Microbiology Lab Practical Flashcards
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover a range of microbiology lab practical tests across hydrolysis, enzyme activity, selective media, and other biochemical assays.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Starch Hydrolysis Test
A positive test shows a clear halo after adding iodine, indicating bacteria produced amylase and broke starch into sugars. A negative test shows no clear halo, with the medium remaining blue/purple after iodine.
Positive:Bacillus cereus
Negative: E. coli
Casein Hydrolysis Test
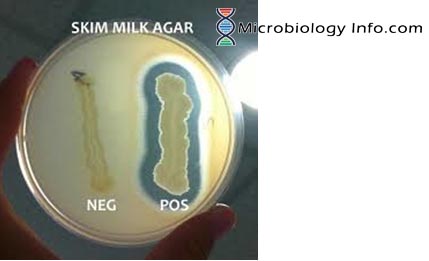
A positive test is indicated by a clear zone around colonies on milk agar, showing that caseinase broke down milk protein. A negative test shows no clear zone, with the medium remaining opaque.
Positive: Bacillus cereus
Negative: E. coli
Gelatin Hydrolysis Test
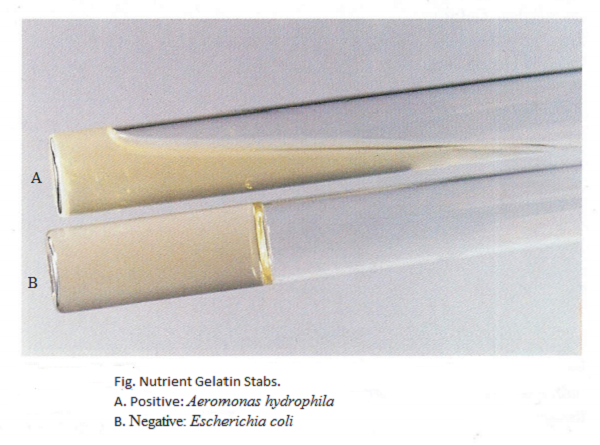
A positive test occurs when the medium remains liquid after refrigeration, signifying that bacteria produced gelatinase, breaking down gelatin into amino acids. A negative test shows the medium solidifies after refrigeration.
Positive: Klebsiella aerogenes
Negative: Staphylococcus aureus
DNase Test
A positive test shows a clear halo on green DNase agar, indicating DNA was broken down by the DNase enzyme. A negative test shows no clear halo, with the medium remaining green.
Positive: Serratia marcescens
Negative: Staphylococcus aureus
Lipid Hydrolysis Test

A positive test appears as a clear halo on Spirit Blue Agar, showing lipase broke lipids into fatty acids. A negative test shows no clear halo, with the medium remaining opaque blue.
Positive: Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Negative: E. coli
Urea Hydrolysis Test
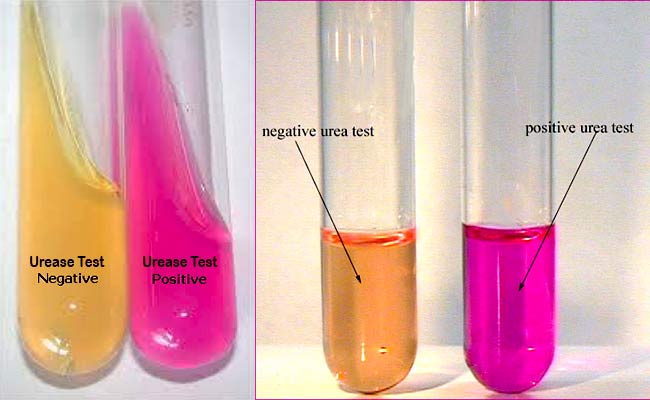

A positive test results in broth turning bright pink, indicating urease produced ammonia and raised pH. A negative test shows the broth remains yellow or orange.
Positive: Proteus mirabilis
Negative: E. coli
Catalase Test

A positive test is indicated by bubbles forming after adding hydrogen peroxide, showing that catalase broke H₂O₂ into water and oxygen. A negative test shows no bubbles forming.
Positive (bubbles = catalase made):
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Negative (no bubbles = no catalase):
Streptococcus pyogenes
Oxidase Test

