Marieb Muscles 1
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
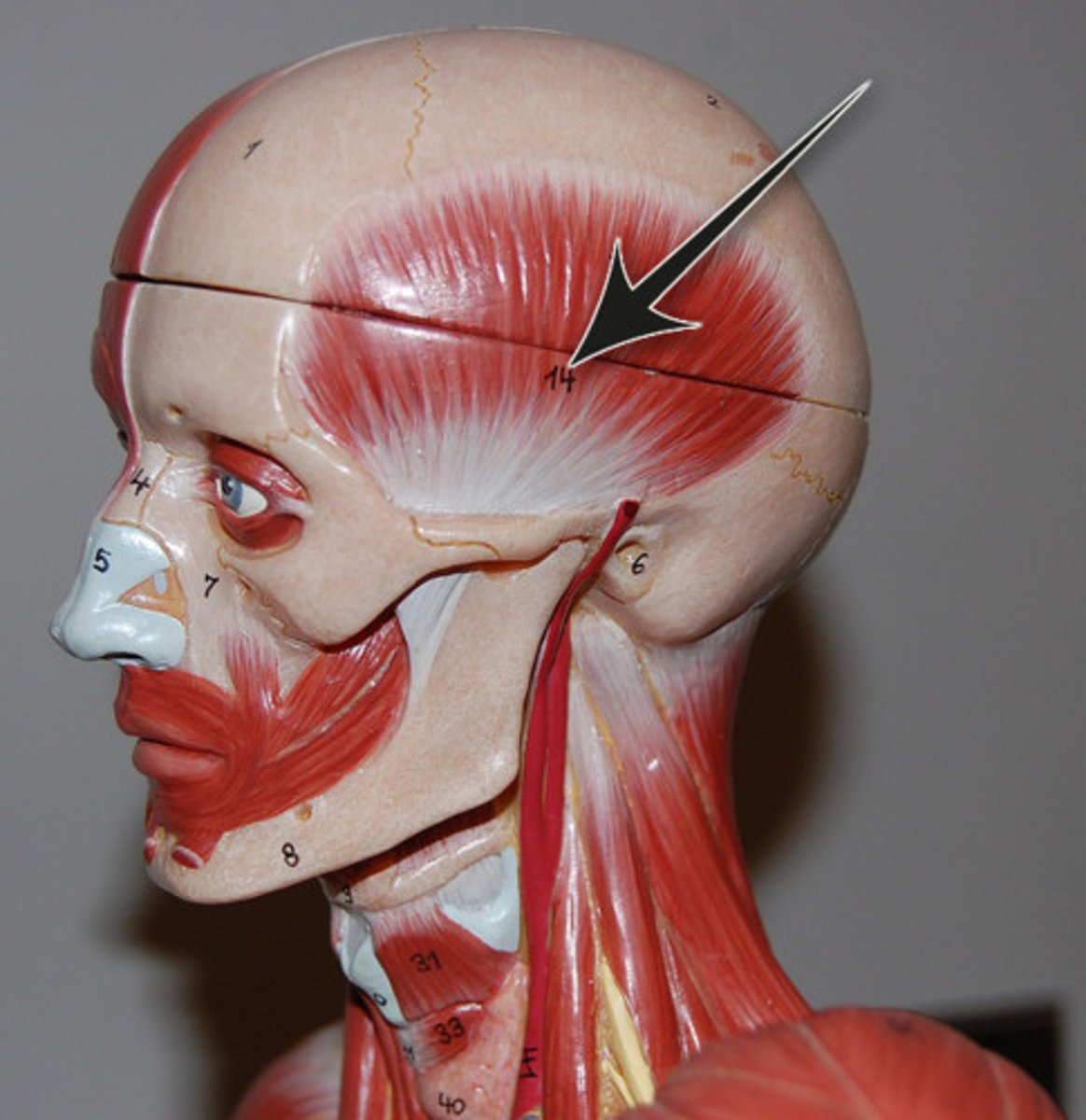
Frontalis (frontal belly of epicranius)
Covers forehead and dome of skull; no bony attachments.
O-epicranial aponeurosis
I-skin of eyebrows and root of nose
A-raises the eyebrows; wrinkles forehead
N-Facial nerve
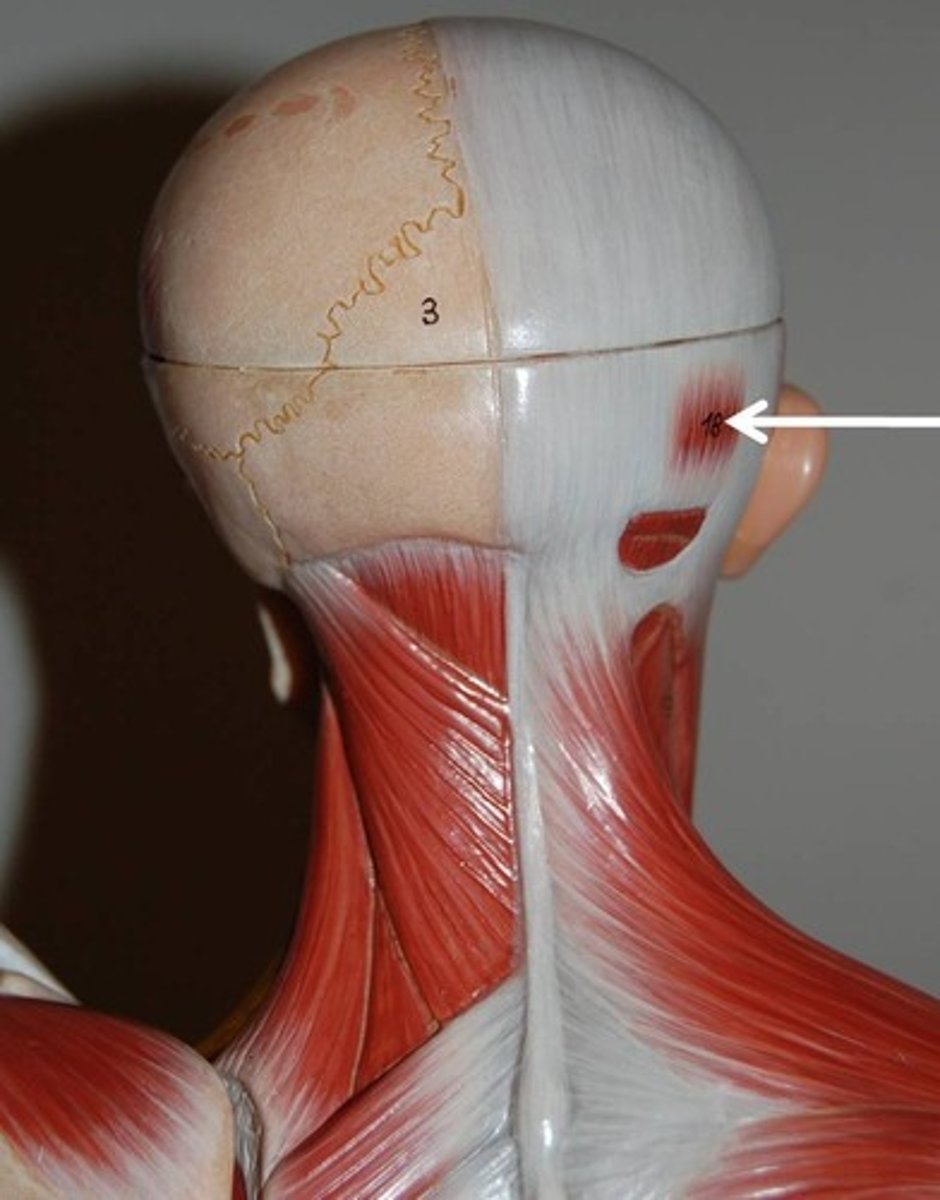
Occipitalis (occipital belly of the epicranius)
Overlies posterior occiput; by pulling on the epicranial aponeurosis, fixes origin of frontal belly
O-occipital and temporal bones
I-epicranial aponeurosis
A-Fixes aponeurosis and pulls scalp posteriorly
N-Facial nerve
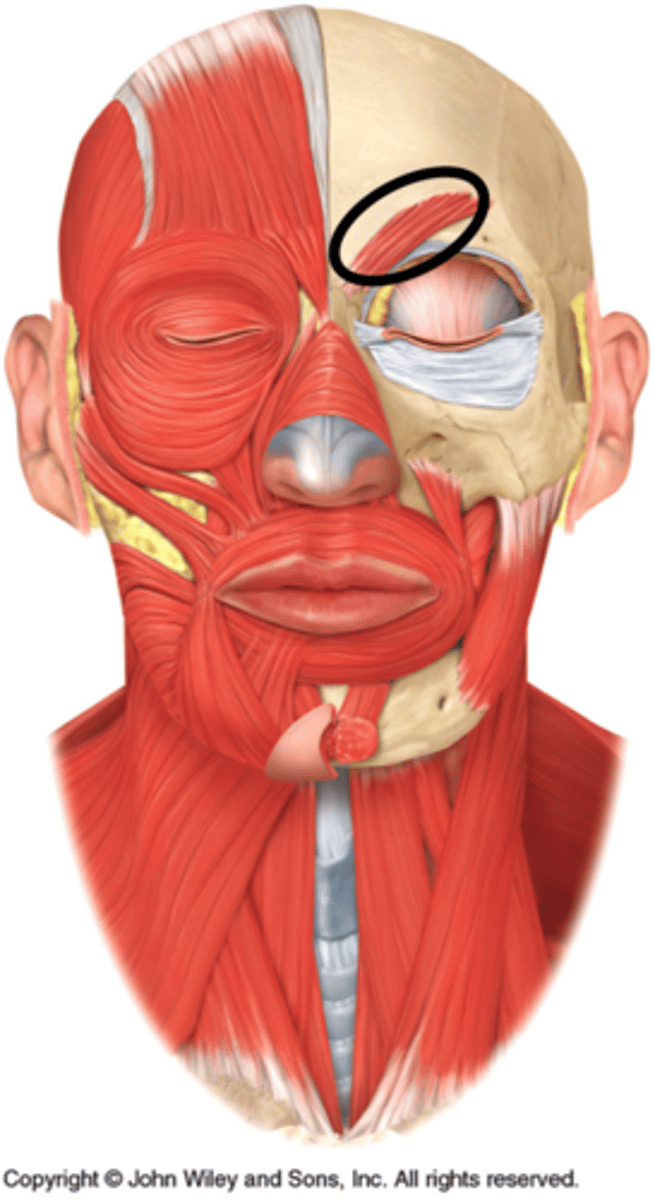
corrugator supercilii
Small muscle; activity associated with that of orbicularis oculi
O-arch of frontal bone above nasal bone
I-skin of eyebrow
A- Draws eyebrows medially and inferiorly; wrinkles forehead vertically (for frowning)
N-facial nerve
orbicularis oculi
thin, flat sphincter muscle of eyelid; surrounds rim of the orbit
O-frontal and maillary bones and ligaments around orbit
I-tissue of eyelid
A-closes eye; produces blinking and squinting
N-facial nerve
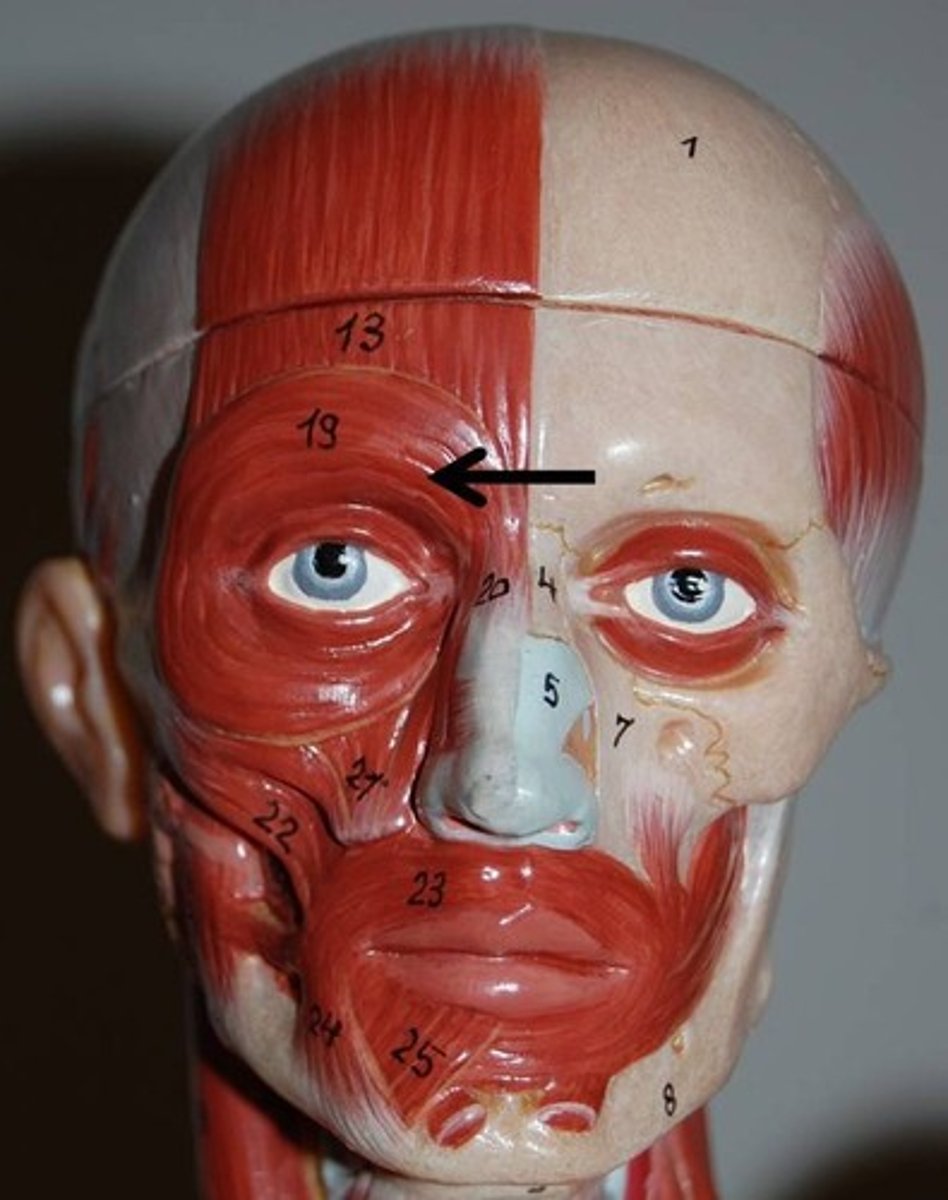
Zygomaticus major and minor
muscle pair extending diagonally from cheekbone to corner of mouth
O-zygomatic bone
I-skin and muscle at corner of mouth
A-Raises lateral corners of mouth (smiling muscle)
N- Facial nerve
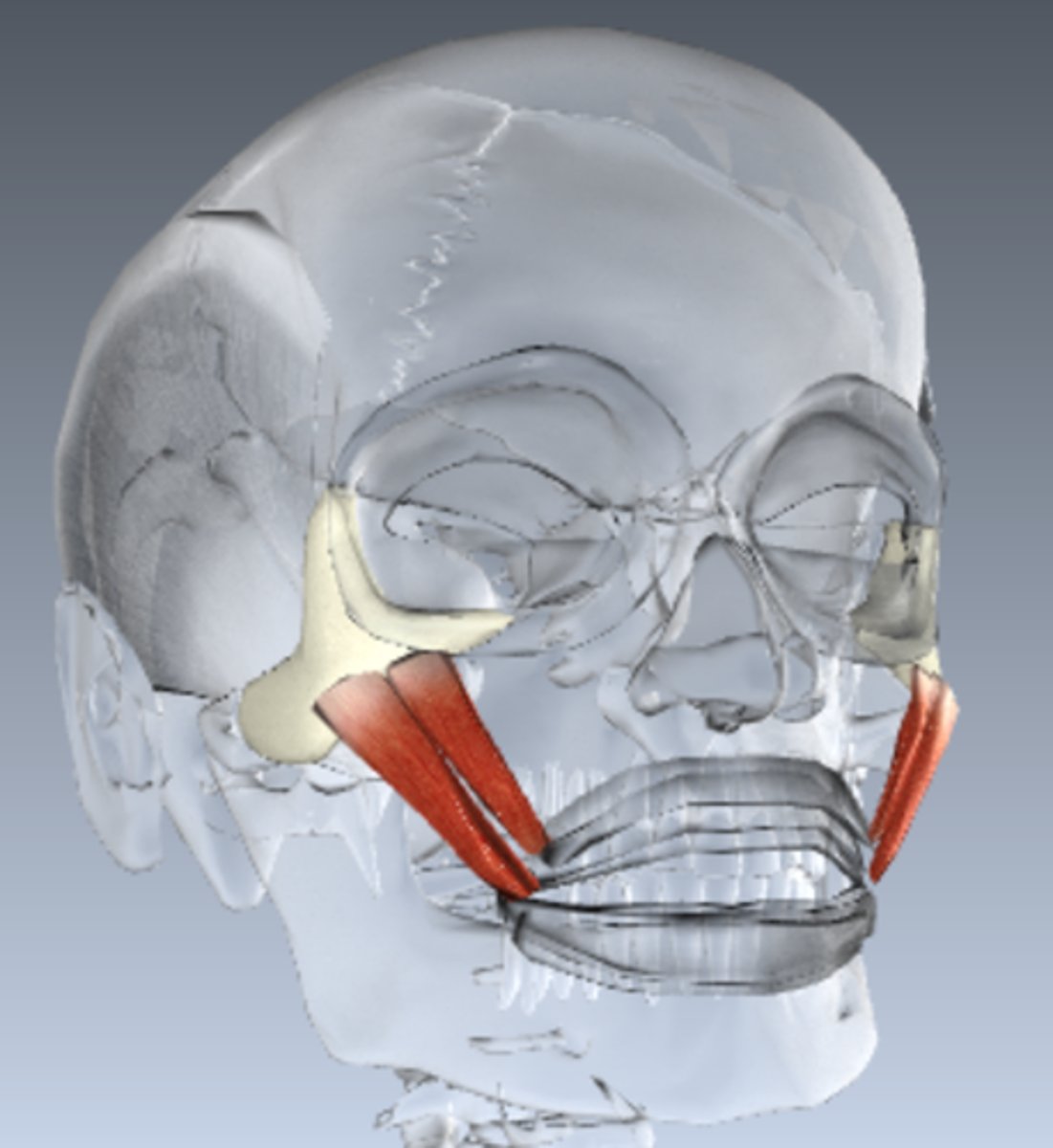
Risorius
Slender muscle inferior and lateral to zygomaticus
O-lateral fascia associated with masseter muscle
I-skin at angle of mouth
A-Draws corner of lip laterally; tenses lips; zynergist of zygomaticus
N-Facial nerve
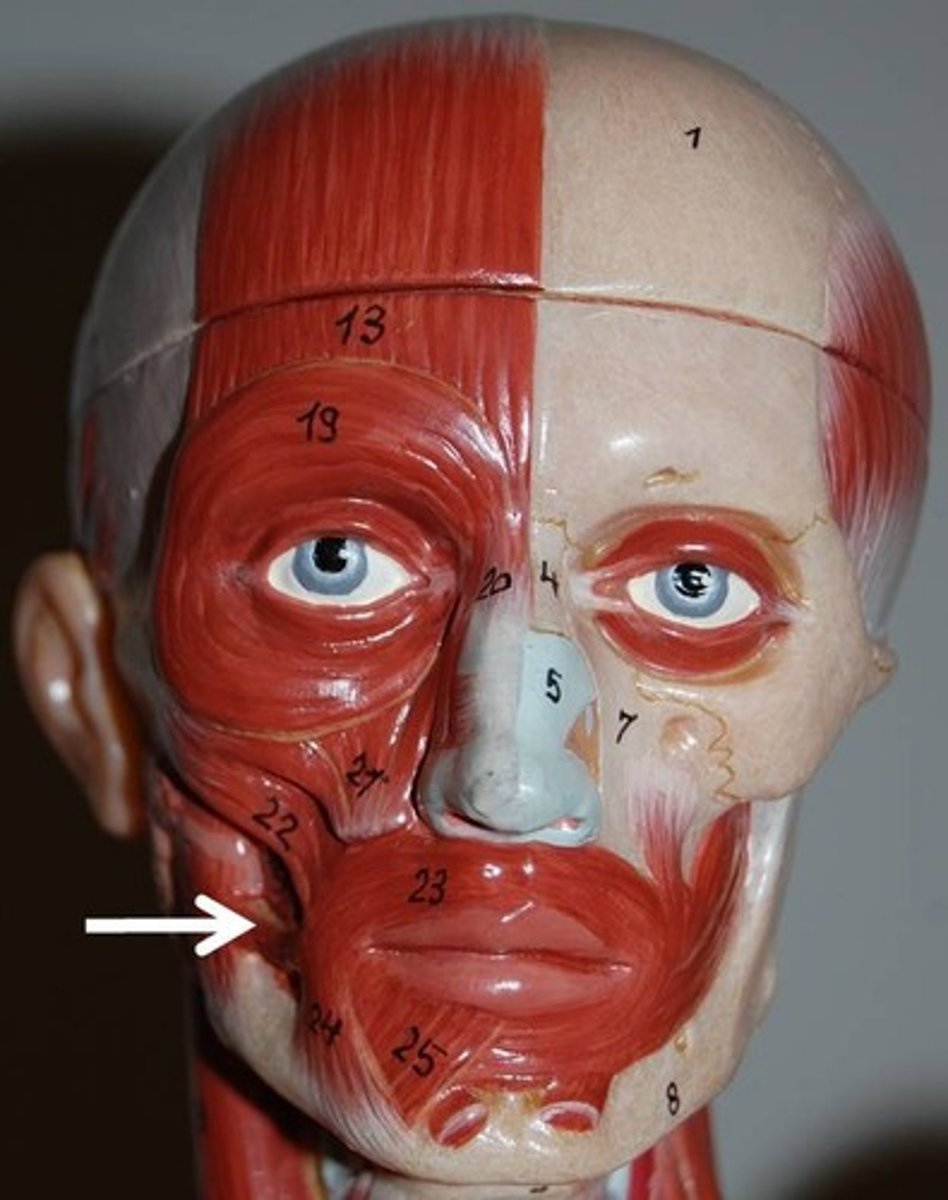
levator labii superioris
The muscle between orbicularis oris and inferior eye margin
O-zygomatic bone and infraorbital margin of maxilla
I-skin andd muscle of upper lip
A-Opens lips; raises and furrows upper lip
