Economics AS general
1/193
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
194 Terms
Scarcity
The imbalance between an infinite number of human wants and a finite quantity of resources within society
What is the definition of utility?
Utility refers to the level of satisfaction a consumer receives from the consumption of a product or service
Demand
The amount demanded by consumers at a given price over a given period of time
Inelastic demand
Where the price of the good has a very low effect on the demand from consumers.
opportunity cost
Cost of the next best alternative use of money, time, or resources when one choice is made rather than another
Basic Economic Problem
There in an imbalance between the unlimited human wants and needs and limited economic resources (scarcity).
supply
The quantity of something that producers have available for sale
What assumptions do we make about consumers, firms and the government?
Consumers act rationally to maximise their utility
Firms act rationally to maximise profits
Governments aim to maximise economic welfare
What does a demand curve show?
How price affects the quantity of goods that can be demanded
Elastic demand
Where a small change in the price of a good or service causes a large change to the quantity demanded.
What is ceteris paribus?
All other variables held constant
What must effective demand include?
The ability and willingness to pay for the product or service
Price Elasticity of Demand
A measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price
demand
the quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy
What is demand?
Demand is the amount demanded by consumers at given prices over a certain period of time.
3 Economic Questions
1. What goods and services should be produced?
2. How should these goods and services be produced?
3. How should these goods be allocated?
Renewable Resources
Resources where their stocks replenish naturally. They are replaceable over time, so long as the rate of extraction does not exceed the natural renewable rate.
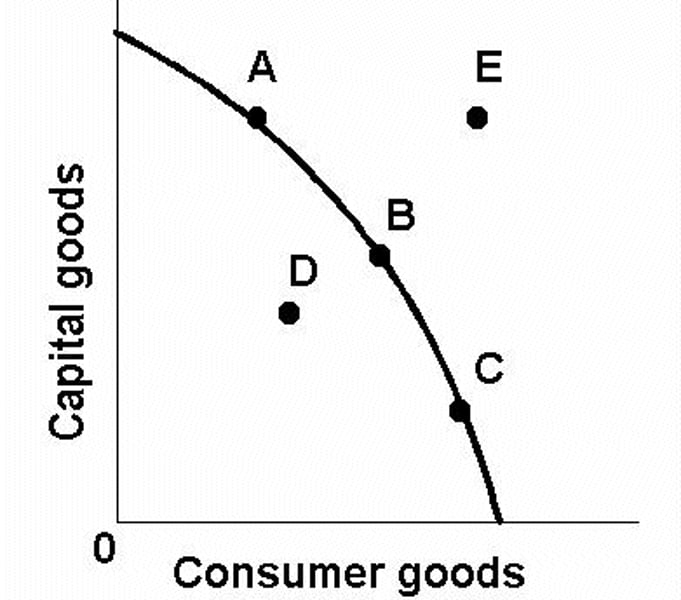
PPF (Production Possibilities Frontier)
a curve that shows the maximum potential output of an economy, when all resources are fully and efficiently employed.
What is the substitution effect?
When there is a rise in price, the consumer will tend to buy more of a low priced good, and less of a high priced one
What is a contraction in the demand curve?
When the price of a product increases, less people are willing or able to buy it, so the quantity demanded decreases.
PED formula
% change in Qd / % change in P
Can economics make scientific experiments?
No as it is a social science involving people
What is an extension in the demand curve?
When the price of a product decreases, more can be bought by consumers, so the quantity demanded increases.
What will a PED value always be?
Negative
factors of production
land, labor, capital, enterprise
What is the income effect?
When there is a rise in price, consumers will suffer a fall in their real incomes.
Non-renewable resources
Resources that are finite and will not replenish so will be eventually completed depleted.
4 things needed to start a business (factors of production)
Land, Labour, Capital, Enterprise
Scarcity
Limited quantities of resources to meet unlimited wants
What causes a shift in the demand curve?
