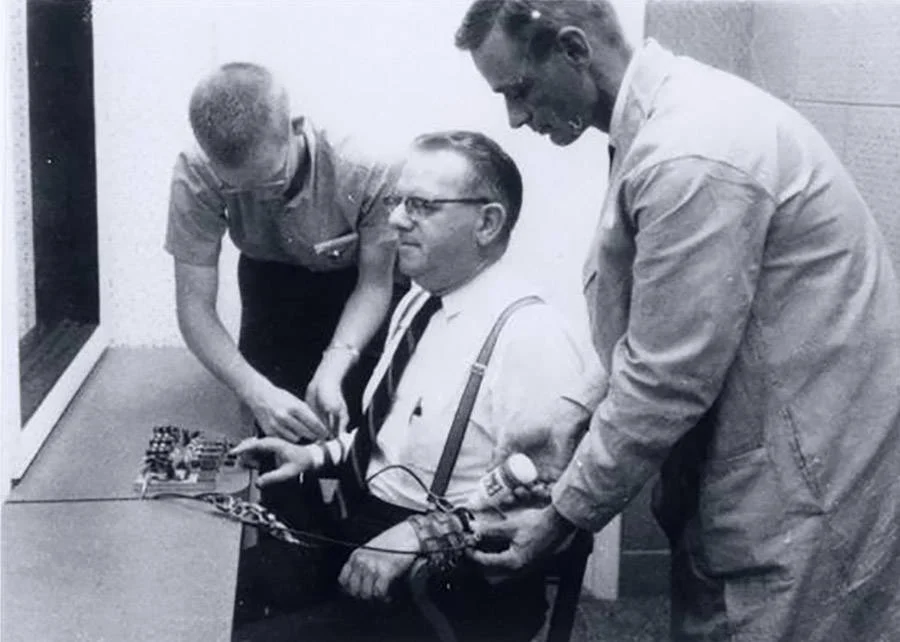
37
New cards
Zimbardo’s Stanford prison experiment
how good people can be transformed into perpetrators of evil, and healthy people can begin to experience pathological reactions - traceable to situational forces.

38
New cards
Dependent vs Independent Variable
39
New cards
__Reinforcement__: Anything that makes a behavior more likely to occur
Positive reinforcement
Negative reinforcement
Negative reinforcement
40
New cards
__Punishment__: Anything that makes a behavior less likely to occur
Positive punishment
Negative punishment
Negative punishment
41
New cards
Positive
adding something
42
New cards
Negative
taking away something
43
New cards
Positive reinforcement
Giving a high five for an achievement
44
New cards
Negative reinforcement
Getting up from the bed to avoid the noisy alarm.
45
New cards
Positive punishment
adding more chores to the list when your child neglects their responsibilities.
46
New cards
Negative punishment
losing party privileges when you continue to do it.
47
New cards
Case Study
In-depth investigation of an individual or a small group
48
New cards
Survey
Measures various elements of human behavior
49
New cards
Naturalistic Observation
Observe behavior in its natural setting
50
New cards
Longitudinal Study
Participants are observed at intervals over a long period of time
51
New cards
Cross-Sectional Study
Compare / contrast people at different age groups at a given time
52
New cards
Experimental approach
Setting up experiments in a controlled environment
53
New cards
Parts of the neuron & how the nervous system functions
\
* Dendrites, soma, nucleus, synapse, neurotransmitters
* Dendrites receive the information and sends the information through the soma…..this information then gets transformed into neurotransmitters through the synaptic cleft.
* Dendrites, soma, nucleus, synapse, neurotransmitters
* Dendrites receive the information and sends the information through the soma…..this information then gets transformed into neurotransmitters through the synaptic cleft.