N-facial nerve
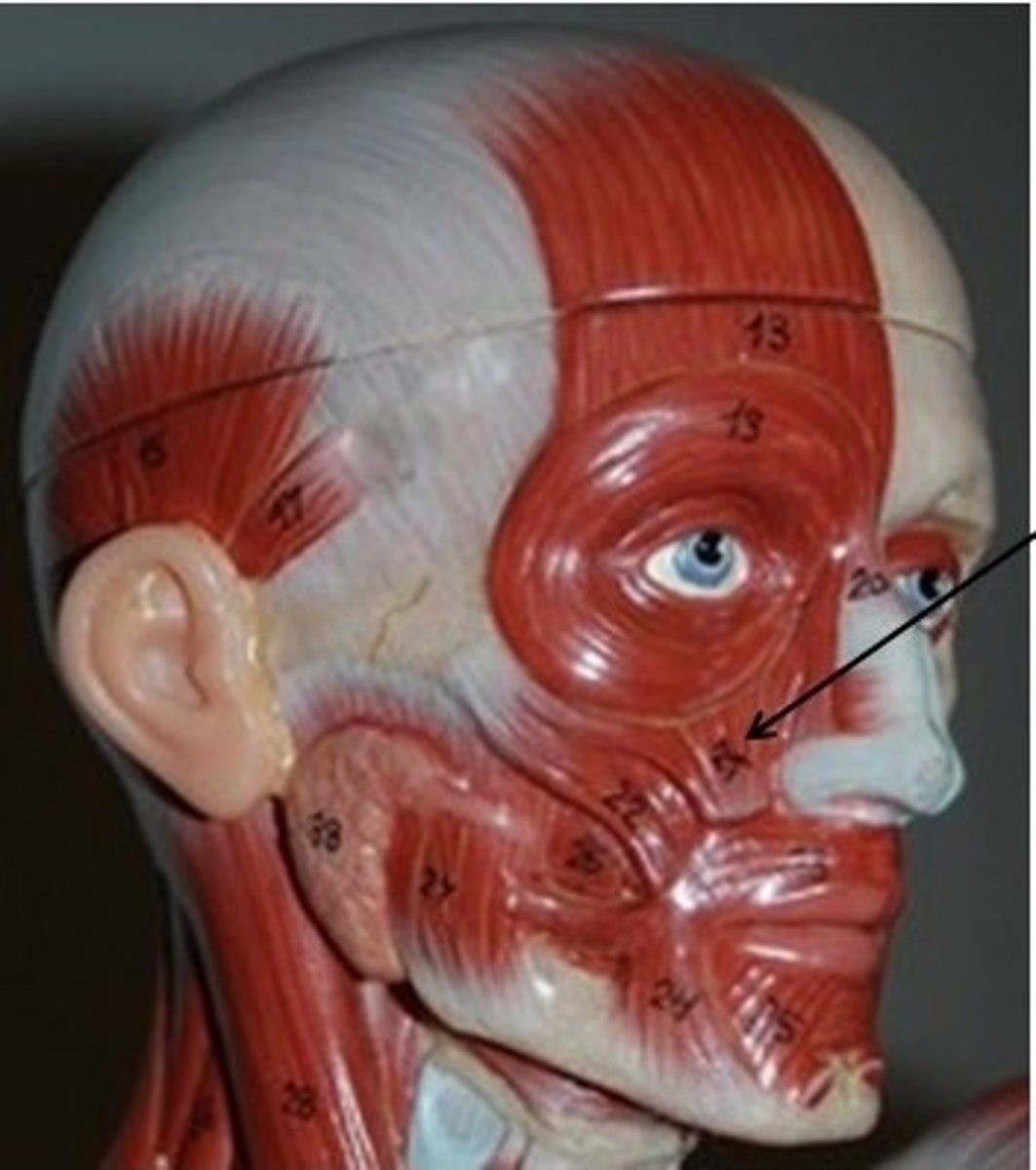
depressor labii inferioris
Small muscle running from mandible to lower lip
O-body of mandible latral to its midline
I-skin and muscle of lower lip
A-Draws lower lip inferiorly (as in pout)
N-facial nerve
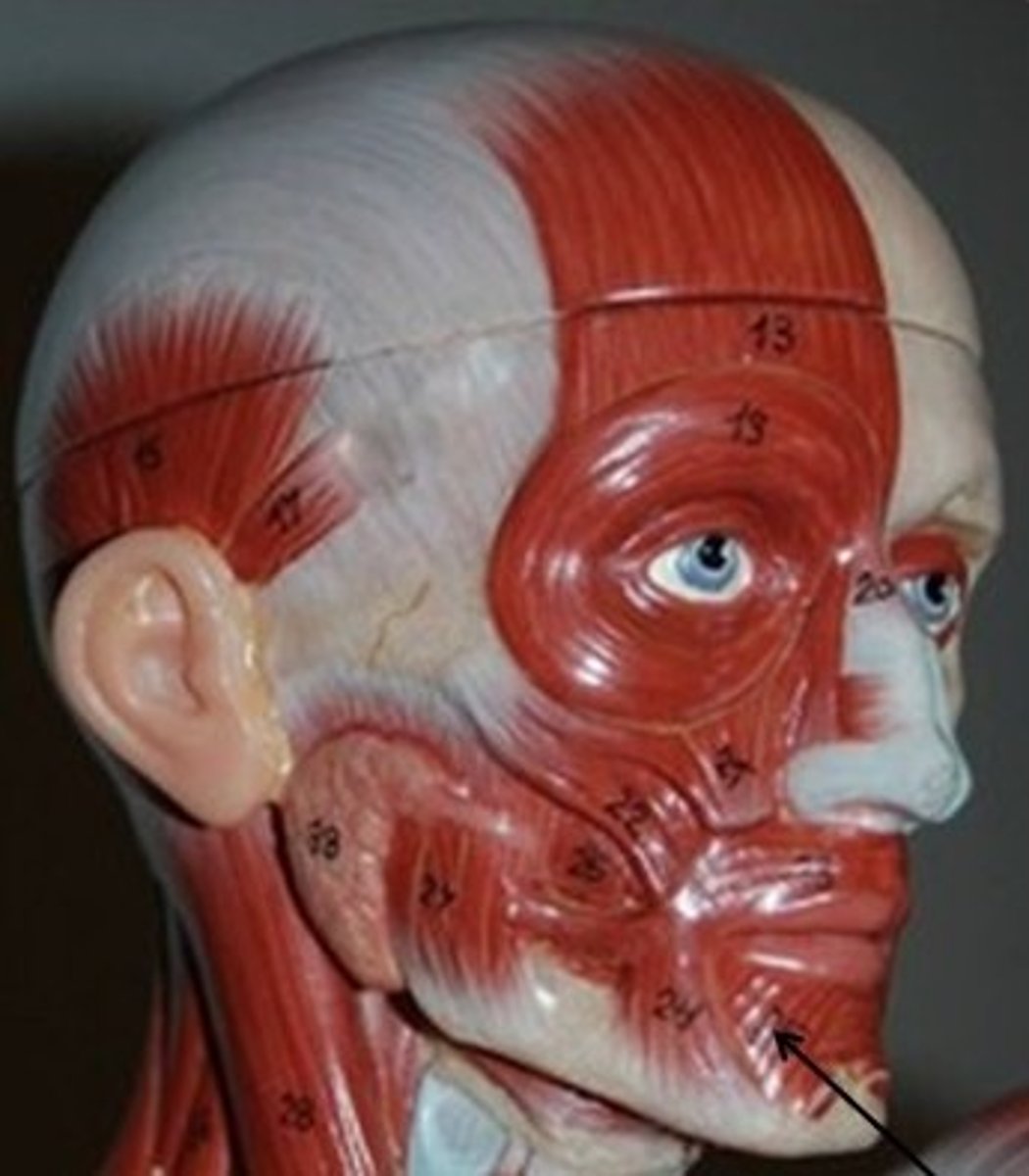
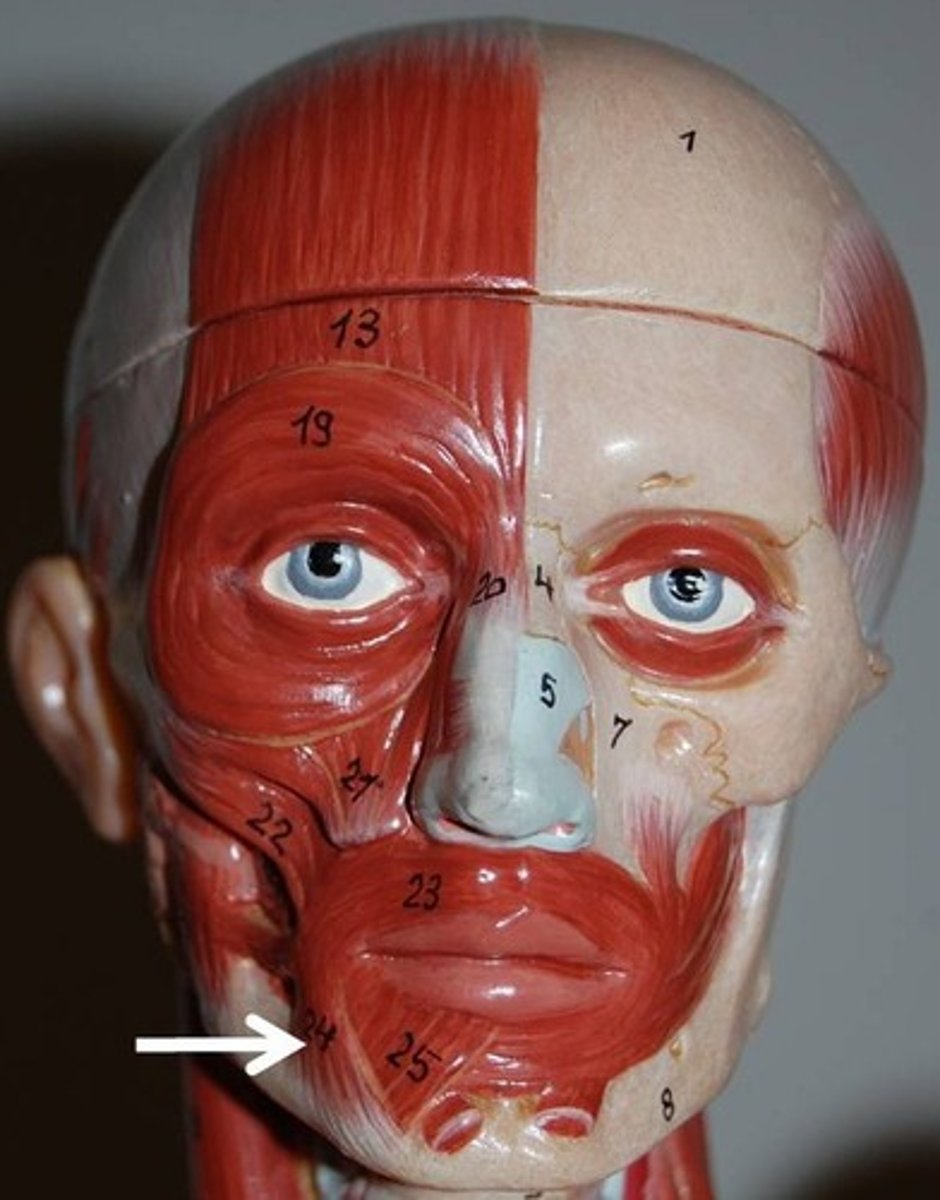
depressor anguli oris
small muscle lateral to depressor labii inferioris
O-body of mandible below incisors
I-skin and mmuscle at angle of mouth below insertion of zygomaticus
A-Draws corners of mouth down and laterally (a grimace); zygomaticus antagonist
N-facial nerve
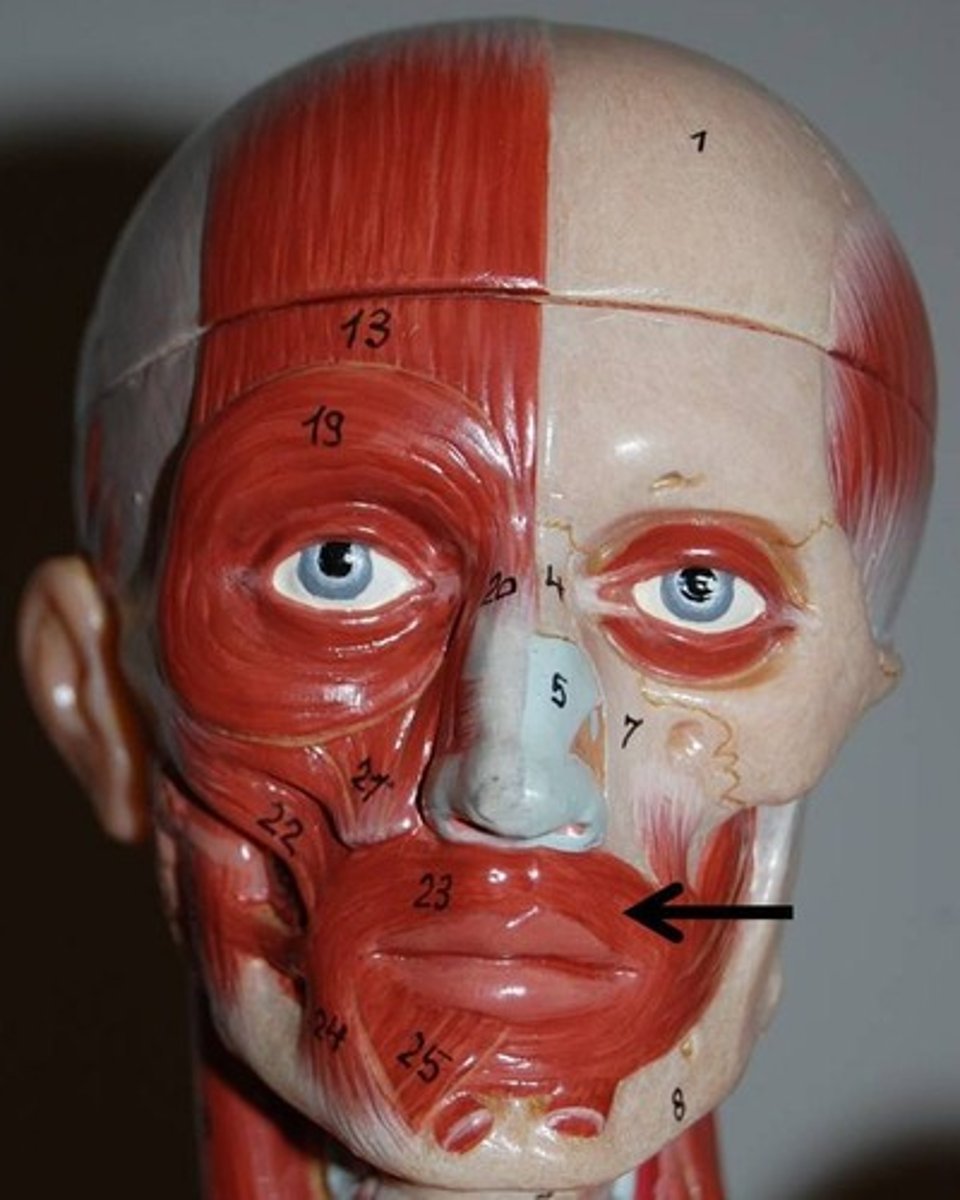
Orbicularis oris
Complicated, multilayered muscle of the lips with fibers that run in many directions; most run circularly
O-arises indrectly from maxilla and mandible; fibers blend with fibers of other facial muscles associated with the lips
I-encircles mouth; inserts into muscle and skin at angles of mouth
A-Closes lips; purses and protrudes llips; kissing and whistling
N-Facial nerve
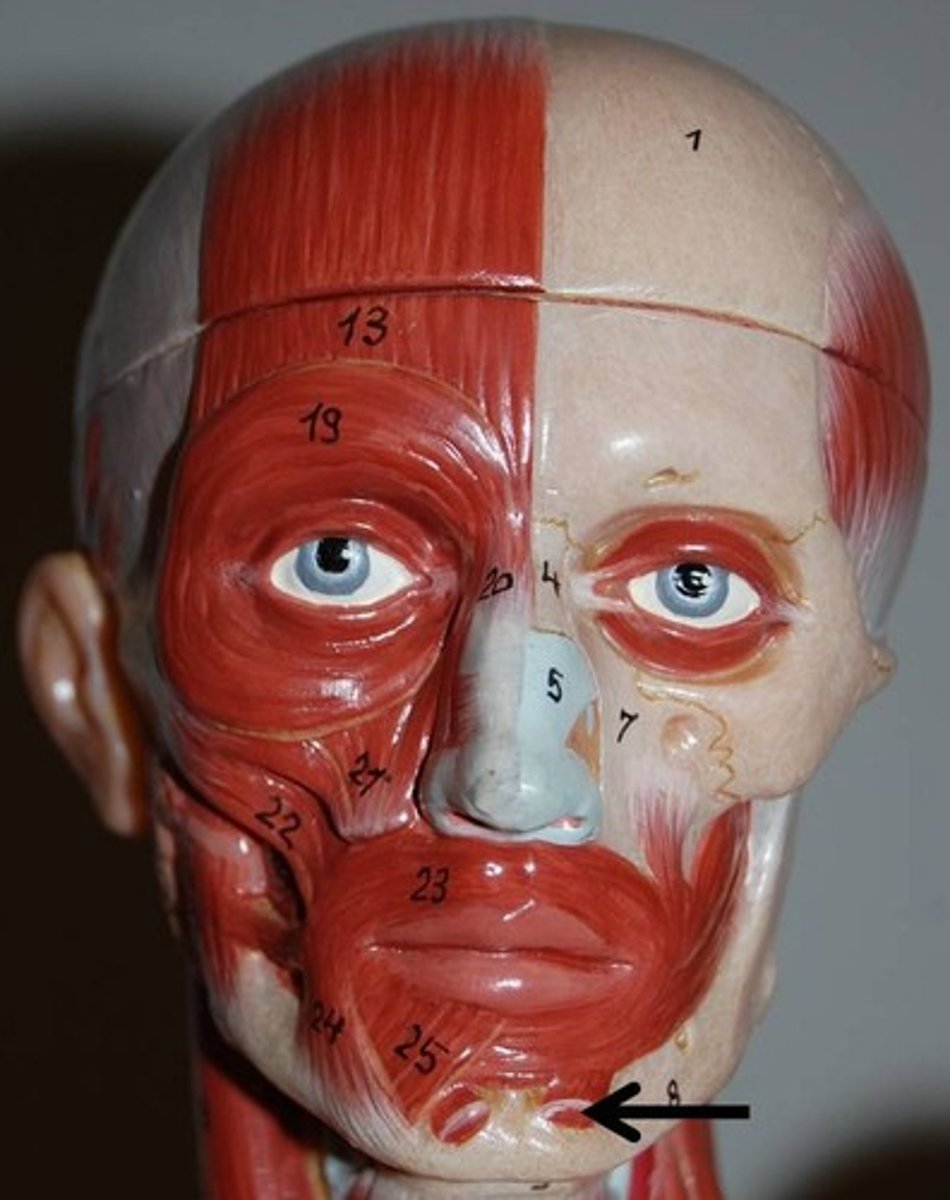
Mentalis
One of muscle pair forming a V-shaped muscle mass on chin
O-mandible below incisors
I-skin of chin
A-wrinkles chin; protrudes lower lip (as in pout)
N-facial nerve
Buccinator
Thin, horizontal cheek muscle; principal muscle of cheek; deep to masseter
O-molar region of maxilla and mandible
I-orbiccularis oris
A-Compresses cheek (as in whistling and sucking); holds food between teeth during chewing; draws corner of mouth laterally; well developed in nursing infants
N-Facial nerve
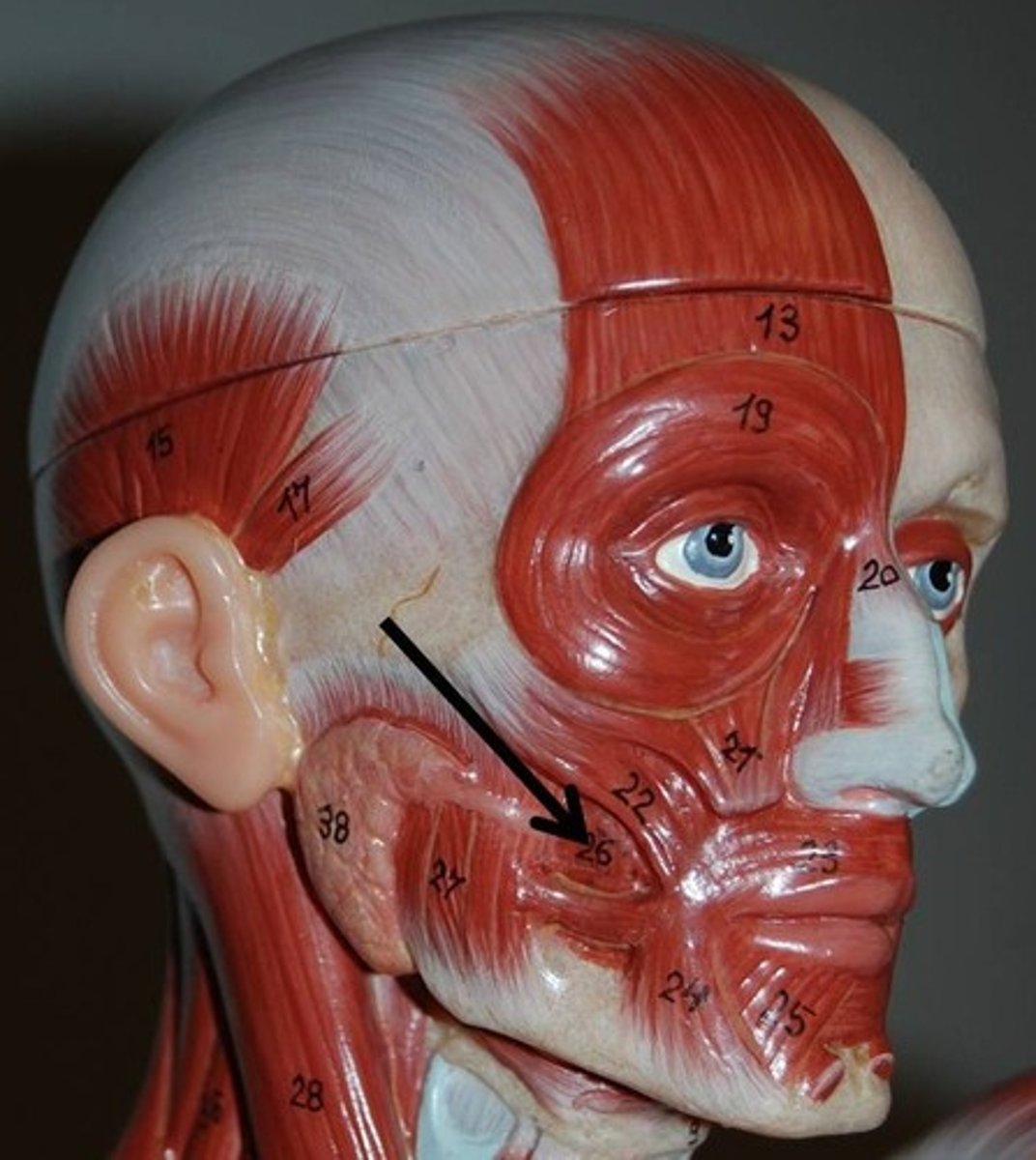
Masseter
Powerful muscle that covers lateral aspect of mandibular ramus
O-zygomatic arch and zygomatic bone
I-angle and ramus of mandible
A-Prime mover of jaw closure; elevates mandible
N-Trigeminal nerve
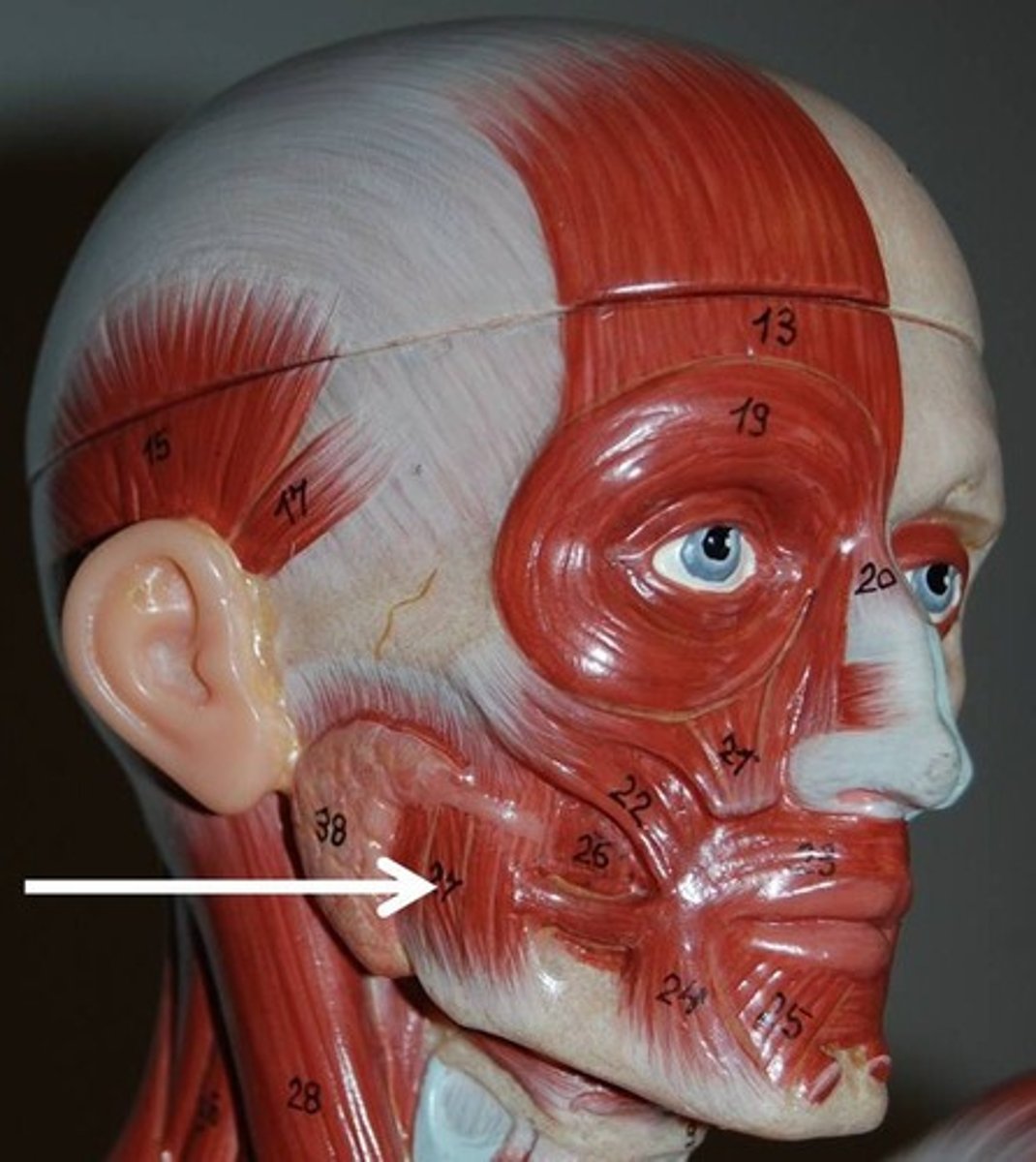
