Test 2 Human Bio
1/162
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Everything since test 1 - up to test 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
163 Terms
Where is tissue placed in the biological levels of organization
After the cell, before the organ
what is a multicellular organism
organisms composed of more than one type of cell
what is the benefit of multicellularity
division of labor, more adaptability, more complexity
What is a tissue/structure
group of cells that have similar structure and function; humans have 200 different cell types that are group into general categories
what are the 4 major types of tissues in humans
Epithelial, Connective, Nervous, Muscle
Functions of Epithelial tissue
Cells joined together forming continuous sheets to cover or line body surfaces
Functions of connective tissue
support body or connect tissues; rich in extracellular matrix
Functions of nervous tissue
Receives, generates and conducts electrical signals
functions of muscle tissue
generates force that facilitates movement
what is an organ structure
collection of two or more tissues that perform a specific function(s); meaning more than one type of cell combining/working together
what are the six basic processes leading to producing tissues and organs
cell division, cell growth, migration, differentiation, apoptosis, cell connections
what are stem cells
cells that can give rise to different types of specialized cells (differentiation), they also have the capacity for cell division.
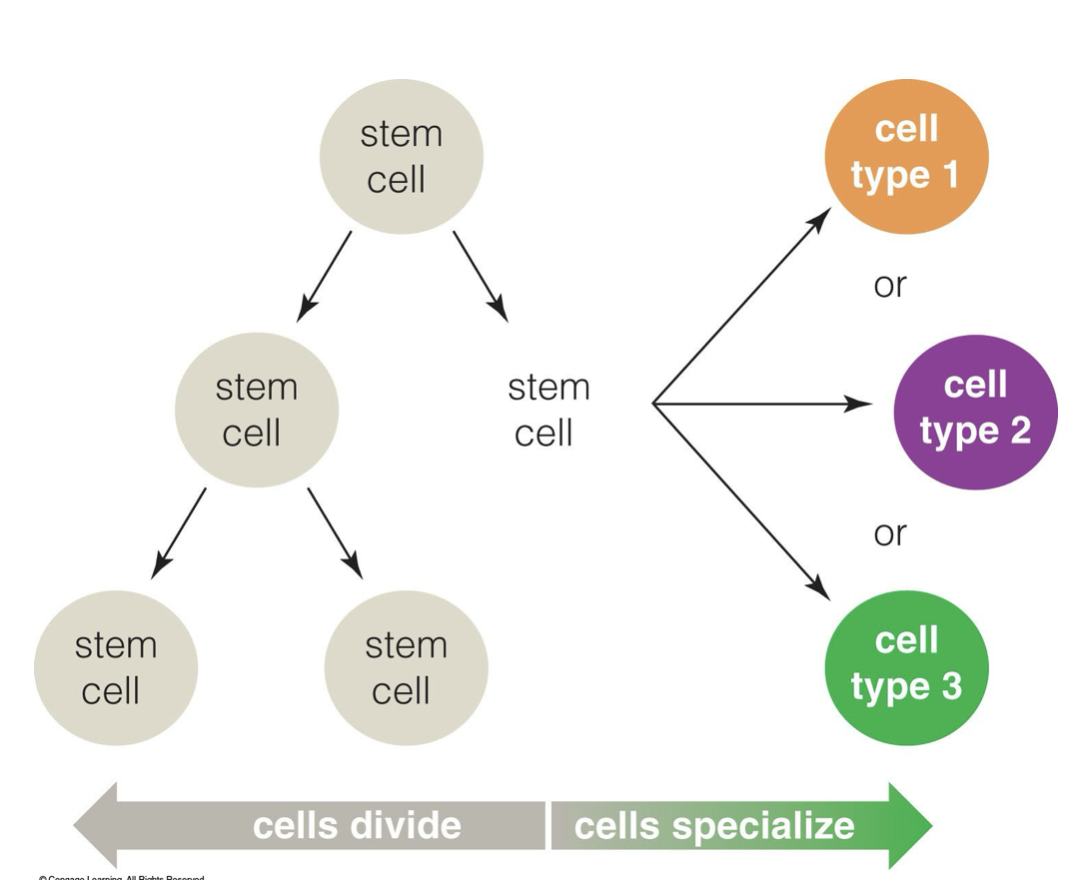
what is apoptosis, why is it important
cell death, it is important for normal development to maintain the proper number of cells. It eliminates cells that have become worn out, infected or cancerous.
