Neu 330 Mod 3: ON/OFF pathways, receptive fields, and colors
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
convergence and ganglion cells
each ganglion surveys different amount of photoreceptors
different amount of input
size determines amount of photoreceptors they receive
Which has larger receptive fields: rods and cones?
rods
a lot of convergence onto ganglion cells
if we increase # of photoreceptors
need larger receptive field
lower usual resolution
Scotopic, mesotopic, photopic range graph
Rods
more sensitive to light
more rods
low resolution
peripheral
cones
high resolution, center
WIDER RANGE of activity
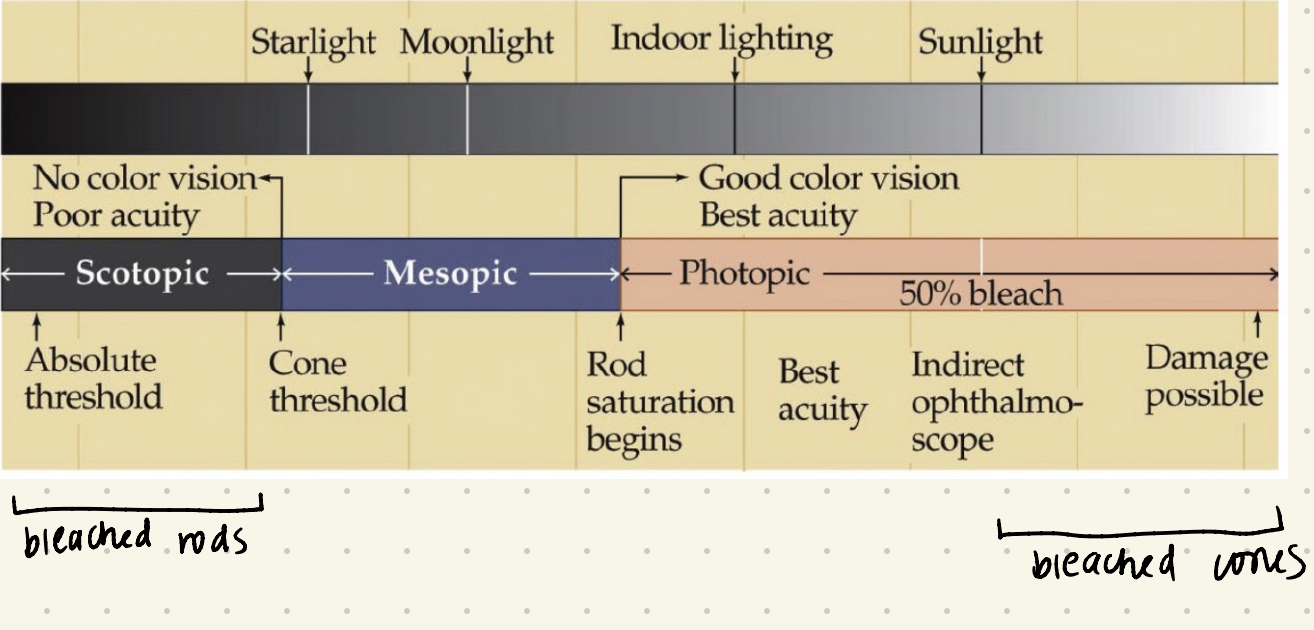
bleaching properties
opsins stop working circumstantially
dark → sunny
bleach cones
sunny —> dark
bleach rods
horizontal cell function (center-surround)
allows bipolar cell to be stimulated by surround photoreceptors
horizontal cells release
GABA
in dark are horizontal cells depolarized or hyperpolarized
depolarized
AMPA receptors are going to be deactivated and let in sodium
depolarized HC
increase GABA → decrease glutamate
How do horizontal cells inhibit photoreceptors (on cells)
in darkness, glutamate released and triggers horizontal cell action
in darkness, hc release GABA to surround
lateral inhibition
on bipolar respond to light in center
in light, photoreceptor hyperpolarizes
on-bipolar → depolarize
on ganglion → depolarize
in darkness what do h-cells do
make GABA
in darkness, what will h-cells do to on pathway of cells in surround
GABA inhibits glutamate release
depolarize
M Cells vs p cells
m cells larger
m cells
transient increase in AP but rapid decrease
p cells
transient increase but prolonged
input and information for m cells vs. p cells
M Cells
rods
movement
depth
subtle light diff
p cells
Cones
color
fine details
L cones encode
red
M cones encode
green
S cones encode
blue
+L-M
activated/excited by red L cones, inhibited by green M cones