HEC002 CH6. AD/AS Analysis of MP & FP
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Great global depression
When GDP declined
In 1930s, Economy experienced recessionary gap (Ye<Yf) (eq inc < full empl inc level)
[high level of unemployment/lack of AD/Bank failures/unequal distr of wealth etc]
diff betw eq level of output (Ye) & full employment level of output (Yf)
Ye (Eq Level of Inc/output)
= level of national inc where AS = AD (where AS & AD intersect/meet)
Yf = Full employment level of output
= where economy is operating on PPC & all existing productive capacity is utilised (all resources fully utilised)
Features of great depression
(1929-1930s) Most severe worldwide economic DOWNTURN of 2oth century
- Began w stock mkt crash in US (1929) & quickly spread globally
*Mass unemployment (25% in US)
*Bank Failures
*Collapse of trade (tariffs)
*Poverty & hardship
*Deflation (decr prices & wages)
Ended1930-1940s due to gov reforms & massive mobilization for WWII
Classical economists approach
Believe high unemployment occurs when wages are above eq, creating surplus in labor mkt
suggested that lower wages = lower employment costs, allowing firms to hire more workers & restore full employment
automatic adjustments of mkt forces move economy back to eq, req no gov int
1) decr PL = incr QD for g&s
2) decr wages = employers willing to employ more people, thus solve unemployment
explain classical approach to restoring full employment in economy
Classical economists believed reducing wages would help restore full employment, as lower employment costs would allow employers to hire more workers & move economy back to eq
Keynesian economists approach
argued that Classical approach fails to solve unemployment, as lowering wages decr inc, C & AD
Suggested direct gov int to incr AD to restore full employment
suggested incr G & decr T (loose FP) during recession, & opp during inflation (tight FP)
also argued:
prices & wages are “sticky” & don’t adjust quickly enough to restore eq
gov int is req to stimulate AD
explain keynesian approach to restoring full employment in economy
Keynesian approach was to incl direct gov int to incr AD & restore full employment. Keynesian economics suggested changing G & T to stabilize economy
3 types of eq
1.Unemployment Equilibrium (Ye<Yf)
· (leads to recessionary gap)
