Health and Illness Course 2: Comprehensive Overview of Electrolyte Balance
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Define electrolyte balance
Interplay of electrolyte intake, absorption, distribution, and output to maintain homeostasis
What are the defining criteria for electrolyte balance?
1. Appropriate intake
2. Optimal distribution
3. Adequate intake/output to achieve proper osmolality
Excessive aldosterone leads to what disease? Too little aldosterone leads to what disease?
Too much = Cushing's disease; Too little = Addisons Disease
When is aldosterone secreted?
When sodium is low
What does aldosterone cause?
sodium and water retention
What is another name for antidiuretic hormone?
Vasopressin
When is ADH secreted/
When sodium is high
What does ADH do?
Retain water and excrete sodium
What is SIADH
Syndrome of inappropriate ADH; excess ADH results in hypervolemia meaning diluted electrolytes
What is diabetes insipidus?
Deficit of ADH results in hypovolemia causing concentrated electrolytes
What do brain natriuretic peptides do?
Inhibit kidneys reabsorption of sodium causing sodium and water loss
What are the critical values for sodium?
<120 or >160
What is the normal value of sodium?
136-145 mEq
What is the overall function for sodium?
conduct impulses, contract and relax muscles, fluid distribution
What are some signs and symptoms of hyponatremia? (CNS, muscular, GI, CV?)
Decreased excitable membrane depolarization and cellular swelling.
CNS - edema, IICP, lethargy, confusion, seizures, coma
Neuromuscular - decreased DTR, muscle weakness
GI - increased motility - cramping, nausea, diarrhea
CV - depends on vascular volume
What are eight causes of hyponatremia?
1. Diuretics
2. GI losses
3. Inadequate intake
4. Excessive diaphoresis
5. Fluid overload
6. CHF
7. Aldosterone deficiency
8. SIADH
What is the treatment for hyponatremia?
1. Increase Na+ intake
2. Restrict oral fluids
3. Strict I&O
4. Daily weight
5. Initiate seizure precautions
6. Monitor response to tx (neuro exam, Urine specific gravity, serum Na+, blood pressure, prevent hypernatremia and fluid overload)
What are some medications you could give someone with hyponatremia?
1. Hypertonic saline
2. Lithium carbonate
3. Conivaptan or tolvaptan (ADH inhibitors)
What are seizure precautions? (SLORP)
1. Oxygen and suction apparatus
2. Rails up and padded
3. Patient in side lying position asap
4. Bed in lowest position
5. Privacy asap
What are seven causes of hypernatremia?
1. Dehydration
2. Fever
3. Acute renal failure
4. Hypertonic enteral feeding w/o water bolus
5. Diabetes insipidus
6. Cushing syndrome
7. Corticosteroids
What are signs and symptoms of hypernatremia?
CNS: Extreme thirst, agitation
CV: depends on vascular volume
Muscular: Muscle twitching; as Na gets higher = decreased/absent DTR
GI: dry/sticky tongue/mucosa
Skin: Dry, flushed skin
How do you treat hypernatremia?
1. Increase h2o
2. restrict sodium
3. Strict I&O
4. Daily weight
5. Monitor response to tx (neuro, urine specific gravity, vitals)
What are medications to treat hypernatremia?
1. Hydration therapy (0.9% NS or 0.45% NS)
2. Diuretics (lasix to promote Na loss)
3. Dialysis
What electrolyte when corrected too quickly can cause demyelination?
Sodium
What are normal values for potassium?
3.5-5.0 mEq/L
What are critical values for potassium?
<2.8 or >6.2
What are some causes of hypokalemia?
1. Loop/thiazide diuretics
2. GI losses
3. Inadequate intake
4. Hyperinsulinism
5. Corticosteroids
6. Cushing's syndrome
What is the overall function of potassium?
Cellular excitability
What are some signs and symptoms of hypokalemia?
1. Respiratory muscle weakness
2. Skeletal muscle weakness (decreased DTR-paralysis)
3. CV: thready pulse, orthostatic hypotension, bradycardia
4. Decreased bowel motility: n/v, constipation, ileus, distention
5. CNS: fatigue, confusion, paresthesias
What is the treatment for hypokalemia?