A positive test shows a color change to blue or purple quickly, indicating the presence of cytochrome oxidase. A negative test shows no color change or a very slow, faint change after 30-60 seconds.
Positive: Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Negative: E. coli
Coagulase Test
A positive test occurs when plasma turns solid, indicating coagulase clotted the plasma. A negative test shows the plasma remains liquid.
Positive: Staphylococcus aureus
Negative: Staphylococcus epidermidis
Nitrate Reduction Test
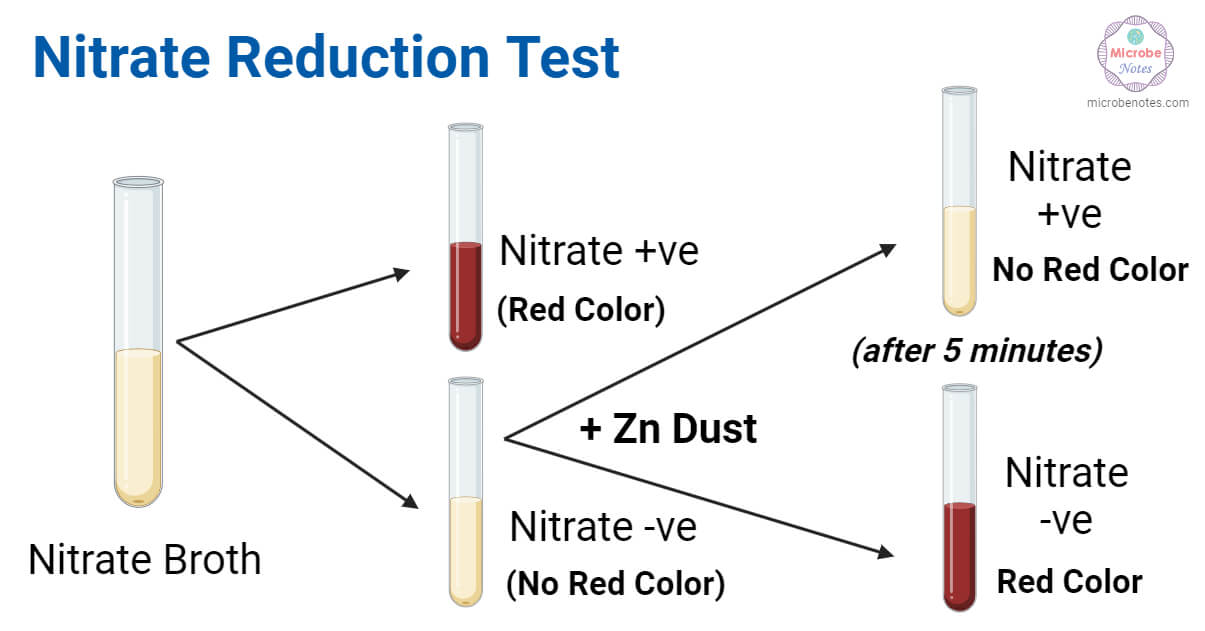
A positive test shows red after reagents or no color after zinc, indicating nitrate was reduced to nitrite or nitrogen gas. A negative test shows no color after reagents (then red after zinc) indicating nitrate was not reduced or was reduced only to nitrate, respectively.
Positive: E. coli, P. aeruginosa
Negative: Alcaligenes faecalis
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) Test