54
New cards
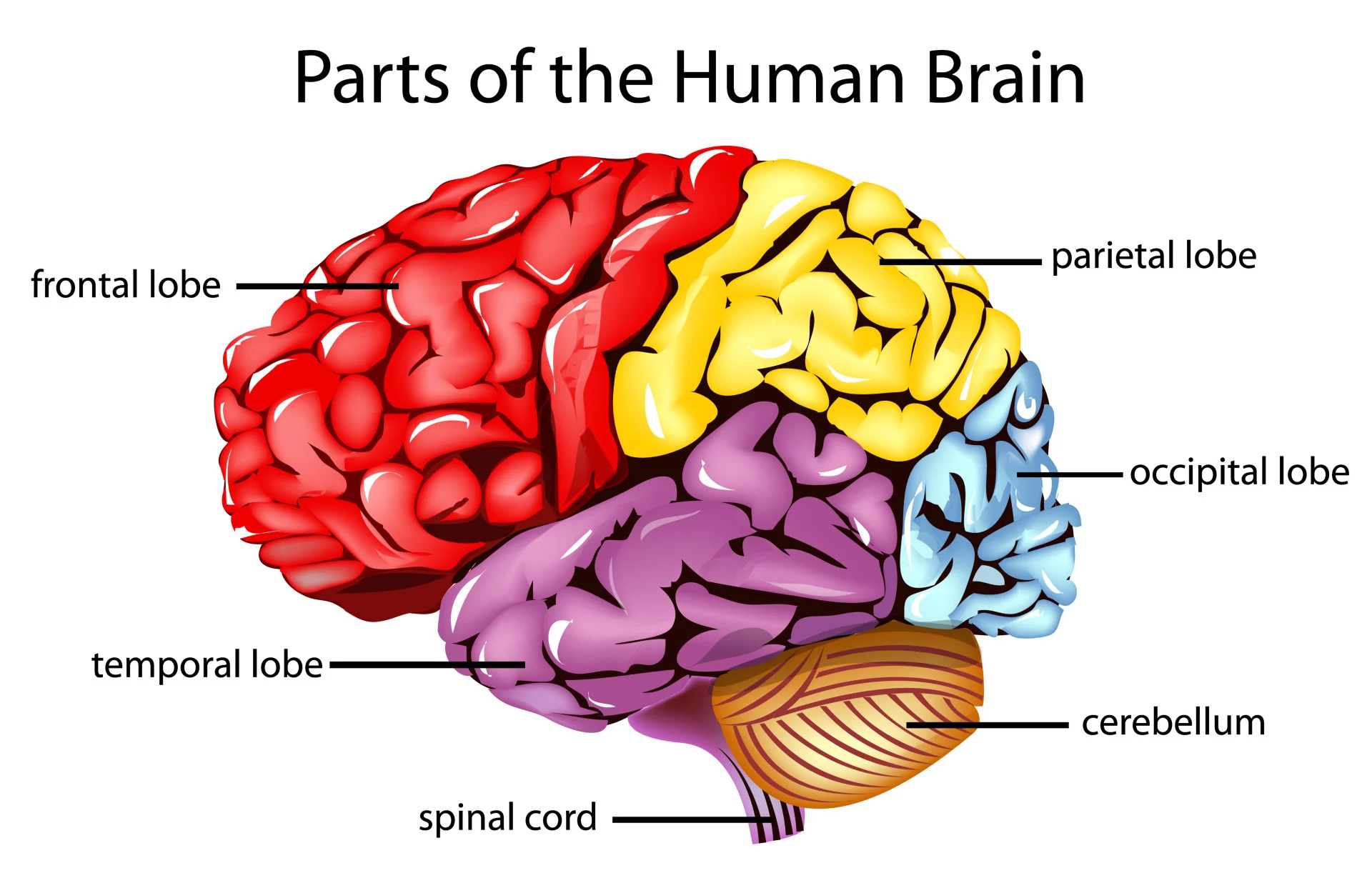
Parts of the brain
\
* Hindbrain vs midbrain vs forebrain
* Hindbrain- top of the spinal cord, basic life support
* Midbrain- integrates simple sensory info and muscle movements
* Hindbrain and midbrain are considered apart of the “old brain”
* Forebrain is considered apart of the “new brain”
* Forebrain- thought and reason
* Hippocampus responsible for creating new memories.