1. ECG monitoring
2. Respiratory assessment
3. Encourage foods high in K
4. Use caution w/ digitalis
5. use caution if patient is receiving TPN
What are some medications that can be used for hypokalemia?
K+ supplement (always assess renal fxn before administration and never give IV push)
What are some causes of hyperkalemia?
1. Potassium sparing diuretics
2. Renal failure
3. Addison's disease
4. Use of salt substitutes
5. Cellular destruction
6. Lack of insulin
What are some signs and symptoms of hyperkalemia?
CV: bradycardia, hypotension, tall peaked T waves, heart block, cardiac arrest, ventricular fibrillation
Neuro: muscle twitching, paresthesias -> muscle weakness, flaccid paralysis -> respiratory failure
GI: Increased motility and diarrhea
What is the treatment for hyperkalemia?
1. ECG monitoring
2. Eliminate K from all meds/IV solutions
3. Restrict potassium
4. Avoid salt substitutes
5. Assess CV, Neuromuscular, and GI
What are some medications for hyperkalemia?
1. Patiromer or Kayexalate (excretes K+ in the stool)
2. Administer 50% glucose w/ regular insulin (monitor blood glucose)
3. Calcium gluconate for cardiac dysrhythmias
4. Dialysis if K+ is critically high
What is the normal value for calcium?
9-10.5 mg/dL
What are the critical values for calcium?
<6 or >13 mg/dL
What two electrolytes have an inverse relationship?
Calcium and phosphate
What does calcitonin do?
Lowers blood calcium levels
What does parathyroid hormone do?
Regulate calcium and phosphorus metabolism
What does hyperparathyroidism do to calcium levels?
Causes hypercalcemia/hypophosphatemia
What does hypoparathyroidism do to calcium levels?
Cause hypocalcemia/hyperphosphatemia
What ares some causes of hypocalceimia?
1. chronic diarrhea
2. inadequate intake
3. Vitamin D deficiency
4. Malabsorption syndromes
5. Acute pancreatitis
6. Hyperphosphatemia
7. Hypoparathyroidism
What is the function of calcium?
Regulate heart rhythms, muscle contraction, blood clotting and bone density
What are some signs and symptoms of hypocalcemia?
1. Increased DTR: Tetany, trousseau and chvosteks sign, paresthesias in hands/feet, lips, nose and ears
2. Bones become less dense
3. CV: hypotension, weak pulse, prolonged QT interval
4. Increased peristalsis
5. CNS: anxiety, irritability, seizures
6. Skin: dry, brittle hair and nails
What is trousseau's sign?
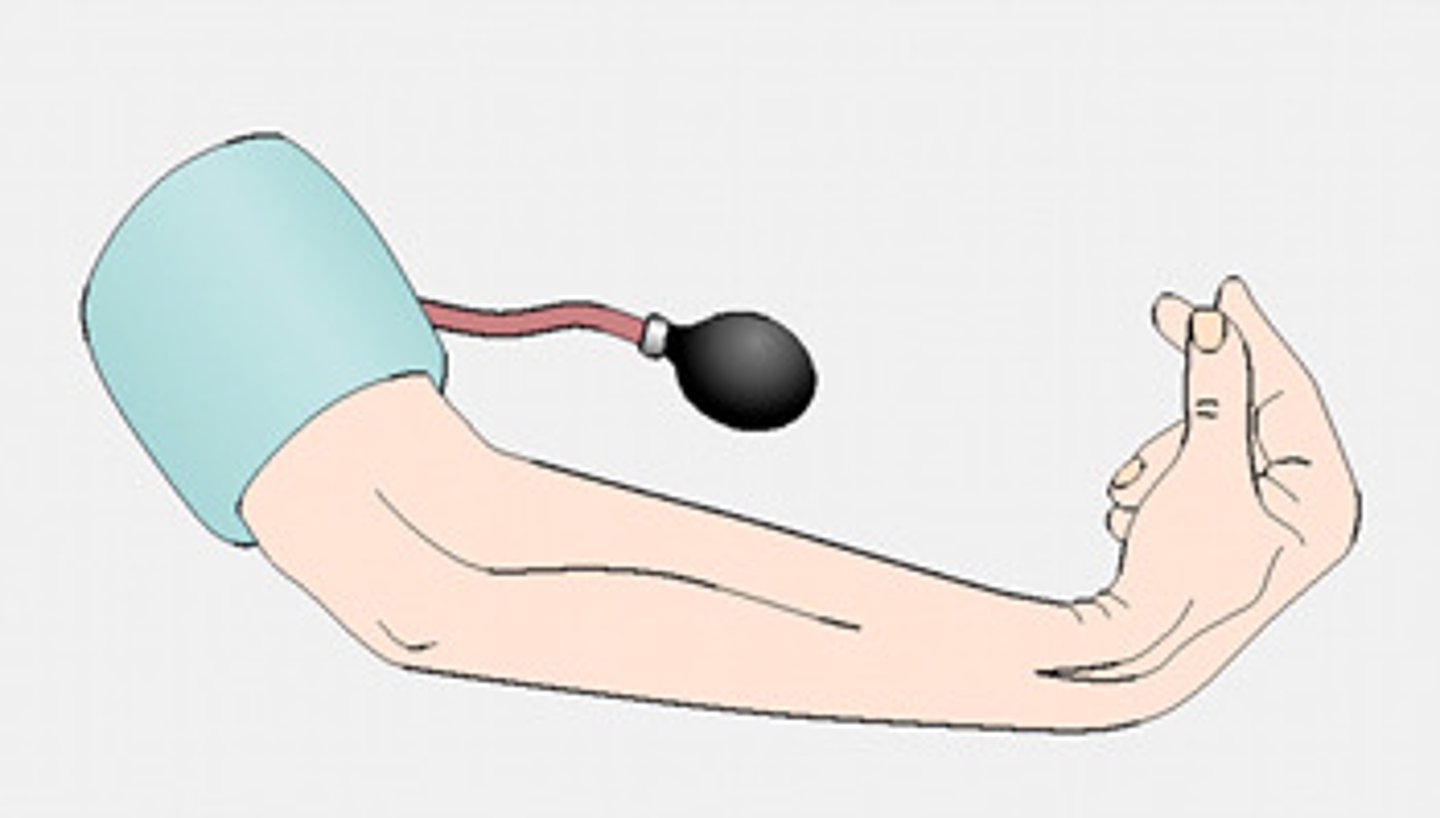
What is Chvostek's sign?
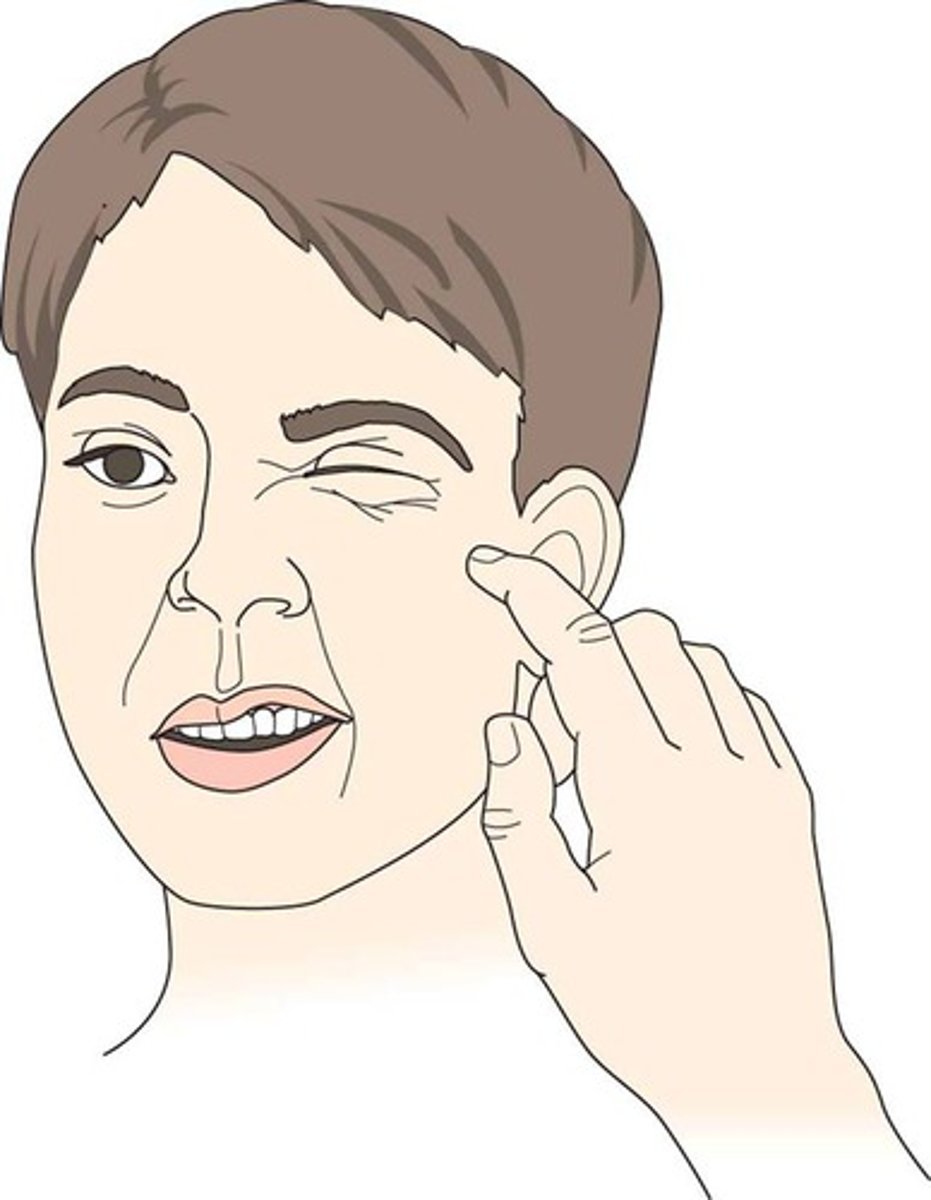
What is the treatment for hypocalcemia?
1. ECG monitoring
2. Implement seizure precautions (and reduce environmental stimuli)
3. Diet high in calcium
4. Beware of digitalis if giving calcium IV
What medications can you give for hypocalcemia?
1. IV calcium gluconate
2. Administer calcium carbonate