2.Above Full Employment Equilibrium (Ye> Yf)
· (leads to inflationary gap)
3.Full Employment Equilibrium (Ye =Yf)
· ( when all ava resources are fully employed)
unemployment eq
(Ye<Yf - recessionary gap)
- Eq inc (Ye-where AD meets AS) < full employment level of inc (Yf)
(Similar to point inside PPC)
As result, national inc, output & employment temporarily below full employment, resulting in recessionary gap
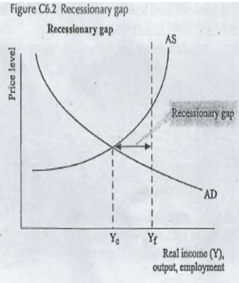
Recessionary gap
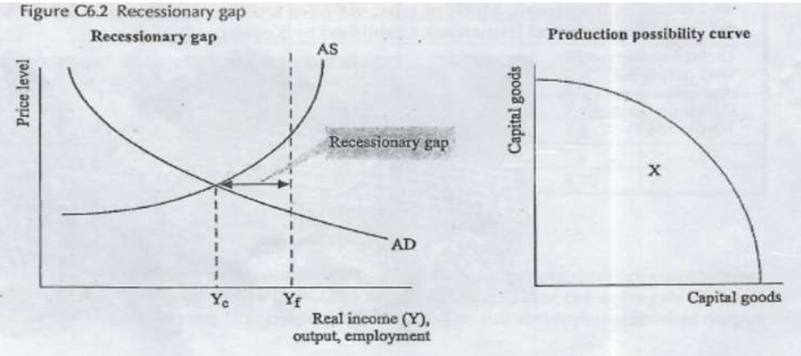
Amount that national inc must incr to reach full employment level of inc
(occurs when economy at below capacity = high unemployment, excess capacity, idle resources (workers & factories)
[Ye<Yf / eq inc<full employ level]
policy settings: traffic light approach
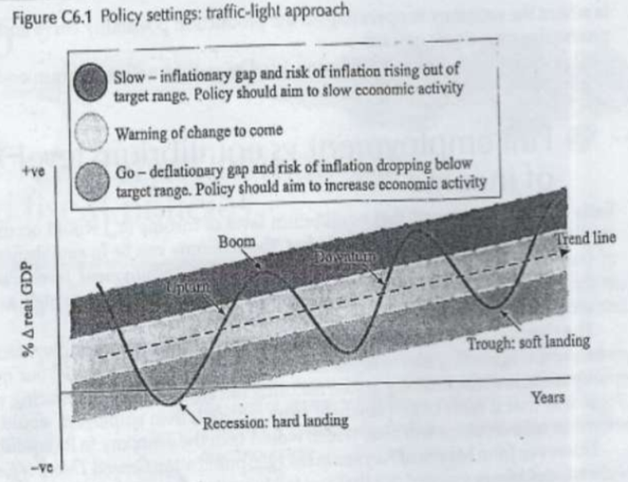
RED: boom - inflationary (PL incr), contractionary FP & MP
GREEN: bust - deflationary (PL decr), expansionary FP & MP
Deflationary gap
Deflation = decr in general PL, deflationary gap = recessionary gap
risk of inflation dropping below target range. Expansionary FP/MP to incr eco activity
How to solve recessionary gap
gov uses macroeconomic (expansionary MP & FP) & microeconomic policies (market reforms)
macroeconomic policies
expansionary FP (incr G, decr T) which leads to:
· Incr budget deficit OR
· Decr budget surplus
[ incr AD, incr PL, employment & output – Ye moves to Yf ]
expansionary MP (incr MS, decr OCR) which leads to:
· Reduced ir (CB decr OCR-> decr ir/ OMO buys -> decr ir)
· Incr C, I & NX
[ incr AD, incr PL & eq level of inc – Ye moves to Yf ]
expansionary/loose MP (tut)
Policy designed to expand growth of money & credit in economy (decr ir, incr MS, decr concern of inflation)
(when CB decr ir & incr MS to maintain price stability)
MP tools that can be used to close recessionary gap (tut - 3)
1. Official Cash Rate (OCR) – decr OCR to decr irs on money mkts
2. Open Market Operation (OMO) – buy gov stocks, expand reserves in BS, secondary expansion of MS, decr market irs
3. Interest Rates (irs) – decr irs = incr C, I & NX = incr AD = incr PL & eq level of inc
explain ways lower irs leads to incr AD (3)
less rewards, so incentive to save decrs. As cost of borrowing decr, C incr (AD incr)
decr D for SAT & incr S of SAT as local investors invest overseas. This decr ER = competitive local exports = incr NX (AD incr)
