OCR A GCSE Chemistry: C1 and C2.2
1/109
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For Chemistry Assessment in November, flashcards from PMT and some are added extras.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
What are the three states of matter?
Solid, Liquid, Gas
Describe the arrangement and movement of particles in solids
The particles are packed closely together in a regular arrangement. The particles vibrate in fixed positions.
Describe the arrangement and movement of particles in liquids
The particles are close together but able to move past each other. The particles vibrate and move around each other.
Describe the arrangement and movement of particles in gases
The particles are well separated with no regular arrangement. The particles vibrate and move freely at high speeds.
How do the relative energies of particles in a solid, liquid and gas compare?
Particles in a solid have the least amount of energy. Particles in a gas have the most energy.
What are the names for the state changes from solid to liquid and vice versa?
Solid → liquid: Melting. Liquid → solid: Freezing.
What are the names for the state changes from liquid to gas and vice versa?
Liquid → gas: Evaporation. Gas → liquid: Condensation.
Describe the forces between particles in solids, liquids and gases
Solids: Strong forces of attraction between particles which keep them in fixed positions. Liquids: Weaker attractive forces than in solids. Gases: Weakest intermolecular forces so particles move randomly.
How does a physical change differ from a chemical change?
A physical change involves changes in the forces between particles. The particles themselves remain the same and the chemical properties remain the same. A chemical change is different as it affects the chemical properties of the substance.
True or false? ‘Physical changes are relatively easy to reverse’
TRUE. Relatively easy to reverse since no new product is formed during the changes of state.
Describe what happens, in terms of particles, when a solid is heated and melts into a liquid
When heated, particles absorb thermal energy and convert it into kinetic energy. The particles in the solid vibrate more, causing the solid to expand until the structure breaks and the solid turns into a liquid.
Describe what happens, in terms of particles, when a liquid is heated and evaporates into a gas
When heated, the particles in a liquid expand. Some particles on the surface gain sufficient energy to overcome the intermolecular forces and evaporate. At the boiling point, all of the liquid particles gain enough energy to evaporate.
Substance A melts at -200oC and boils at -183oC. What state is A at -174oC?
Gas
Substance B melts at -5oC and boils at 23oC. What state is A at -7oC?
Solid
Why do solids, liquids and gases expand when heated?
When a substance is heated the molecules vibrate faster. This causes the space between the atoms to increase.
What is an advantage of the current particle model?
It provides a simple understandable model to explain the three states of matter.
‘Particles in the particle model are represented by _’ Fill in the gaps (Higher only)
Inelastic spheres
What are the limitations of the particle model? (Higher only)
Doesn’t take into account forces of attraction between particles. The amount of energy required to cause a change of state depends on these forces. Doesn’t take into account the size of particles and space between them. The nature of particles depends on the structure and bonding of a substance.
Liquid A has a higher boiling point than liquid B. What does this tell you about the forces between the particles in liquid A? (Higher only)
Liquid A has greater forces of attraction between the particles.
What is meant by the terms element and compound?
Elements are substances made up of only one type of atom. Compounds are made up of atoms of different elements.
What are the three subatomic particles in an atom?
Protons, Neutrons, Electrons
Who described atoms as ‘solid spheres’?
John Dalton
What was Dalton’s theory?
Atoms cannot be created, divided or destroyed. Atoms of the same element are exactly the same and atoms of different elements are different. Atoms join with other atoms to make new substances.
What discovery caused the Dalton model of an atom to change?
The discovery of subatomic particles
How did JJ Thomson discover the electron?
Thomson conducted an experiment using a cathode ray tube. The beam moved towards the positively charged plate so he knew the particles must have a negative charge.
Describe the atomic model proposed by JJ Thomson
The plum pudding model: Negative electrons scattered through a positively charged material.
Who designed and carried out the gold foil experiment?
Ernest Rutherford designed the experiment. Geiger and Marsden carried out the experiment.
What did Rutherford discover from his gold foil experiment?
He shot a beam of positively charged particles into a sheet of gold foil. Most particles passed straight through indicating that atoms were mostly empty space. A few particles were deflected and a few bounced directly back showing that there must be a positively charged nucleus.
Describe Rutherford’s model of the atom
Mass is concentrated in the central nucleus. Mostly empty space. Electrons travel in random paths around the nucleus.
What change did Niels Bohr propose to the nuclear model of an atom?
Electron shells around the nucleus.
Describe the structure of an atom
- A small central nucleus made up of protons and neutrons (positively charged). - Electrons orbit (move around) the nucleus in shells (negatively charged).
Where is the mass of the atom concentrated?
In the nucleus
Compare the sizes of the nuclear radius and the atomic radius
The nuclear radius is much smaller than the atomic radius.
Compare the typical size of atoms and small molecules
Atoms and small molecules are both incredibly small. Small molecules are larger than atoms because they are made of atoms. The typical atomic radii and bond length are in the order of $10^{-10}\text{m}$.
