MES Quiz 3 Study Set
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
year names
______ _____ were a system of dating used by kings of Akkad
each year was named after major events during a king’s reign
military campaigns
construction projects
administrative appointments
appear at the end of documents to provide a calendrical system
summerian
_______ king list
gave an idea of the family history of a king and how long they ruled for
in Uruk, Lugalzagesi became king; he ruled for 25 years
Nippur
house of the god Enlil and the seat of kingship
Enlil
deity _____ confers kingship upon human kings at Nippur
_____ sanctions the events of the kingdom
mostly the king does something and then tells everyone the event was sanctioned by ____
E-kur
___- ___ was the name of the temple for Enlil
Sargon
_____ conquers Uruk and kills Lugalzagesi before Enlil in Nippur
becomes the new “king of the land of Akkad and Sumer”"
needed to kill Lugalzagesi to get legitimacy
rules for 56 years
monuments
_____ are in good shape because
the French dug them from Susa in Iran where they were relocated after Akkad was looted
kingship
Sargon was very important to the legendary image of an ideal ______ in Mesopotamia
had many fictitious legends written about him
said to have conquered the “upper and lower sea”, “totality of the lands under the heavens”, “from sunrise to sunset”
legend, 1500
the _____ of Sargon was written ____ years after his rule
he was elevated to a hero
supposedly was the illegitimate son of a priestess and then basically copied the story of Moses
empire
what makes Sargon’s state an _____?
standing army!!
rare!
used to conquer cities and force compliance
created vassal states
owe loyalty oath and give annual taxes
get protection from the king
supra-regional control
political propaganda
56
Sargon reined ___ years! Long time in antiquity!
army
Sargon kept a standing ____ and supposedly fed them himself
5,400 men!
Naram-Sin
Sargon’s grandson
people later on blamed him for the Akkad collapse, but it was actually his son who was the last ruler of Akkad
bragged about subjugating people never before conquered
implemented the idea of governors who rule over the vassal states
individuals
legacy of the Akkad EMPIRE
_____ could now shape their role in society
kings had absolute power and wanted peoples’ loyalty only to them
later generations villainized Naram-Sin b/c they didn’t like that he was so powerful
ancient near east
ANE stands for _____ ____ _____
martu, amurru
terms for the Amorites
____ - sumerian term meaning “west” or “westerners”
______ - Akkadian equivalent to the sumerian term
ur III
Amorite language was mentioned in the ___ ____ period
old babylonian, 2000
the ____ ______ (OB) period (after _____ BC) included Amorite clues in
personal names
tribal names
Genealogies of Hammurabi, shamshi-adad, etc
“Amorite” things: sheep, donkeys, wool, daggers, textiles, silver, and figs
phrasebook translating OB into Amorite
God Martu (“the Amorite”) created
Amurru
the name of a Late Bronze Age state in the northern Levant (Amarna Letters)
from 1400 BC
first
by early _____ millennium BC, legacy of Amurru includes:
as ancestor of legendary past, Neo-Assyrian and biblical texts
as toponym in N. Levant
zone of uncertainty, 2200
the ____ _ _________ (3000 - _____)
agricultural exploitation of marginal zones of >200mm annual rainfall
grazing lands (sheep/goats) and hunting/capture of migratory animals (onagers, gazelle)
agropastoral
the growth of ________ communities
engaged in pastoralism, agriculture, and hunting
more than 300,000 people settled at sites of 5-60 hectares
settlement pattern peaked 2500-2200 BC
ends DRAMATICALLY, 2200BC
planned
emergence of large, _____ communities like Al Rawda
most towns were round in the zone of uncertainty
wool
all the towns in the zone of uncertainty had a shared environmental and economic niche
____ production
emergence of guild-like communities
all engaged in procuring ___ and weaving it into textiles
great revolt, Naram-Sin
the _____ _____ happened in 2213 to the “King of the Four Quarters of the Earth” aka _____-___
people were getting tired of living under the same ruler
most of the constituents started a rebellion
_____-___ put down the rebellion
stele, deity
____ of Naram-Sin is the monument that accounts for the Great Rebellion
says that Naram-Sin is now a _____
he is wearing horns which makes him a god
legend
the ____ of Naram-Sin
he crossed the Euphrates River and reaches Bashar (the AMORITE mountain)
the goddess Ishtar helps Naram-Sin
PROVES that the bend in the Euphrates is where the Amorites live
2200, 1900, 4.2 KBP
Climate change happens _____, ____ BC / _._ ____ event
major aridification event starts
gradual onset
catastrophic to Zone of Uncertainty
migration
the climate change event in 2200 BC affects the people living in the Zone of Uncertainty
forced ______
settlement decline in Zone of Uncertainty
creates population pressures in other areas
people moved to more humid areas
>300,000 refugees from Upper Mesopotamia
Settlement expansion
South Mesopotamia
North Levant
lasts until 1900 BC!!