What are the two types of apoptosis pathways
mitochondrial pathway (intrinsic): suicide
death receptor pathway (extrinsic): murder
what type of cells do not want to die/ don’t have the mechanisms for intrinsic apoptosis
cancer cells; they keep dividing
what is the process of apoptosis (programmed cell death)
cell shrinks and forms rounder due to the destruction of nucleus and cytoskeleton
plasma membrane forms blebs- irregular extensions that break away
eliminates cells
what is the difference in apoptosis in developing animals and adult animals
developing animals: apoptosis sculpts tissues and organs
adult animals: apoptosis maintains proper number of cells in tissues and organs
what is epithelial tissue
tissue made of tightly packed cells and cell junctions
it lines body cavities and surfaces, and found in glands
what is basement membrane
it anchors epithelial tissue on one side to underlying connective tissues
it’s a thin layer of carbohydrates and proteins
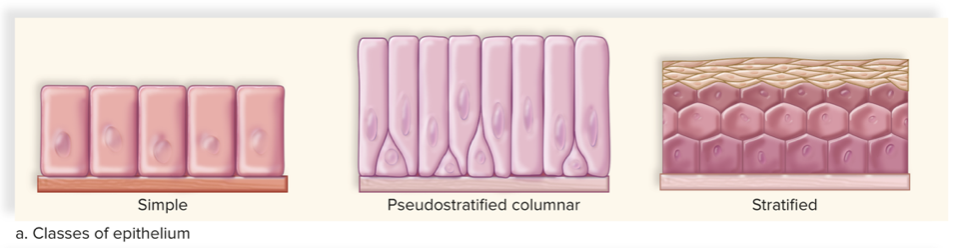
how is epithelial tissue named
for the number of cell layers and shape
what are the three layer types of epithelial tissue
simple, pseudostratified, stratified
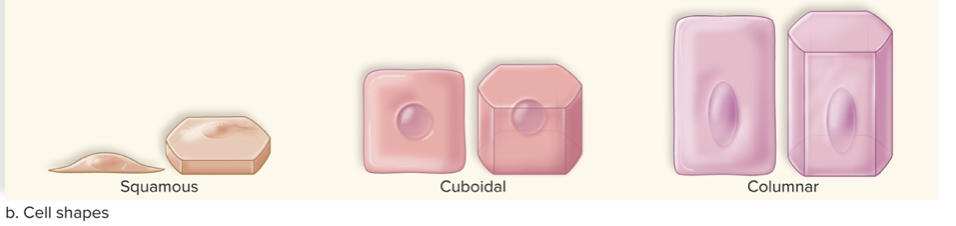
What are the three cell shapes of epithelial tissue
Squamous, cuboidal, columnar
function and location of the simple squamous epithelial tissue
diffusion, filtration, secretion
found in lining of blood vessels, lung air sacs
function and location of the simple cuboidal epithelial tissue
absorption and secretion
found in glands, ovary surfaces, iris of eye, kidney tubules
function and location of simple columnar epithelial tissue
absorption and secretion
found in stomach, intestines, uterus
function and location of pseudostratified columnar epithelial tissue
secretion and mucus movement
found in the throat, nasal passages, sinuses, trachea, male genital ducts
often has cilia which helps move mucus
appears stratified, but every cell touches basement membrane
function and location of stratified squamous epithelial tissue
protection and pathogens
found in skin, mouth, throat, vagina
function and location of stratified cuboidal epithelial tissue
protection and secretion
found in ducts of sweat glands
function and location of stratified columnar epithelial tissue
protection and secretion
found in male urethra, salivary glands
what is transitional epithelia
cells change shape in response to tension (cuboidal to squamous)
found in urinary bladder
glands
one or more cells that make and secrete a product
develop from epithelium
what are the two types of glands and their functions
exocrine: secrete substances (enzymes) through ducts/tubes, they stay in place and function
endocrine: make hormones that are released into surrounding fluid/bloodstream, they usually travel everywhere
What are the three main components of connective tissue
specialized cells, ground substance (matrix), and protein fibres
ground substance
noncellular material between the cells
provides nutrients, supports cells
can be solid or fluid
what are the three types of protein fibres, describe them
collagen fibres: flexible and strong
reticular fibres: thin, branched collagen fibres
elastic fibres: contain elastin, a protein that stretches and recoils
what are the three main types of connective tissue
fibrous, supportive, fluid
what is fibrous connective tissue
tissue containing lots of fibres, connecting 2 different tissues through fibres
what cell is in fibrous connective tissue
fibroblasts, separated by matrix
what are the two main forms of fibrous connective tissue and their main functions
loose (elasticity/diffusion) and dense (support)
describe the structure of loose vs dense fibrous connective tissues
loose: fibroblasts, other cells, fibres loosely arranged in semifluid matrix
dense: densely packed collagenous fibres, fibroblasts, less matrix
where is loose fibrous connective tissue found
under skin, around organs, supports epithelium
where is dense fibrous connective tissue found
tendons and ligaments; connect muscles to bones, bones to bones.
