6.3 Manipulating Genomes
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
Somatic Gene Therapy
The insertion of a normally functioning gene into a patient to cure a genetic disorder
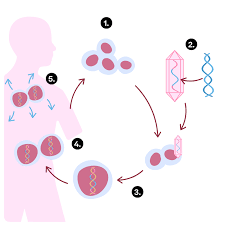
What happens in somatic gene therapy?
The DNA of somatic cells (body cells) are changed.
What is cystic fibrosis?
The genetic disorder where an individual produces too much mucus and it's hard to clear
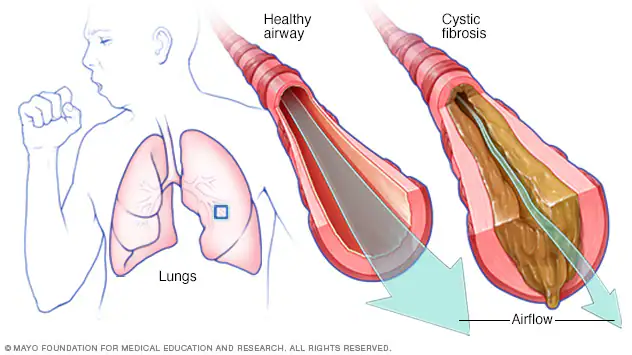
1) What is somatic gene therapy in cystic fibrosis?
A harmless virus is genetically modified to carry a normal copy of the CFTR gene.
2) Somatic gene therapy in cystic fibrosis
The virus is dripped into the lungs through a thin tube inserted into the nose.
3) Somatic gene therapy in cystic fibrosis
Once inside the lungs, the virus enters the lung cells and delivers the healthy CFTR gene into the lung cell’s nucleus, where it becomes part of the cell’s DNA.
4) Somatic gene therapy in cystic fibrosis
As the lung cells divide, they carry the normal gene, allowing them to produce functional CFTR protein, helping to relieve symptoms of cystic fibrosis.
Advantages of Somatic Gene Therapy
Targets specific tissues in need of treatment
Extends life span
Disadvantages of Somatic Gene Therapy
Cannot be passed to offspring
Gene is introduced to a body cell (but not a reproductive cell)
Only some cells get the functional gene
It is temporary and needs repeating
What are germline cells?
Cells that eventually become sperm or eggs
Germ Line Cell Gene Therapy
A faulty allele is replaced with a functional allele in germ line cells or a very early embryo.
The effects of this are permanent and can be inherited.
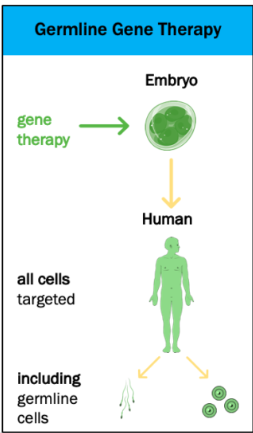
Advantages of Germ Line Cell Gene Therapy
Can be passed to offspring
Gene is introduced to zygote
All cells get functional allele
Permanent
Disadvantages of Germ Line Cell Gene Therapy
Cannot target a specific tissue
Ethical implications
How does inserting a new gene into a chromosome affect the functioning of other genes in that chromosome?
Frameshift
Altered triplets
Adjacent genes on the same chromosome switched on or off
Gene Manipulation examples:
Insect resistance in GM soya
GM pathogens for research
Pharming
Insect resistance in GM soya
Soya is genetically modified to produce Bt proteins.
Bt proteins are toxic to many pests and resistant to weed killer.
This means farmers don’t need to spray insecticides, and can spray weed killer to get rid of weeds and don’t kill the soya.