* Amygdala- emotion
* Hindbrain vs midbrain vs forebrain
* Hindbrain- top of the spinal cord, basic life support
* Midbrain- integrates simple sensory info and muscle movements
* Hindbrain and midbrain are considered apart of the “old brain”
* Forebrain is considered apart of the “new brain”
* Forebrain- thought and reason
* Hippocampus responsible for creating new memories.
* Amygdala- emotion
55
New cards
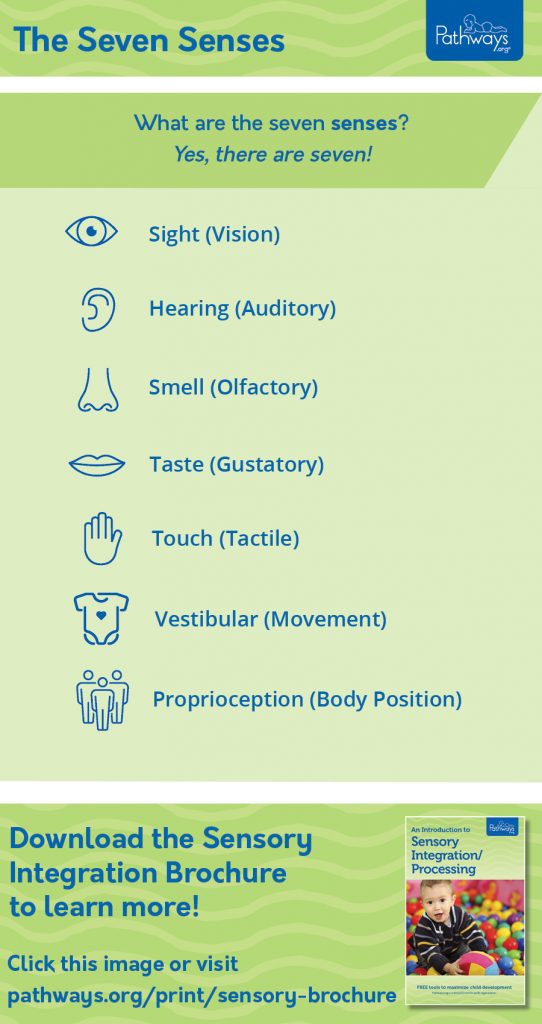
7 senses function
\
* Vision - your eye gathers light, which is focused on retina, and then transduction converts the light to a neural stimulus.
* Hearing- the transduction of sound waves into auditory neural signals
* Touch- pain is a response to potential dangers, and isn’t a weakness that is leaving the body.
* Taste- a chemical sense, as apposed to previous energy senses….flavor of food is actually a combo of tase and smell
* Smell- olfactory bulb connecs to the brain via the amygdala and hippocampus ( the limbic system: emotion+memory)
* Vestibular: how your body is oriented in space ( semicircular canals— balance)
* Kinesthetic: the position and orientation of specific body parts
* Vision - your eye gathers light, which is focused on retina, and then transduction converts the light to a neural stimulus.
* Hearing- the transduction of sound waves into auditory neural signals
* Touch- pain is a response to potential dangers, and isn’t a weakness that is leaving the body.