what are the three subtypes of loose fibrous connective tissue
areolar, reticular and adipose connective tissue
adipose tissue structure and function
stores fat
little extracellular matrix,
energy storage, insulation, cushioning
around heart, kidneys, under skin
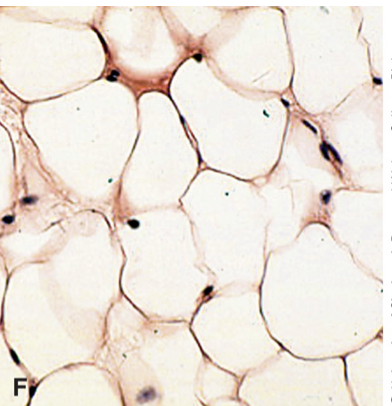
what are the cells found in adipose tissue
adipocytes- cells filled with liquid fat
what are the main functions in supportive connective tissue
structure, shape, protection, leverage for movement
what are the two types of supportive connective tissue
cartilage and bone
structure of cartilage
lacks matrix mineralization → more flexible than bone
matrix is solid but flexible
lacks direct blood supply→ heals slowly
what are the cells of cartilage called and where are they kept
chondrocytes & chondroblasts
kept in lucanae (small chambers)
what are the three types of cartilage and how are they distinguished
distinguished by types of fibres found in their matrix
hyaline cartilage: fine collagen fibers
elastic cartilage: elastic fibers
fibrocartilage: strong collagen fibres
where might you find the three different types of cartilage
hyaline: tip of nose, ends of long bones, fetal skeleton
elastic: outer ear
fibro: disks between vertebrae
structure of bone tissue
most rigid connective tissue
matrix made of collagen and calcium salts
salts surround protein fibres → elasticity & strength
what are the types of cells that form the matrix in bone tissue and their difference
osteoblasts: edge of bone for bone generation
osteoclasts: centre of bone for bone resorption
bone cells in general: osteocytes
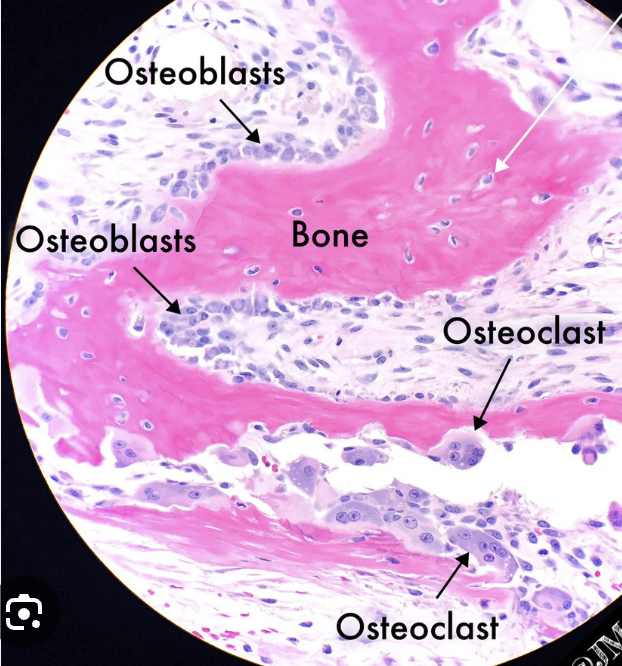
what are the two types of bone tissue
compact and spongy
structure and function of compact bone tissue
makes up the shafts of long bones
consists of osteons
central canal has blood vessels and nerves

label this picture with: osteon, central canal, osteocytes
central canal: the hole
osteon: the dark lining around the hole
osteocyte: dark specks all around the tissue
structure and function of spongy bone tissue
inside the ends of long bones
lighter than compact bone tissue
where might you find bone tissue
in bones of skeleton
what are the two types of fluid connective tissue
blood and lymph
structure of blood- fluid connective tissue
fluid matrix called plasma
cellular components called formed elements
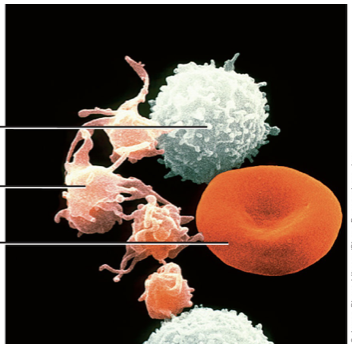
what are the three formed elements in blood, their functions and label them
white blood cells (leukocytes): fight infection
platelet (thrombocytes): pieces of cells that clot blood
red blood cells (erythrocytes): carry oxygen
all connective tissue has three components, but where is the fibre component in fluid connective tissue?