Advantages of Insect resistance in GM soya
- Widely used in organic farming where no chemicals sprayed onto plants
- Results in higher crop yield
- Less expensive
- Less labour
Disadvantages of Insect resistance in GM soya
Pollinators and predators may be damaged by the toxins from the Bt protein
Insects might become resistant to the toxic Bt protein
Genes might spread to wild populations, creating "superweeds"
Reduces biodiversity

Ethical concerns with Insect resistance in GM soya
Patenting issues
GM pathogens for research
Scientists can genetically modify pathogens to develop medical treatments
Advantages of GM pathogens for research
Used in medical and epidemiological research to find treatments
Disadvantages of GM pathogens for research
There are health and safety risks to the researcher and the wider public
Ethical concerns with GM pathogens for research
Used in biological warfare
State 1 valid concern people have about genetic modification
Increase in antibiotic resistance
Pharming
The genetic modification of animal, creating transgenic organisms
Example of Pharming
Some pigs have been genetically engineered to express a fatty acid for higher levels of omega 3

Advantages with Pharming
Animals with the desired gene can lead to:
- Decreased disease risk
- Faster growth rate
- Production of a human protein in milk that we can harvest
Disadvantages with Pharming
Unknown risks of genetic modification
Ethical concerns with Pharming
Ethically grey to put human genes into animals.
Creating transgenic animals that might cause the animal harm.
Welfare of the animal might be at risk.
Issues relating to patenting and technology transfer
e.g. Making genetically modified seeds available to poor farmers.
Patenting is where a company that creates a GM seed legally prevents others from using it without payment.
Advantages of patenting
Allows the company who created the GM seed to make profits on their design

Disadvantages of patenting
Patented seeds can only be used for the year, then new seeds have to be brought.

Ethical concerns with patenting
Poor farmers who actually need drought resistant crops cannot afford to buy the GM seeds.

Why are there few ethical concerns around genetically engineering bacteria?
Few animal rights issues to consider
Safety of genetic engineering in bacteria has been established
What is not a valid concern about genetic modification?
That the use of human embryos in stem cell production is unethical
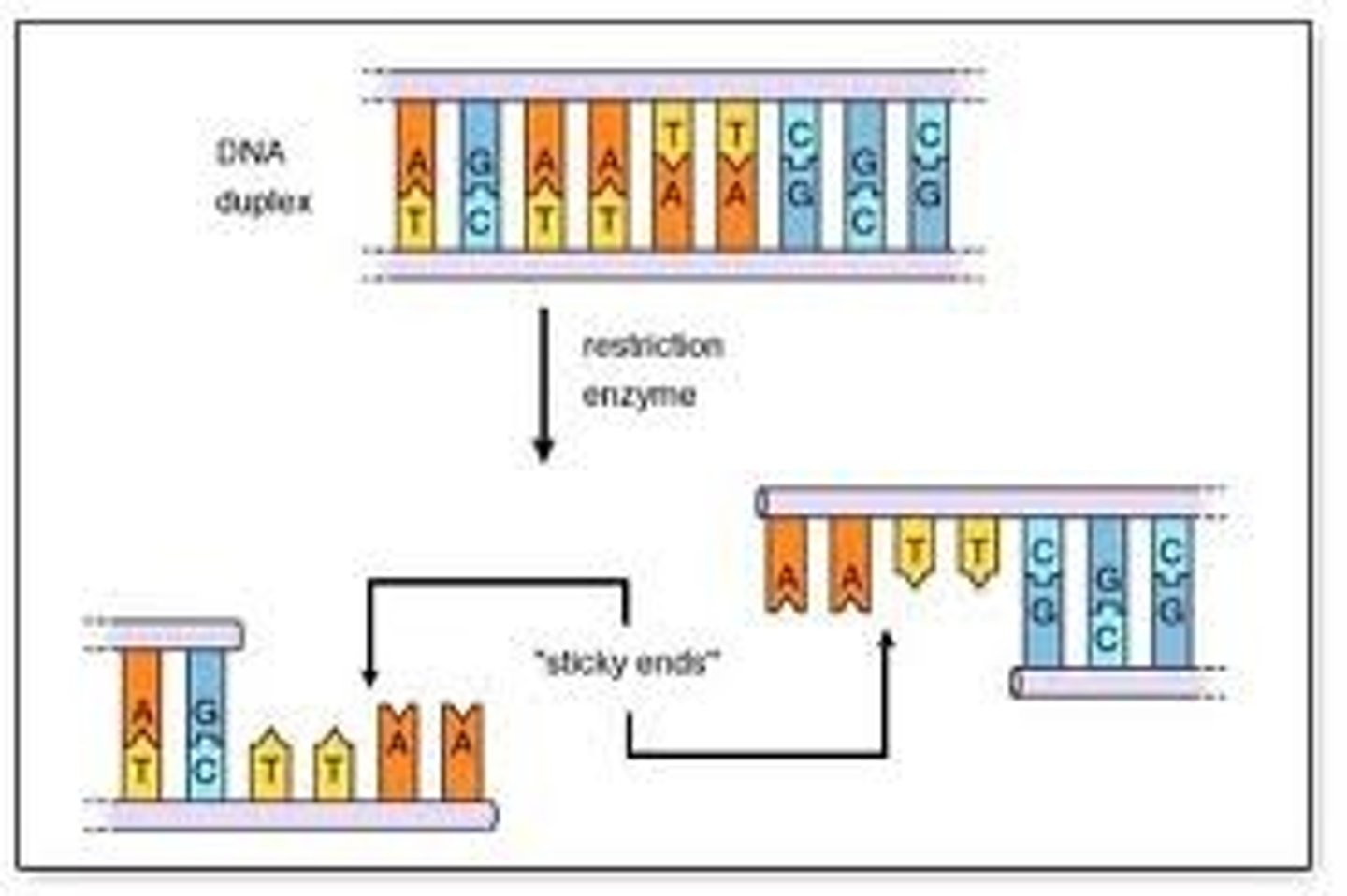
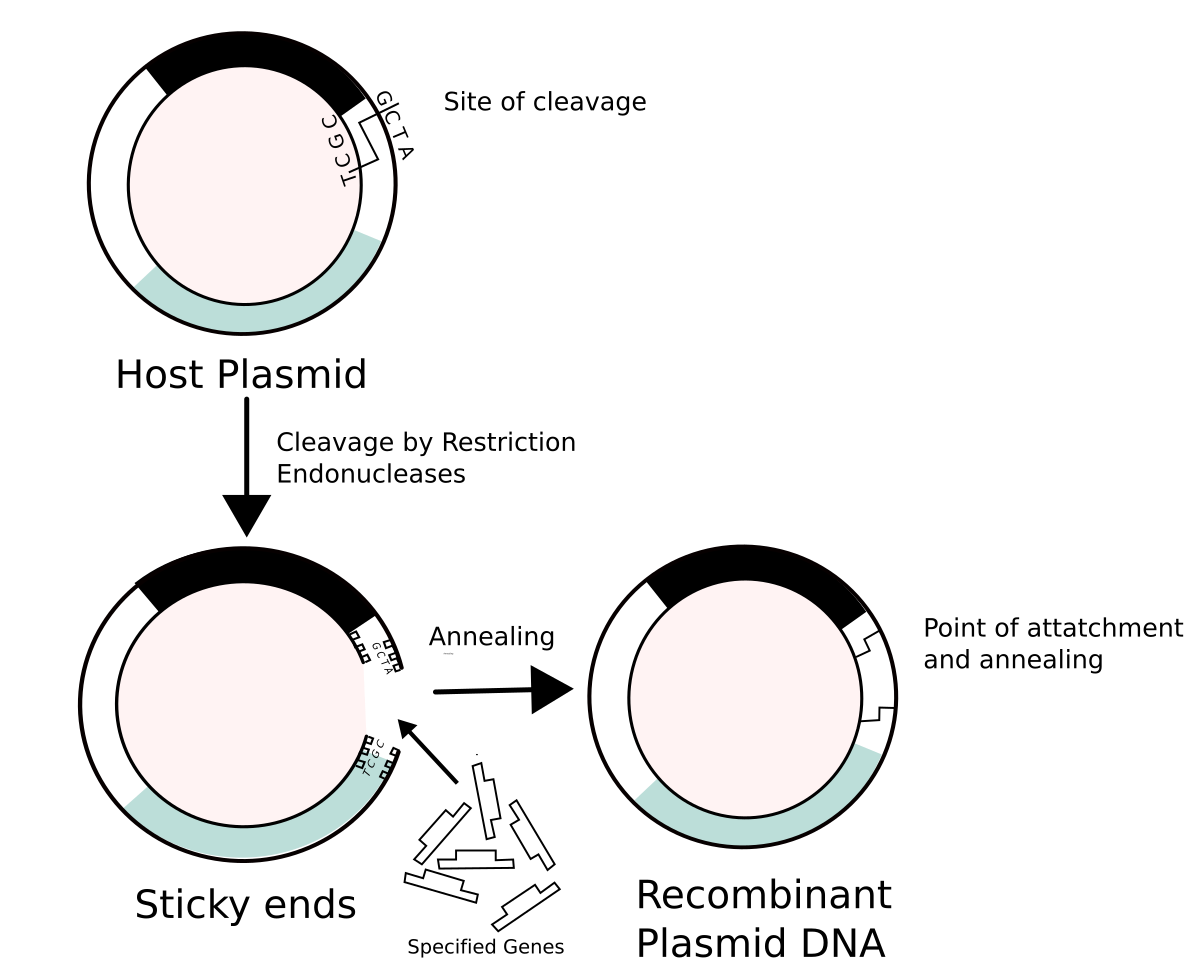
What are restriction endonucleases?
Restriction enzymes
They are enzymes used to cut the desired gene from DNA.
What can the desired gene also be called?
cDNA
1) Isolating the desired gene
Restriction endonucleases are used to cut the desired gene from DNA. This creates sticky ends, which makes it easier for the gene to be inserted elsewhere.
