lecture 23 - motor system ll part a
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
what detect changes in muscle length?
Muscle spindle proprioceptors
What is Muscle spindle proprioceptors?
Aligned in parallel with muscle; detect increase in muscle length.
What are the 2 types of skeletal muscle fibers and types of motor neuros they have?
Alpha motor neuron innervate extrafusal fibers that provide force
Gamma motor neuron innervate intrafusal fibers that control spindle
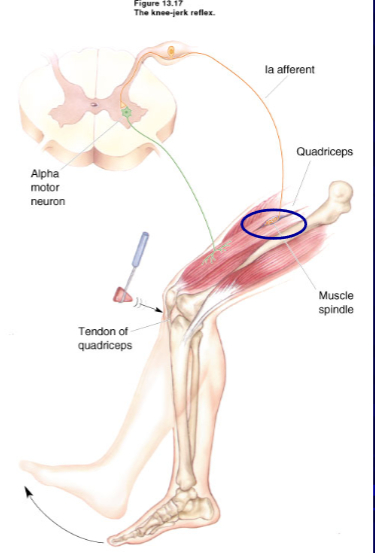
muscle stretch (myotatic ) reflex
where does response originate ?
input?
output?
- originates in muscle (myotatic) bc intrinsic group lA proprioceptors that send fibers via spinal or cranial nerves
INPUT = add weighted load to increased muscle length
OUTPUT = increased a.p's in group la leads to alpha m.n discharge --> triggers muscle contraction in homonymous muscle
muscle tone
continuous, passive partial contraction of muscles due to muscle stretch reflex
purpose of myotatic reflex
- slows muscle contraction as the force increases
- allows fine control of exploratory movements such as active touch
- important in fine motor activity (ex: contractions requiring a steady but not too powerful grip)
- protects muscle from overloading & getting damaged
motor neuron excitability depends on
combined input from local, central & peripheral sources
What is the results in muscle contraction?
Alpha motor neurons must receive continual afferent input from the proprioceptors via Group la fibers.
When is muscle tone lost?
if the dorsal roots of group 1a fibers are cut, then the muscle stretch reflex is eliminated and muscle tone is lost.
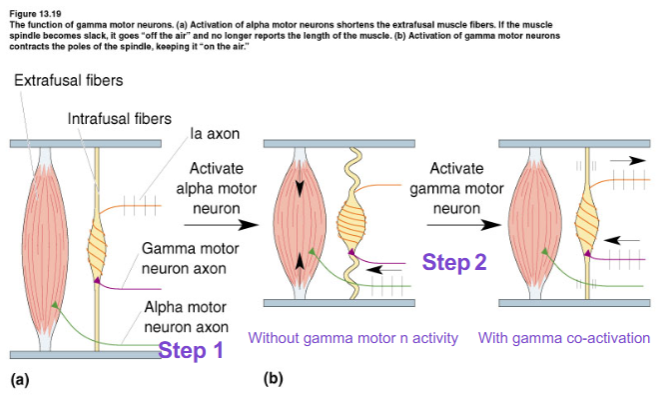
What do gamma motor neurons innervate?
Intrafusal muscle fibers inside the muscle spindle.
What is the direct effect of gamma activation?
Causes intrafusal contraction
What is the functional purpose of gamma co-activation?
Keeps the muscle spindle responsive to stretch even when the muscle contracts
Why are alpha and gamma MNs co-activated?
So extrafusal fibers (force) and intrafusal fibers (spindle sensitivity) adjust together.
Golgi tendon organ
It is situated in series with muscle designed for detecting TENSION.
INPUT: increase in muscle tension.
OUTPUT: increases A.P. firing rate in Groub lb proprioceptive afferents.
What keeps muscle spindle proprioceptors responsive?