What are the relative masses of a proton, neutron and electron?
Proton: 1, Neutron: 1, Electron: 1/1836
What are the relative charges of a proton, neutron and electron?
Proton: +1, Neutron: 0, Electron: -1
What is an ion?
An atom or molecule with a positive or negative charge.
How is an ion formed?
When an atom or molecule gains or loses electron(s). Positive ions are formed when an electron is lost. Negative ions are formed when an electron is gained.
What does the atomic number tell you about an element?
The atomic number is unique to each element and tells you the number of protons an element has.
What is the mass number?
The combined total of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom of an element.
What are isotopes?
Atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
How does the atomic number and mass number differ between isotopes of the same element?
Atomic number is the same as an element always has the same number of protons. Mass number is different as there are different numbers of neutrons.
Why do atoms contain equal numbers of protons and electrons?
Atoms have a stable overall charge of 0. Protons are positively charged and electrons are negatively charged so they must be present in equal numbers for charges to balance.
How can you calculate the number of neutrons, given the mass number and atomic number of an element?
Number of neutrons = mass number - atomic number
Boron has the atomic number 5 and mass number 11. How many protons, electrons and neutrons does boron have?
5 protons, 5 electrons, 6 neutrons
Sodium has the atomic number 11 and mass number 23. How many protons, electrons and neutrons does the $\text{Na}^{+}$ ion have?
11 protons, 10 electrons (one has been lost to form the positive ion), 12 neutr
What is the meaning of relative atomic mass?
The average mass of an atom of an element compared to 1/12th the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
What is the meaning of relative formula mass?
The weighted mean average masses of the formula units compared to 1/12th the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
What is the meaning of relative molecular mass?
The mean average mass of one molecule of an element or compound compared to 1/12th the mass of one atom of carbon-12.
How is relative formula mass calculated?
Add together the relative atomic masses of each of the elements in the chemical formula.
What is the relative formula mass of Ca(OH)2?
Calcium relative atomic mass = 40. Oxygen relative atomic mass = 16. Hydrogen relative atomic mass = 1. So formula mass = 40 + 2(16+1) = 74
What is the empirical formula?
The smallest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound.
What is the molecular formula?
The formula that shows the actual number of atoms of each element in the compound.
Write the empirical formulae of CH4 and C4H10?
CH4 → CH4. CH4 is already in the smallest possible ratio. C4H10→ C2H5
What is the molecular and empirical formulae of the compound below?
Molecular formula: C2H4Br2. Empirical formula: CH2Br
What is an alloy?
A mixture of two or more metals.
What are metals and where are they found in the periodic table?
Metals are elements which react to form positive ions. They are found on the left side of the periodic table.
What are non-metals and where are they found in the periodic table?
Non-metals are elements which react to form negative ions. They are found towards the top right of the periodic table.
What are the general properties of metals?
Shiny, Good conductors, Dense, Malleable and ductile, High melting and boiling points
What are the general properties of non-metals?
Dull appearance, Poor conductors, Lower density than metals, Low melting and boiling points, Brittle
How are positive and negative ions formed?
Positive ions are formed when a metal loses an electron. Negative ions are formed when a non-metal gains an electron.
What is the chemical equation for the reaction between magnesium and oxygen?
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO. Mg forms the ion Mg2+ and oxygen forms the ion O2-.
How are elements arranged in the periodic table?
Elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number so that elements in the same group (column) have similar properties.
Why do elements in the same column have similar properties?
They have the same number of outer shell electrons. This determines how they react.
What does the period (row) number tell you about all the elements in that row?
They all have the same number of shells of electrons. e.g. all elements in period 4 have 4 electron shells.
What does group (column) number tell you about all the elements in that group?
They all have the same number of outer electrons. e.g. all elements in group 2 have 2 electrons in their outer shell
Describe the difference between a covalent and ionic bond
A covalent bond forms when two non-metals share a pair of electrons. An ionic bond forms between a positive metal ion and negative non-metal ion. Covalent bonds only occur between non-metals and they do not involve any charged particles while ionic bonds include both metal and non-metal ions.
Describe the bonding in an ionic compound
Ionic bonds form between positive metal ions and negative non-metal ions. Ionic compounds are held together by the electrostatic attraction between these oppositely charged ions.
Why do ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points?
The strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions require a lot of energy to overcome.
When do ionic compounds conduct electricity? Why?
Ionic compounds conduct electricity when molten or aqueous because the ions are free to move to carry charge. When solid, the ions are fixed in the ionic lattice so don't conduct electricity.
Describe the bonding in simple molecules
Covalent bonds, formed when two non-metals share a pair of electrons.
Why do simple molecules have low boiling points despite containing strong covalent bonds?
To change state, simple molecules need to overcome the intermolecular forces, not the covalent bonds. Simple molecules are held together by weak intermolecular forces which require little energy to overcome.