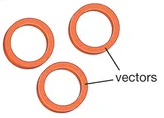
What is a plasmid in this process?
It is a circular piece of DNA used as a vector
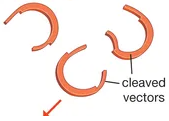
2) Plasmid
A plasmid is cut using the same restriction enzymes.
This produces complementary sticky ends that match the gene.
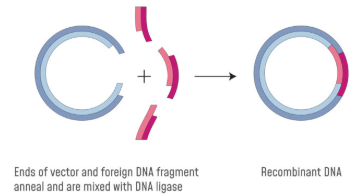
3) Recombinant DNA
The desired gene (cDNA) is inserted into the plasmid.
The complementary base pairs anneals using the enzyme DNA ligase.
It forms recombinant DNA.
4) Marker
A marker is often included with the desired gene. This helps identify which cells have successfully taken up the new DNA.
Give examples of a marker
Fluorescent marker
Gene for antibiotic resistance
5) Electroporation
The recombinant DNA is inserted into the host cell using electroporation.
An electric shock makes the cell surface membrane temporarily porous, so the plasmids can enter the host cell.
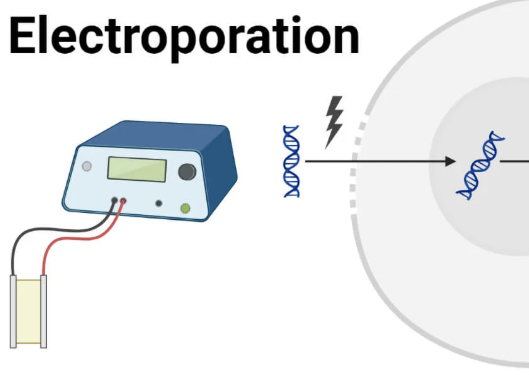
6)
The host cell divides by mitosis, reproducing the recombinant DNA too and producing the desired protein.
What’s electrofusion?
Electrofusion combines 2 different cells.
1 cell with the desired gene, 1 host cell.
The cells are placed next to each other and given an electric pulse.
The electric shock will cause their membrane to temporarily break, allowing them to fuse into 1 hybrid cell.
The new hybrid cell contains genetic material from both original cells.
This hybrid can be grown into a GM organism.