* Taste- a chemical sense, as apposed to previous energy senses….flavor of food is actually a combo of tase and smell
* Smell- olfactory bulb connecs to the brain via the amygdala and hippocampus ( the limbic system: emotion+memory)
* Vestibular: how your body is oriented in space ( semicircular canals— balance)
* Kinesthetic: the position and orientation of specific body parts
56
New cards
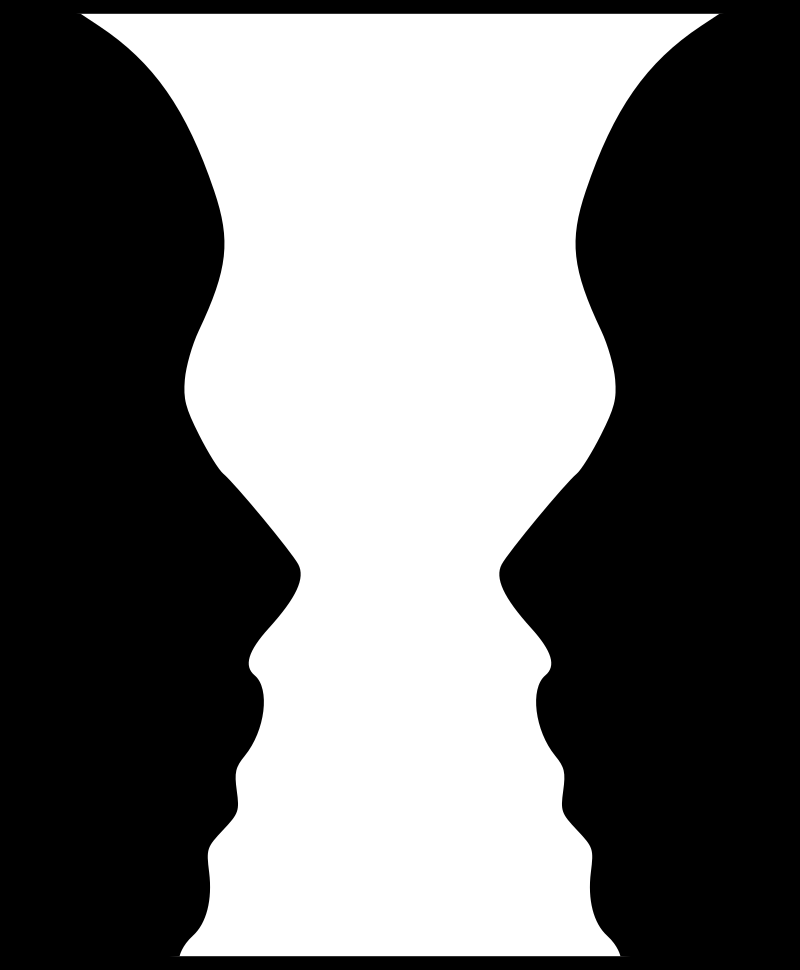
Rules of perception
Figure-ground relationships
57
New cards
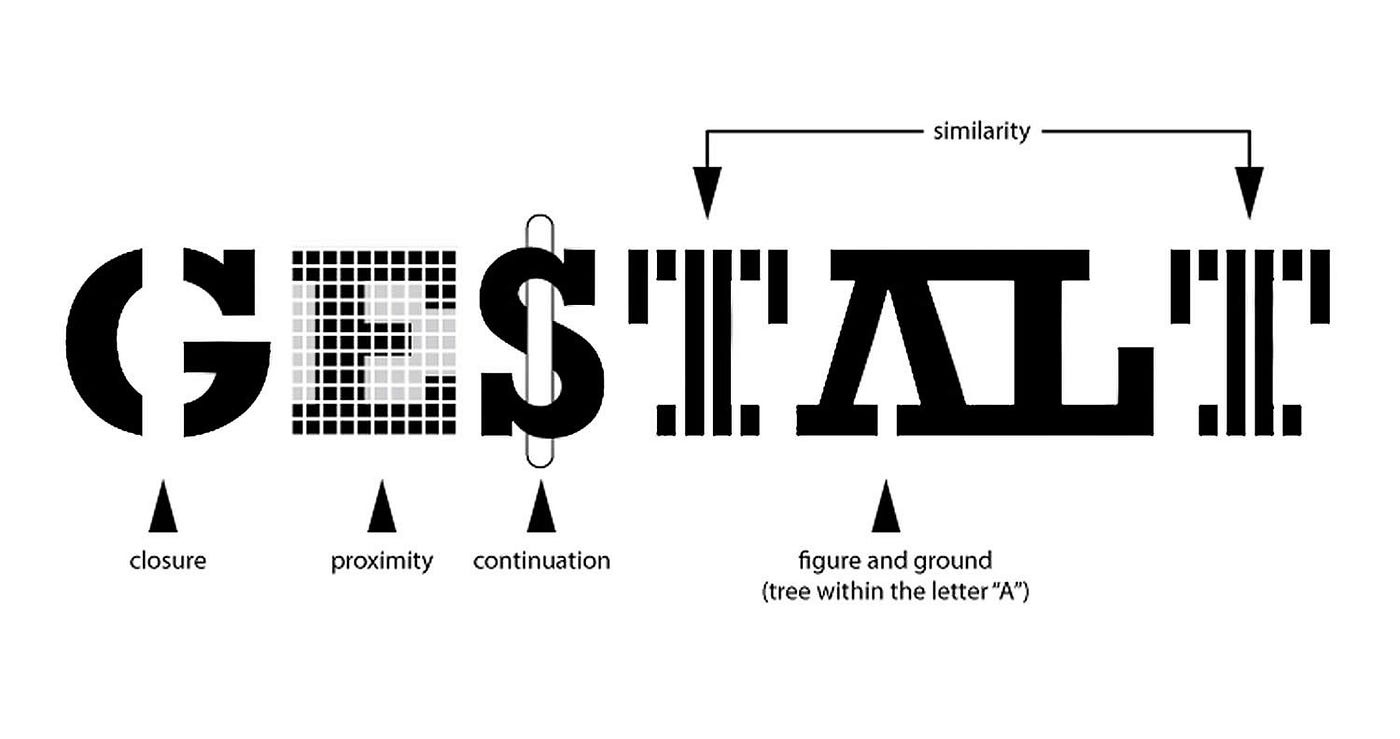
Gestalt Rules