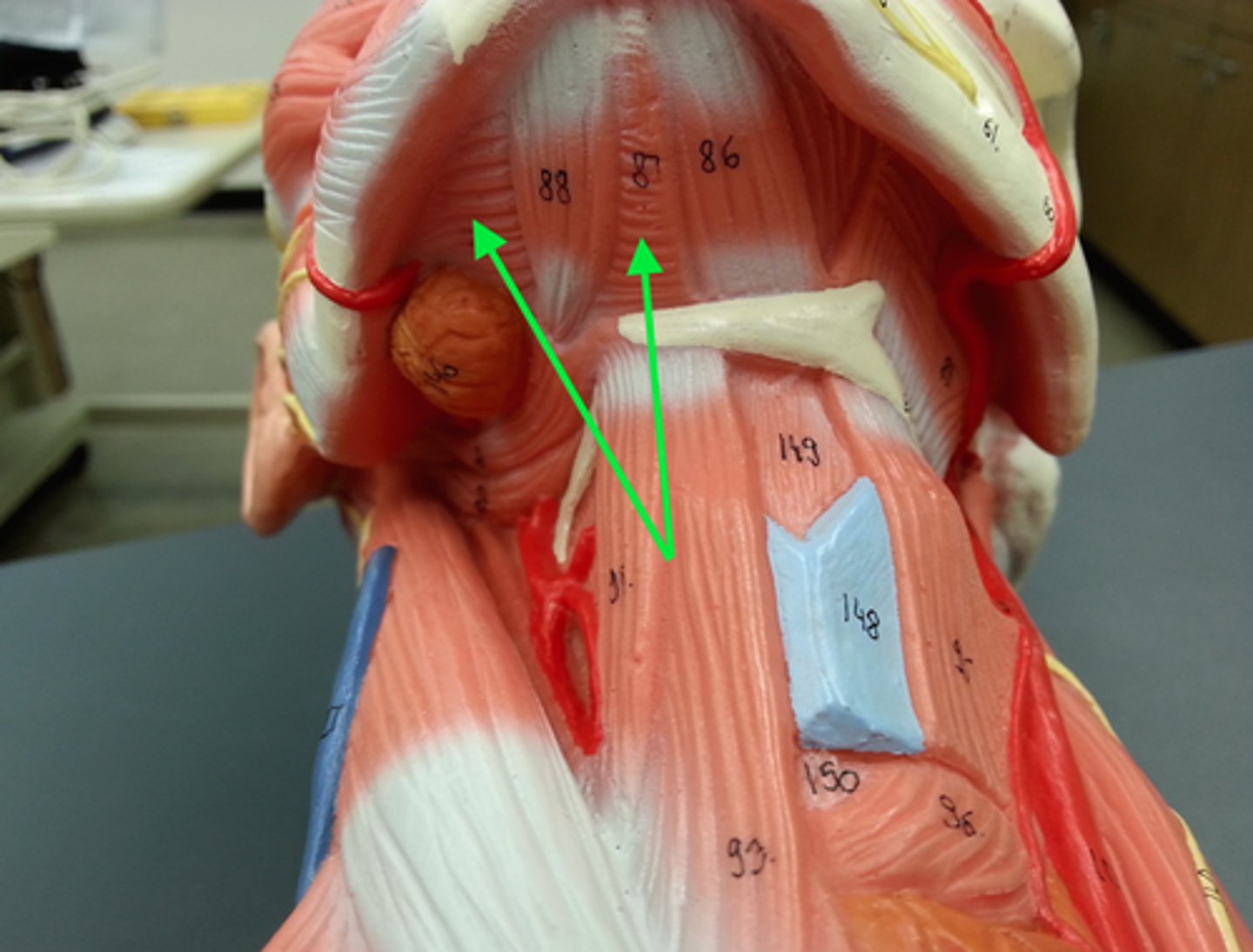
Temporalis
Fan-shaped muscle that covers parts of the temporal, frontal, and parietal bones
O-temporal fossa
I-coronoid process of mandible via a tendon that passes deep to zygomatic arch
A-closes jaw; elevates and retracts mandible
N-trigeminal nerve
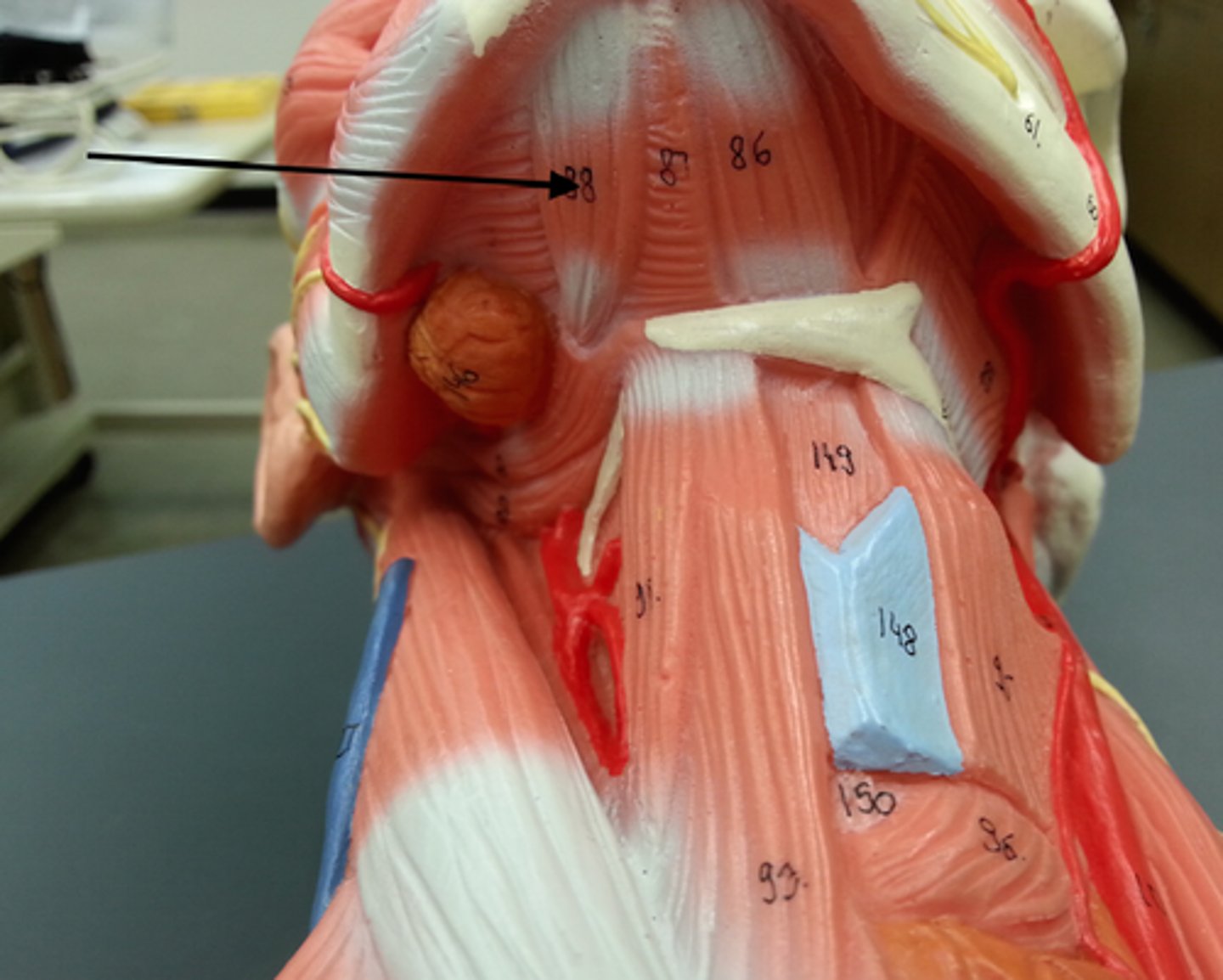
suprahyoid muscles
Muscles that help form floor of oral cavity, anchor tongue, elevate hyoid, and move larynx superiorly during swallowing; lie superior to hyoid bone; includes digastric, stylohyoid, mylohyoid, geniohyoid
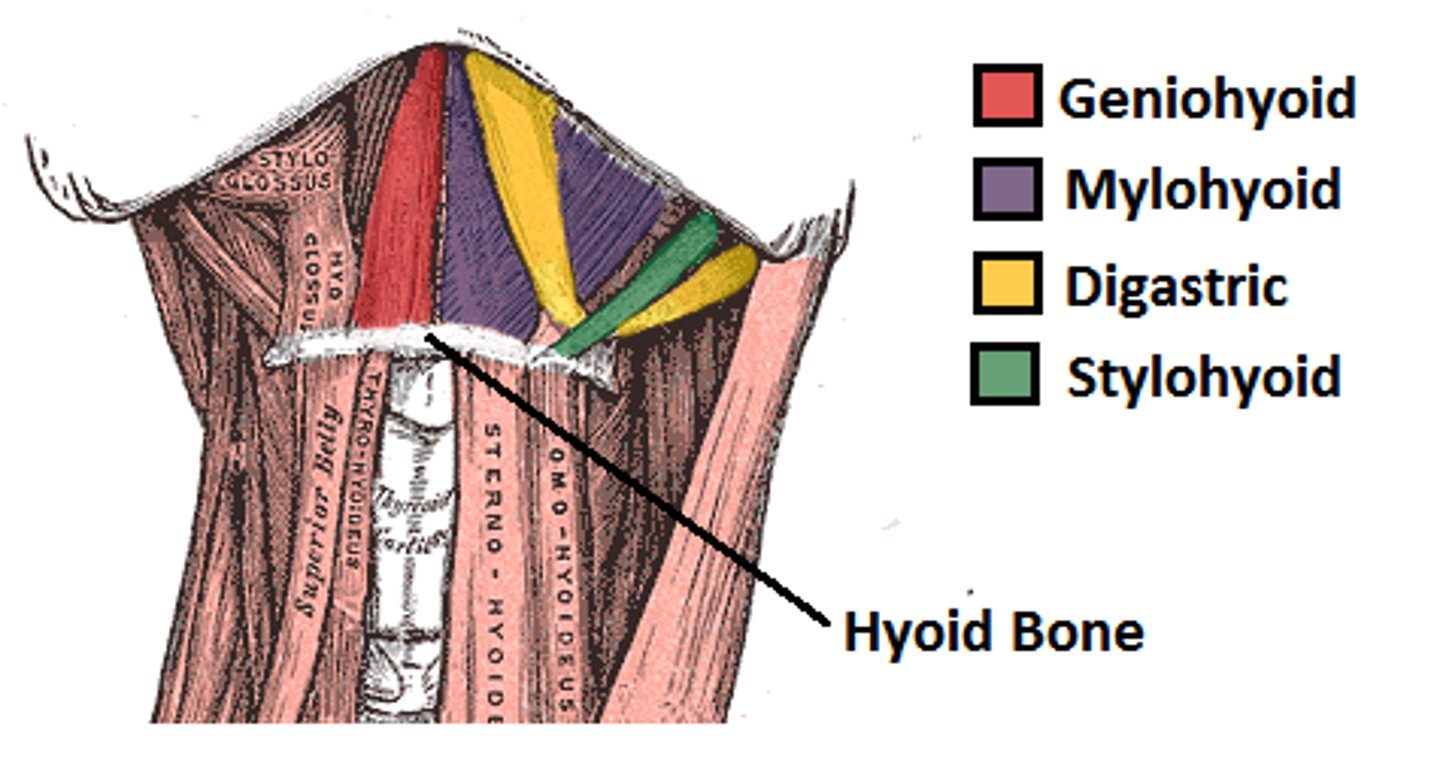
Digastric
Consists of tw bellies united by an intermediate tendon, forming a v shape under the chin
A-open mouth and depress mandible; acting in synergy, the digastic muscles elevate hyoid bone and steady it during swallowing and speech
Stylohyoid
Slender muscle below angle of jaw; parallels posterior belly of digastric muscle
A-Elevates and retracts hyoid, thereby elongating floor of mouth during swallowing
Mylohyoid
Flat triangular muscle just deep to digastric muscle; this muscle pair makes a sling that forms the floor of the anterior mouth
A-Elevates hyoid bone and floor of mouth, enabling tongue to exert backward and upward pressure that forces food into pharynx
Geniohyoid
Narrow muscle in contact with its partner medially; runs from chin to hyoid bone deep to mylohyoid
A-pulls hyoid bone superiorly and anteriorly, shortening floor of mouth and widening pharynx to receive food
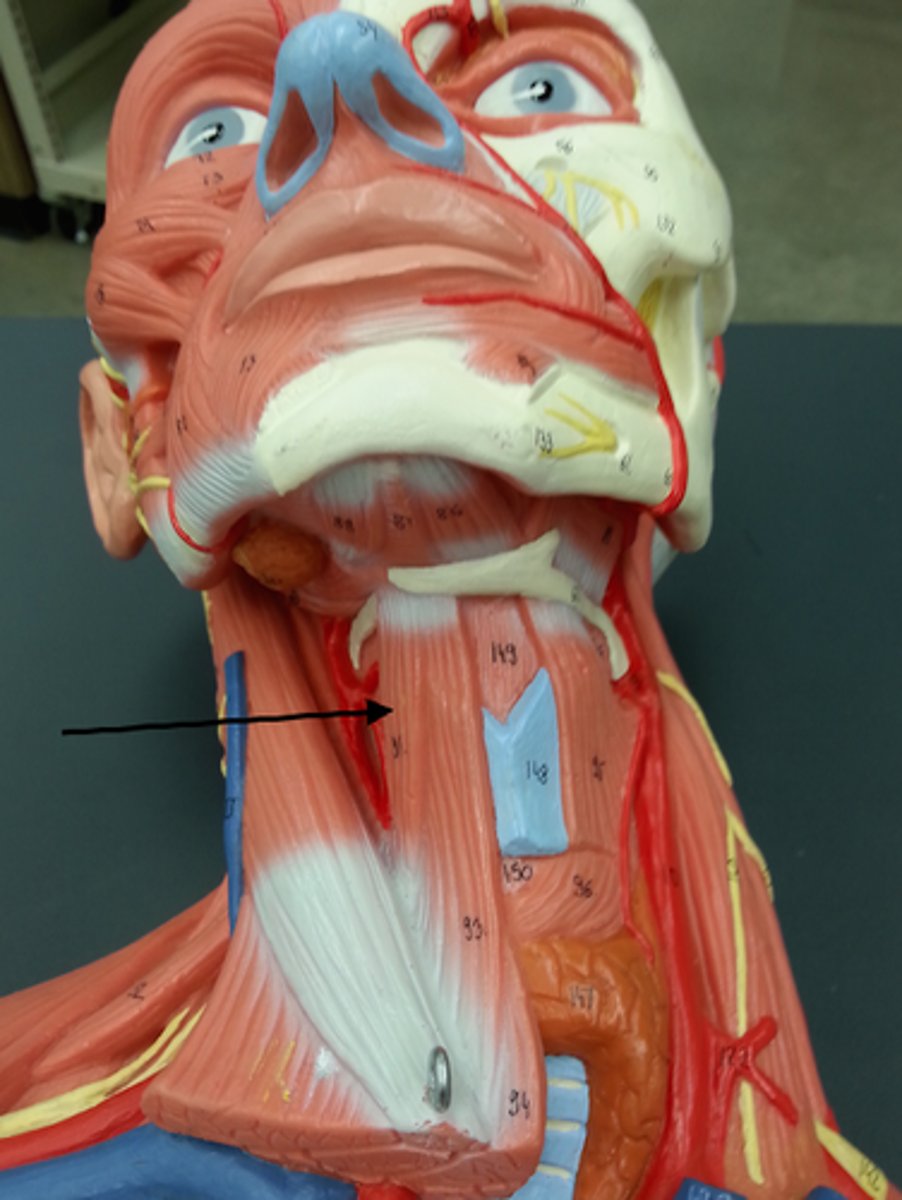
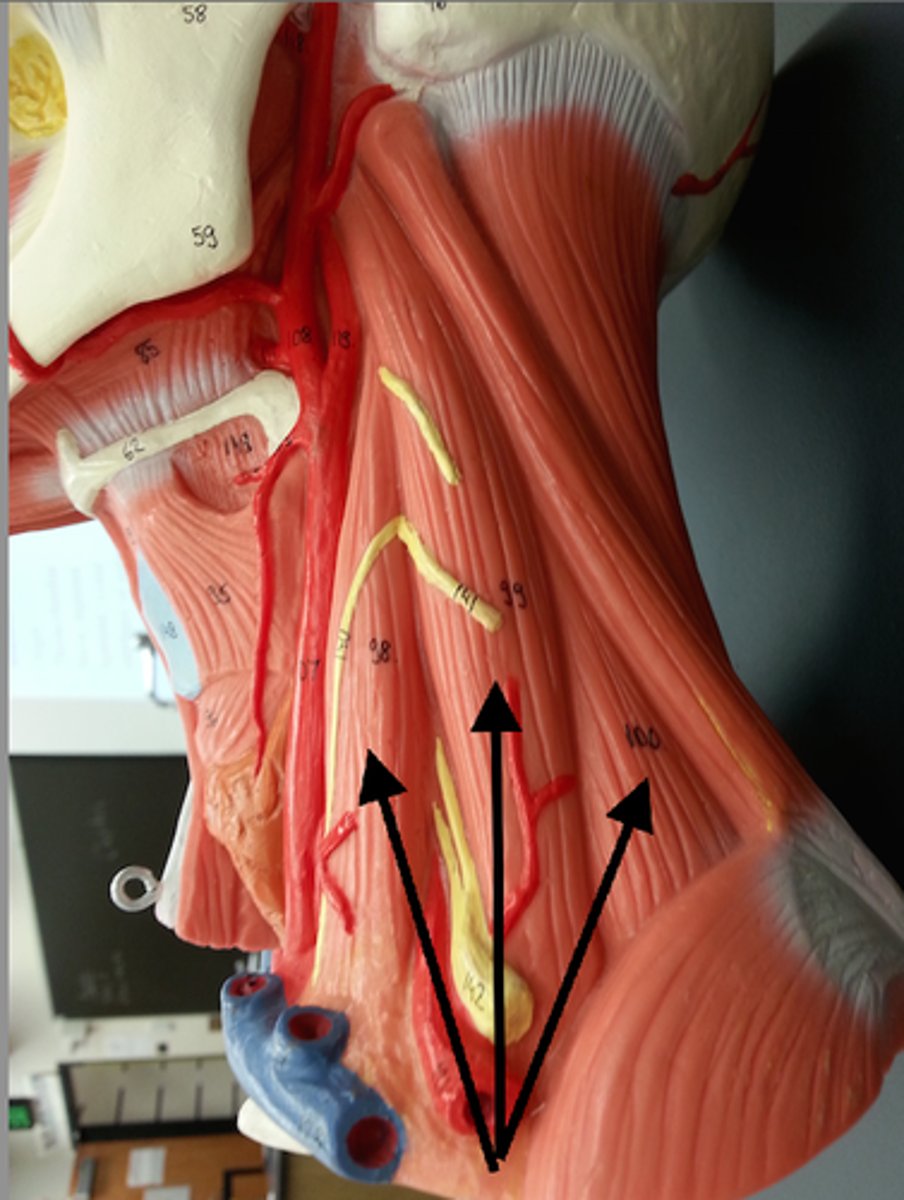
infrahyoid muscles
Straplike muscles that depress the hyoid bone and larynx during swallowing and speaking; includes sternohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid, omohyoid
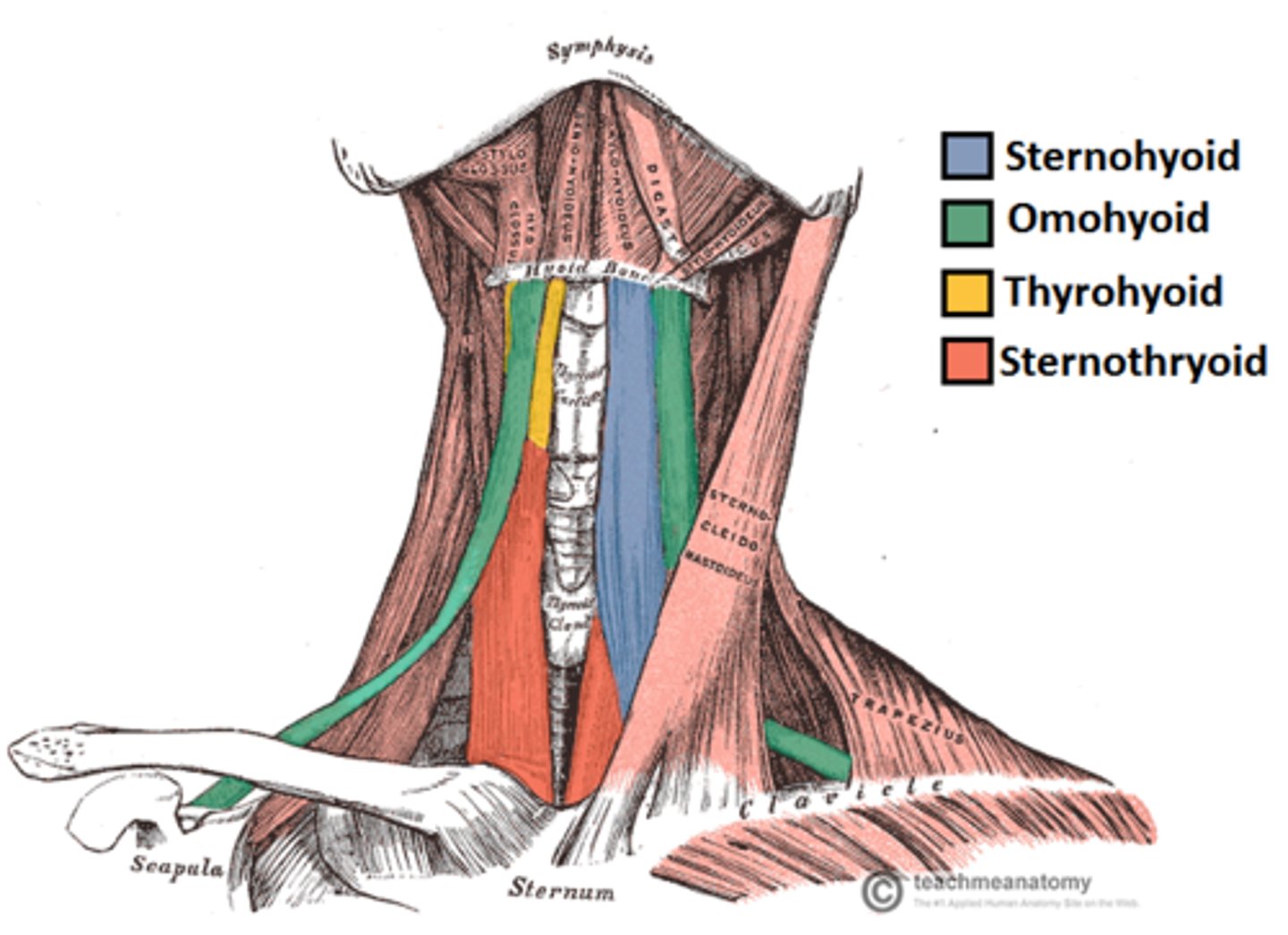
Sternohyoid
Most medial muscle of the neck; thin; superficial except inferiorly, where covered by sternocleidomastoid