Fiber in this type is super tiny, it has it but we cannot see it, there are not always fibers in blood
structure of lymph
derived from fluid surrounding tissue
only contains white blood cells; looks more watery/pale
lymphatic vessels absorb excess fluid and return lymph to cardiovascular system
muscular tissue ____ the body
moves
myocytes
cells in muscle tissues, called muscle fibers
myofibrils
protein fibres of muscles that are involved in contractions
sarcoplasm
the cytoplasm of muscle tissue cells
sarcolemma
the plasma membrane of muscle tissue cells
three types of muscle tissue
skeletal, smooth, cardiac
skeletal muscle; structure, function, location
structure: sarcoplasm filled with myofibrils, long cylinder cells, multiple nuclei, striated/striped
function: contraction moves skeleton, voluntarily body movement
location in muscles attached to skeleton
What are the two striation types of the skeletal muscle
cross section and longitudinal section
Smooth muscle; structure, function, location
structure: spindle shaped cells, one nucleus, no striations
function: movements of bodily substances, involuntary
location: blood vessel walls, digestive track walls
Cardiac muscle: structure, function, location
Structure: branching striated cells, single nucleus, cells connected by discs
Function: pumping of blood, involuntary
Location: Wall of the heart
Name and describe the two components of intercalated discs that connect cardiomyocytes
Transverse (Velcro): crosses at right angle to myofibrils, adhesion junctions
Lateral (Communication): Parallel to myofibrils, Gap junction
What does nervous tissue consist of
neurons and neuroglia
name the three primary functions of neurons
sensory input, integration, motor output; they are the senders/receivers of signals
neuroglia functions
to support and nourish the neurons, they do not involve in electrical signals
what is the size/abundance of neuroglia
outnumber neurons 9 to 1
take up more than half the volume of brain
three components we mention of a neuron structure
cell body/soma, dendrites, axon
cell body/soma structure and function
contains nucleus and organelles
cell body processes incoming signals and generates outgoing signals
dendrites structure and function
extensions of cell body, single or branching
receive incoming signals from other neurons to give to its cell body
axon structure and function
extension of cell body, varied length
can be branches or wrapped in myelin
has axon hillock near cell body
axon terminals send signals to other cells
what are the three types of neuroglia we mention
astrocytes, microglia, myelin sheath
astrocytes functions
metabolic support
form blood-brain barrier
maintain concentration of ions in extracellular fluid
microglia functions
immune function
remove cellular debris
myelin sheath functions
insulating layer around axons (interrupted by nodes of Ranvier)
produced by oligodendrocytes in CNS and Schwann cells in PNS
Anatomical terms refer to a body that is ___
upright, standing; humans
ventral and anterior means
to the front
dorsal or posterior means
toward the back
meaning of superior vs inferior
superior: toward the head
inferior: toward the feet
medial vs lateral
medial: closer to body midline (heart, nose)
lateral: away from midline (lungs, eyes)
proximal vs distal when referring to an appendage
proximal: closer to body
distal: away from body
organ
a group of tissues performing a common function
no structural similarities between tissues; multiple cells included
organ system
group of organs with similar function
maintains structure and function of body
some organ systems ______ while others are found _____
occupy specific cavities, throughout the body
organs and cavities are lined with ____
membranes
some secreting fluid
how many organ systems make up human body
13; they work together
what is known as an accessory of organ systems; helps to operate them
other structures and glands
What are the 2 main cavities in our body
Ventral and Dorsal
What 3 cavities are within ventral cavity
thoracic, abdominal, pelvic