Change in real incomes
Size oor age distribution of the population
Tastes fashions or preferences
Prices of substitute or complement goods
The amount of advertising or promotion
Interest rates
Ceteris Paribus
The assumption that all other factors remain the same.
How is PED determined from a demand curve?
It is shown by the inverse of the gradient.
What is a positive statement?
Statements based on facts which can be proven or disproven.
Complementary goods
Products and services that are used together. When the price of one falls, the demand for the other increases (and vice versa).
What value of PED shows an elastic good?
Between -1 and -10
What is total utility?
The amount of satisfaction a person . derives from the total amoun t of a product consumed
Fundamental economic problem
scarcity
Land
Space for production to take place, including natural resources, raw materials, the fertility of soil and resources found in the sea.
Labour
Number of people working in an economy, and all involved in the production of goods and services.
YED formula
% change in quantity demanded / % change in income
What is marginal utility?
The change in total utility from consuming an extra unit of product
Substitution effect
When there is a rise in price, the consumer will tend to demand more of a relatively lower-priced good, and demand less of the more expensive good, and vice versa.
What value of PED shows an inelastic good?
Between 0 and -1
What is a normative statement?
Statements that are based on VALUE judgements and so are therefore subjective
Normal good
A good that consumers demand more of when their incomes increase.
Perfectly elastic
Where the PED value is close to infinity, a small increase in price will cause a drop in demand to almost nothing (e.g. plastic bags).
What is the economic problem?
The fact that human wants are infinite but resources are limited in supply. This is known as scarcity.
What is the law of diminishing marginal utility?
It states that as consumption of a product is increased, the consumer's utility increases but at a decreasing rate
Capital
Any man-made aid to production, such as machines, buildings, IT equipment or the resources involved with the project.
PED formula
% change in quantity demanded / % change in price
Enterprise
An entrepreneur who brings together other factors of production so that goods and services can be produced and takes the risk involved in production.
XED formula
% change in quantity demanded of good X / % change in price of good Y
What is price elasticity of demand (PED)?
The responsiveness of quantity demanded due to a change in price
Inferior good
A good that consumers demand less of when their incomes increase.
Perfectly inelastic
Where the PED is almost 0, quantity demanded does not respond at all to changes in price e.g. water.
Capital goods
Goods utilised by a firm or economy to produce consumer goods and services.
PES formula
% change in quantity supplied / % change in price
What is the equation for PED?
% change in quantity demanded / % change in price
Income effect
The change in the quantity demanded of a good that results from a price rise decreasing consumers' purchasing power and therefore real incomes, and vice versa.
Revenue
The price of a product multiplied by the units sold.
If PED is elastic, what should you do to increase revenue?
Decrease prices
What questions does the problem of scarcity raise?
What to produce, how much to produce and when to produce.
Consumer goods
Final products for societal consumption.
What causes a movement in the supply or demand curve?
Change in price
What value will PED always be?
Negative
Determinants of Supply
Anything other than price of the current item that influences production decisions, including cost of raw materials, cost of labor, level of technology used to produce, number of producers in the market, price of related products, and expected future price.
Opportunity cost
The cost of the next best alternative foregone when an economic choice is made.
Determinants of Demand
Anything other than price of the current item that influences consumer buying decisions, including income, tastes and preferences, price of related items (substitutes and complements), number of consumers in the market, and expected future price.
What values of PED make a good price inelastic?
0 to -1
What causes a shift in the supply or demand curve?
A change to any factor other than price
If PED is inelastic, what should you do to increase revenue?
Increase prices
What are the 4 factors of production?
Land, labour, capital and enterprise
What is unitary elasticity?
When the percentage change in quantity demanded = percentage change in price, this means the revenue stays the same no matter what price is changed to.
Definition of renewable resource?
Rate of consumption is lower than rate of production
Production Possibility Frontier (PPF)
A diagram that illustrates the maximum potential output of an economy when all resources are fully employed.
Supply
The quantity of goods that sellers are willing to sell at any given price over a given period of time.