A-depresses larynx and hyoid bone if mandible is fixed
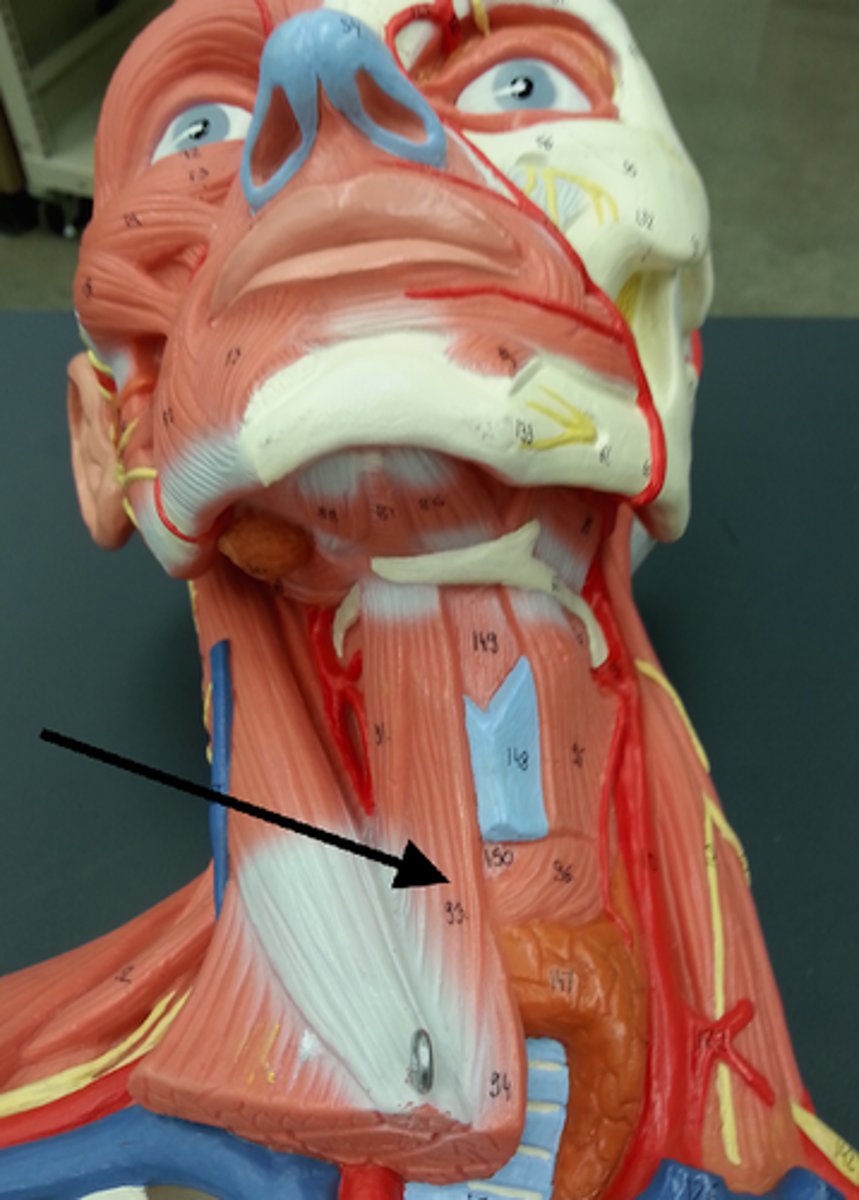
Sternothyroid
Lateral and deep to sternohyoid
A-depresses larynx and hyoid bone
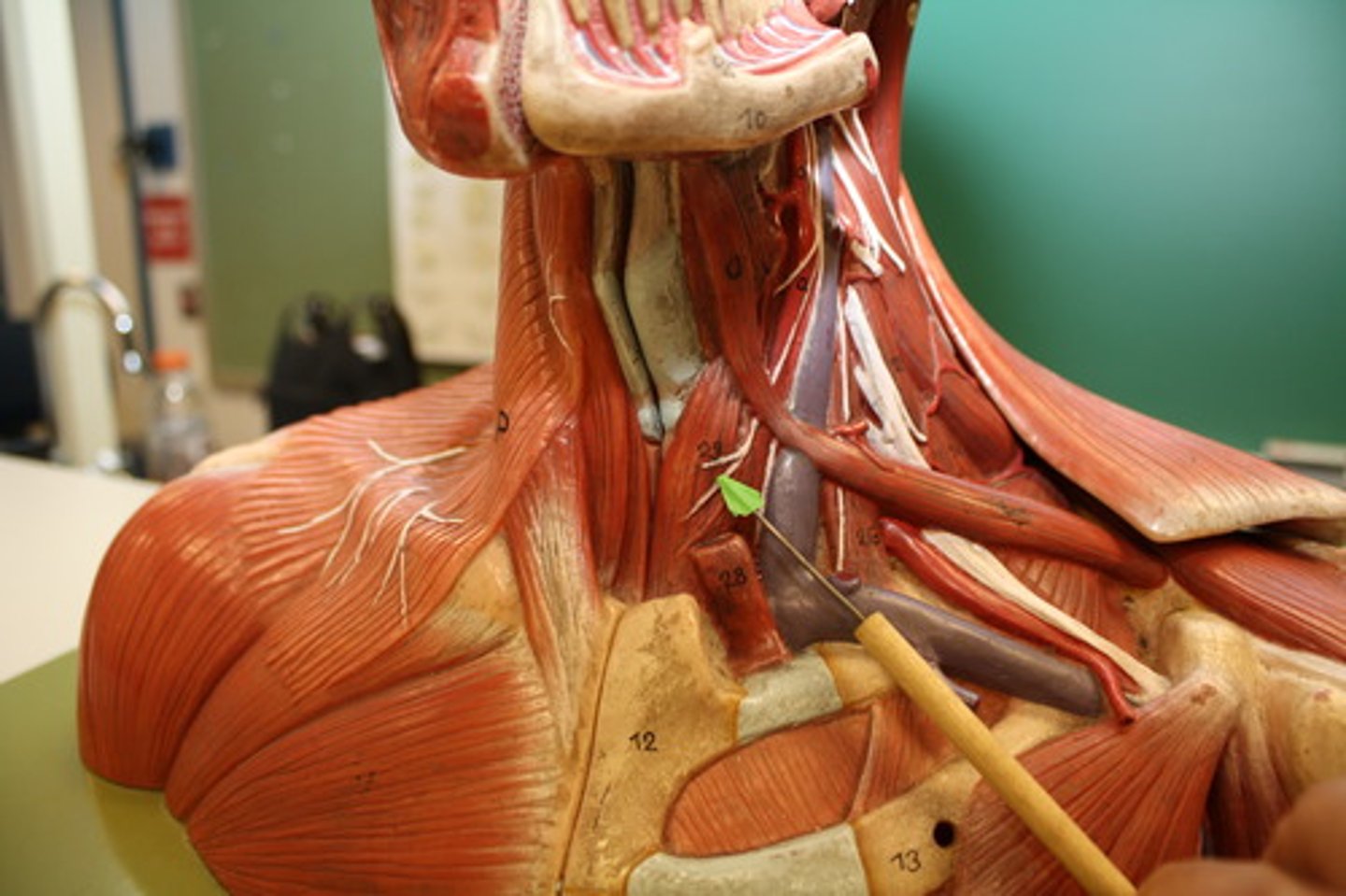
Omohyoid
Straplike muscle with two bellies united by an intermediate tendon; lateral to sternohyoid
A-depresses and retracts hyoid bone
Thyrohyoid
Appears as a superior continuation of sternothyroid muscle
A-depresses hyoid bone or elevates larynx if hyoid is fixed
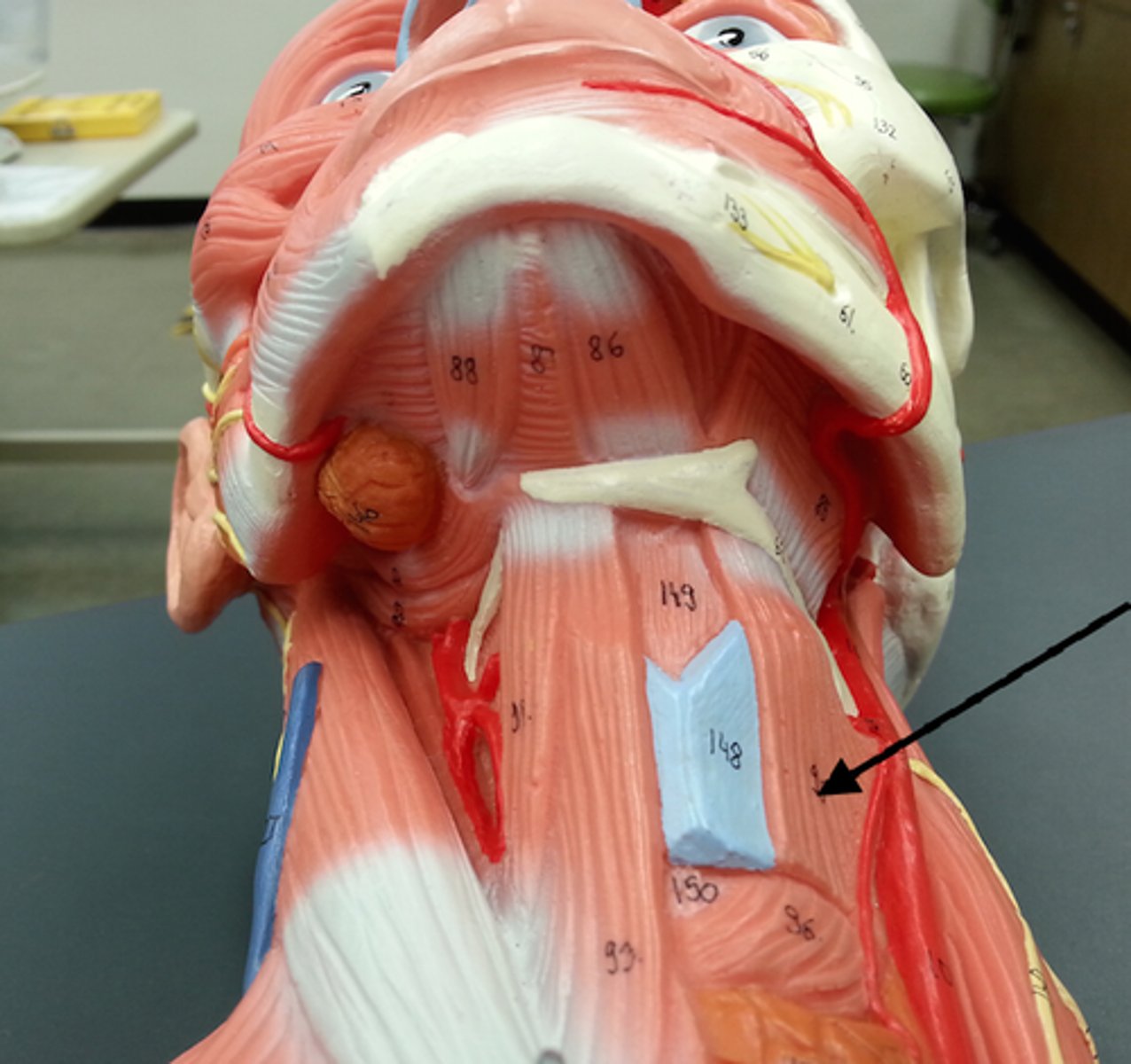
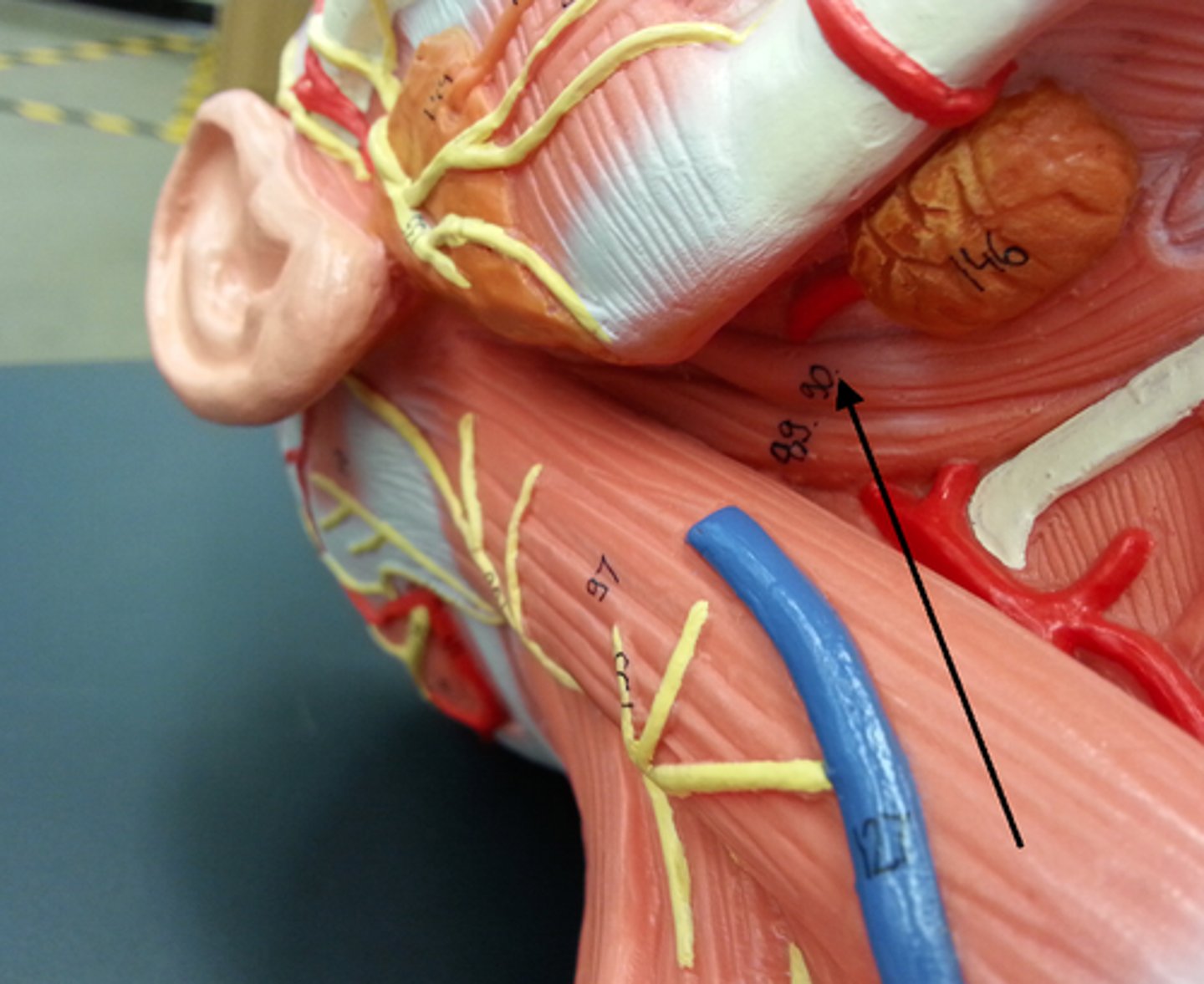
Sternocleidomastoid
Two-headed muscle located deep to playsma on aterolateral surface of neck; fleshy parts on either side of neck delineate limits of anterior and posterior triangles; key muscular landmark in neck
O-manubrium of sternum and medial portion of clavicle
I-mastoid process of temporal bone and superior nuchal line of occipital bone
A-Flexes and laterally rotates the head
N-Accessory nerve
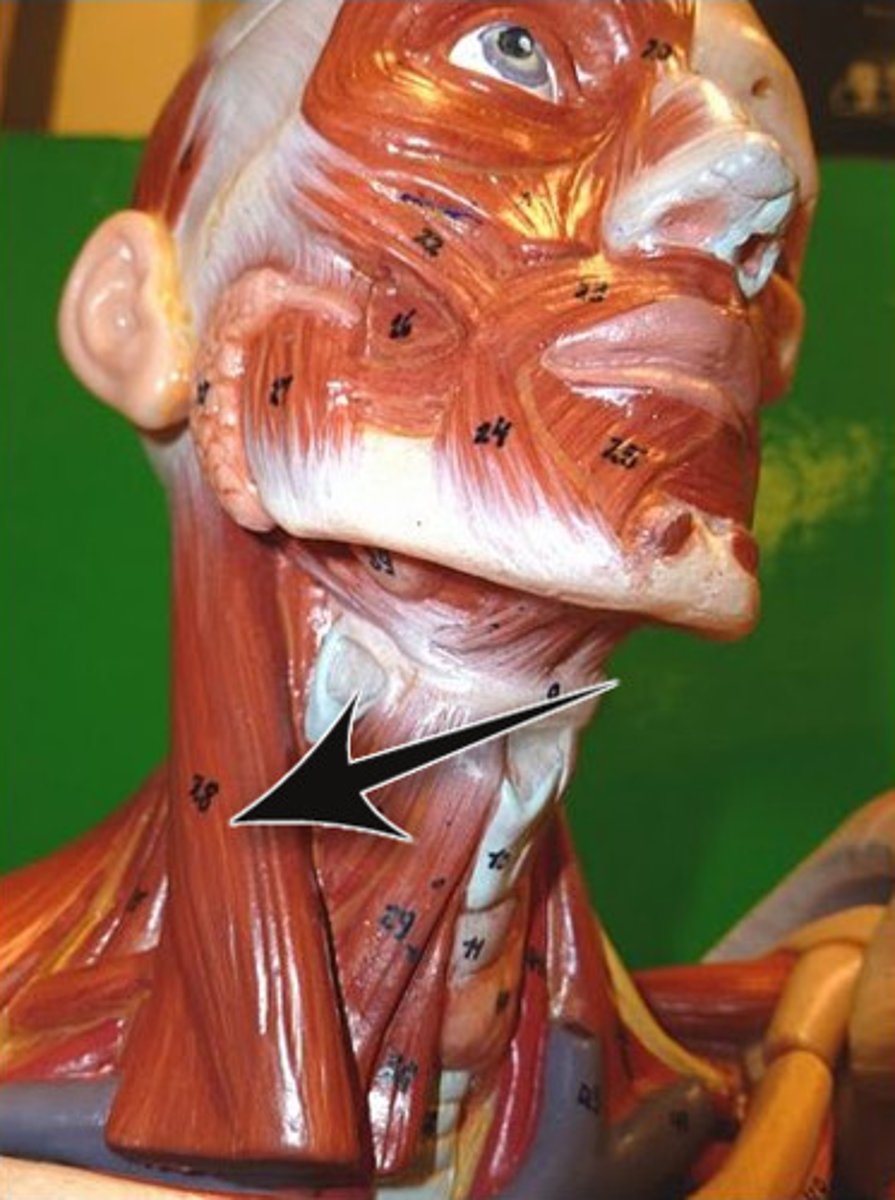
Scalenes (anterior, middle, posterior)
Located more on laterally than anteriorly on neck; deep to platysma and sternocleidomastoid
A-Elevate first two ribs (aid in inspiration); flex and rotate neck
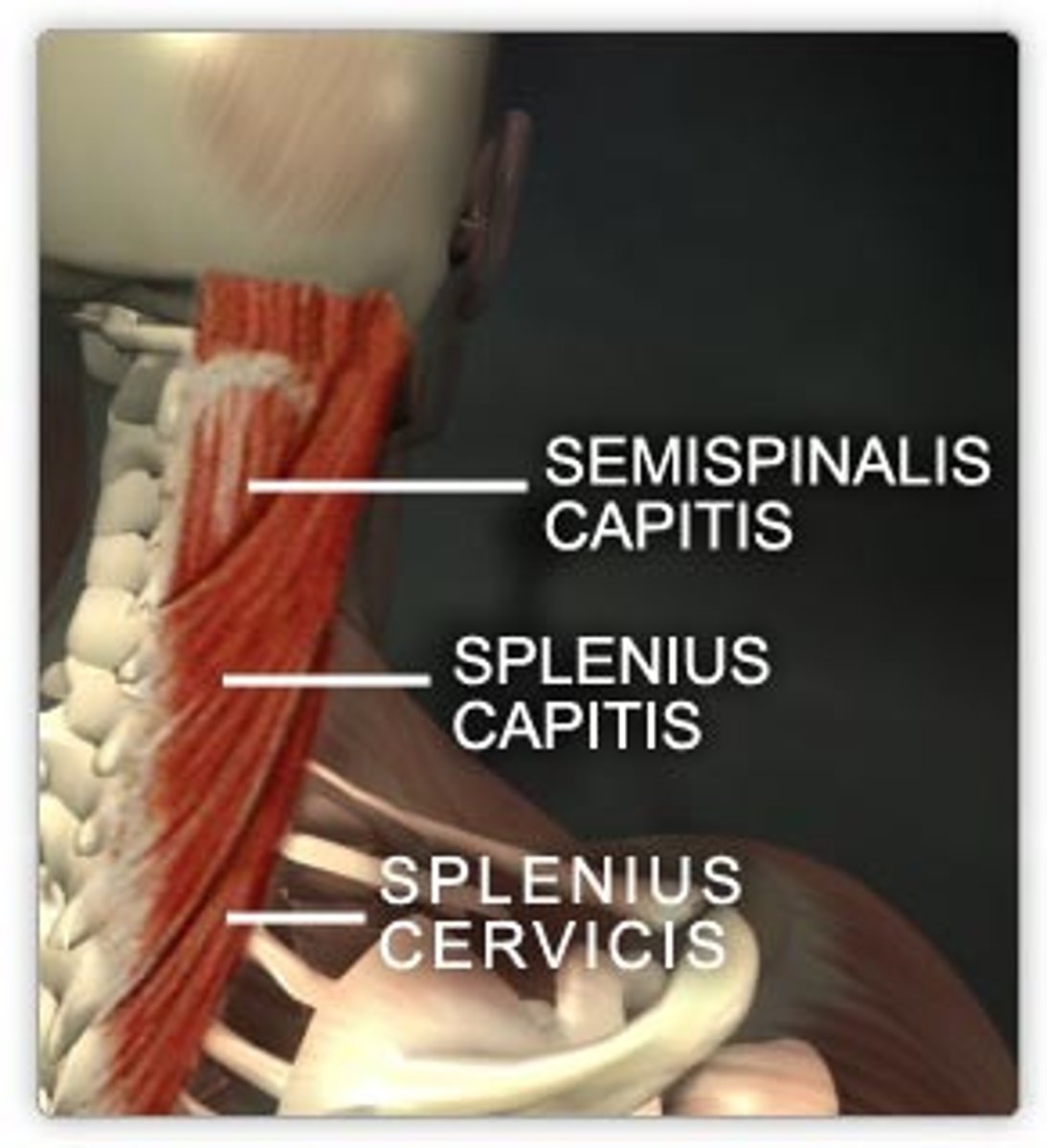
Splenius (capitis and cervicis portions)
Broad bipartite superficial muscle (capitis and cervicis parts) extending from upper thoracic vertebrae to skull; capitis portion known as "bandage muscle" because it covers and holds down deeper neck muscles
A-extend or hyperextend head; when splenius muscles on one side are activated, head rotates and bends laterally toward same side
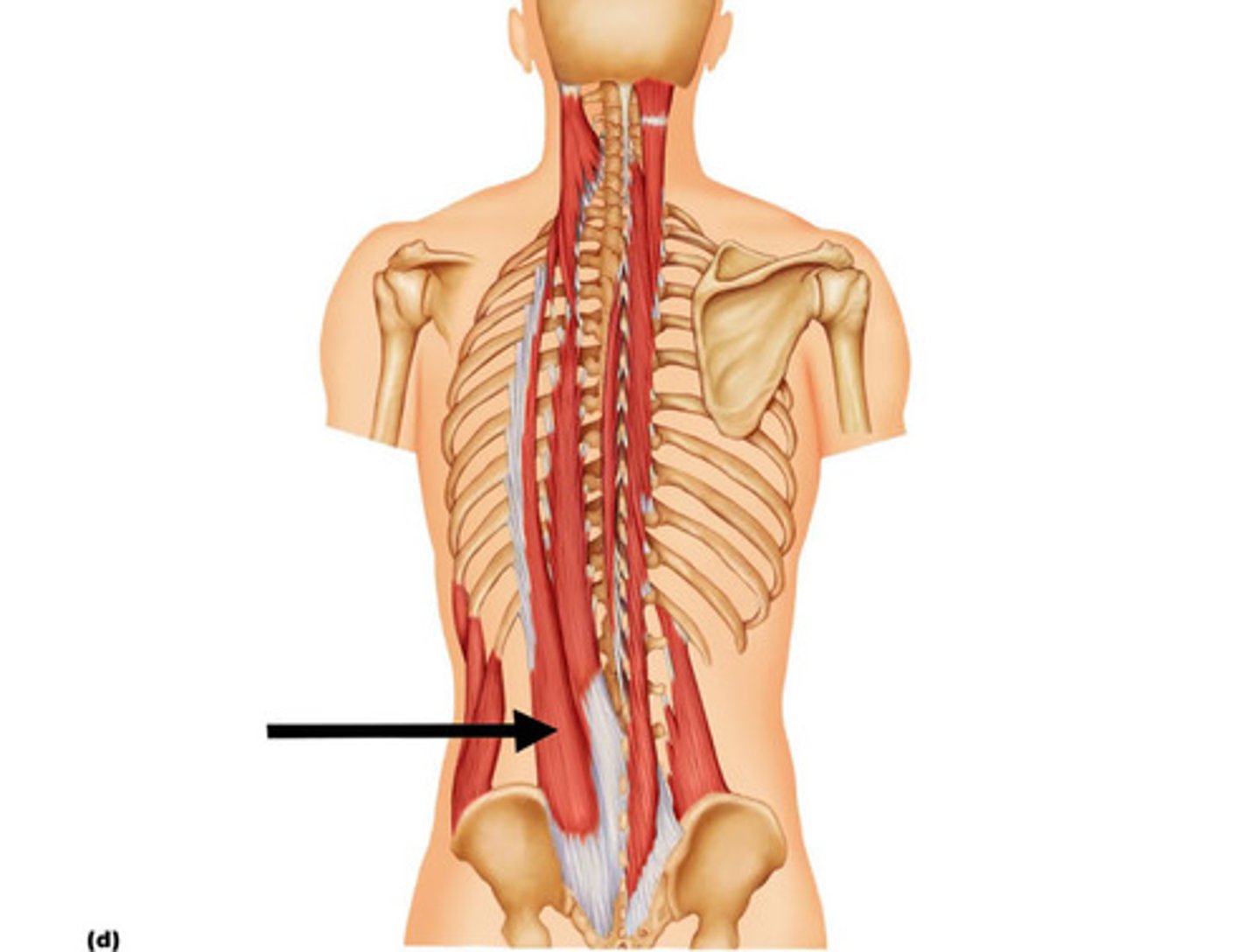
erector spinae (sacrospinalis)
prime mover of back extension; each side consists of three columns-the iliocostalis, longissimus, and spinalis muscles-forming the intermediate layer of intrinsic back muscles.