7) Testing for marker
Finally, scientists test the cells to check if the gene was successfully taken up.
If a fluorescent marker was used, they check for fluorescence
If an antibiotic resistance marker was used, they grow the cells in antibiotics. Only the ones with the gene will survive.
Alternative methods to extract the desired gene
Using reverse transcriptase
Reverse transcriptase
You start with the mRNA (rather than the desired DNA) and you reverse it using reverse transcriptase to return to the cDNA (complementary DNA).
cDNA can now be inserted into a plasmid just like a normal gene.
What is recombinant DNA?
DNA combined from 2 sources
Vectors for Plants
Plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Vectors for Bacteria
BAC (Bacteria artificial chromosome), virus
Vectors for Animals
BAC, plasmids, virus
What does PCR stand for?
Polymerase chain reaction
What is PCR used for?
Used to amplify DNA
What is a primer?
A short single-stranded sequence of DNA.
Primers anneal to a specific complementary sequence on the DNA strand we want to replicate.
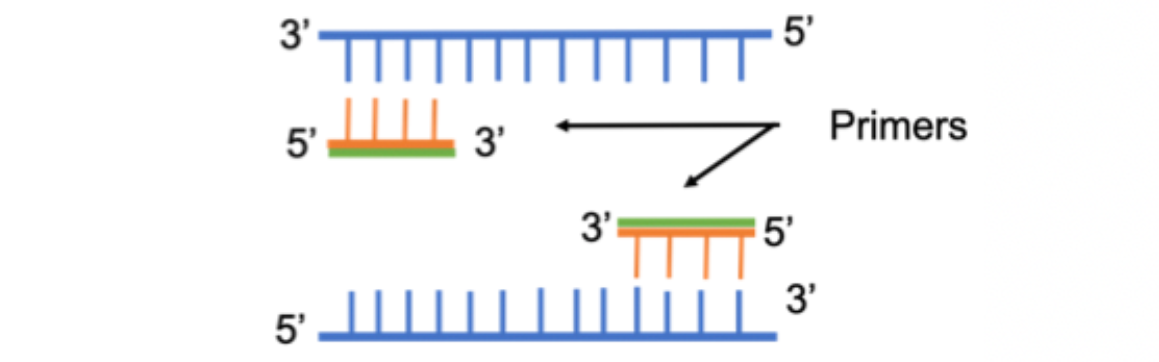
1) PCR - Denaturation
Heat the DNA fragment to 95C to break the hydrogen bonds between the strands, separating them into single strands
2) PCR - Annealing
Cool the solution to allow the primers to anneal to the specific DNA sequence to be replicated.
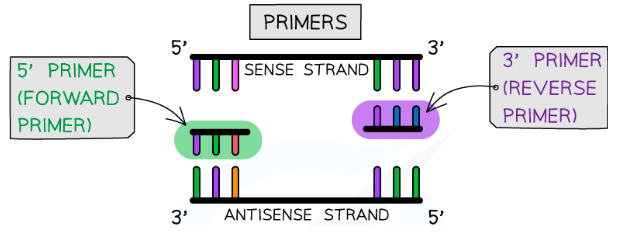
3) PCR - Elongation
Once the primers has annealed to the DNA sequence, then heat the DNA to the optimum temperature of Taq DNA polymerase.
Features of Taq DNA polymerase
Taq DNA polymerase is thermostable and does not denature at 95C, so PCR can be cycled repeatedly without stopping.
4) PCR - Elongation
Taq DNA polymerase joins free nucleotides to the 3’ end of the primers, building the new DNA strand.
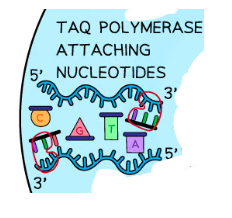
5) PCR
The result is 2 new DNA fragments.
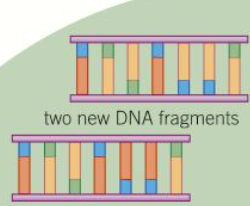
Amplifying DNA calculation
Each round, the number of DNA doubles. Therefore the formula 2ˣ can be used to calculate the number of strands. ˣ is the number of cycles.