decr cost of borrowing for firms = more profitable inv opps/decisions, incr I (AD incr)
microeconomic policies
(market reforms): ex. Deregulation of Labour mkt & Increasing Efficiency in certain industries (infrastructure) would incr productivity, hence incr AS
impact of incr in AD
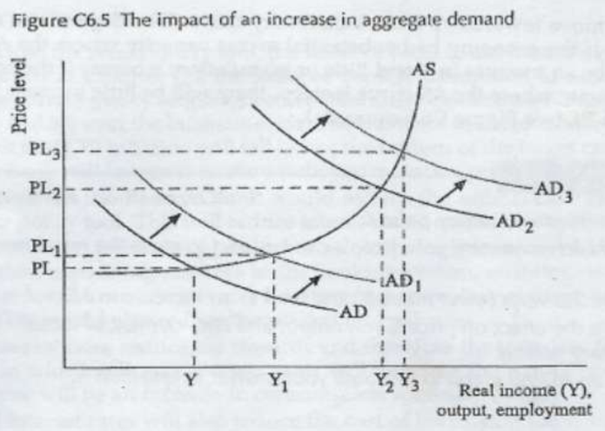
gov runs expansionary FP to close recessionary/deflationary gap
Achieved either by tax cuts (decr T) OR incr G (or both)
è Leads to decr Budget Surplus/ incr Budget Deficit
expansionary FP (tut)
occurs when gov spending is greater than its revenue (G>T)
(run by gov by incr J & decr W from circular flow (decr T, incr G -> incrs AD & may result in budget deficit)
TAX CUTS (incr AD)
1- Decr inc tax (incr disp inc, incr C, incr AD)
2- Decr company tax (incr dividends, incr disp inc, incr I, incr AD)
impact of tax cuts (effect on PL, output & employment)
depends on slope of AS curve (level of national inc)
1-FLAT = excess prod capacity (small incr PL, large incr output)
(incr output/national inc>inflationary impact)
2-STEEP = higher output level (approaching full employment level of output) (large incr PL, small incr output)
(inflationary impact>impact on inc & employment)
impact of expansionary FP
(decr T incr G)
= results in budget deficit (G>T)
how deficit affects macroeconomy
depends on how it was funded. either by
printing more money OR
selling assets/gov stock
why some govs dont run budget deficits
Today, most economies committed to balancing budgets over business cycles hence, some govs have moved away from running budget deficits bc:
1) High-long term debt is risky - interest payment incr
2) Credit rating agencies may downgrade country
3) Weakens investor confidence
4) Can cause inflationary pressure
inflationary gap
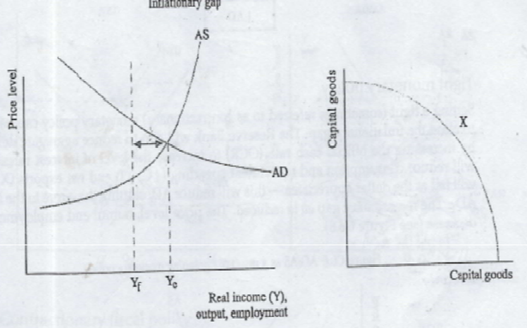
Amount eq national inc must fall so that Ye = Yf
(occurs when economy is at over-full capacity = full employment & inflationary pressure)
[Ye>Yf / eq inc>full employ level]
why gov concerned ab inflationary gap
gov concerned ab existence of inflationary gap, bc of lack of capacity/resource constraints o prod this level of output at existing PL
· will be pressure for resource cost to rise -> cause PL to rise
how to close inflationary gap