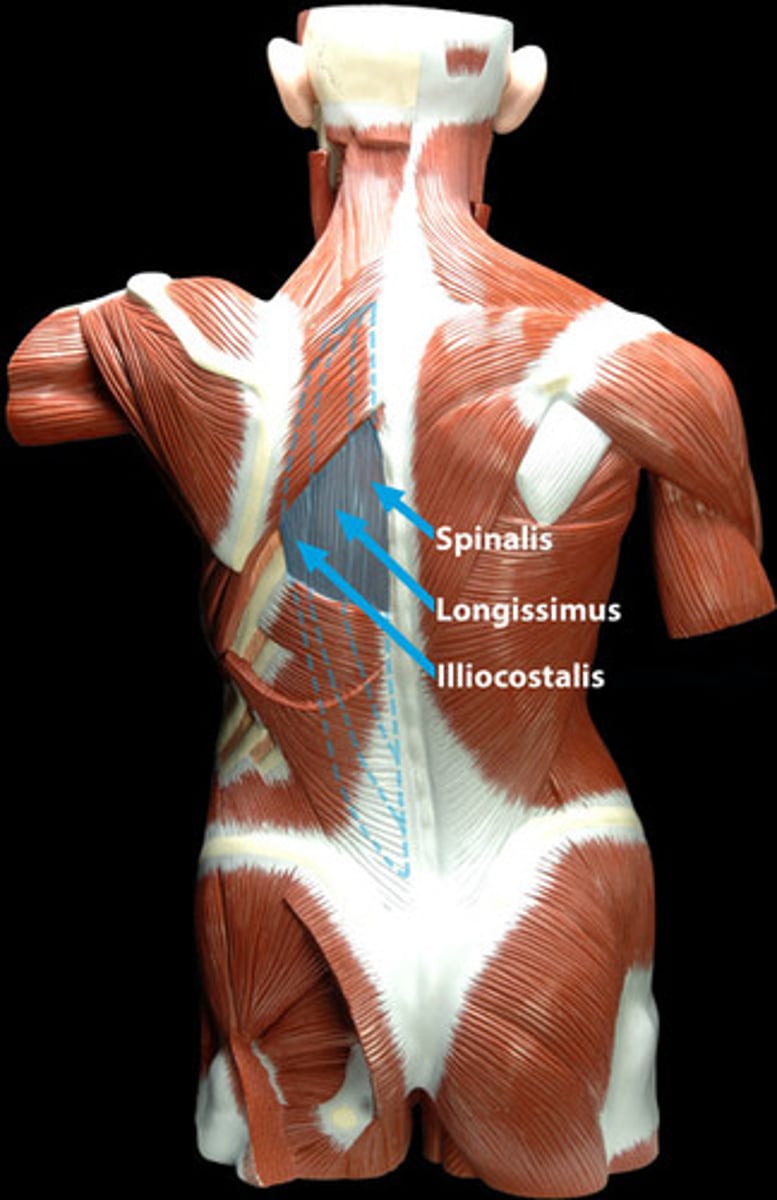
Iliocostalis
Moster lateral muscle group of erector spinae muscles; extend from pelvis to neck
A-extend and laterally flex the vertebral column
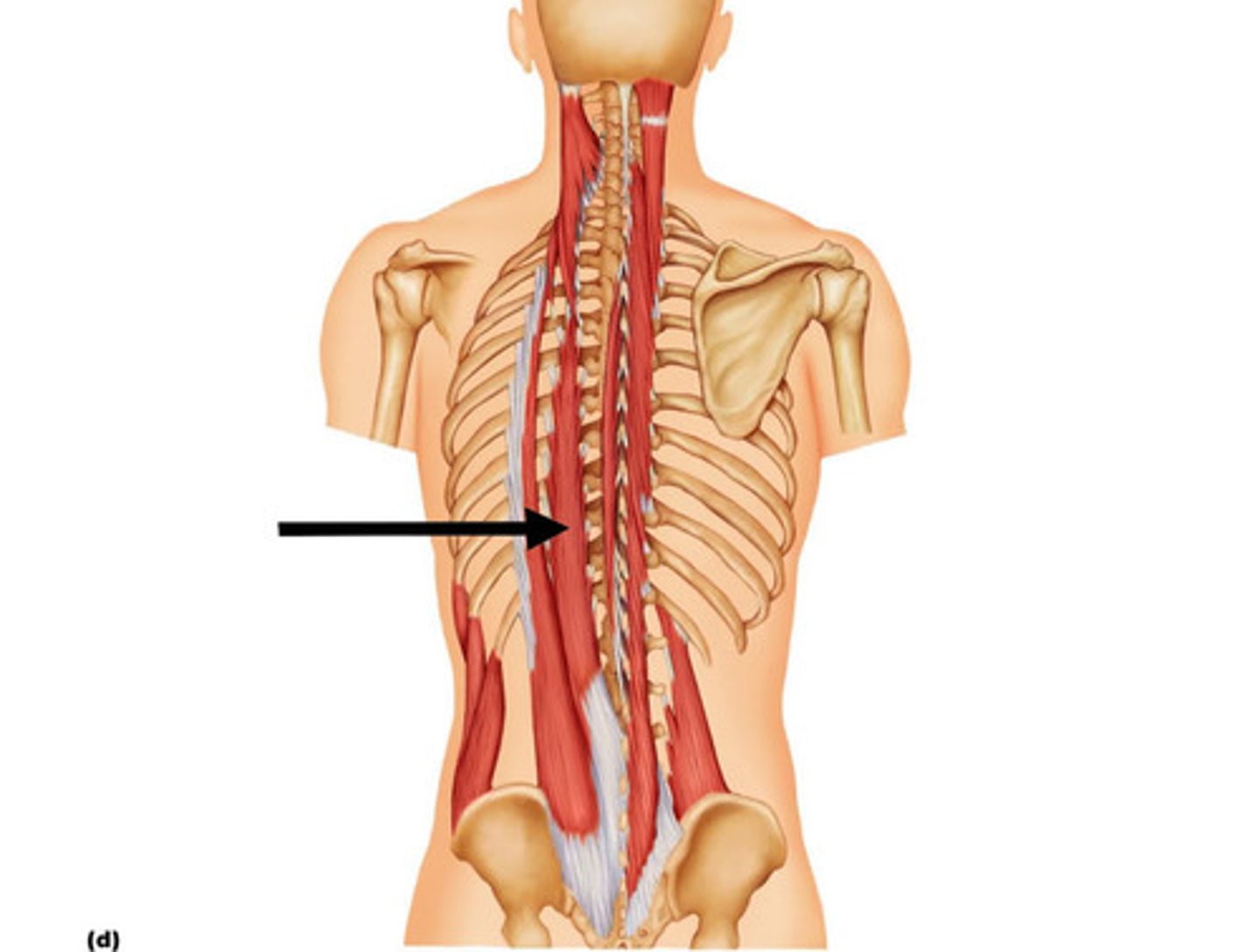
Longissimus
Intermediate tripartite muscle group of erector spinae; extend by many muscle slips from lumbar region to skull; mainly pass between transverse processes of vertebrae
A-Thoracis and cervicis act together to extend and laterally flex vertebral column; captitis extends head and turns the face toward same side
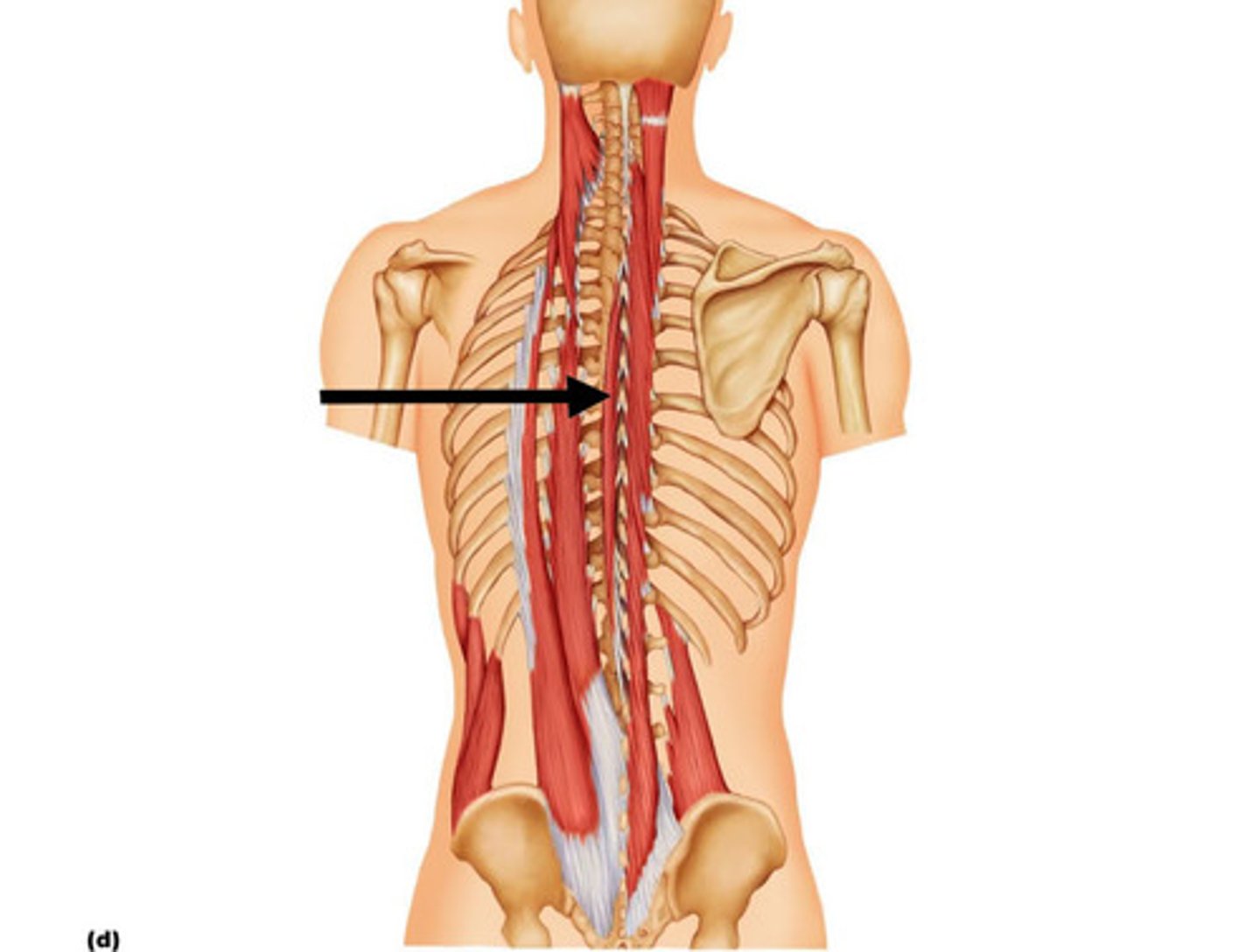
Spinalis
Most medial muscle column of erector spinae; cervicis usually rudimentary and poorly defined
A-extends vertebral column
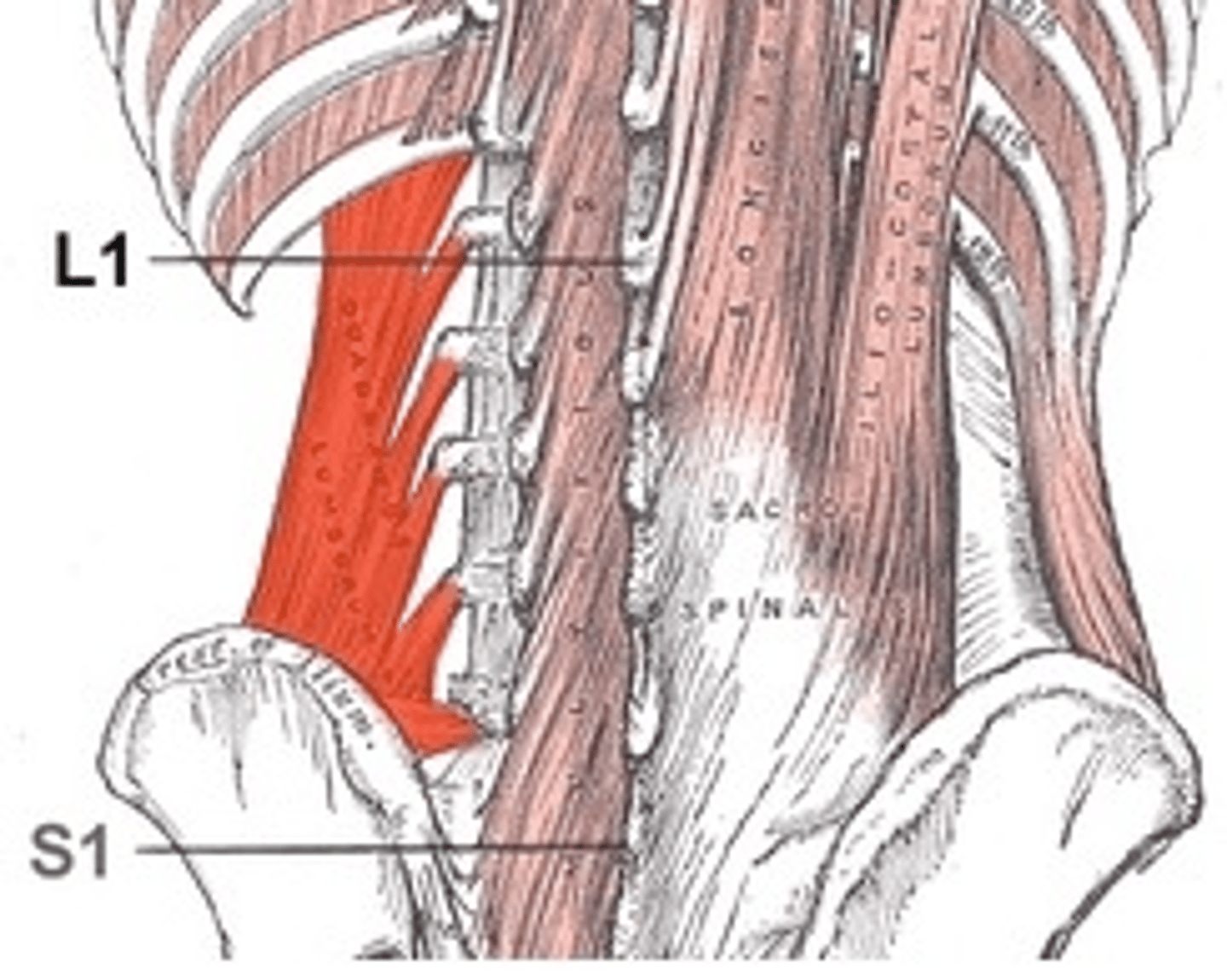
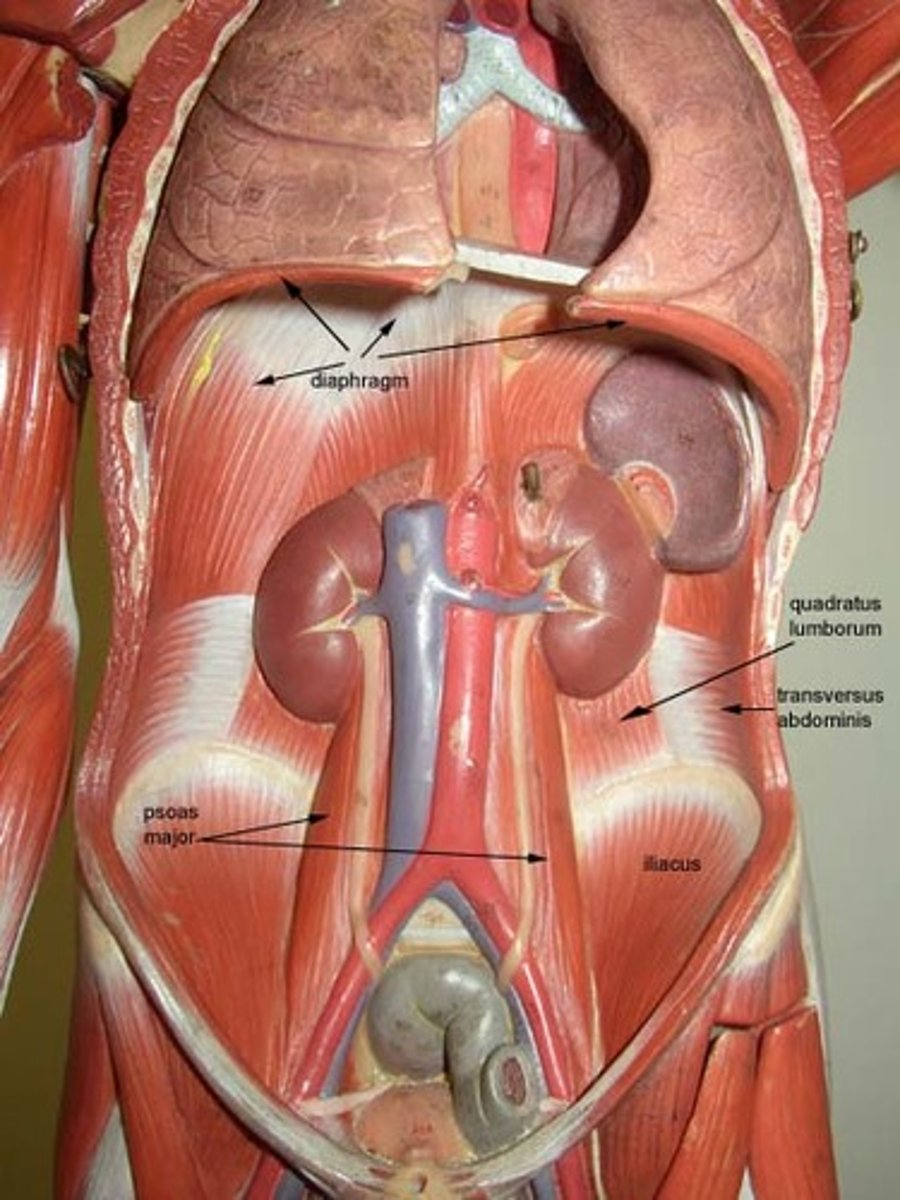
Quadratus Lumborum
Fleshy muscle forming part of posterior abdominal wall
A- laterally flexes vertebral column when acting separately; when pair acts jointly, lumbar spine is extended and 12th rib is fixed; maintains upright posture; assists in forced inspiration
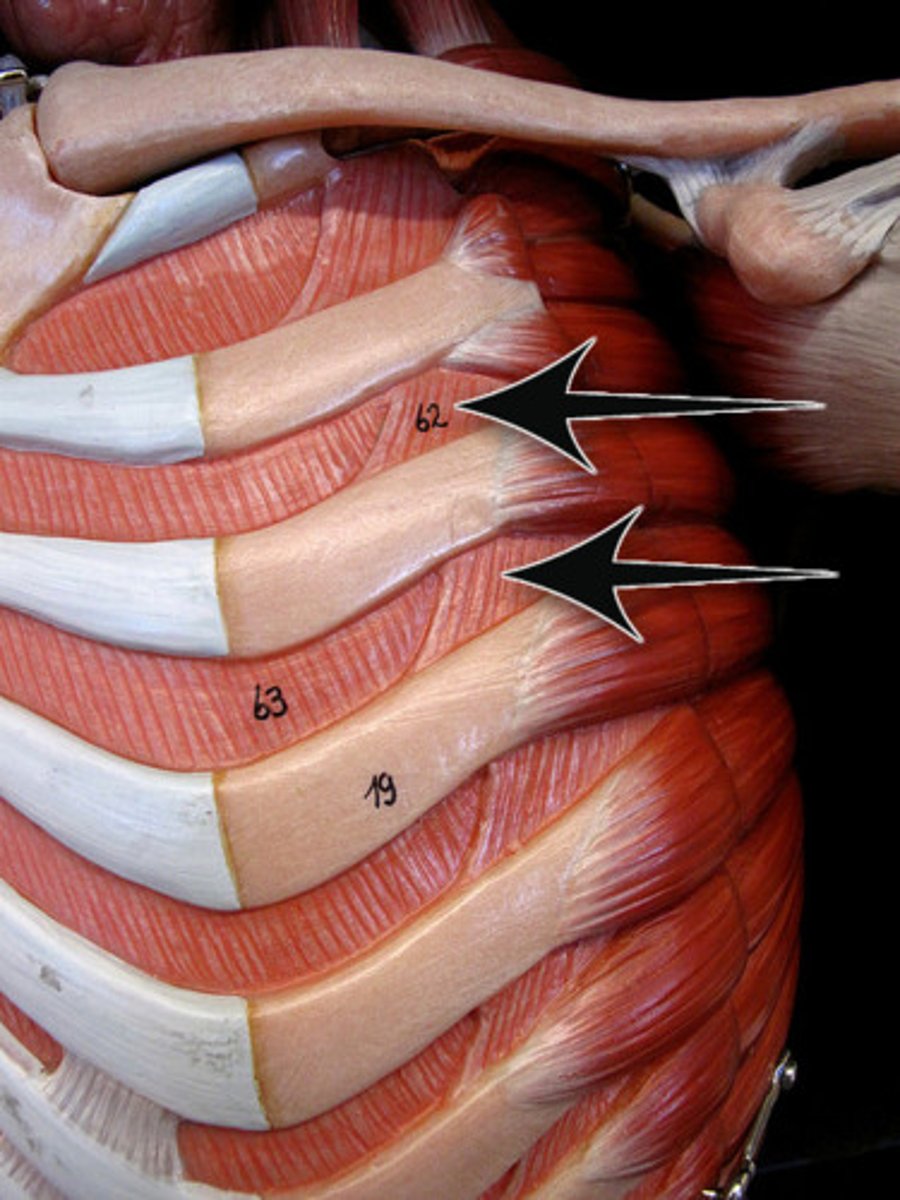
external intercostals
11 pairs lie between ribs; fibers run obliquely (down and forward) from each rib to rib below; in lower intercostal spaces, fibers are continuous with external oblique muscle, forming part of abdominal wall
A-with first ribs fixed by scalene muscles, pull ribs toward one another to elevate rib cage; aid in inspiration; synergists of diaphragm
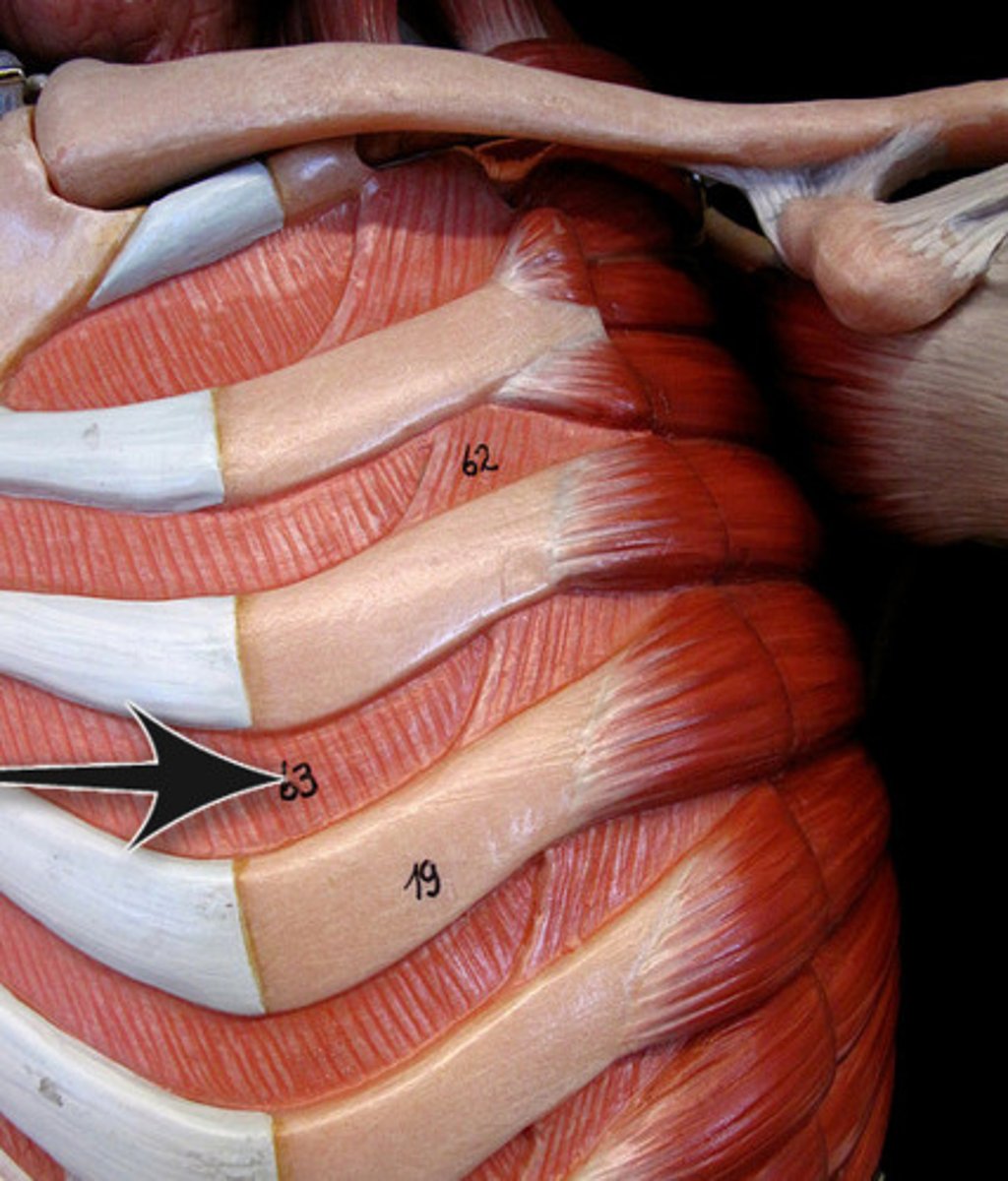
internal intercostals
11 pairs lie between ribs; fibers run deep to and at right angles to those of external intercostals; lower internal intercostal muscles are continuous with fibers of internal oblique muscle of abdominal wall
