Chapter 13-Clinical Psychology
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Diagnosis and Statistical manual of Psychological disorders (DSM-5)
Diagnosis tool for mental disorders, list criteria and looks at a variety of contexts
Comorbity
co-occurrence of 2+ disorders
Phycological disorder
Persistent disturbance or disfunction in behavior, thought, or emotion
Signs
Objectively observed (someone else)
Symptoms
Subjectively reported (Yourself)
Syndrome
Cluster of physical/mental symptoms of a type of condition that tend to occur simultaneously
Psychopathology
the study of psychological disorder or the disorders themselves
abnormal psychology
studies behavior/causes
Clinical physcology
studies diagnosis/treatment
Point prevelance
% of people in a given population that have something at a given point in time
lifetime prevelance
% of people in a pop that suffer from something over any given time
Mood-related disorder Genetic causes
85% of variability thought to be genetic
issues with neurotransmitters
concordance rate 2x higher in identical twins
Mood-related disorder psychological causes
negative cognitive schema
negative ways of viewing the world
explanatory style
How a person explains the bad things that happen to them
Mood-related disorder social causes
interpersonal stress
societal crises
Major depressive disorder (MDD)
need 1 major, 4 minor symptoms
must be most of the day, every day, for 2 weeks
men 7-15%, women 20-25%
women have higher rumination
MDD minor symptoms
Change in appetite, weight loss/gain
Sleep disturbances
fatigue/low energy
Psychomotor agitation
Diminished ability to think, concentrate, make decision
Feelings of worthlessness or self-guilt/blame
Thoughts of death or suicide
MDD Major symptoms
depressed mood
lost of interest/pleasure
Anhedonia
Bipolar disorder (Manic episode)
3 symptoms for most of the day, most days, for 3 weeks
inflated self-esteem/grandiosity
fast talking
thoughts are racing
decreased need for sleep
distractibility
increase in goal directed activity/movements that serve no purpose
excessive engagement in risky activities
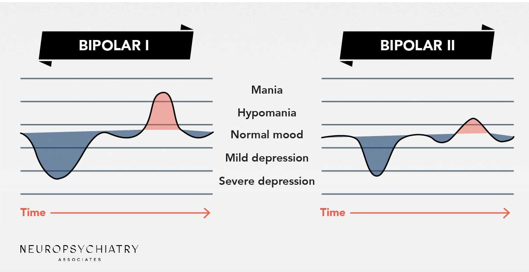
Bipolar 1
Needs at least 1 manic episode, does not have a depressive episode (but it’s often common)
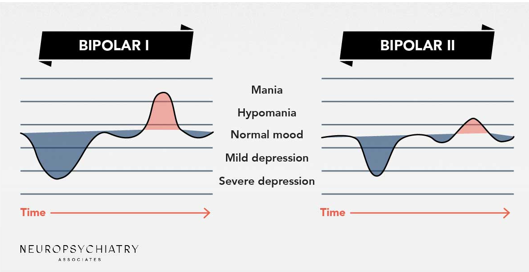
Bipolar 2
Needs at least a hypomania episode (lesser, less than once a week) but must have a depressive episode following
Traumatic/stressor disorders
anxiety related disorders triggered by events that involved actual/threatened death, injury, sexual violation, ect.