What is the main advantage of PCR when it is used as a part of the process to sequence the genome of an endangered species?
Only a small sample of DNA is required
Uses of DNA profiling
Paternity tests
Forensics
Assessing disease risk
Classification/species identification
Introns
Non-coding regions of the DNA
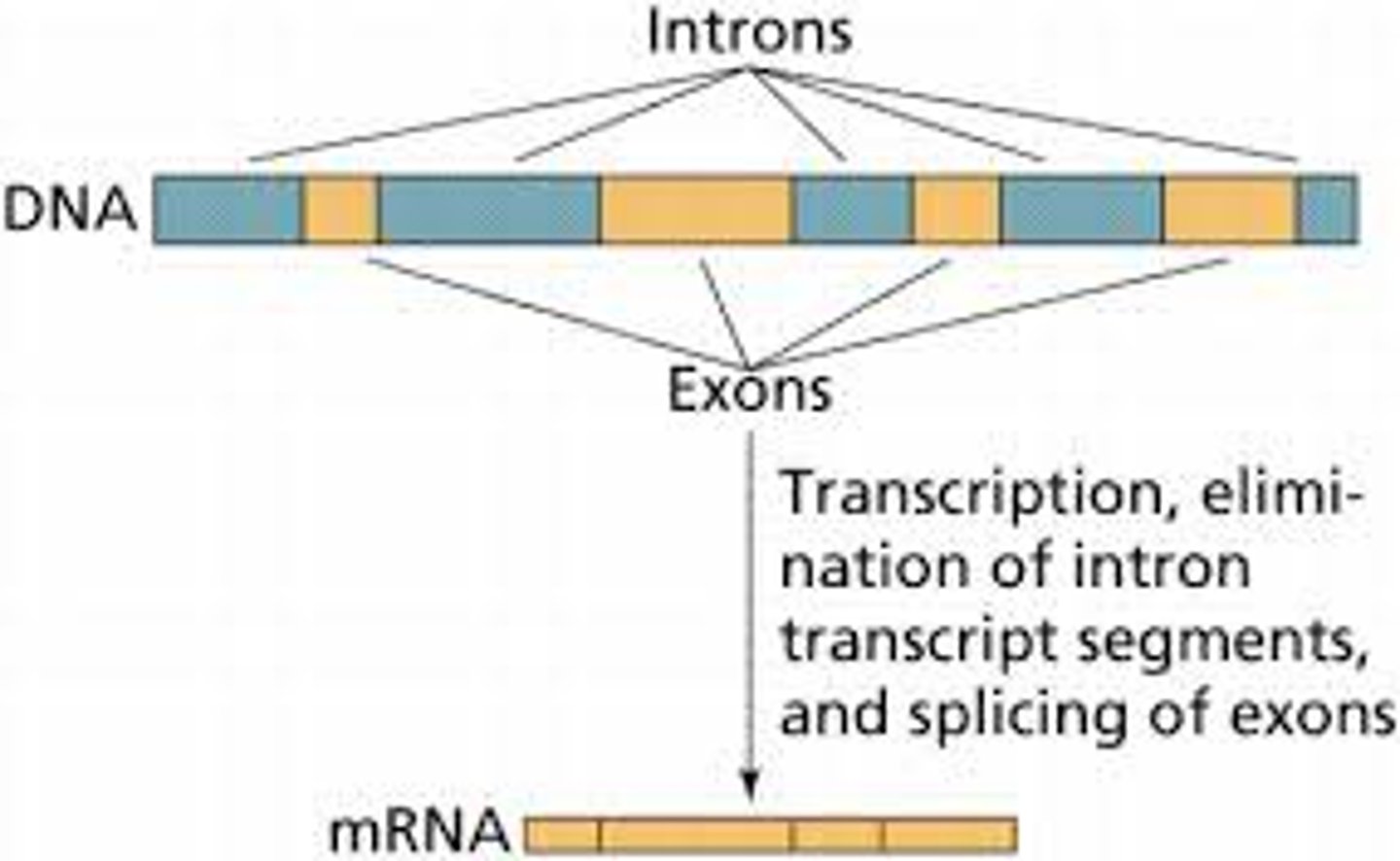
Explain why some regions of DNA can be described as non-coding
These regions are not present in mature mRNA and are not translated
Suggest why non coding regions of DNA show more variation
They aren’t selected against. They don’t affect survival.