A-draw ribs together and depress rib cage; aid forced expiration; antagonistic to external intercostals
Diaphragm
Broad musclee pierced by the aorta, inferior vena cava, and esophagus, forms floor of thoracic cavity; dome shaped in relaxed state; fibers converge from margins of thoracic cage toward a boomerang shaped central tendon
A-prime mover of inspiration; flattens on contraction
Rectus abdominis
Medial superficial muscle pair; extend from pubis to rib cage; ensheathed by aponeuroses of lateral muscles; segmented by three tendinous intersections
A-Flex and rotate lumbar region of vertebral column; fix and depress ribs, stabilize pelvis during walking, increase intra-abdominal pressure
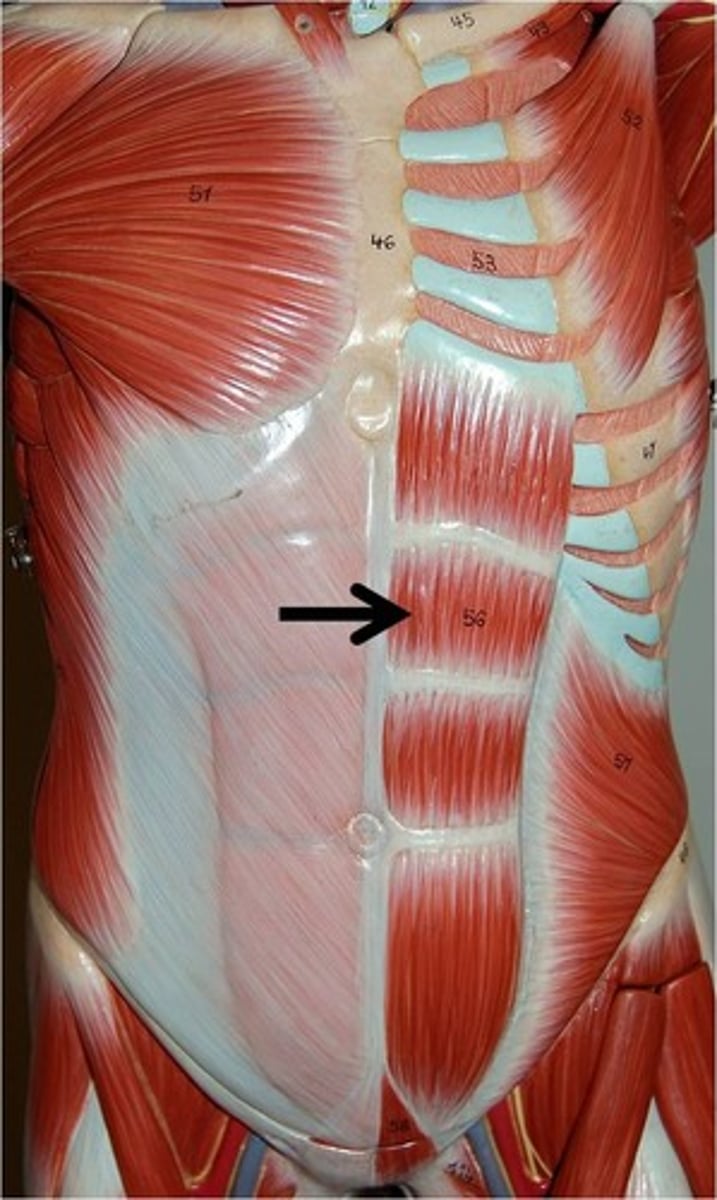
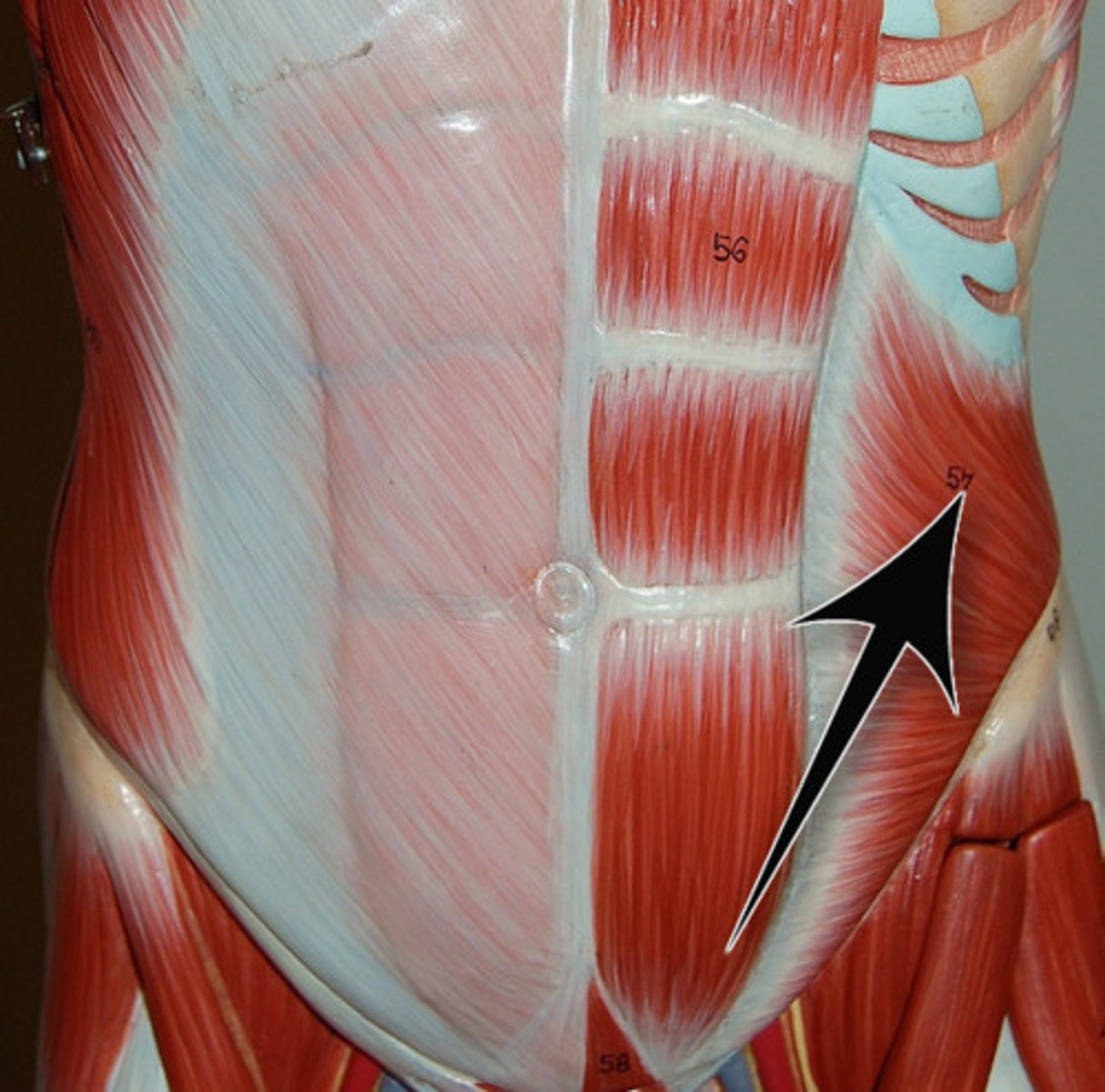
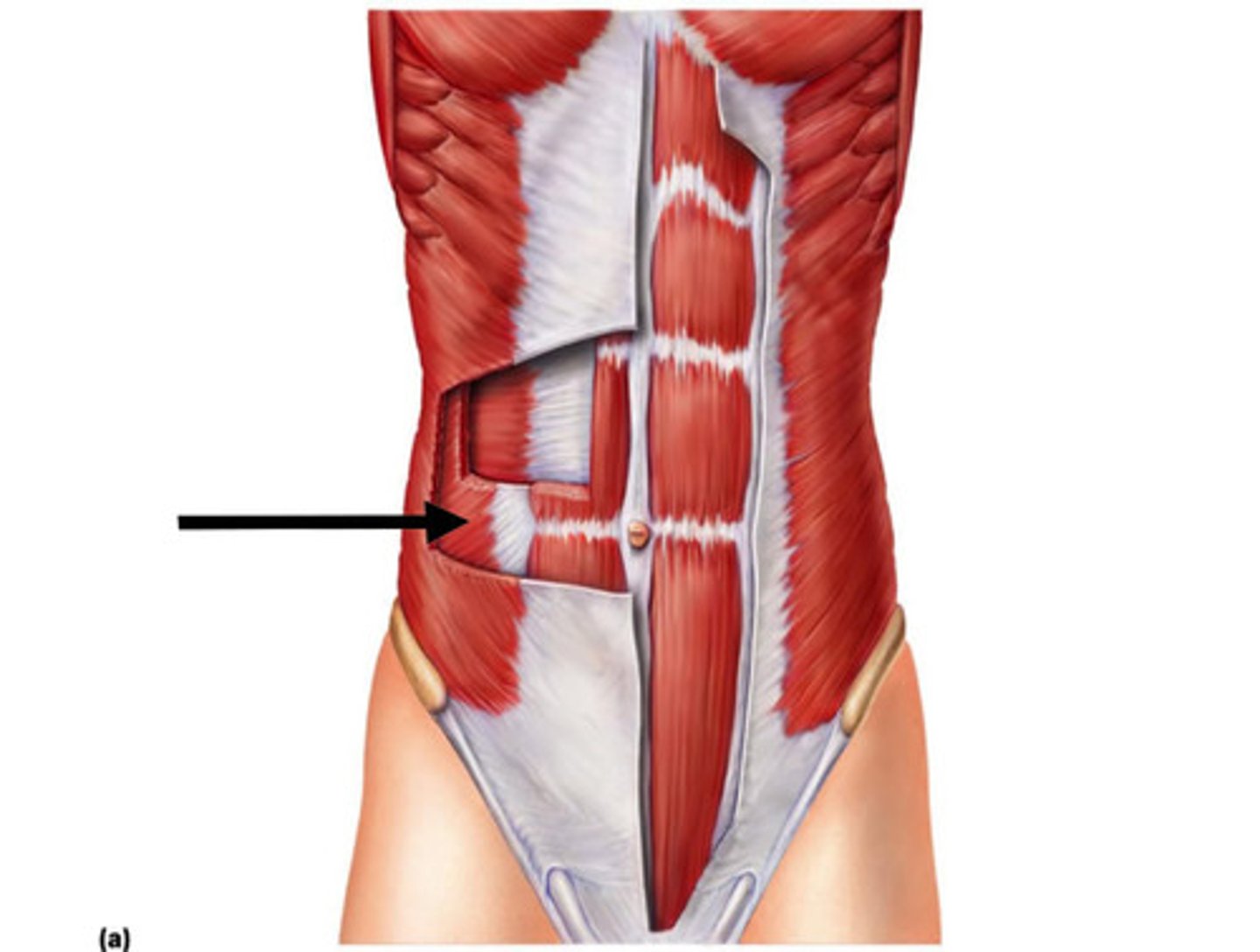
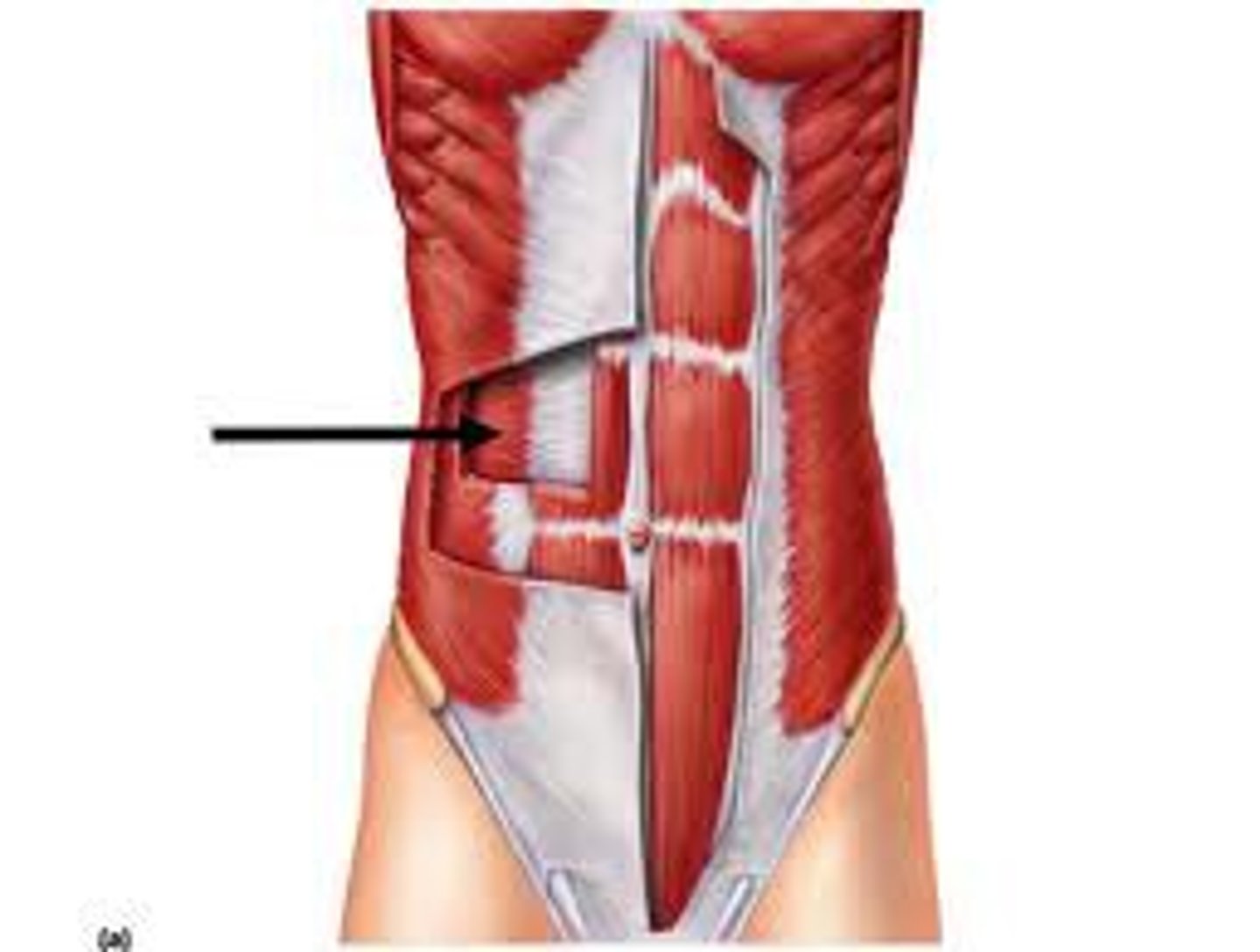
external oblique
Largest and most superficial of the three lateral muscles; fibers run downward and medially; aponeurosis turns under inferiorly, forming inguinal ligament
A-Compresses abdomen; laterally flexes and rotates vertebral column
internal oblique
flexes and rotates vertebral column; compresses abdominal wall; trunk rotation and lateral flexion
transversus abdominis
compresses abdominal contents
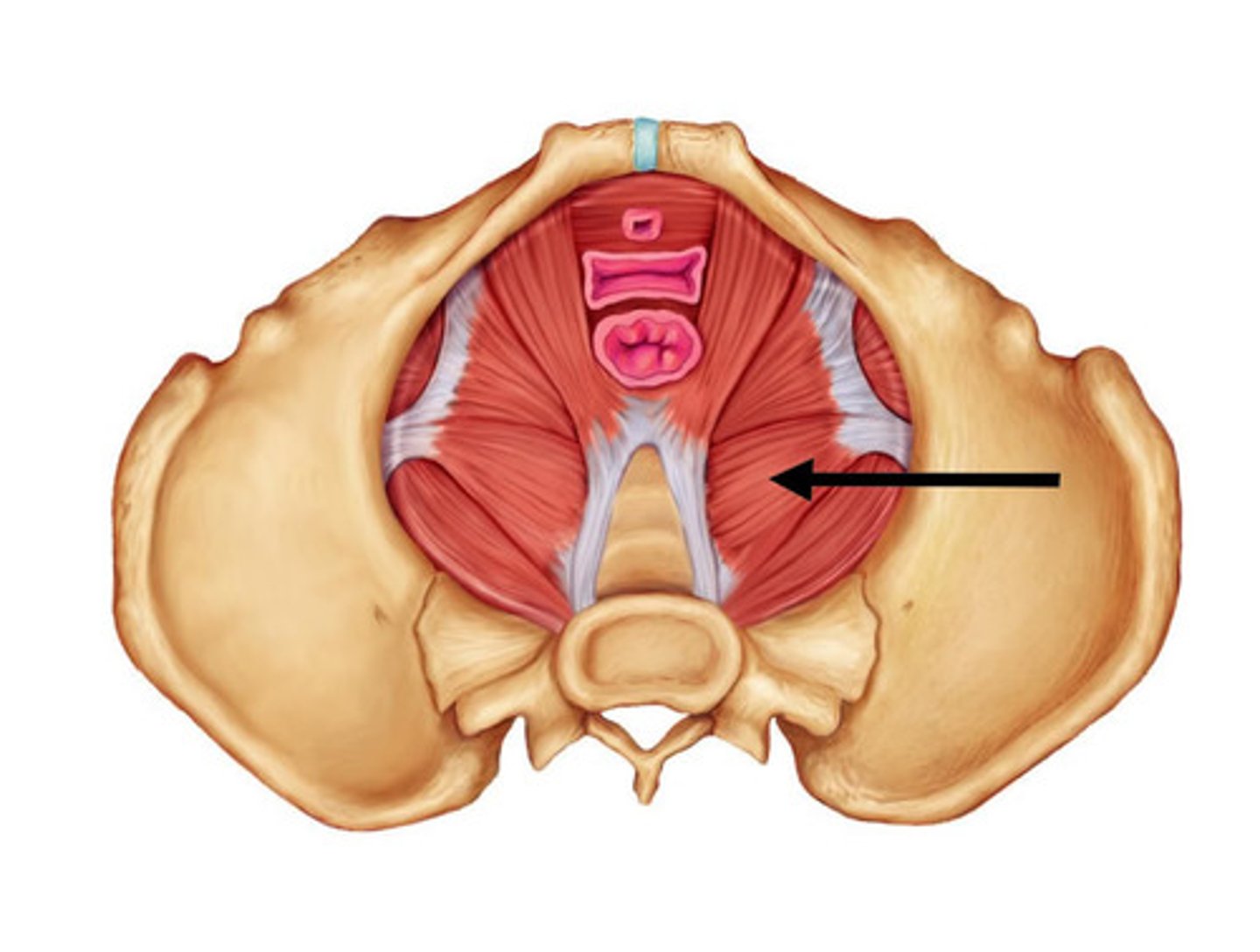
levator ani
Supports pelvic viscera and provides sphincter-like action in anal canal and vagina
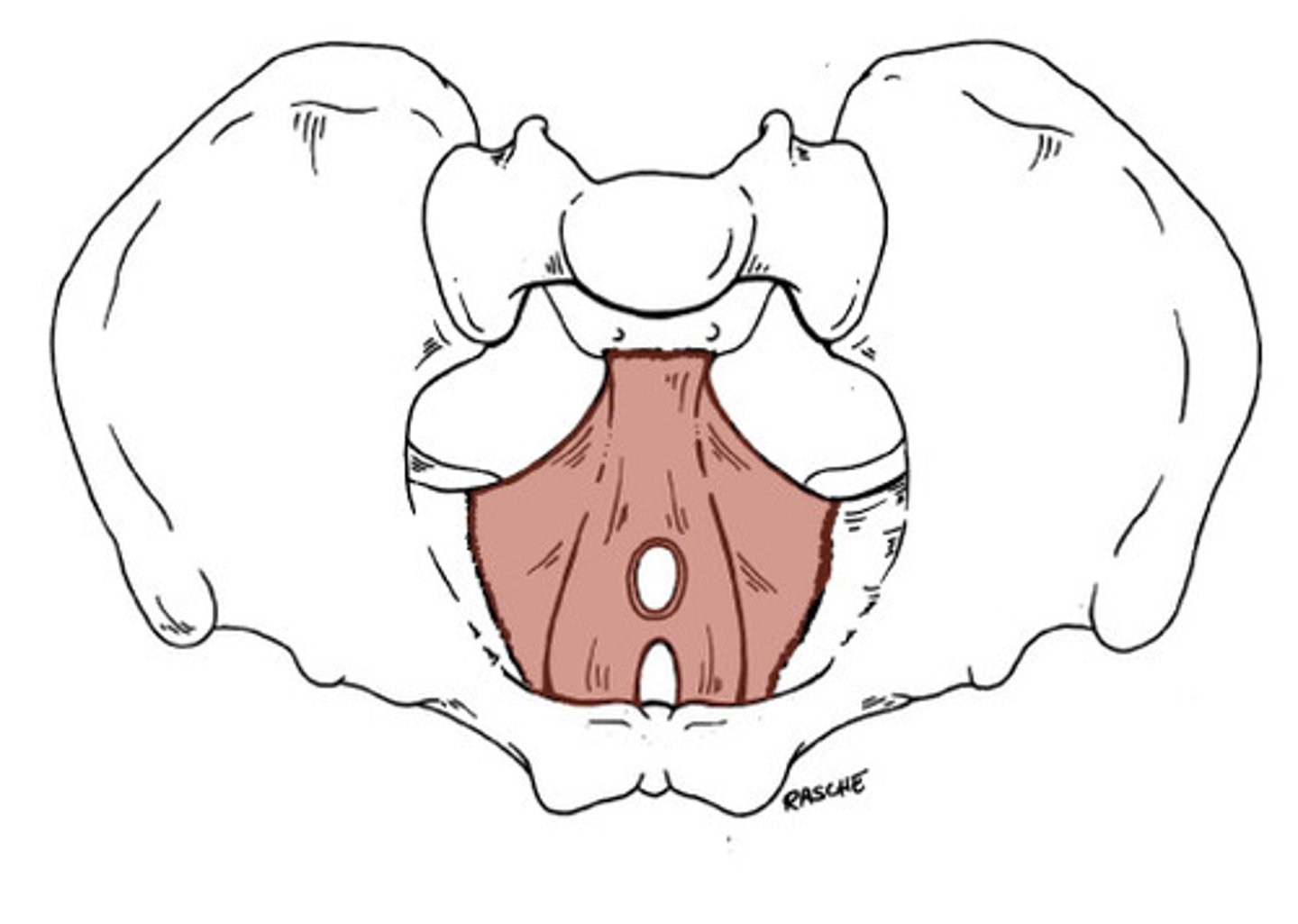
Coccygeus
Posterior to levator ani; supports pelvic organs
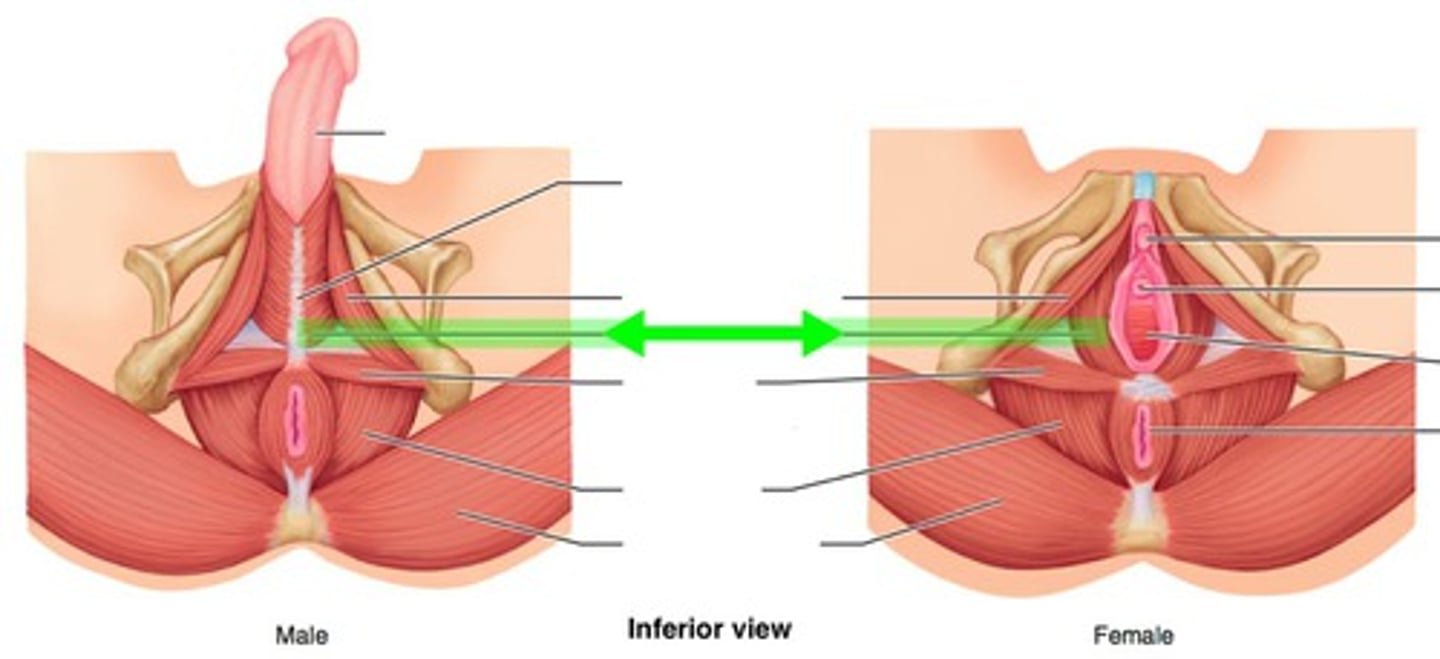
Ischiocavernosus
