ecawns market failure 2
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
+ve ext
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
diagram for +ve ext
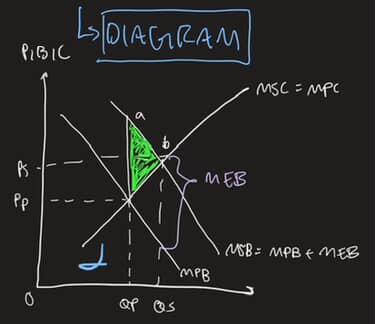
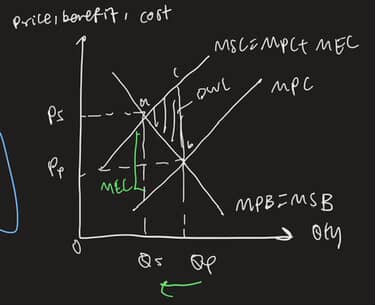
diagram for -ve ext
def for +ve ext
spillover benefits to third parties → not directly involved in con/prod of g/s itself
—> may be generated by prod/con in market
—> not internalise by c/p
MSB
MPB + MEB
underallocation
MSB > MPB
GOVT INT (3)
subsidies
rules and regulatios
direct and joint provision
govt int - subsidies - def
-on activities generating ext benefit on 3rd parties
-prod/con internalise +ve ext
govt provide subsidy to prod, decrease price to con
govt directly give con (CDC voucher)
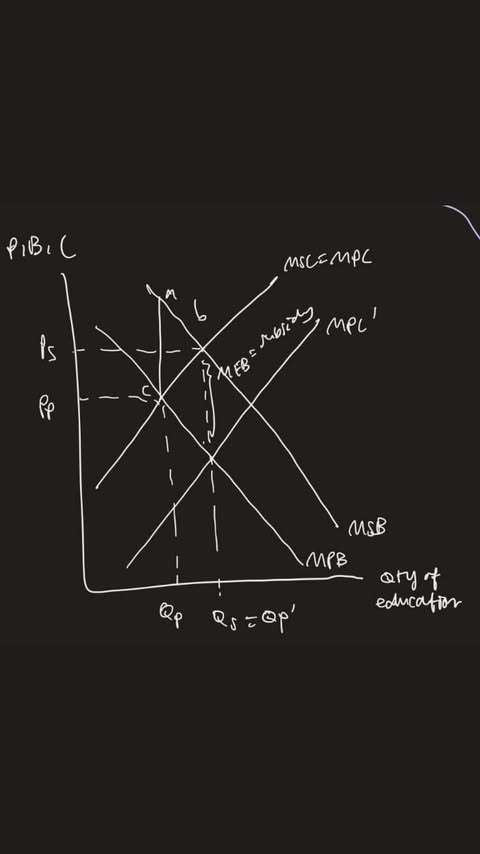
govt int - subsidies- mechanism
granting subsidy = MEB at QS
decrease MPC
force con/prod to internalise MEB to third parties
decrease shift of MPC curve → mpc to mpc’
outcome:
new priv optimal qty Qp’ (MPB=MPC’)
coincide with QS (MSB=MSC)increase in con/prod, Qp to Qp’)
cause DWL to be eliminated
allocative eff
social welfare maximised
conc:
-subsidies incentivise prod and con
—> increase
—> internalise +ve ext in decision making
(prod: subsidise R&D)
govt considerations - limitations - subsidy (3)
info gap
—> hard to attach monetary value to ext benefits (over/under est)
uncertainty and time lag
increase expenditure by govt, unsustainable in long term
govt considerations - unintended conseq - subsidy (2)
productive inefficiency in firms
(less incentive to stay efficient in long run, prod at lowest cost possible)
inequity
increase producers profits due to lower unit cop
increase unequal income distribution between con and prod
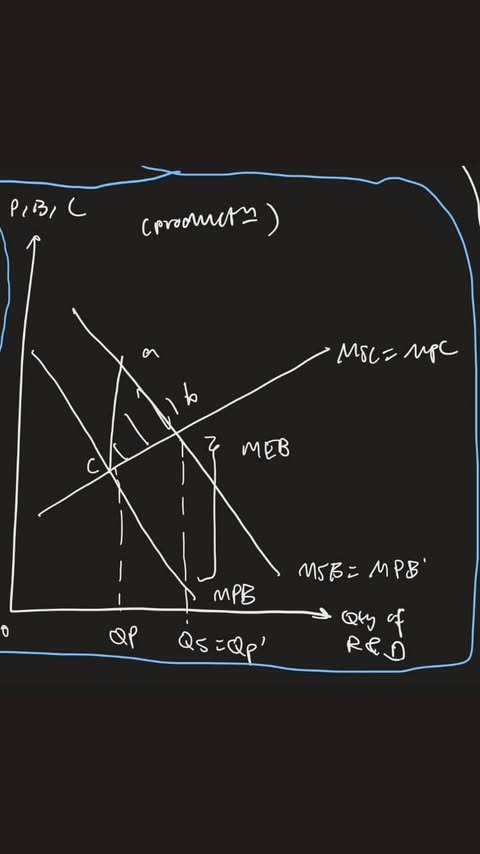
govt int - rules and reg (legislation)
enhance priv benefits of prod/cons
(eg: enforcement of patents (copyright) —> yay innovation thru r&d, no risk of imitation)
firms ++ priv benefits from innovation
upward shift of MPB curve (MPB to MPB’)
MEB eliminated (other firms x benefit)
MPB’=MSB
outcome:
new priv optimal qty (MPB’=MPC) QP coincide with QS (MSB=MSC)
allocative efficient, social wf maximised, X market failure
govt consid - rules and reg (legislation) - limitations (2)
info gap
—> in patent protection:
regulations too tight — discourage companies to innovate, consumers no access to btr quality
overly long — abuse market dominance, exploit consumere
high admin cost
govt consid - rules and reg (legislation) - intended conseq
law compel prod/con take actions
certain faster outcomes
direct and joint provision (def)
govt increase avail of goods that generate +ve ext in market —> be closer to social optimal lvl
direct provision
govt provide g/s —> producing + outsourcing production frm priv firm
outsourcing: govt pay for prod at lower cost
OBJ: maximise social welfare
joint provision
govt and profix maxx priv firms both provide g/s in market OR
involved in diff parts of the production of g/s
govt consid direct + joint - unint conseq (3)
improve affordability of essential good
—> govt provide necessities, reduce inequity
→ if left to priv firms, increase price charged, make lower ses left out
productive ineff by govt
—> absence of profit motive, lack of incentivee to keep cost low
—> complacency
—> govt x incentive to improve on its production and quality
productive and or dynamic inefficiency
—> lack of competition
—> complacent after winning contract, exclusive rights to prod g/s for specified time frame
—> increase cost than necessary incurred
—> lower in quality, lower consumer welfare
productive efficiency
g&s prod at lowest possible avg COP based on current tech
dynamic efficiency
improvement in quality/range
improvement production process, decrease COP over time due to innovation and investment in new technologies.
govt consid - direct joint - limitations (2)
info gap
political pressures
govt consid - direct joint prov - intended conseq
more certain outcomes
faster outcomea
govt consid - joint - +ve conseq
help boost production + meet higher demand
public-priv partnerships tap on expertise and experience of priv firms —> greater innovation in public sector