Why are simple molecules unable to conduct electricity?
They have no overall charge.
How and why do boiling points of simple molecules change as the size of the molecules increases?
As the size of the molecule increases, the strength of the intermolecular forces also increases. Larger simple molecules have higher boiling points as more energy is required to overcome the intermolecular forces.
Describe the bonding in giant covalent structures
Many strong covalent bonds (shared pair of electrons).
Why do giant covalent structures have very high melting points?
All of the atoms in the structure are covalently bonded to other atoms. These strong covalent bonds must be broken to melt the substance which requires a lot of energy meaning the melting point is very high.
What type of bonds are found in polymers?
Covalent bonds
Why are polymers solids at room temperature?
Polymers are simple molecules so their melting point depends on the strength of the intermolecular forces. As the molecules are very large, the intermolecular forces are strong so require a lot of energy to overcome in order to melt the polymer.
Describe the structure and bonding in metals
Metallic bonding. Giant structure with positive metal ions held in a sea of delocalised electrons.
Why are metals able to conduct electricity?
The delocalised electrons are free to move throughout the structure so can carry charge through the metal.
Why are metals typically very malleable?
The atoms in metals are arranged in uniform rows that can easily slide over one another. This allows metals to be bent and shaped.
Why do metals have relatively high melting points?
They have very strong metallic bonding. A lot of energy is required to overcome the electrostatic attraction between the positive ions and negative electrons.
Draw a dot and cross diagram for methane, CH4
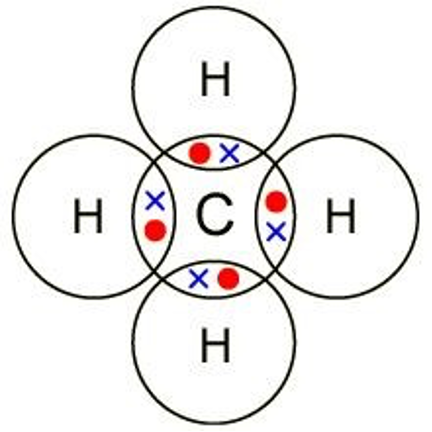
Draw a dot and cross diagram for NaCl
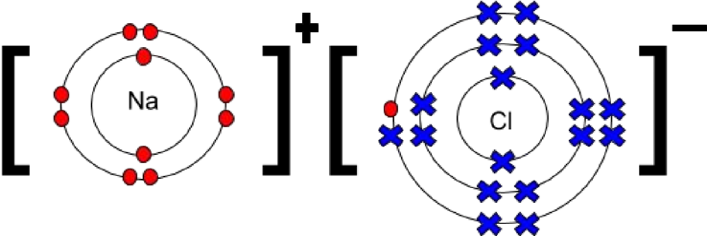
What is a limitation of dot and cross diagrams?
Don’t show the 3D arrangement of molecules.
What is a benefit of using ball and stick models to represent molecules? In what way are they limited?
They show the 3D shape and how atoms are bonded. - They don’t model electrons.
What is the highest electron configuration when looking at the first three shells?
2, 8, 8
What is the most desirable electron configuration?
All atoms want to have a full outer shell so this would be 8 electrons in the outer shell (or 2 if the atom only has one shell).
Why are the noble gases (group 0) very unreactive?
They have very stable electron configurations due to their full outer shell of electrons. This means they don’t want to lose or gain electrons so are unreactive.
Why might an element with the electron arrangement of 2, 8, 1 be very reactive?
It’s very reactive because it can lose an electron (becoming a positive ion) to obtain the stable configuration 2,8.
How did Mendeleev order his early periodic table?
In order of increasing atomic mass. In some places, the order was changed slightly so that elements of similar properties would be grouped in the same column.
Why did Mendeleev leave gaps in his periodic table?
For undiscovered elements. He used elements around these gaps to predict properties of the missing elements.
Some elements in Mendeleev’s table did not fit with the expected properties. How has this been modified in the modern periodic table?
The elements are now ordered by increasing atomic number rather than increasing atomic mass.
How many covalent bonds can carbon form?
Four
Describe the structure of graphite
Each carbon atom bonded to 3 other carbon atoms. Layers of hexagonal rings of carbon atoms. One delocalised electron per carbon atom.
Describe the properties of graphite
Soft/ slippery because the weak intermolecular forces between layers allow the layers to slide over one another. Electrical conductor because it contains delocalised electrons which are free to carry charge.
Describe the structure of diamond
Each carbon atom is covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms. No charged particles.
Describe the properties of diamond
Very hard and very high melting point due to strong covalent bonds. Doesn’t conduct electricity because there are no charged particles.
What is a fullerene?
A molecule made up of carbon atoms, shaped like a closed tube or hollow ball.
Name two fullerenes
Graphene, C60 (buckminsterfullerene)