What values of PED make a good price elastic?
anything less than -1
3 determinants of demand elasticity
1. Can the purchase be delayed?
2. Are adequate substitutes available?
3. Does the purchase use a large portion of income?
Diminishing returns
When an economic decision is made which leads to a loss of money overall.
3 determinants of supply elasticity
1. Time
2. Spare capacity
3. Stockpiling
What value of PED makes a good unit elastic?
-1
What is an extension of the supply curve?
When the price of the good rises, the sellers will want to sell more of that good, and so the supply increases
What factors affect the PED value?
-Availability of substitute goods
-Type of good (necessity vs luxury)
-Starting price and magnitude of rise
-How product breadth is defined
-Nature of product (addictive)
-Durability (long lasting or not)
-Long-run cheap option, short term may go more expensive
-Proportion of income spent on it
Definition of non renewable resources?
Rate of consumption is greater than rate of production
What is the opportunity cost?
The cost of the next best alternative forgone when another option is chosen.
What should a government do to maximise tax revenue, and put consumers off certain products, bearing in mind price elasticity of demand?
Apply taxes to price inelastic products such as tobacco or alcohol, and tax elastic products they want to discourage consumers to buy, such as polluting cars.
What value of PED makes a good perfectly inelastic?
0
What is a contraction in the supply curve?
When the price of a good falls, sellers are less willing to sell, and so the supply decreases
3 economic questions
1. What goods and services should be produced?
2. How should these goods and services be produced?
3. Who consumes these goods and services?
Constant marginal returns
When there is no change to the overall quantity of output no matter where along the PPF you decide to operate.
Specialisation
When we concentrate on producing a particular good. It can happen at any level within and economy. You can specialise in a good or a service.
perfectly inelastic demand
the case where the quantity demanded is completely unresponsive to price and the price elasticity of demand equals zero
What value of PED makes a good perfectly elastic?
- infinite
What factors will cause a shift to the supply curve?
Costs of production, productivity of the workforce, subsidies (government grants to reduce production costs), technology increases the efficiency of production.
Income elasticity of demand (YED)
The responsiveness of demand for a good or service to a change in real income.
What is a PPF?
A production possibility frontier illustrates the maximum potential output of an economy when all resources are fully employed
YED formula
% change in quantity demanded / % change in income
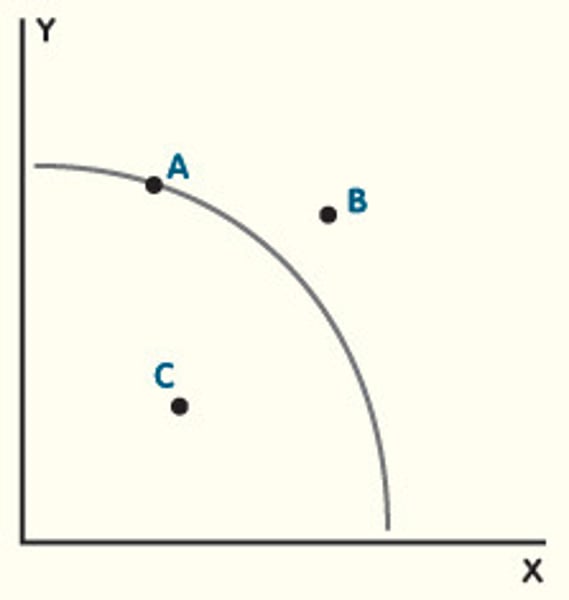
Identify what each point on the following PPF diagram means.
A) All resources are fully and efficiently employed
B) Currently unobtainable. Only obtainable with economic growth
C) Not all resources are being fully employed
Advantages of specialisation
-Higher output
-Higher quality products
-Greater choice of product (so improved living standards) for consumers due to international trade
-Economic efficiency increases (productivity)
-Reduced unit costs (in a firm)
-Increased international competitiveness
Equilibrium price
The point where supply and demand meet, where the two curves cross.