Figure- Ground segregation, Closure, Proximity, Continuity, Similarity, Past Experience, Symmetry/Equlibrium
58
New cards
Perceived motion
Looks like things are moving, when they aren’t

59
New cards
Monocular cues
\
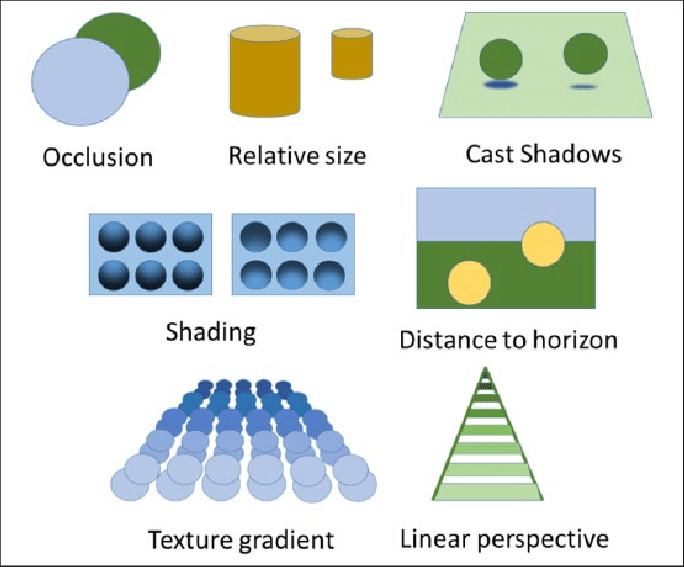
* linear perspective → 3-dimensional point of view instead of 2
* Relative Size Cue → sizes may look similar….for example a person being the same height as the Eiffel tower., however this is just an illusion
* Interposition Cue → circle that covers the shape behind it makes us just think that the circle is in front and the square and the triangle follows.