A positive test shows yellow colonies, indicating the bacteria ferments mannitol and tolerates salt. A negative test shows pink/red colonies or no growth.
Positive: Staphylococcus aureus
Negative: Staphylococcus epidermidis (pink)
Novobiocin Sensitivity Test
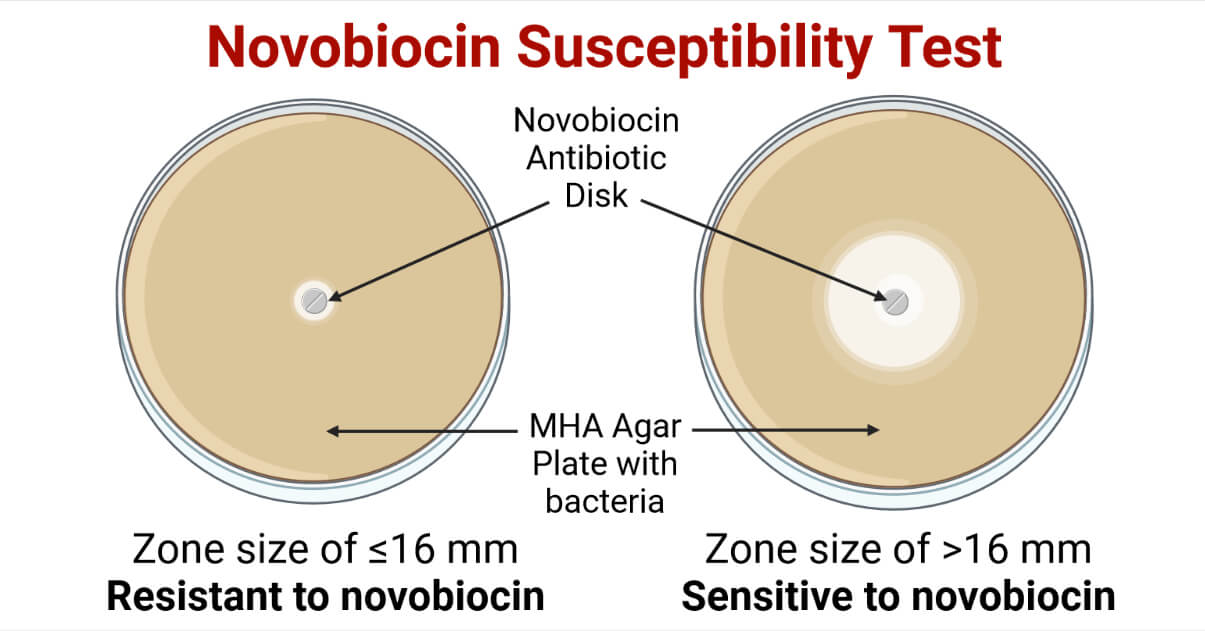
A positive test shows a zone of inhibition around the disk, indicating the bacteria are sensitive to novobiocin. A negative test shows no zone of inhibition or a very small zone.
Positive: Staphylococcus epidermidis
Negative: Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Methyl Red (MR) Test

A positive test shows red broth, indicating strong acid from glucose (mixed acid fermentation). A negative test shows yellow or orange broth.
Positive: E. coli
Negative: Klebsiella aerogenes
6.5% NaCl Test

A positive test occurs when the broth turns cloudy, indicating salt tolerance (halophile). A negative test shows the broth remains clear (no growth/salt tolerance).
Positive: Enterococcus faecalis
Negative: Streptococcus mitis/oralis
Bile Esculin Test
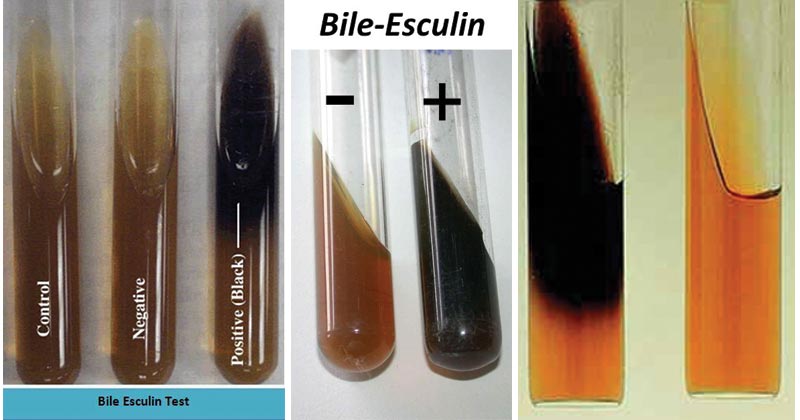
A positive test shows a black slant, indicating esculin was hydrolyzed in the presence of bile. A negative test shows the slant remains brown or tan.
Positive: Enterococcus faecalis
Negative: Streptococcus mitis/oralis
Blood Agar (Hemolysis) Test