gov could close inflationary gap by (macroeconomic policies) (decr AD):
contractionary FP
contraftionary MP
contractionary MP
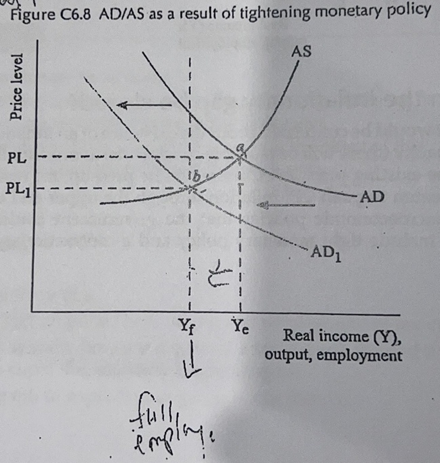
(incr ir)
- CB incr ir (cost of borrowing), decr I, C & NX = decr AD
- Incr D for SAT, decr S for SAT = currency appreciation = decr cost of prod = incr AS (decr AD & incr AS = decr inflationary pressure)
contractionary FP
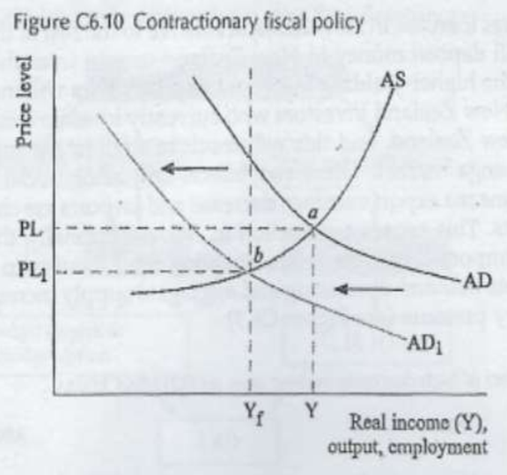
(decr G, incr T)
- Incr T -> gov charges, user-pay charges (health & education services)
- Decr G -> health, education, decr benefits, social welfare entitlements
(incr op bal: if og op bal neg (deficit) = deficit decr
“ “ “ “ pos (surplus) = surplus incr)
factors affecting AD
Incr NX (currency depr, easy access to overseas mkts, incr taste & pref overseas)
Incr C (decr ir, decr inc tax, incr tr)
Incr I (decr ir, incr business confidence, incr inv for later sale, incr ava of profitable inv opps)
Incr G
factors affecting AS
▲s nominal wage rates | (Incr nominal wage rates = incr cost of prod = decr AS) |
▲s imported raw materials costs | (Incr world P of oil = incr cost of prod = decr prod = decr AS) |
▲s productivity | (Incr productivity = incr AS: Improved work practices, Incr I, Incr education & training of workers) |
▲s technology | (Incr tech = incr output = incr AS) |
▲s other factors | (Factors affecting prod ex. Incr gov charges = decr AS) |
illustr recessionary gap
illustr effect of expansionary FP on economy w large recessionary gap
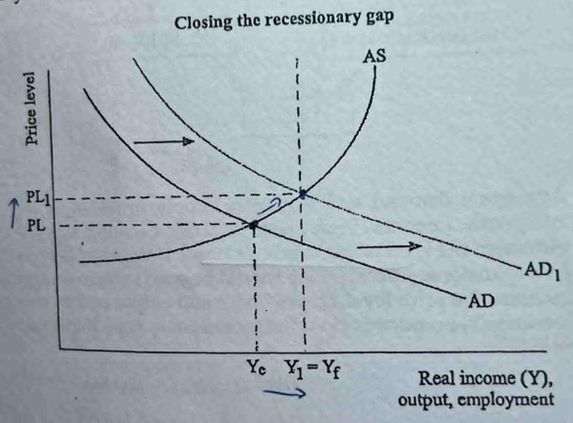
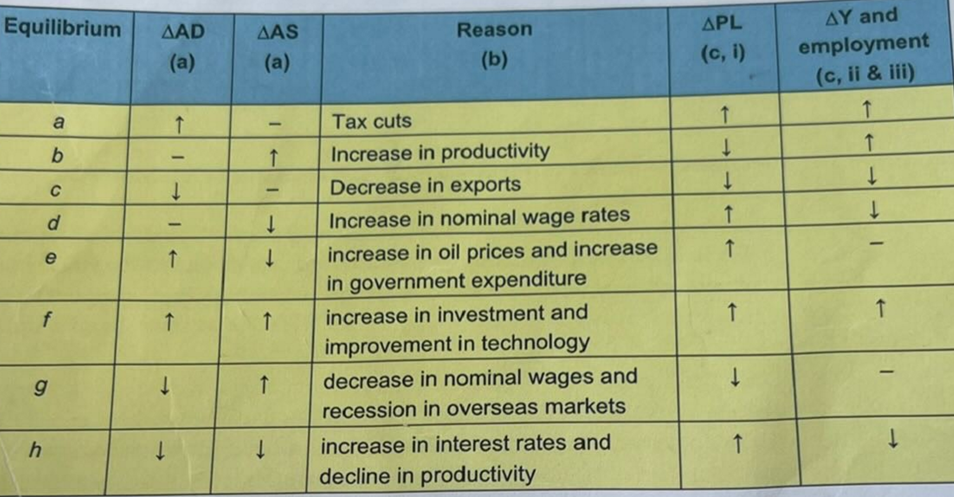
for each change in EQ, identify change in AD/AS, the reason, change in PL & change in Y & employment
descr what happens to labour & factories during low level of output (recessionary gap)
bc of recessionary gap (where eq inc (Ye) < full employment level of inc (Yf)), there is unemployment & workers & factories are idle/under-utilised/unemployed.
recessionary gap indicates excess capacity in economy/amount of real GDP/labour & factories that need to be incr to reach full employment.
reasons for downward sloping of AD curve (3)
i. g&s expensive so monetary assets lose purch power, C decr, AD decr
ii. PL incr so irs (cost of borrowing by hholds & firms) incr, C&I decr, AD decr
iii. PL incr = incr P of exports, less competitive in overseas mkts = decr NX, AD decr