* Texture Gradient- the perception of the texture/surface of the thing at hand…..ex. Epcot…when we get farther away from the ball, we think its smooth, when it reality, once you get up close, you see its gradient texture.
* Shadowing
* linear perspective → 3-dimensional point of view instead of 2
* Relative Size Cue → sizes may look similar….for example a person being the same height as the Eiffel tower., however this is just an illusion
* Interposition Cue → circle that covers the shape behind it makes us just think that the circle is in front and the square and the triangle follows.
* Texture Gradient- the perception of the texture/surface of the thing at hand…..ex. Epcot…when we get farther away from the ball, we think its smooth, when it reality, once you get up close, you see its gradient texture.
* Shadowing
60
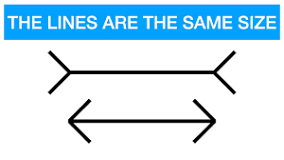
New cards
Muller-Lyon Illusion
perception is culturally based
61
New cards
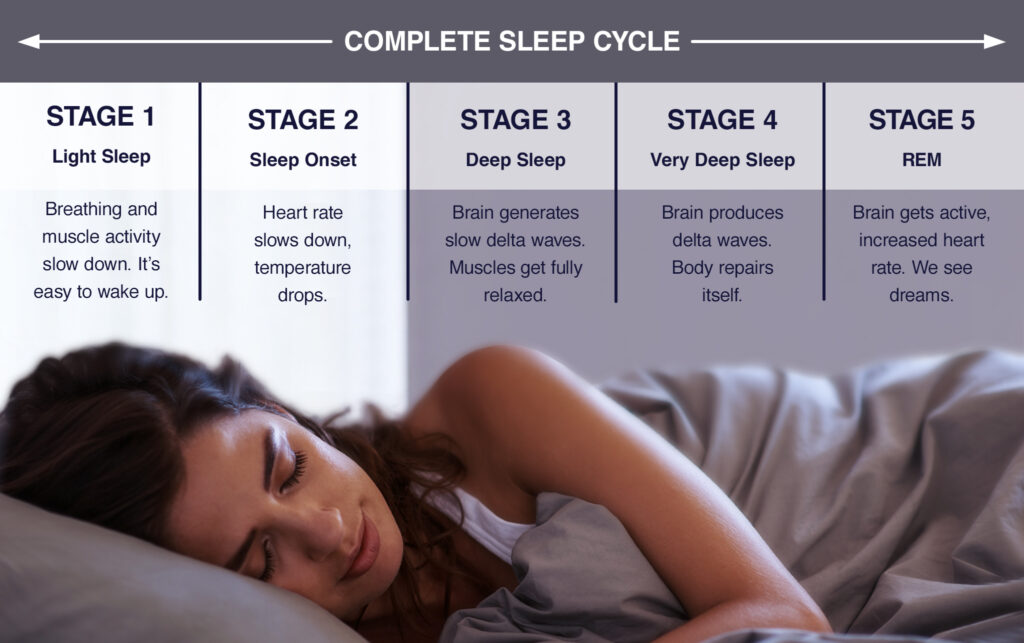
Sleep
Five stages
* 1. From awake to asleep
* 2. Memory consolidation
* 3. Deep Sleep
* 4.Deep Sleep
* 5. Rapid Eye movement (REM)
* 1. From awake to asleep
* 2. Memory consolidation
* 3. Deep Sleep
* 4.Deep Sleep
* 5. Rapid Eye movement (REM)
62
New cards
Circadian rhythm
24- hour cycle of metabolic and thought processes taht govern sleep/wake
63
New cards
Sleep disorders
\
* __Insomnia__: Persistent problems falling asleep or staying asleep
* __Sleep apnea__: Stop breathing for short periods of time during the night
* __Narcolepsy__: Unpredictable periods of intense sleepiness (REM)
* __Sleepwalking & night terrors__: Typically occur in children during the first few hours of stage 4 sleep
* __Insomnia__: Persistent problems falling asleep or staying asleep
* __Sleep apnea__: Stop breathing for short periods of time during the night
* __Narcolepsy__: Unpredictable periods of intense sleepiness (REM)
* __Sleepwalking & night terrors__: Typically occur in children during the first few hours of stage 4 sleep
64
New cards
\
* Psychoactive drugs
* Psychoactive drugs
\
* Depressants slow down the same body processes (heroin, alchohol)
* Stimulants speed up body processes (caffeine, nicotine)
* Hallucinogens or psychdelics cause changes in perception of reality, hallucinations, and etc. (mushrooms, Marijuana)
* Depressants slow down the same body processes (heroin, alchohol)
* Stimulants speed up body processes (caffeine, nicotine)
* Hallucinogens or psychdelics cause changes in perception of reality, hallucinations, and etc. (mushrooms, Marijuana)
65
New cards
Tolerance & withdrawal
needing more and more of that drug in order to tolerate it. However, trying to withdraw from it will be very difficult to do the side effects.