Traumatic/stressor disorders genetic causes
Can be inherited
Traumatic/stressor disorders psychological causes
maltreatment in childhood= increase likelihood of development
Post-Traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Exposure to traumatic event
direct, witness, learned it happened to a family member/friend, repeated exposure (Ex. EMT)
At least one DSM symptoms every day occurs for 1+ month
Symptoms must create distress for functional impairment
PTSD Instruction symptoms
Reliving tramaua
Flashbacks
nightmares
PTSD Avoidance symptoms
avoiding anything that reminds them of the event
Thoughts/feelings
people
objects
situations
places
PTSD cognitive/mood changes symptoms
decline in cognition and change in mood
forgetting parts of event
self-blame
negative outlook
constant negative feelings
PTSD Arousal and reactionary changes symptoms
increased arousal
Irritable/”fired up”
problems with sleep/concentration
exaggerated startle response
Schizepherenia
Disruption of basic psychological processes, distorted reality, altered emotion, disturbance of thought, motivation, or behavior
lowered volume in frontal/temporal lobes
increased volume in ventricles
3x concordance rate in identical twins
Positive symptoms
Symptoms that add to a person’s experience
Schizophrenia positive symptoms
Delusion
Hallucination
disorganized speech
Negative symptoms
Symptoms that take away from a person’s experience
Schizophrenia negative symptoms
emotional withdrawal
poverty of speech
indication of absent/insufficient normal behavior/motivation
“something’s off”
Affective flattening
lack of emotional expression
Catatonic behavior
abnormal behavior, speech, withdrawal
Dopamine hypothesis (schizophrenia)
idea that schizophrenia forms bc of abnormally high elvles of activity in brain circuits sensitive to dopamine
Social anxiety disorder
anxious about being watched, evaluated, or judged
Panic disorder
sudden occurrence of psychological and Physiological symptoms that add to a feeling of stark terror
Generalized Anxiety disorder (GAD)
chronic worrying accompanied by 3+ symptoms
Restlessness
fatigue
concentration problems
irritability
muscle tension
sleep disturbances
Phobias
marked, specific, and excessive fear and avoidance of specific objects, situations, or activities
Preparedness theory
idea that we’re biologically predisposed to certain fears (Ex. heights, snakes)
Diathesis-Stress model
Genetic predispostion+stress=disorder
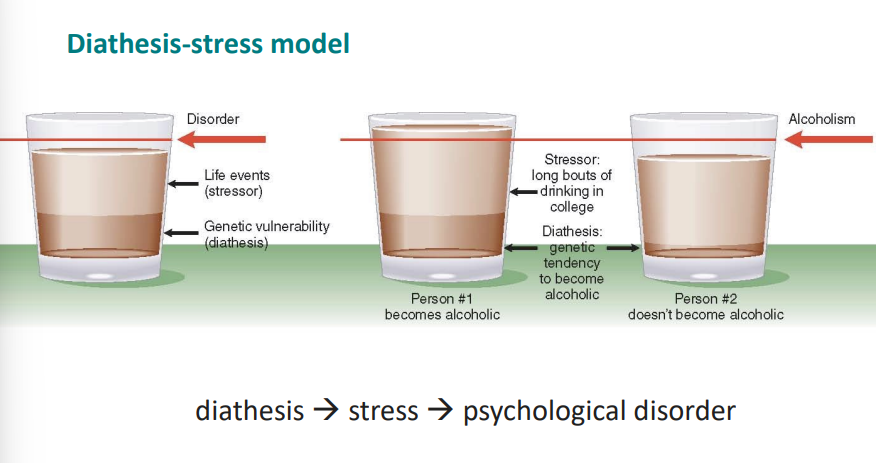
Clinical assessment
A process used by mental health professional to evaluate a person’s functioning and formulate a treatment plan
Self-report
A test,measure,or survey that relies on a patient to provide information about their thoughts, feelings, or symptoms their
Projective tests
A test where people are asked to interpret an ambiguous prompt to asses their current wellness
OCD obessions
Unwanted, intrusive thoughts or images that cause distress
Ex. fear of contamination, random thoughts of harming oneself
OCD Compulsions
reparative behaviors or mental acts people feel they’re driven to do
Ex. Excessive cleaning, flipping a light switch 7 times
Autism spectrum disorder
A neurological and developmental disorder that impacts how people interact, communicate, learn, and behave
ADHD
A chronic developmental disorder that affects a person’s ability to focus and control their behavior
Cluster A personality disorders
Often includes dysfunctional patterns of thinking/behavior that reflect suspicion or lack of interest in others
Ex. paranoid personality disorder, schizoid personality disorder
Cluster B
involves unpredictable, dysfunctional, and emotional thoughts and behaviors that can keep changing
Ex. BPD , Narcissistic personality disorder
Cluster C
Personality disorders that involve anxious thinking or behaviors
Ex. Avoidant personality disorder, Obsessive compulsive personality disorder