Why do we use introns for genetic profiles?
- In most people, the genome is very similar
- Using coding sequences of DNA would not provide unique profiles
- Introns contain repeating sequences
STRs
Short tandem repeats
2-4 base pairs repeated 5-15 times
VNTRs
Variable number tandem repeats
20-50 base pairs repeated from 50 to several 100 times
What is the name for the sequence of bases that is repeated in Short tandem repeats (STRs) and variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs)?
The core sequence
1) DNA Profiling
Extract the DNA
2) DNA Profiling
Amplify the DNA fragment with PCR
3) DNA Profiling
Cut the DNA with restriction enzymes
4) DNA Profiling
Separate DNA fragments using electrophoresis. The DNA will be separated based on their mass.
5) DNA Profiling
Transfer fragments to paper
6) DNA Profiling
Apply a radioactive probe.
Use x-rays to view the position of DNA fragments
7) DNA Profiling
As a result, you create genetic profiles, which can be used in paternity tests, forensics, and for analysis of disease risk.
What is computational biology?
A branch of biology that uses simulations and mathematical models to explore biological systems
What is bioinformatics?
An area of science uses computer technology to collect, store, analyse, and share biological data such as sequences of nucleotides in DNA or sequences of amino acids in proteins
List the uses of bioinformatics
Rapid comparison of newly sequenced alleles with other sequences
Amino acids sequences / protein structures are held in database
Computer modelling of new protein structure from base sequences
Allows access to large amounts of data on DNA and proteins.
Information is universal
What field of science can bioinformatics be used in?
Epidemiology
What is epidemiology?
The study of how diseases spread, their patterns, causes, and their effects in populations.
What is a key aspect of modern epidemiology?
It allows the comparison of DNA sequences of viruses/bacteria to other known DNA sequences and structures.
How does gene sequencing now occur?
It occurs using “high throughput sequencing” and “next generation sequencing”, where multiple sets of DNA are sequenced together (massive parallel sequencing)
What does sequencing allow for?
Synthetic biology
What is synthetic biology?
A field of science that involves redesigning organisms for useful purposes by engineering them to have new abilities, solving problems in medicine, manufacturing, and agriculture.
Why is epidemiology beneficial?
It allows scientists to:
Identify the source of the outbreak
Identify vulnerable populations
Design vaccination programmes to target certain individuals
Sequencing also allows for proteomics. What is proteomics?
The large scale study of a set of proteins produced in an organism, system, or biology context
Why compare genomes?