maintains erection
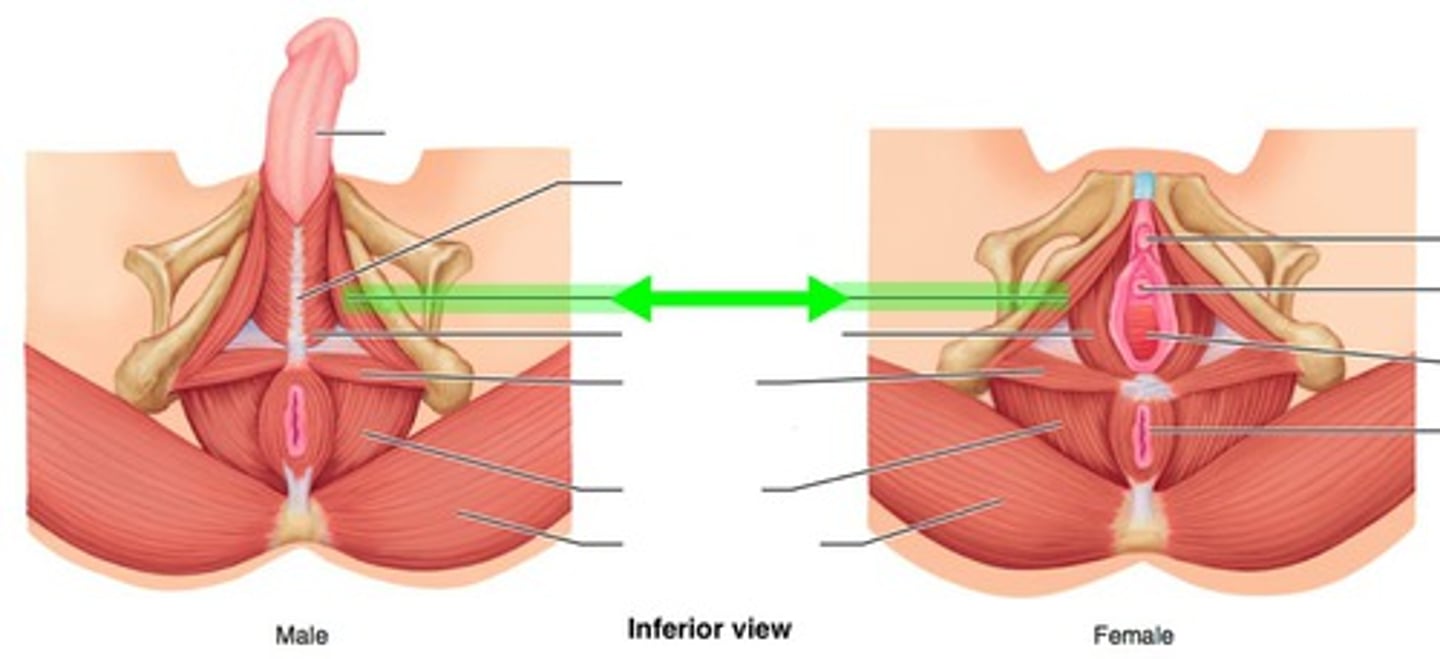
Bulbospongiosus
empties male urethra; assists in erection of penis or clitoris
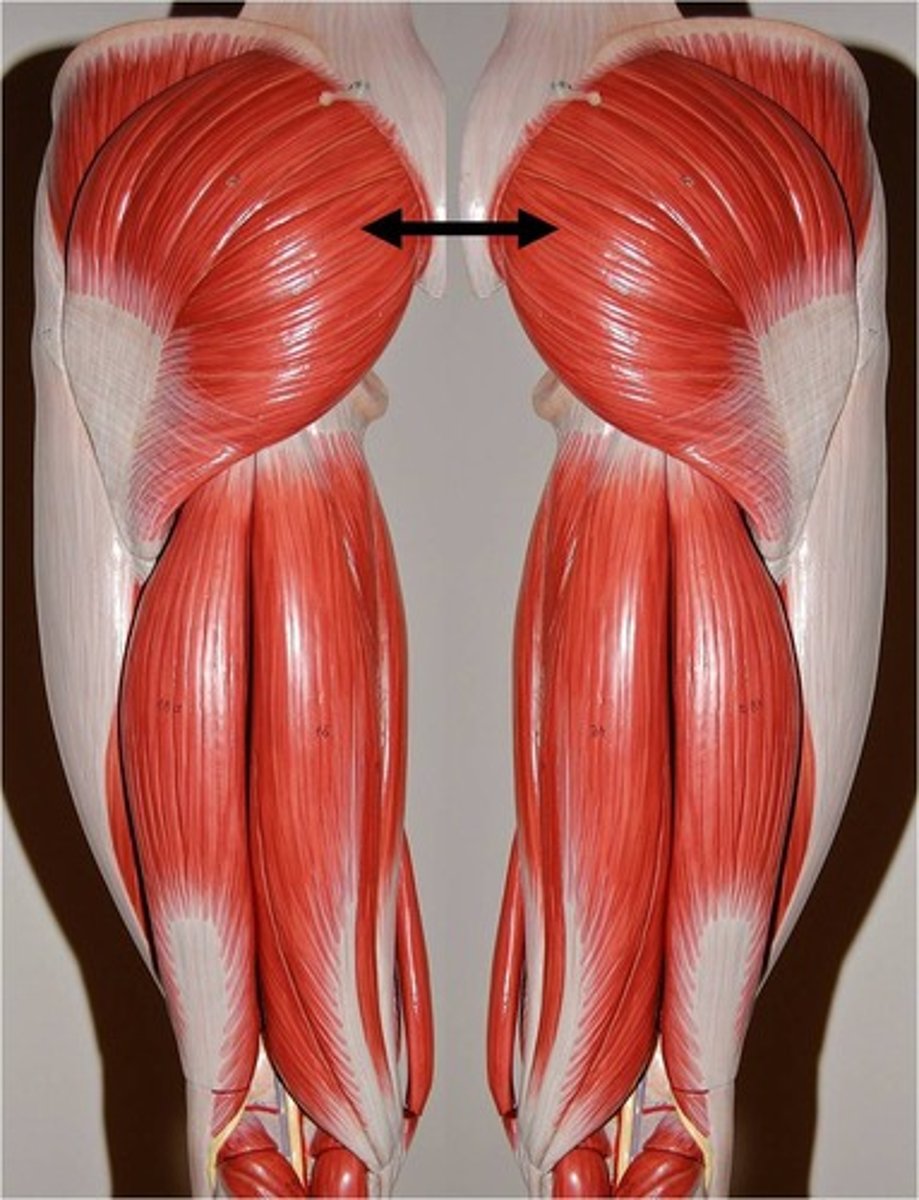
gluteus maximus
extends thigh at hip; laterally rotates thigh
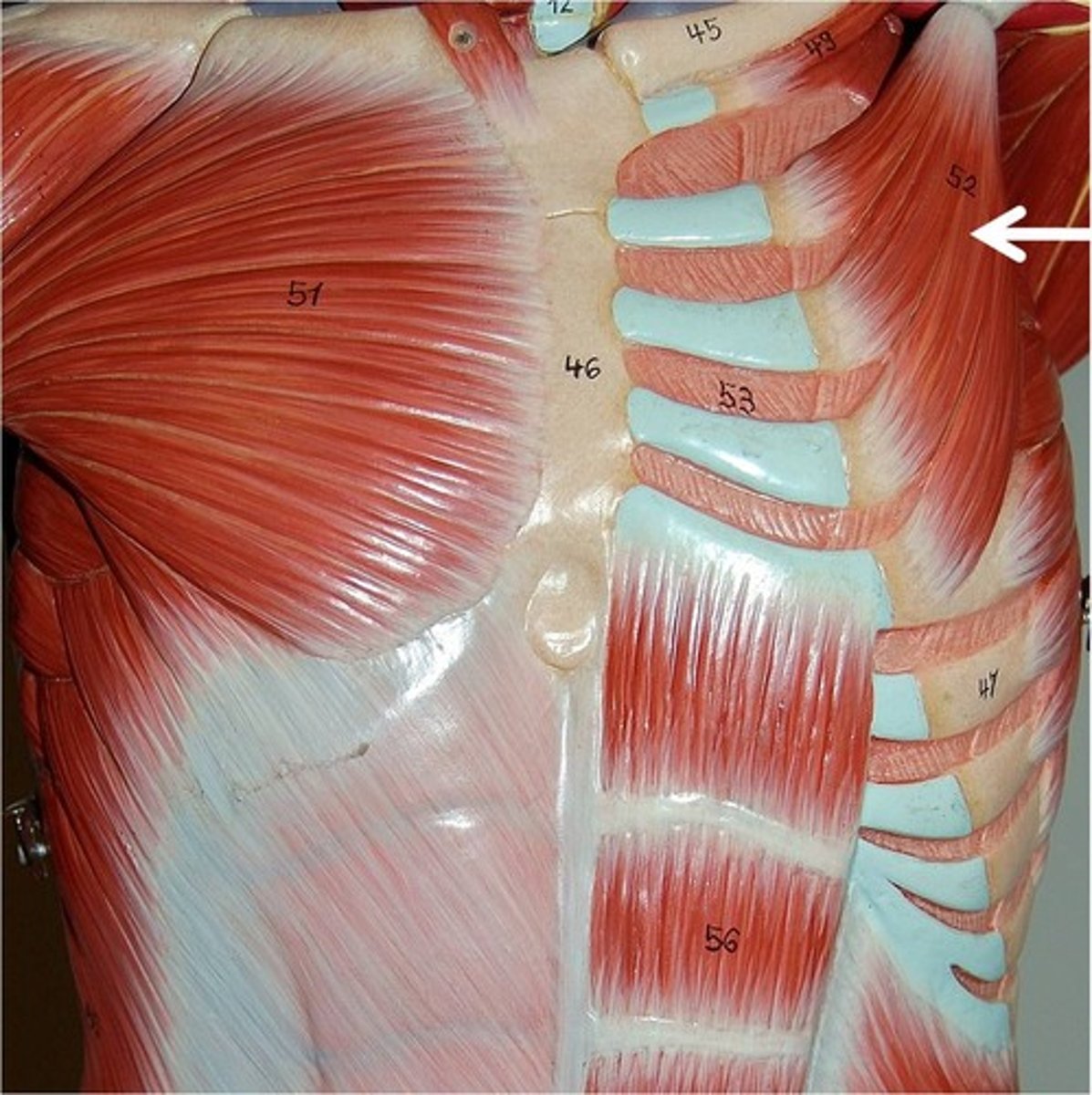
pectoralis minor
protracts and depresses scapula
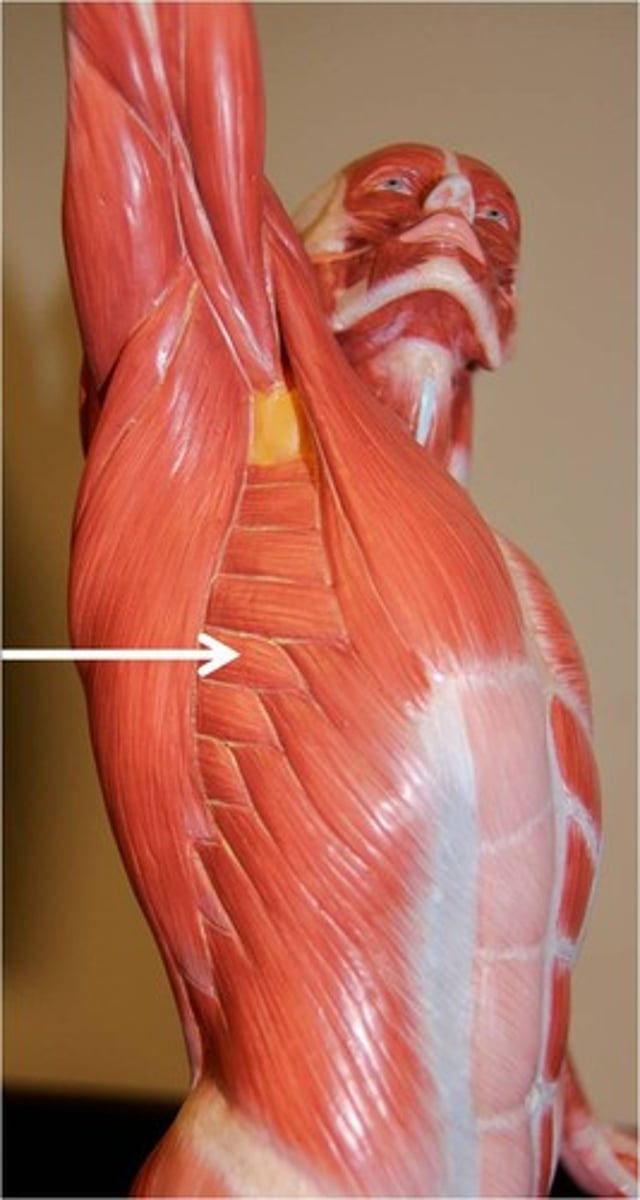
serratus anterior
Fan-shaped muscle; lies deep to scapula, deep and inferior to pectoral muscles on lateral rib cage; forms medial wall of axilla; origins have serrated appearance; paralysis results in winging of vertebbral border of scapula away from chest wall, making arm elevation impossible
O-by series of muscle slips from ribs 1-8
I-entire anterior surface of vertebral border of scapula
A-Rotates scapula so its inferior angle moves laterally and upward; prime mover to protract and hold scapula against chest wall; raises point of shoulder; called boxer's muscle
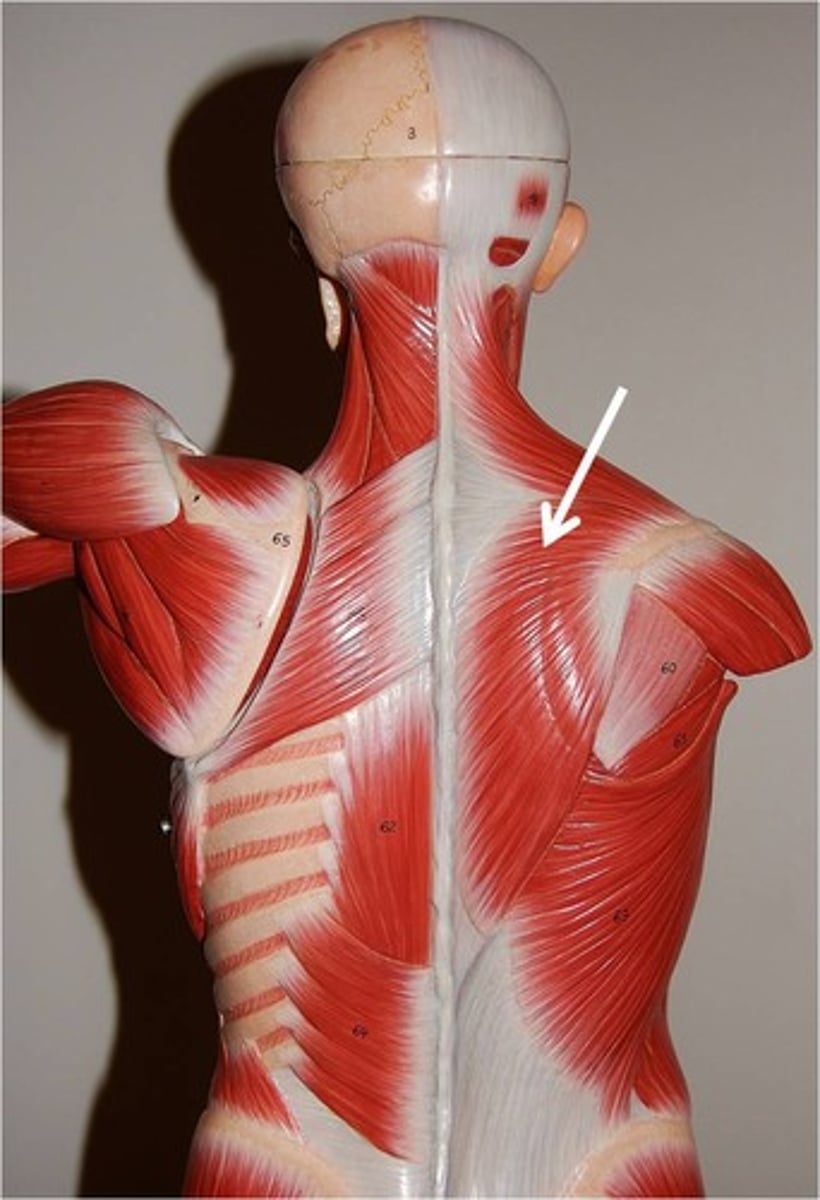
Trapezius
Most superficial muscle of posterior thorax; flat and triangular in shape
O-occipital bone, ligamentum nuchae, and spinous processes
I-acromion and spine of scapula
A-Stabiliizes, elevates, depresses, retracts, and rotates the scapula; rotates the arm
N-accessory nervie (cranial nerve XI)
levator scapulae
Located at back and side of neck, deep to trapezius; thick straplike muscle
A-elevates/adducts scapula
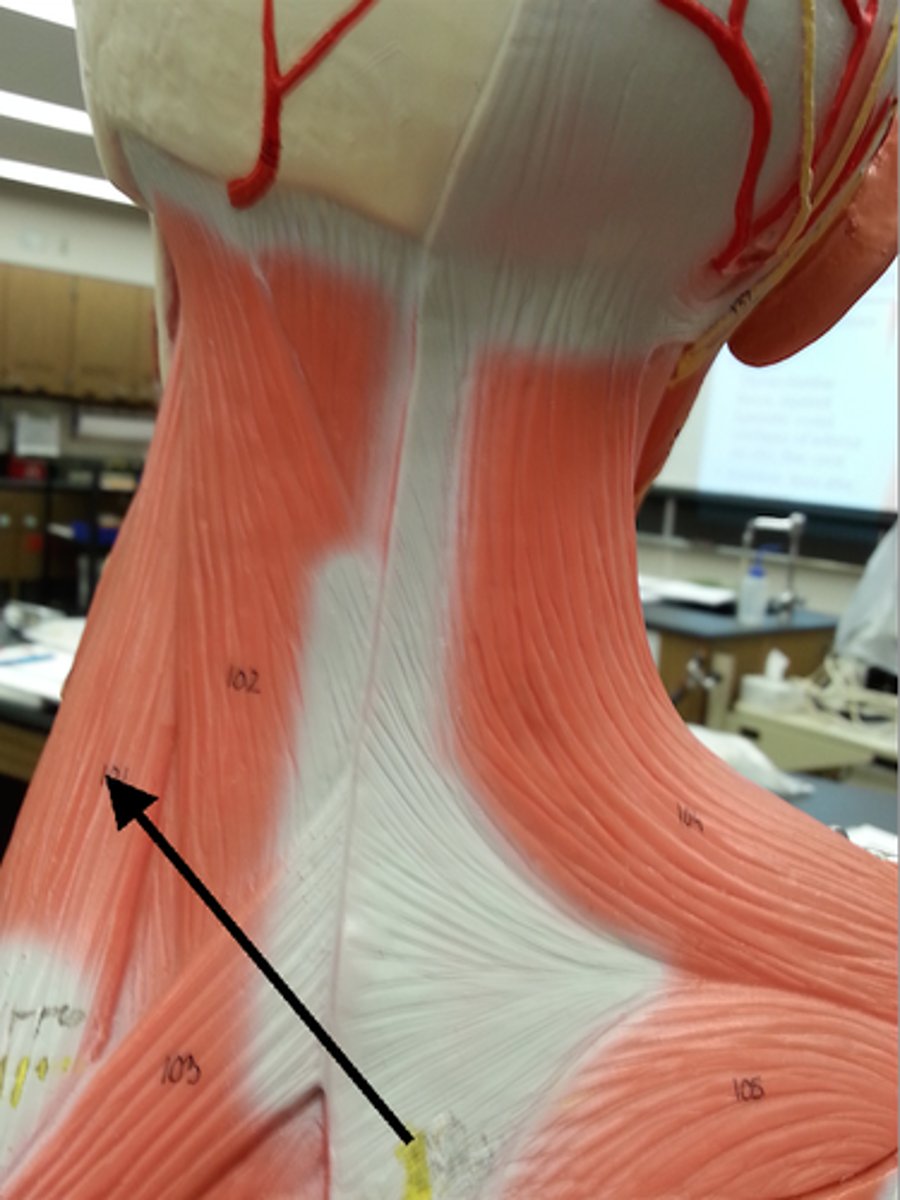
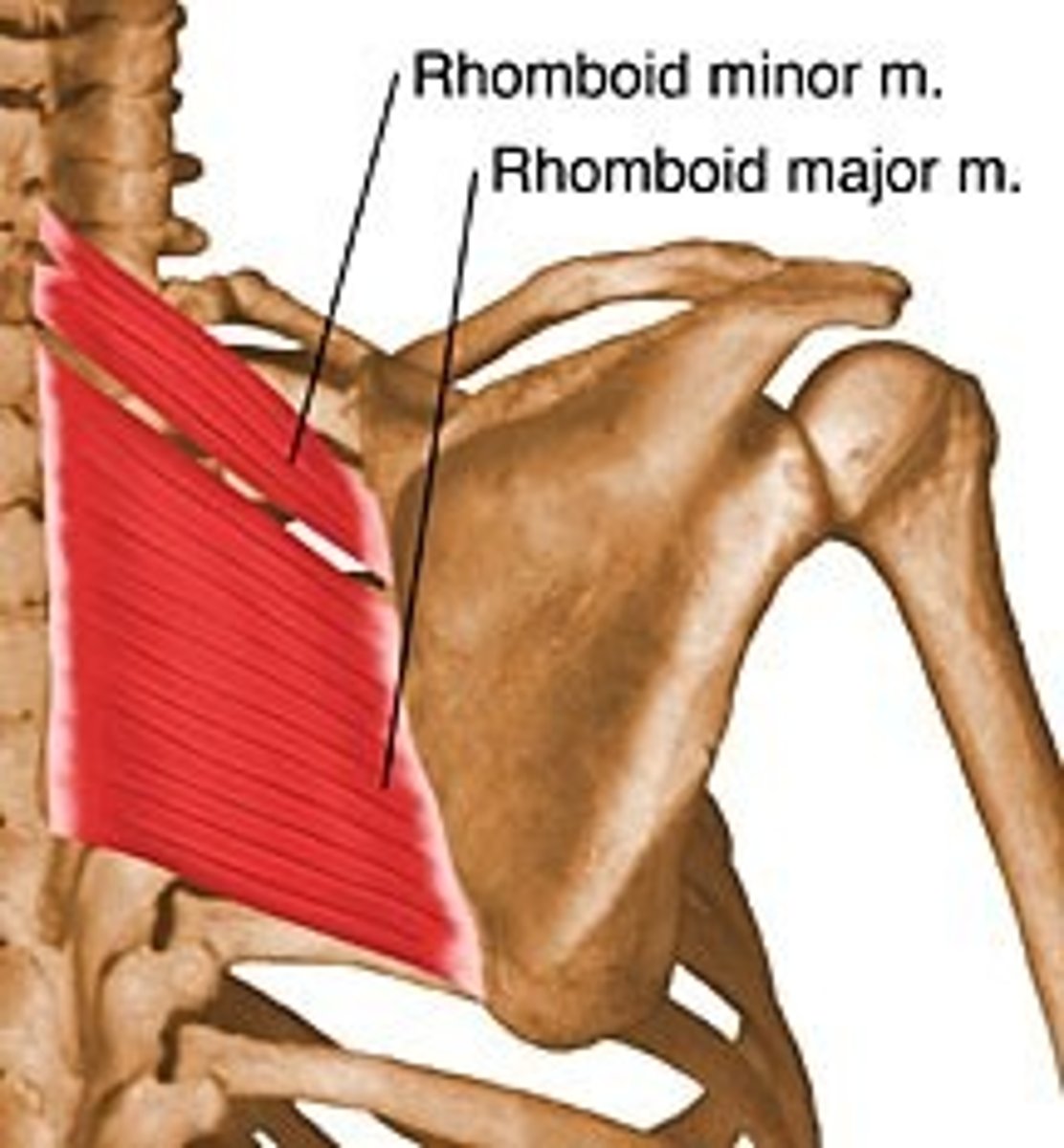
Rhomboids (major and minor)
Two roughly diamond shaped muscles lying deep to trapezius and inferior to levator scapulae; rhomboid minor is the more superior muscle;
