Chapter 4: Gravity and Orbits
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is gravity?
An attractive force between objects with mass.
What is the relationship between gravity, mass, and weight?
The weight of an object is the force of gravity on the object and may be defined as the mass times the acceleration of gravity, w = mg.
Define mass and define weight.
Mass is the amount of matter in a material
Weight is the force of gravity acting on an object
e.g. Your weight on the Moon is lighter than it is on Earth because the weight of gravity on the Moon is different than that of Earth
Define Newton's Law of Gravitation.
The Law of Universal Gravitation states that the gravitational force between two points of mass is proportional to the magnitudes of their masses and the inverse square of their separation

What keeps the planets orbiting around the sun?
The gravitational pull of the sun
What is the gravitational constant (Newton's constant)?
G = 6.673 x 10^11
If the distance between the Earth and Sun were cut in half, the gravitational force between these two objects would:
Increase by a factor of 4 (you can find this by plugging in random numbers in to Newton's Law of Gravitation equation)
If you shrank Earth to a smaller radius but kept the same mass, the gravitational force between Earth and the Moon would:
Stay the same: the distance between the Earth and the Moon would remain the same
If you shrank Earth to a smaller radius but kept the same mass, everyone's weight on Earth would:
Increase: the distance between people and the center of the Earth would decrease and therefore the gravitational force would be larger
You can use Newton's law of gravitational force to solve for this
Define free fall
Free fall: gravity is the only force acting on an object
What is uniform circular motion?
When an object moves in a circular motion at a constant speed
What is centripetal force?
a force that acts on a body moving in a circular path and is directed toward the center around which the body is moving.
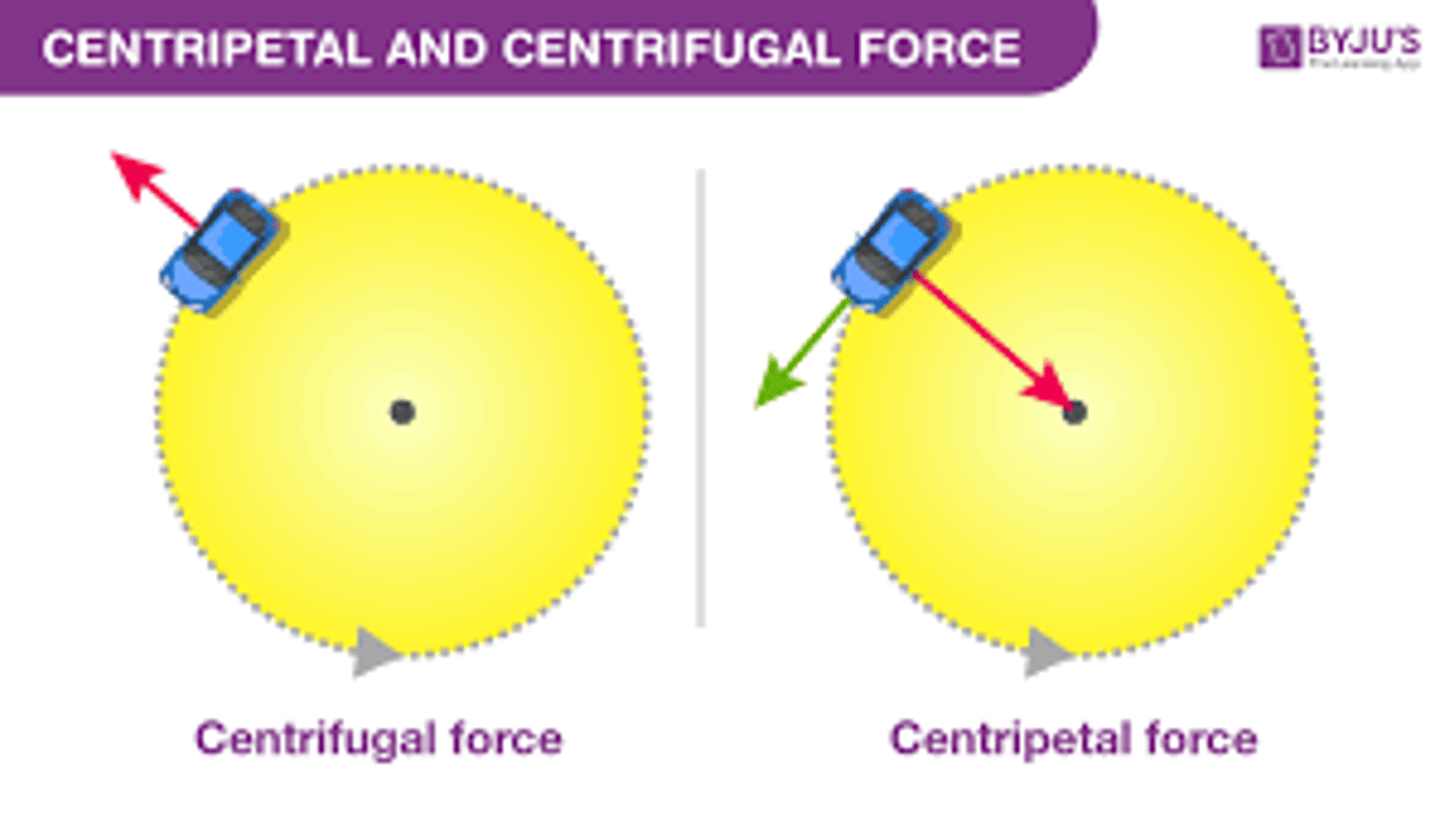
What is circular velocity?
The particular speed that an object must have in order to move around a circle
What is a satellite?
any object that orbits another object in space
What is a bound orbit?
When a satellite is gravitationally ground to the object that it it orbiting
How do you calculate circular velocity?
velocity is v = (2 * Pi * r) / T, where r is the radius of the circle the object moves in, and T being its time period
Compared to your mass on Earth, on the Moon your mass would be
the same - matter does not change
If you went to Mars, your weight would be
lower because Mars has lower mass and a smaller radius that together produce a lower gravitational force
How do you calculate gravitational force?
The strength of gravity between two objects is directly proportional to their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
How does distance affect circular speed?
Circular speed is larger as the distance decreases
List the four giants in increasing order of escape speed
Uranus
Neptune
Saturn
Jupiter
Astronauts in a space shuttle can float while orbiting Earth. Why are these astronauts weightless?
They are falling around Earth at the same rate as the shuttle.
Let's define the gravitational pull between Earth and the Sun as 1 Earth-pull. What is the pull that Mercury has on the Sun in Earth-pulls? Mercury has a mass of 0.055 Earth masses. Mercury is located at 0.39 AU from the Sun.
.36 Earth-pulls
In what direction is the force on the planet?
Toward the sun
For a pair of objects, the center of mass is located
along the line between the two objects, closer to the more massive object.
As two objects orbit one another, they are always
on opposite sides of the center of mass, traveling in opposite directions in space.
The connection between gravity and orbits enables astronomers to measure the __________ of stars and planets
Masses
Spring tides occur only when:
the Moon is in new or full phase.
List the phases of the moon in each season, from strongest tide to weakest tide
Full Moon in January
New Moon in July
First Quarter Moon in July
Third Quarter Moon in January
If the Moon had twice the mass that it does, how would the strength of the lunar tides change?
The highs would be higher and the lows would be lower because the push and pull of the moon would be stronger
If an object crosses from farther to closer than the Roche limit, it
may be torn apart.
What is the Roche limit?
the closest distance from the center of a planet that a satellite can approach without being pulled apart by the planet's gravitational field.