Positive results include clear zones for β (complete breakdown), greenish zones for α (partial breakdown), and no change for γ (no lysis, indicating a negative result for hemolysis).
β (Beta): Clear zone → complete RBC breakdown (Streptococcus pyogenes)
α (Alpha): Greenish/brown zone → partial RBC breakdown (Streptococcus pneumoniae, S. mitis)
γ (Gamma): No change → no lysis (Enterococcus faecalis)
💡 Remember: Beta = clear, Alpha = green, Gamma = none
Indole Test
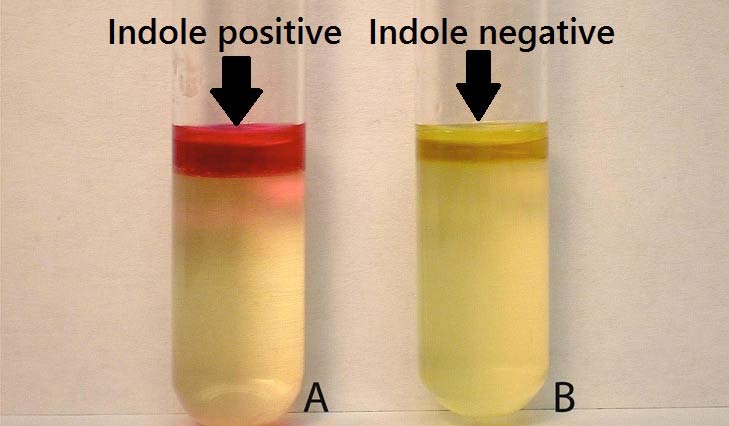
A positive test shows a red ring after adding Kovac’s reagent, indicating tryptophanase produced indole. A negative test shows a yellow or brown ring.
Positive: E. coli
Negative: Klebsiella aerogenes
Voges-Proskauer (VP) Test
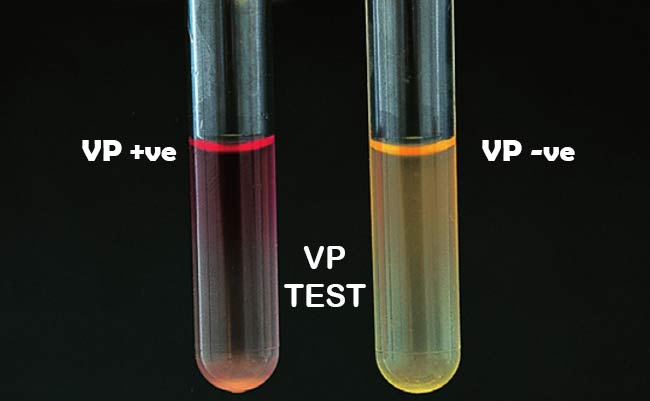

A positive test shows a red layer indicating bacteria produced acetoin as a neutral end product. A negative test shows no color change, or a yellow/brown layer.
Positive: Klebsiella aerogenes
Negative: E. coli
Citrate Test

A positive test shows a blue slant with growth, indicating that the organism uses citrate as its carbon source. A negative test shows a green slant with no growth.
Positive: Klebsiella aerogenes
Negative: E. coli
Sulfur Reduction Test (SIM)

A positive test results in a black precipitate, indicating cysteine desulfurase produced H₂S gas. A negative test shows no black precipitate.
Positive: Proteus vulgaris
Negative: E. coli
Motility Test (SIM)
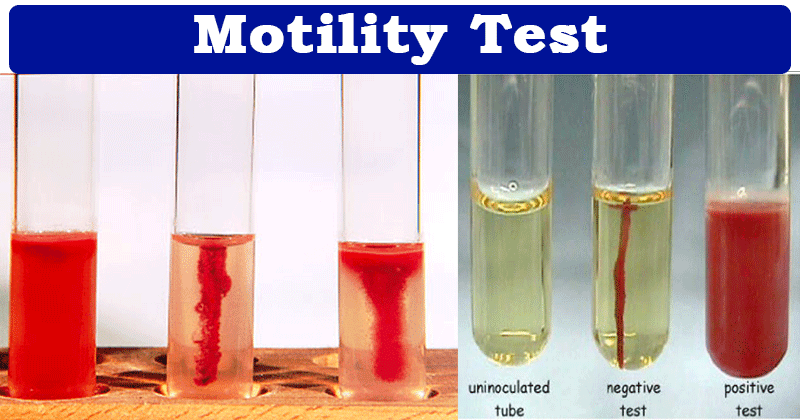
A positive test shows cloudy growth spreading from the stab line, indicating motility. A negative test shows growth only along the stab line.
Positive: Proteus vulgaris
Negative: Klebsiella aerogenes
Indole Test (SIM)