The genome is universal
Evolutionary relationships (phylogeny)
Compare bases sequence to predict the function of an unknown protein
Compare between and within species
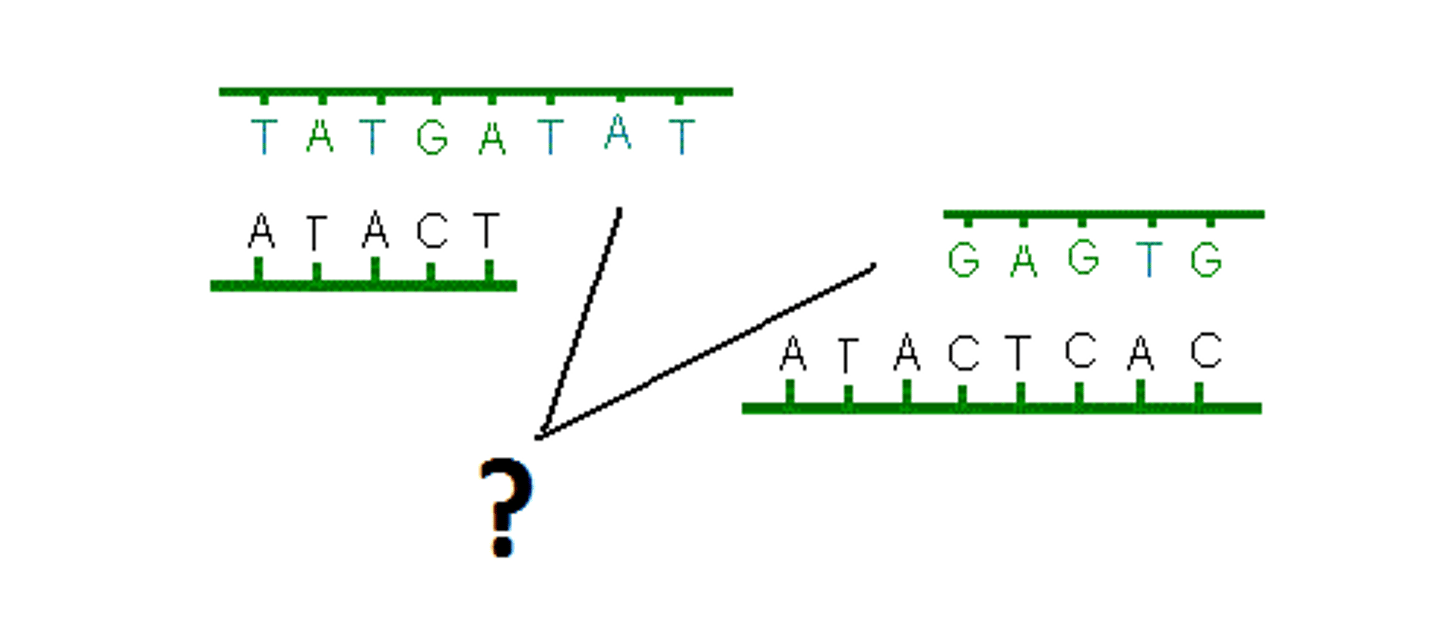
What is the general name for the process that determines the order of nucleotides in a length of DNA?
DNA sequencing
Main technique for sequencing DNA
Sanger sequencing / chain termination technique
How is DNA sequenced?
Extract DNA
Cut DNA into fragments of various lengths
Amplify
Sequence DNA fragments
Place fragments in order by matching overlapping regions
dNTP vs ddNTP
dNTPs are nucleotides that are building blocks of DNA.
ddNTPs are nucleotides that are used in the Sanger sequencing method.
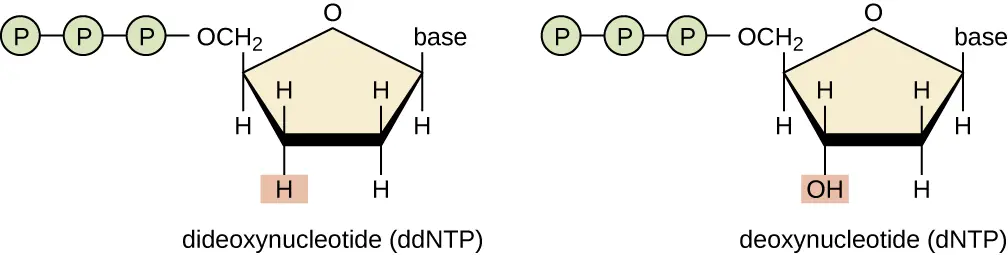
What is the name used for ddNTP used in DNA sequencing because they prevent further elongation of the DNA molecule when they are inserted into the molecule?
Terminator bases
1)
The DNA for sequencing is mixed with solutions. The solutions are:
Primers
DNA nucleotides
DNA polymerase
A Terminator base (A, G, C, or T)
2)
Place the mixture in a thermal cycler. This rapidly changes temperature at programmed intervals in repeated cycles.
What happens at 96C?
The double stranded DNA separates into 2 single strands
What happens at 50C?
The primers anneal to the DNA strand