affects Amorite and other communities
southern
resettlement in ______ Mesopotamia after the climate change events in 2200-1900 BC
hypertrophic growth due to Amorite, Gutain, and relocations of foreign populations
Amorite neighborhood names appear!
Sippar-Amnanum
Sippar-Yahrurum
no
did the climate change event bring down the Akkadian Empire?
yes
did the climate change event affect communities in marginal zones?
wetter
long term effects of climate change resettlement
increased settlement in _____ areas: river valleys, further west, further north
significant impact on social interactions and cultural trajectories
Akkad
the decline of _____
the Sumerian king list said “who was king, who was not king”
then Uruk kings were overtaken by the Gutains
Gudea of Lagash
______ ___ _______ (2150-2100 BC) (king during the Gutain interlude)
votive stele of ______ __ ______ in temple of Ningirsu
he wants to be powerful so he emulates powerful kings of the past
just copied monuments and pictures of rulers from the past
good transitional leader when the Amorites come in
Ur-Nammu
from Akkad to Ur the timeline of kings:
Stele of Naram-Sin → Votive stele of Gudea → stele of -____ (Ur III Period)
language
legacy of Akkad:
Akkadian becomes main _____
sumerian literary/specialist
model for royal inscription genre
model of Mesopotamian kingship, empires, divination of rulers
ur III state
the __ __ _____ (2113 - 2006 BC)
sat on the Persian gulf
Ur-Nammu founded it
not a long-lived dynasty
ur-nammu
founder of the Ur III Dynasty
ur III
if you find an ancient tablet, most likely it’s from the __ ___ period
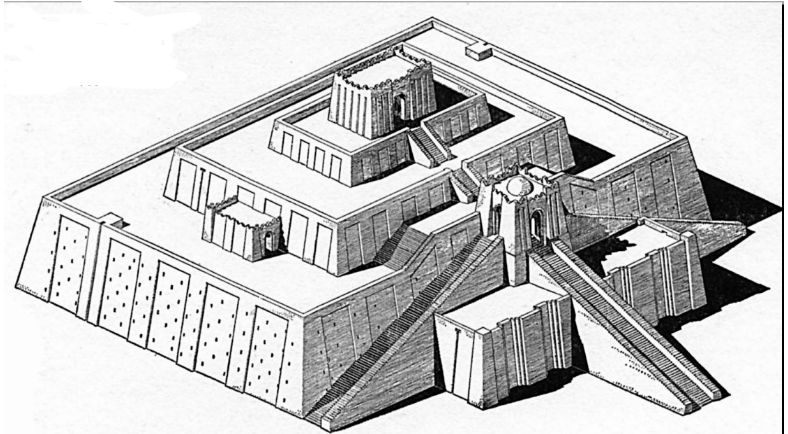
ziggurat, ur-nammu
this is the ______ of ________
legal
the Ur III Period created the basis for Sumerian ____ traditions
drew upon tradition of Sumerian laws
became the basis for later legal traditions (Hammurabi)
Laws
____ of Ur-Nammu
similar to later Code of Hammurabi
Ex) if a man commits a homicide, they shall kill that man
Ex) River Ordeal (leave it up to the gods)
most of the laws abided by local procedures
if a Gutain committed the crime, the Gutains would deal with it
but, if people didn’t work it out, they had something to fear and a rulebook to follow
Amorite
persistent _______ migration in the Ur III Period
2028 BC - Sulgi raids ______ and builds “The Wall of the Land
2034 BC - Su-Sin builds wall “That which Keeps Tidnum at a distance)
an _____ tribe
Ibbi-Sin, last king of Ur wrote a letter about the problem of _______ security threat
tribal
_____ identities of Amorites trump their identity as Amorites
Naplanum, Larsa
______ was an Amorite civil servant that eventually became king of _____
marked as Martu with over 90 different texts about him
Founder of Amorite dynasty at _____
proved that foreign members of a community could rise in society and eventually end up in control after the city’s collapse
immigration
growth in settlements during Ur III Period largely due to ______
occupations
Amorite names seen in all _______ in Ur
mercenary/civil service (rank of “Chief of the Amorites)
later Old Babylonian settlements with Amorite names
hypertrophic
Amorites and other resettled communities contributed substantially to _______ growth in southern Mesopotamia during Ur III and shaped Babylonia’s cultural trajectory
names
before Akkadian empire, 2500-2250 BC
individuals with Amorite ______ in texts
Levantine Amorite kings ruling western lands
tribes
during Akkadian Empire (2250-2150 BC)
Amorite ______ resist Akkadian empire
language
during Ur III Dynasty (2100-2000 BC)
Amorite ______ legitimized
Amorite mercenaries and civil servants to state
dynasties
during Old Babylonian Period (2000 - 1600 BC)
Amorite _______ established across Mesopotamia and Levant
Amorite language in bilingual texts
Eric Hobsbawn
____ _______ created the idea of an “invented tradition”
invented tradition
________ ______ is a set of practices normally governed by overtly or tacitly accepted rules and of a ritual or symbolic nature, which seek to inculcate certain values and norms of behaviour by repetition, which automatically implies continuity with the past. In fact, where possible, they normally attempt to establish continuity with a suitable historic past
Sumerian king list
the _____ _____ _____ (SKL)
in Sumerian (NOT Old Babylonian!) 1800 BC
ends during reign of Damiq-ilishu
follows prototype from Ur III
was built off many other lists that already existed
everyone made their own list that ended at their dynasty
political charter, linear
the Sumerian King list was a ______ ______ that was meant to legitimize the Isin Dynasty
NOT a historical narrative of kings
manuscripts vary widely
provides _____ description to kingship, despite some contemporaneity
way to establish your dynasty as legitimate
laments
sumerian literary genres:
political charters
poetry
temple hymns
______
wisdom and proverbs
laws
akkadian
spread of ______ literature:
AFTER Sumerian (after 2000 BC)
illustrates the spread of cuneiform scribal training and influence of tradition
by 1600 BC, ______ is lingua franca for ANE
scribal
Old Babylonian literature and scribalism
people were speaking Akkadian, but copying down Sumerian texts
literature is preserved because of _____ training
eduba
____ (house of tablets) are scribal schools within OB elite households
canons
____ were fixed forms that formed gradually
a thing about a literature that does not change
curse of akkad, e-kur
the _____ __ _____
written in Sumerian
after fall of Akkad 2100-2000 BC
describes rise and fall of the city of Akkad
attempts to explain why the city collapsed
hubris of Naram-Sin!
blames the fall of Akkad on Naram-Sin’s destruction of ______ (house of Enlil in Nippur)
a cultural perception of events that came before
epics
Old Babylonian Literary Genres:
poetry
hymns
laments
wisdom and proverbs
lists/spelling lists/dictionaries
_____
marriage of martu
the _____ __ _____ (Sumerian)
a goddess wants to marry a “Martu” but people warn her that the Martu are basically barbarians, but she still wants to marry him
intermarriage was popular and this doesn’t prove that people thought the Amorites were barbaric
shepherd
the king as a ______ was a popular image
in Law of Hammurabi there’s a prologue and epilogue that says Hammurabi is a shepherd and also a noble king
a _____ is a person who takes care of a group of people
epic of gilgamesh
the ____ __ ______
first found in Nineveh in 1920 BC; 80 fragments found since
most popular mesopotamian story
in different languages and versions over 2500 years
there are two different versions:
OB version that shorter (1800-1600 BC)
Assyrian “standard” version that’s longer (800-700 BC);
includes flood story and was compiled by a priest Nineveh
opening lines
_____ _____ were usually the ancient name of an epic
surpassing all other kings
the Old Babylonian opening to the Epic of Gilgamesh