A positive test shows a red top layer after adding Kovac’s, indicating tryptophanase broke down tryptophan. A negative test shows a yellow or brown top layer.
Positive: E. coli
Negative: Enterobacter aerogenes
Lysine & Ornithine Decarboxylase

A positive test shows a purple color after incubation, meaning the bacteria produced decarboxylase enzymes that broke down the amino acids into alkaline end products (cadaverine or putrescine).
A negative test stays yellow, meaning only fermentation happened and no enzyme was made.
Lysine Positive: Escherichia coli
Lysine Negative: Citrobacter freundii
Ornithine Positive: Klebsiella aerogenes
Ornithine Negative: Klebsiella pneumoniae
Phenylalanine Deaminase
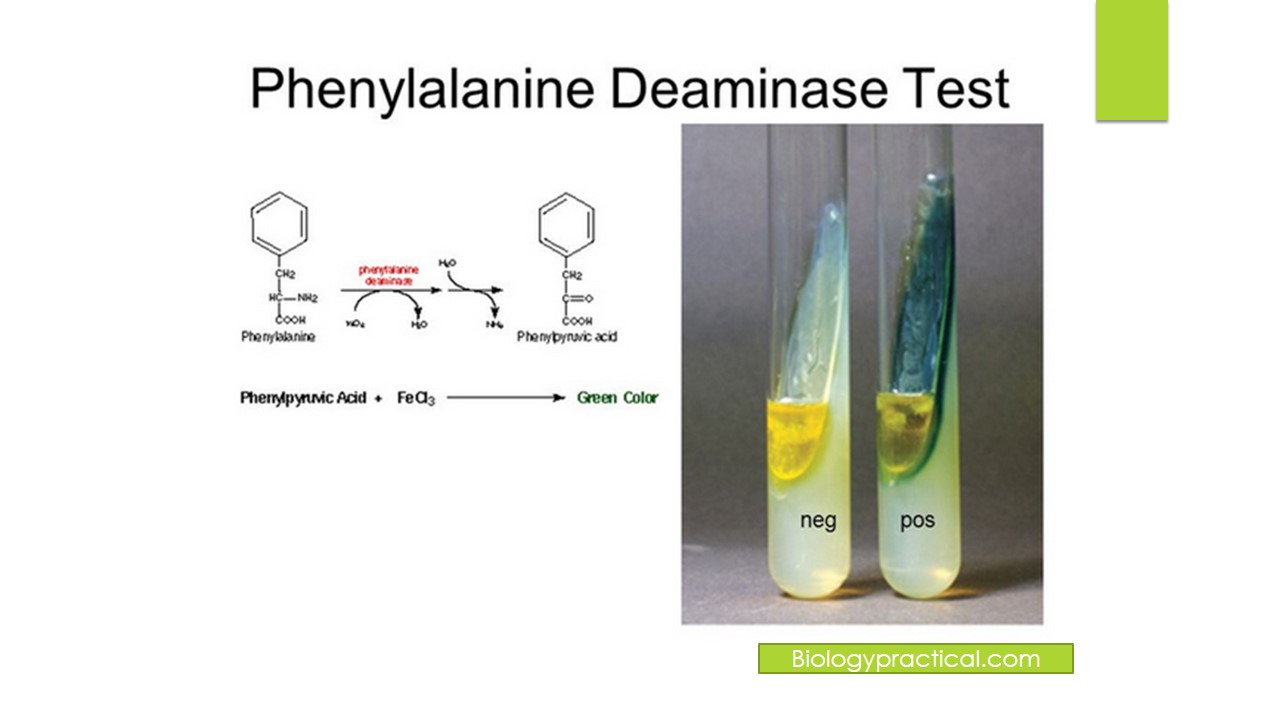
A positive test turns green after adding ferric chloride, showing that bacteria produced phenylalanine deaminase, breaking phenylalanine into phenylpyruvic acid.
A negative test shows no color change, meaning no deamination occurred.
Positive: Proteus mirabilis, Morganella morganii
Negative: Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae