Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
History
Originally called Dementia Praecox which into concepts of “madness” and cognitive decline into one disorder
“Split mind”- destruction of forces connecting one function to another
Normal connections most people experience don’t occur here, split between thought and emotion
Delusions
Bizarre and strongly held beliefs despite significant evidence to contrary
Delusions of Grandeur
e.g., I am god, I am god’s representative on Earth, belief you are Satan or Satan’s minion, usually exclusively a view about self
Delusions of Persecution
Forces are conspiring to cause you or your loved ones harm (e.g., supernatural forces, government branches)
Delusions of Reference
Belief that coincidences aren’t just coincidences, have to determine the message
Cap Gras
People in your life have been replaced by someone else
Hallucinations
Bizarre sensory perceptions that do not exist in reality
Other people don’t have access to your sensory experiences
Can involve any of the 5 senses
Auditory most common than visual
Disorganized speech
Problems with verbal communication, cognition doesn’t match speech
Tangentality
Talking about something and then transition to something else, somehow connect back to original point
Loose Associations
Neologisms, “clanging”, get stuck on meaningless aspects of conversation
Grossly Disorganized or Catatonic Behavior
Agitation or immobility
Catatonia
Waxy flexibility, inability to move body parts
Inappropriate affect
Abnormal ways of locomoting/gross motor movements
Echoproxia
Copy what others are doing
Negative symptoms
Abscense or insufficiency of normal behavior
Negative symptoms: Flat Affect
Not expressing emotion at all, can’t gage how person feels
Negative symptoms: Avolition
No desire to do anything
Negative symptoms: Alogia
Poverty of speech content or speech production, person can talk, but doesn’t say anything
Negative symptoms: Anhedonia
Lack of interest in things one used to find enjoyable, no pleasure found in anything
Schizophrenia Criterion
2 of the symptoms for at least 1 month
Schizophrenia Course
Total course must be 6 months with active phase lasting at least 1 month
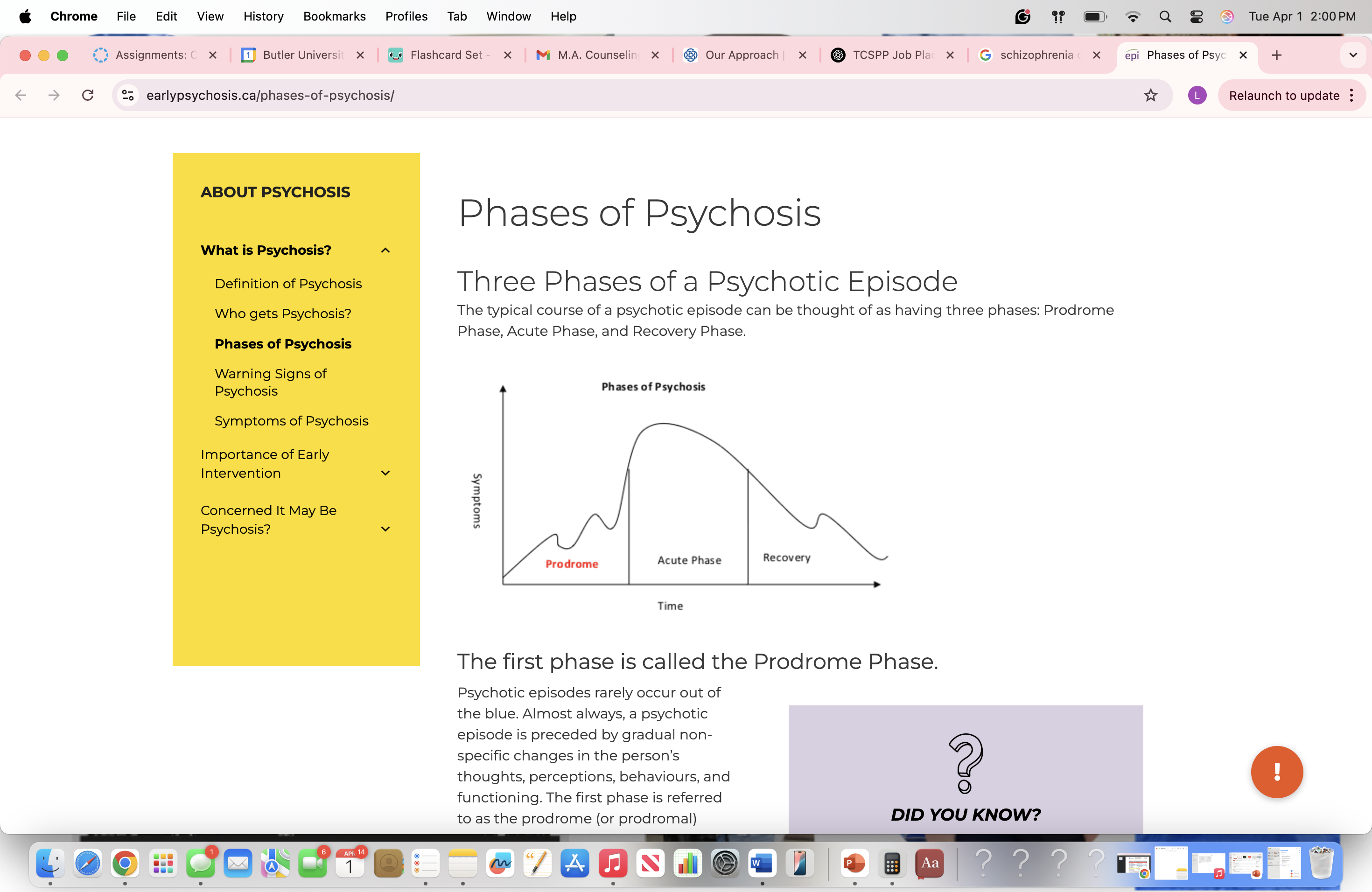
Who gets schizophrenia?
Mean age at onset: 25, large range around the mean
Gender differences: men onset slightly earlier, after not many differences
Lifetime prevalence: 1%
Somewhat higher incidence in African Americans
Generally episodic course
Genetics
Need biological component to create disorder
Monozygotic twins 60% in common, 15% dyzgotic twins
Dopamine Hypothesis
Proliferation of D2 receptors (in striatum), excessive amount of D2 receptors, excessive amount of dopamine
Underactivity in D1 receptors (in prefrontal cortex)
Glutamate hypothesis
Possibly NMDA receptor deficiency
Serotonin
Probably involved, but not clear how
Ventricular enlargement
More severe cases have larger ventricles, also correlated with how long disorder has been occurring, causes other brain parts to shrink
Ventricular size in childhood doesn’t seem to predict size in adulthood
Hypofrontality
Decreased activity in broca’s area as active as if they were speaking, seen under fmri
Possible consequence in D1 underactivity
Brain registers auditory hallucinations as if you were speaking
Misorganized cells in schizophrenia
Perinatal Development
More people with schizophrenia born in February
Being stressed compromises immune response, which would impact third trimester as it occurs in November/December, height of cold/flu season
Hypoxia
Potential risk if baby suffers around time of birth (cord wrapped around baby’s neck)
Biological Markers
Seem to be associated with increased risk of schizophrenia
These are factors that don’t directly cause schizophrenia, but seem to be related to genes that predict schizophrenia
Olfactory bulb: decreased sense of smell
Smooth-pursuit eye movement: decreased ability to track smooth moving object
Neuroleptics (First-generation antipsychotics)
Blocks dopamine receptors
60-75% of people have a reduction in symptoms, but people don’t like taking them
Side effects: anticholingeric effects, extrapyamidal effects, tardive kinesia
Very high rate of non-complicance, highest: 75%
Atypical Antipsychotics (Second Gen.)
Specifically blocks D2 receptors, also blocks 5-HT2 receptors
Much more tolerable side effect profile
Problem: Agranulocytosis (Clorezil only): patients had a harder time fighting illness, because broke down immune cells
Side effect: drastic weight gain
Muscarinic agonists (Cobenfy)
Facilitate Ach Muscarinic M4 and M1 receptors
Which then modulates D2 and NMDA
Side effect of manipulating muscarinic: uncontrollable vomiting
Modulated here to reduce nausea
Very new drug, unsure how effective it will be
Helps improve positive and negative symptoms, more tolerable side effect profile
Psychosurgery
Not used anymore, didn’t effect symptoms, made symptoms easier to manage
Schizophrenogenic family (mother)
Cold, dominant, rejecting mother
Double-bind communication (kid can never come out ahead)
Verbal behavior doesn’t match nonverbal behavior
No empirical support
Led to development of family therapy
Expressed emotion
Criticism, hostility, and emotional overinvolvement
Relapse: expressed emotion at home increases relapse rates
City life
More people live in city than suburbs, social drift hypothesis
Cognitive-Behavior Therapy
Adjunctive treatment only (need to occur with medication)
Can’t process reality without medication
Thought influences emotion and behavior
Interpretations of experience paramount
Beliefs are possibilities, not facts
Delusions are VERY strongly held beliefs
Medications marks delusions and hallucination less viable, CBT helps manage
Strategies
Normalizing, generating alternatives, behavioral experiments
Explain as many exaggerated version of normal experience
Develop as many possible plausible alternative as possible
Behavioral experiments have to be extremely collaborative, people respond generally well
Brief Psychotic Disorder
At least 1 schizophrenia symptom for at least 1 day, but no more than a month
Must be one of the positive symptoms, return to normal functioning after
Schizophreniform Disorder
Two schizophrenia symptoms for at least 1 month, but less than 6 months
Duration is too short
Delusional Disorder
Delusions are present at least a month, but delusions aren’t bizarre, plausible
Delusional Disorder: Erotomanic type
Believing someone of a higher status is in love with you
Delusional Disorder: Grandiose type
Believe you have a greater status, power, wealth than you actually do
Delusional Disorder: Jealous Type
Believe partner is being unfaithful
Delusional Disorder: Persecutory type
Persecution is reasonably plausible
Delusional Disorder: Somatic type
Some sort of physical defect or medical condition that isn’t true
Shared Psychotic Disorder
Being near someone suffering from disorder causes you to begin to buy into others delusions
Schizoaffective disorder
Schizophrenia symptoms than appearance of depressive symptoms