3. Administer vitamin D
Administer phosphate binding meds in patients with renal disease
What are causes of hypercalcemia?
1. Hyperparathyroidism
2. Vitamin D overdose
3. Lithium use
4. Malignancy
5. corticosteroid therapy
6. Thiazide diuretics
7. Renal failure
8. Immobility
9. Excessive oral intake of calcium or vitamin D
What are signs and symptoms of hypercalcemia?
CV: Mild: tachycardia and HTN, Severe or prolonged: decreased HR, heart blocks, cardiac arrest
Neruomusc: decreased DTR, weakness, confused
Skeletal: fractures, deep bone pain
GI: decreased motility
What is the treatment for hypercalcemia?
1. Monitor I&O
2. Monitor vitals
3. Assess for mental status changes
4. Eliminate calcium in diet and meds
5. Encourage large amounts of fluid (3-4L/day)
6. Mobilize pt
7. Partial parathyroidectomy
What are some medications for hypercalcemia?
1. Hydration therapy
2. IV phosphate
3. Loop diuretics
4. IM calcitonin for hypercalcemic crisis (emergency)
5. Renal dialysis
What are the normal values for magnesium?
1.8-2.6 mg/dL
What are the critical values for magnesium?
<1.0 or >6.0
What is the primary function of magnesium?
Muscle relaxation
What are some causes of hypomagnesemia?
1. Loop/thiazide diuretics
2. GI losses
3. Malabsorption disorders
4. Inadequate intake
5. Alcohol use disorders
What are signs and symptoms of hypomagnesemia?