66
New cards
Types of learning
\
* Classical conditioning- is the association between a neutral stimulus and a stimulus that produces a reflexive, involuntary response
* Classical conditioning- is the association between a neutral stimulus and a stimulus that produces a reflexive, involuntary response
67
New cards
Memory = encoding
\
* Encoding- split-second holding for incoming sensory info
* Encoding- split-second holding for incoming sensory info
68
New cards
Memory storage
\
* short-term memory + long-term memory
* short-term memory + long-term memory
69
New cards
Memory retrieval
\
* retrieving information from sensory memory with external cue/recognition
* retrieving information from sensory memory with external cue/recognition
70
New cards
Types of learning
Operant conditioning- is learning based on the consequences of one’s behaviors
71
New cards
Types of learning
\
* Observational learning- is also known as modeling ….Bobo Doll experiment
* Observational learning- is also known as modeling ….Bobo Doll experiment
72
New cards
Types of learning
\
* Latent learning- is learning that becomes obvious only once a reinforcement is given for demonstrating it
* Latent learning- is learning that becomes obvious only once a reinforcement is given for demonstrating it
73
New cards
Types of learning
\
* Insight learning- occurs when one suddenly realizes how to solve a problem
* Insight learning- occurs when one suddenly realizes how to solve a problem
74
New cards
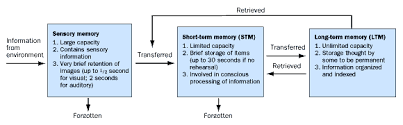
Three Box Model
\
* Sensory memory…something that ur senses are picking up
* Short term memory (working memory)…up to 30 seconds …about 7 items
* Long term memory ….storage is unlimited ..and the memory lasts long forever
* Sensory memory…something that ur senses are picking up
* Short term memory (working memory)…up to 30 seconds …about 7 items
* Long term memory ….storage is unlimited ..and the memory lasts long forever
75
New cards
Deep processing
\
* Deep processing leads to a more durable memory trace
* Deep processing leads to a more durable memory trace
76
New cards
Shallow Processing
Shallow processing leads to a fragile memory trace that is vulnerable to decay.
77
New cards
Where is memory stored?
\
* Memory is stored everywhere….mostly in the cerebellum and cerebral cortex
* Memory is stored everywhere….mostly in the cerebellum and cerebral cortex
78
New cards
\
* Nativist Theory
* Nativist Theory
* Language acquisition device during “critical period” in development
\
\
79
New cards
Conflicting motives
* __Approach-Approach conflict__: choose between two good options
* __Avoidance-Avoidance conflict__: choose between two bad options
* __Approach-Avoidance conflict__: one option has both good and bad elements
* Multiple Approach-Avoidance conflict: two+ options with both good and bad elements
* __Avoidance-Avoidance conflict__: choose between two bad options
* __Approach-Avoidance conflict__: one option has both good and bad elements
* Multiple Approach-Avoidance conflict: two+ options with both good and bad elements