Co-activation of gamma motor neurons
Golgi Tendon Organ Reflex (Reverse Myotatic Reflex
Also known as Clasp-knife Reflex
the end result of it relaxation of muscle by incresing tension
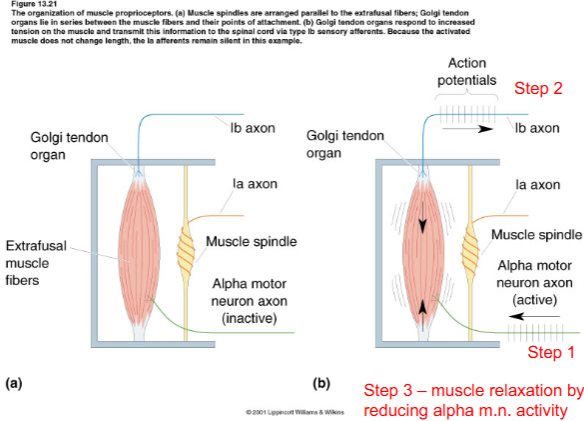
What receptor triggers the Reverse Myotatic Reflex?
Golgi tendon organ
Which afferent fiber type mediates the Reverse Myotatic Reflex?
Group lb afferents
What do Group Ib afferents do in this reflex?
Activate an inhibitory interneuron in the spinal cord.
What is the effect of the inhibitory interneuron?
It inhibits the alpha motor neuron of the homonymous muscle.
What happens to the muscle when tension increases?
The muscle relaxes (protects against excessive force).
Resiprocal Inhibition
contraction of homonymous muscles (flexors) accompanied by the relaxation of antagonist muscles (extensors)
The steps as well
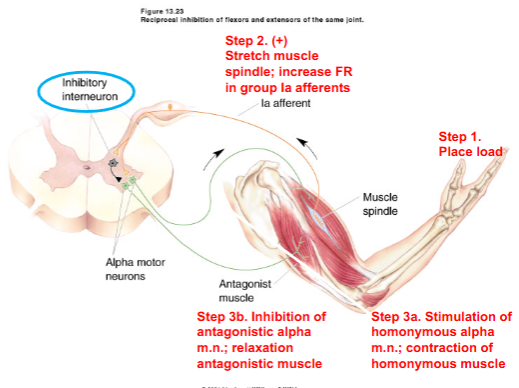
What does Reciprocal inhibition allow
inhibitiory interneuron allows for opposite response (relaxation) of antagonistic muscle
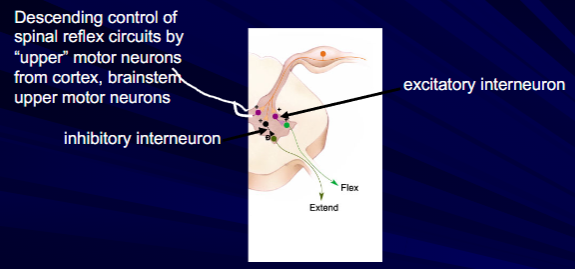
What does Spinal reflex circuits contain?
contain inhibitory and excitatory interneurons and are modified by descending inpout from brain.
motor neuron excitability depends on the combined inpout from local, central and peripheral sources.
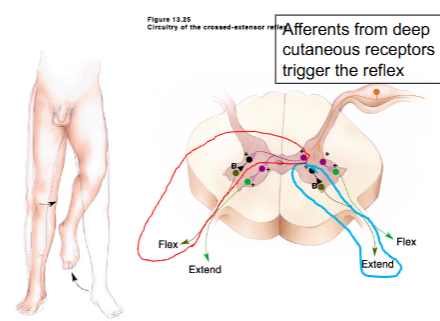
What is Crossed Extensor reflex
coordinated motor reflexes depend on reciprocal inhibitioin and reciprocal innervation
Wha does reciprocal innervation do in crossed extensor reflex?
inhibitory interneurons inhibit motor neuron controlling contralateral flexors
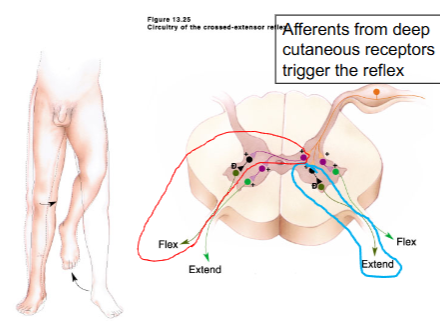
Wha does reciprocal inhibition do in crossed extensor reflex?
inhibitory interneuron allows inhibition of ipsilateral extensors