CV: Increased cardiac activity (tachycardia, a-fib vent-fib, MI)
Neuromuscular: Tense muscles (tetany, increased DTR, seizures, chvostek and trosseau's signs)
GI: decreased motility (constipation, n/v, cramping)
What is the treatment for hypomagnesemia?
1. Seizure precautions
2. Cardiac monitoring
3. Can treat with diet if mild
What medications can be used to treat hypomagnesemia?
1. IV magnesium sulfate
2. Magnesium oxide or gluconate PO
3. Include magnesium if TPN
What is important to know about IV magnesium sulfate?
1. never give IV push
2. monitor DTR
3. Monitor urine output
4. Stop IV infusion if urine output <100 mL in 4 hours
What are some causes of hypermagnesemia?
1. Acute or chronic kidney disease
2. Antacids containing magnesium
3. Large amounts of IV mag given to treat HTN in pregnancy
4. Adrenal insufficiency
What are some signs and symptoms of hypermagnesemia?
CV: decreased cardiac activity (bradycardia, vasodilation, MI, hypotension)
CNS: suppression (drowsy, lethargic, coma)
Neuromuscular: muscle weakness (decreased DTR)
Respiratory: Depression
What is the treatment for hypermagnesemia?
1. Avoid Mg in meds/diet
2. Cardiac monitoring
3. Monitor kidney fxn
4. Monitor RR and BP
5. monitor DTR
6. Mechanical ventilation for respiratory failure
What medications are given for hypermagnesemia?
1. Give fluids to excrete magnesium if kidneys functioning.
2. Renal dialysis (if kidneys not functioning)
3. Loop diuretics
4. IV calcium gluconate (emergencies)
What is the normal value for phosphate?
2.5-4.5 mg/dL
What are critical values for phosphate?
<1.5 mg/dL
What are causes of hypophosphatemia?
1. Intestinal malabsorption or malnutrition
2. Hyperparathyroidism
3. Excessive use of antacids or diuretics
What are signs and symptoms of hypophosphatemia?
CNS: confusion, seizures
Neuromuscular: Muscle weakness, bone pain, paresthesias
Respiratory: Decreased RR -> Failure
What is the treatment for hypophosphatemia?
1. Fall bundle and seizure precautions
2. Encourage high phosphorus diet - add to tube feedings
What medications can be given for hypophosphatemia?
1. PO phosphates with vitamin D
2. IV phosphorus limited to those with severe hypophosphatemia
What are causes of hyperphosphatemia?
1. Increased intake
2. Acute/chronic renal failure
3. hypoparathyroidism
4. Excess vitamin D intake
5. Muscle necrosis - rhabdomyolysis
What are signs and symptoms of hyperphosphatemia?
Neuromuscular: Increased muscle excitability (tetany, chvostek and trousseau's sign, increased DTR)
GI: n/v, anorexia
What is the treatment for hyperphosphatemia?
1. Seizure precuations
2. Neuro assessment
3. Avoid foods with phosphate
4. Increase fluids
5. Renal dialysis
What are medications given for hyperphosphatemia?
1. Calcium supplements (if calcium deficient)
2. Phosphate binders w/ meals
3. Calcitriol
4. Loop diuretics
5. Hydration therapy
What are some foods high in calcium?
1. Dairy produts
2. Green leafy vegetables
3. Canned salmon and sardines/fresh oysters
What are some foods high in potassium?
1. Bananas, oranges, cantaloupe, honeydew melon, apricotes, grapefruit
2. Dried fruits
3. Legumes, whole grains
4. Spinach/leafy greens
5. potatoes/sweet potatoes
6. Juices
7. Meats, poultry, fish
What are some foods high in magnesium?
1. Pumpkin seeds
2. Nuts
3. Spinach
4. Soymilk
5. black beans/kidney beans/black-eyed peas
6. Dark chocolate
7. Whole wheat bread
8. Avocados
9. potatoes
10. Rice
11. Salmon, halibut, mackerel and pollock
12. Broccoli
What are some foods high in sodium?
1. Bread and rolls
2. Pizza
3. Sandwiches
4. Cold cuts/meats
5. Soup
6. Burritos/tacos