A-stabilize scapula
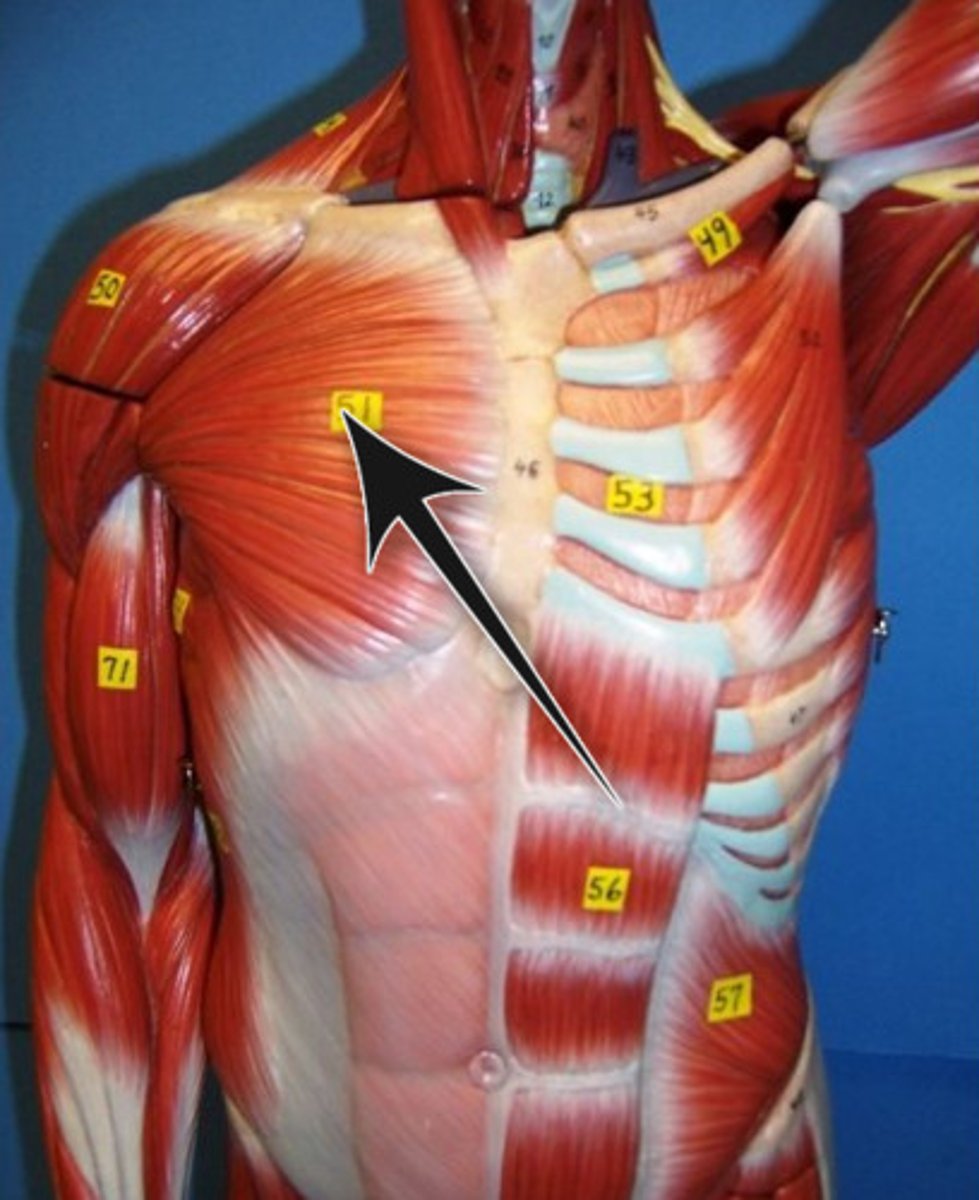
Pectoralis major
Large, fan-shaped muscle covering superior portion of chest; forms anterior axillary fold; divided into clavicular and sternal parts
A-adducts and medially rotates arm against resistance
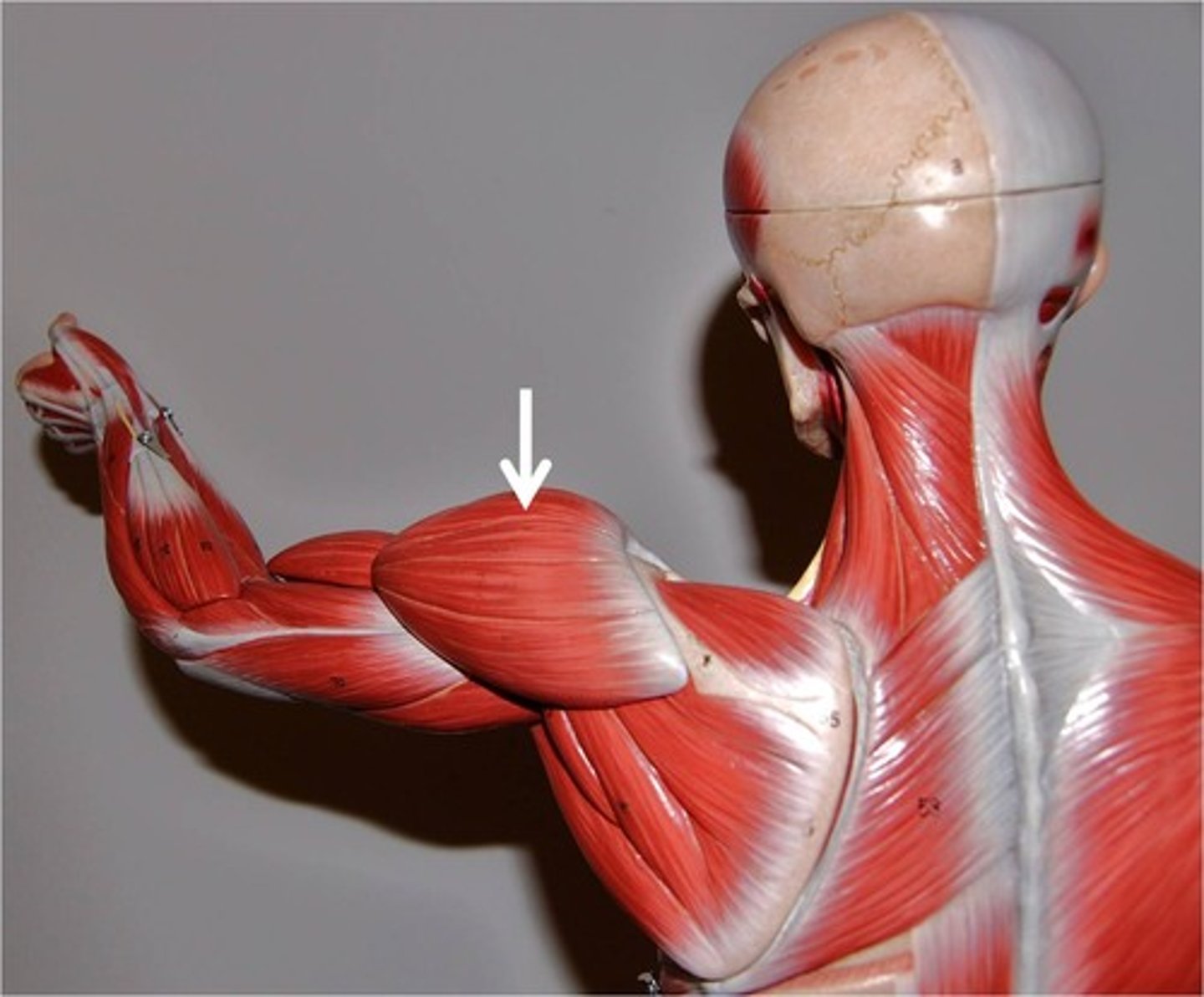
Deltoid
Thick, multipennate muscle forming rounded shoulder muscle mass; a common site for intramuscular injection, particularly in males, where it tends to be quite fleshy
A-Prime mover of arm abuction when all its fibers contract simultaneously
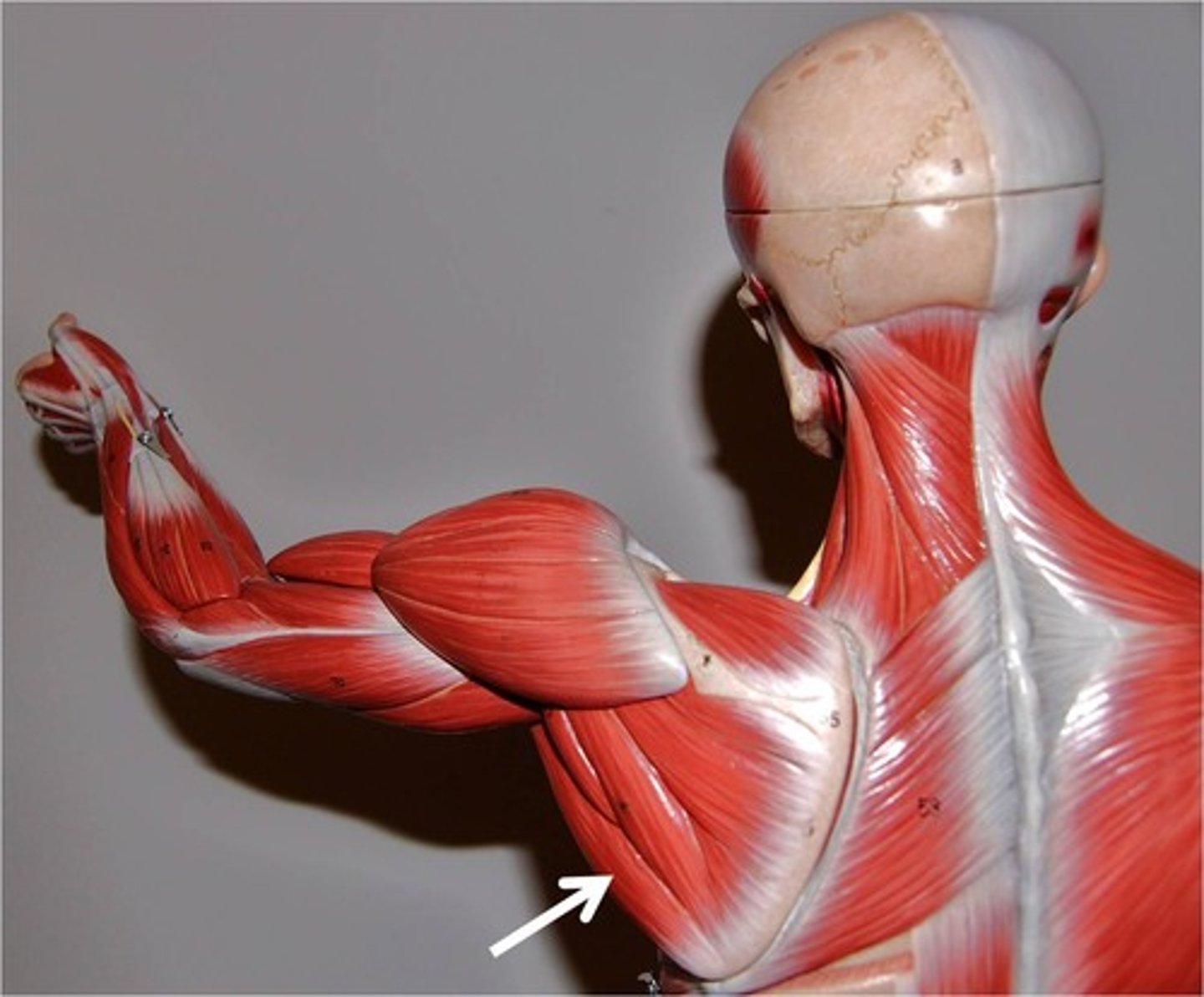
latissimus dorsi
Broad, flat, triangular muscle of lower back; extensie superficial origins; covered by trapezius superiorly; contributes to the posterior wall of axilla
A-prime mover of arm extension; powerful arm adductor; medially rotates arm at shoulder
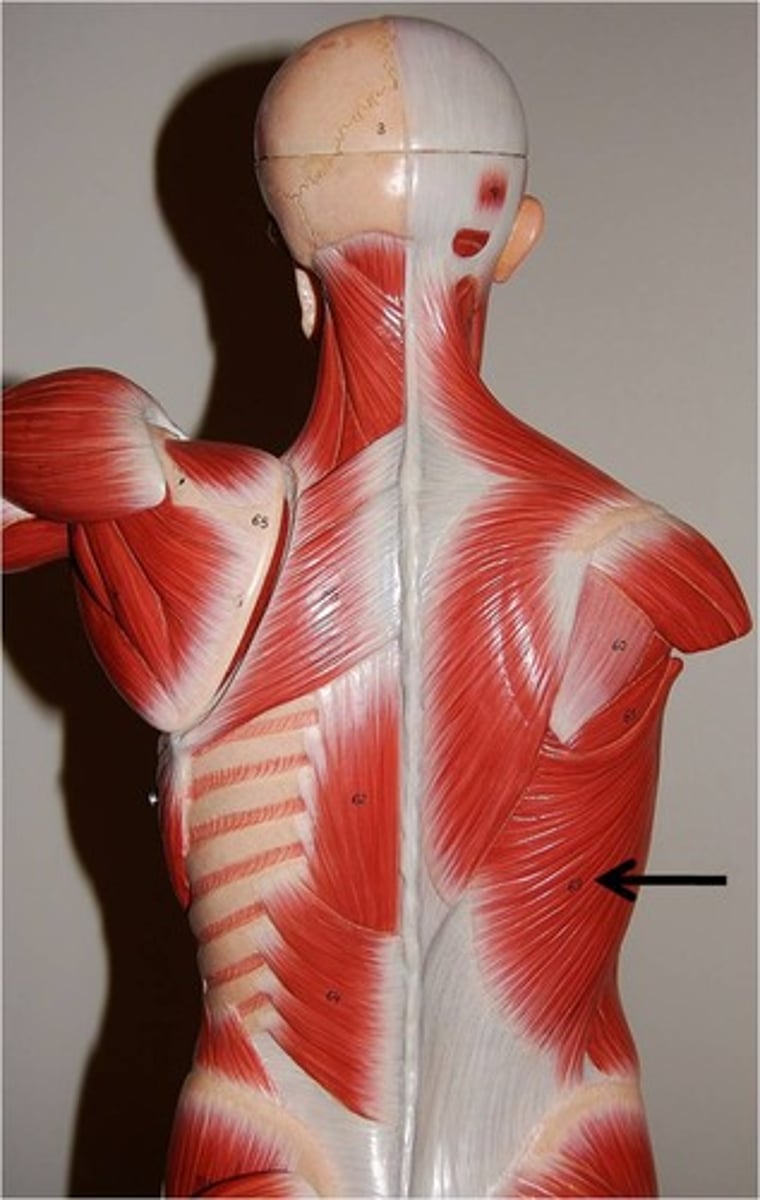
subscapularis
Forms part of posterior wall of axilla; tendon of insertion passes in front of shoulder joint; a rotator cuff muscle
A-Chief medial rotator of arm, assisted by pectoralis major; helps hold head of humerus in glenoid cavity, stabilizing shoulder joint
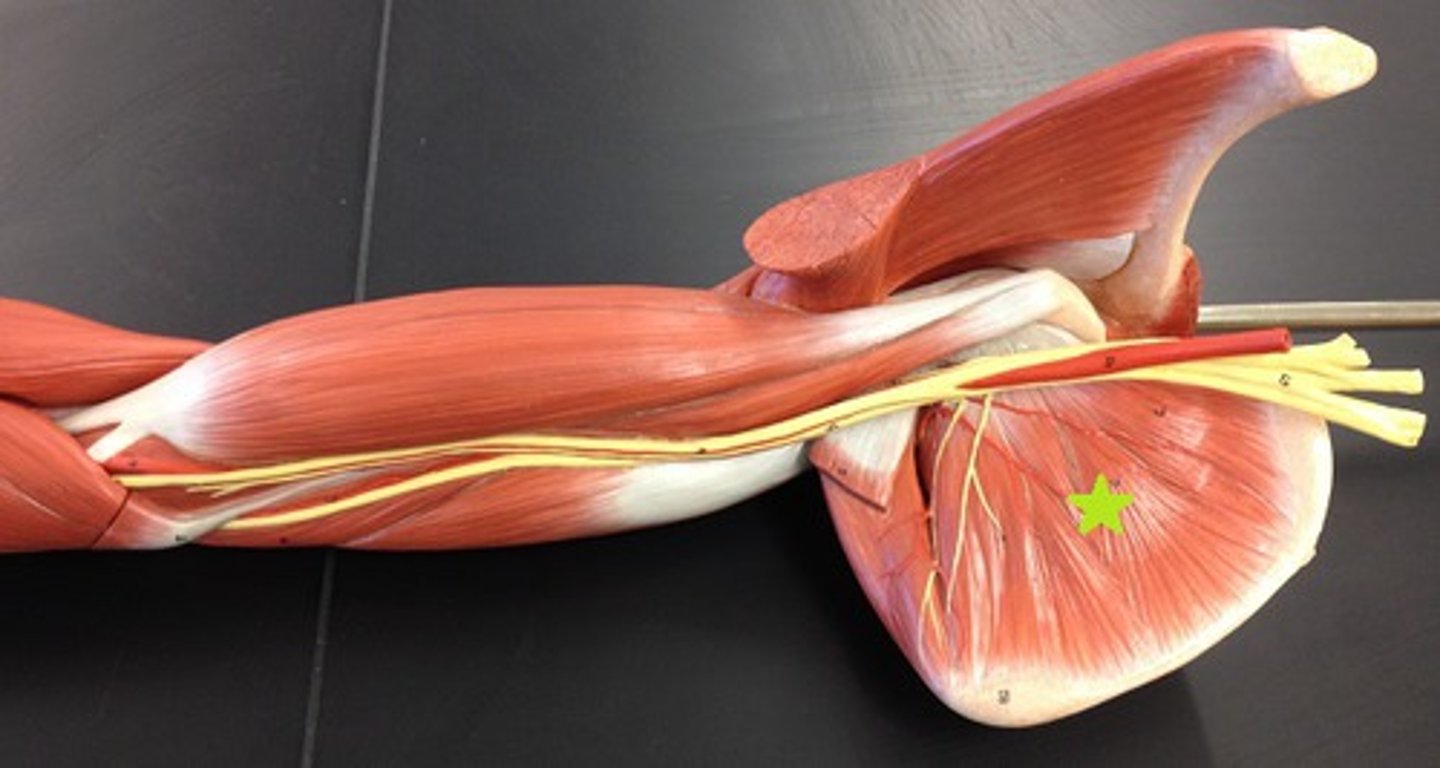
Supraspinatus
Named for its location on posterior aspect of scapula; deep to trapezius; a rotator cuff muscle
A-Initiates abduction of arm, stabilizes shoulder joint; helps prevent downward dislocation of humerus
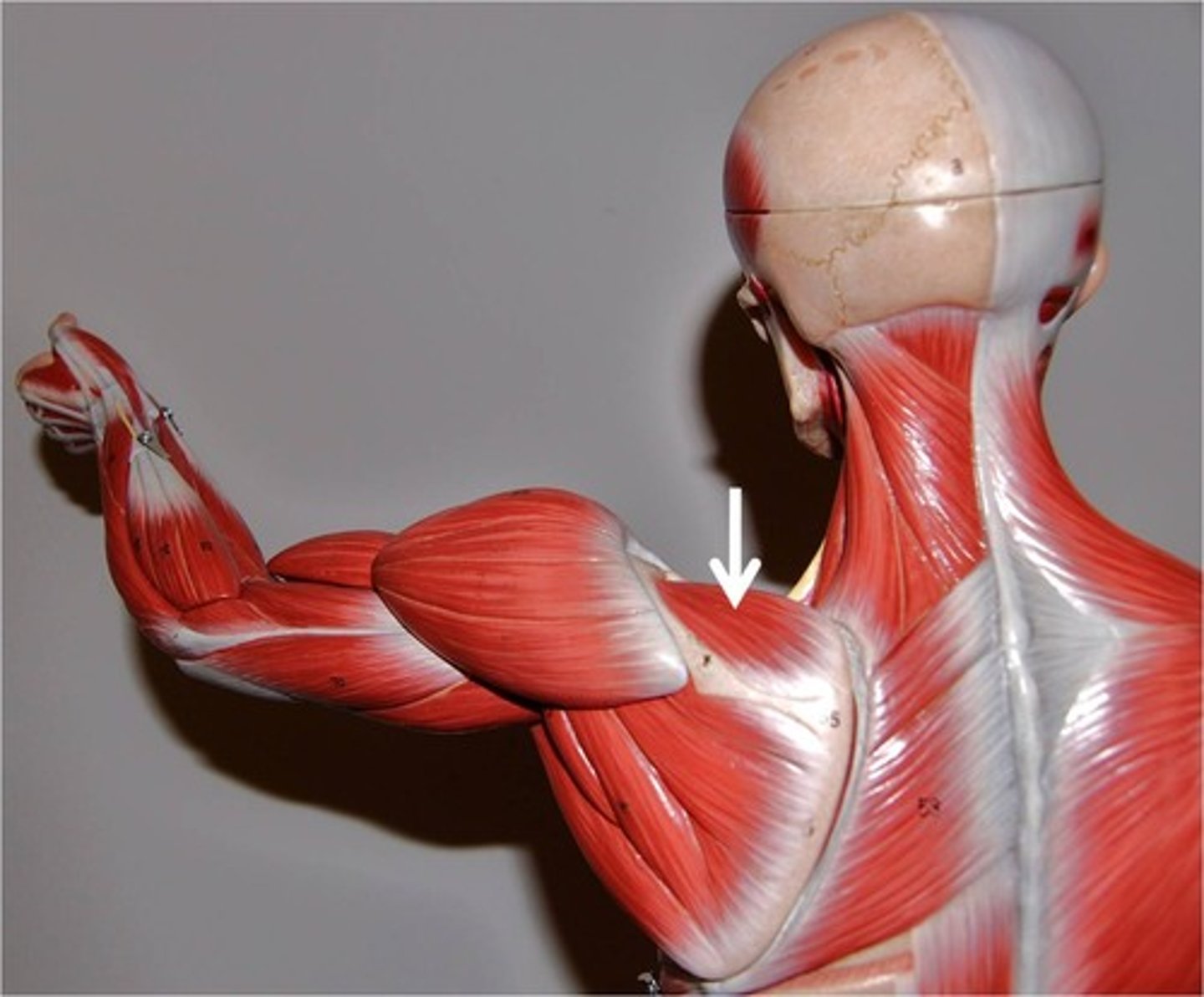
Infraspinatus
Partially covered by deltoid and trapezius; named for its scapular location; a rotator cuff muscle
A-Rotates arm laterally; helps hold head of humerus in glenoid cavity, stabilizing shoulder joint
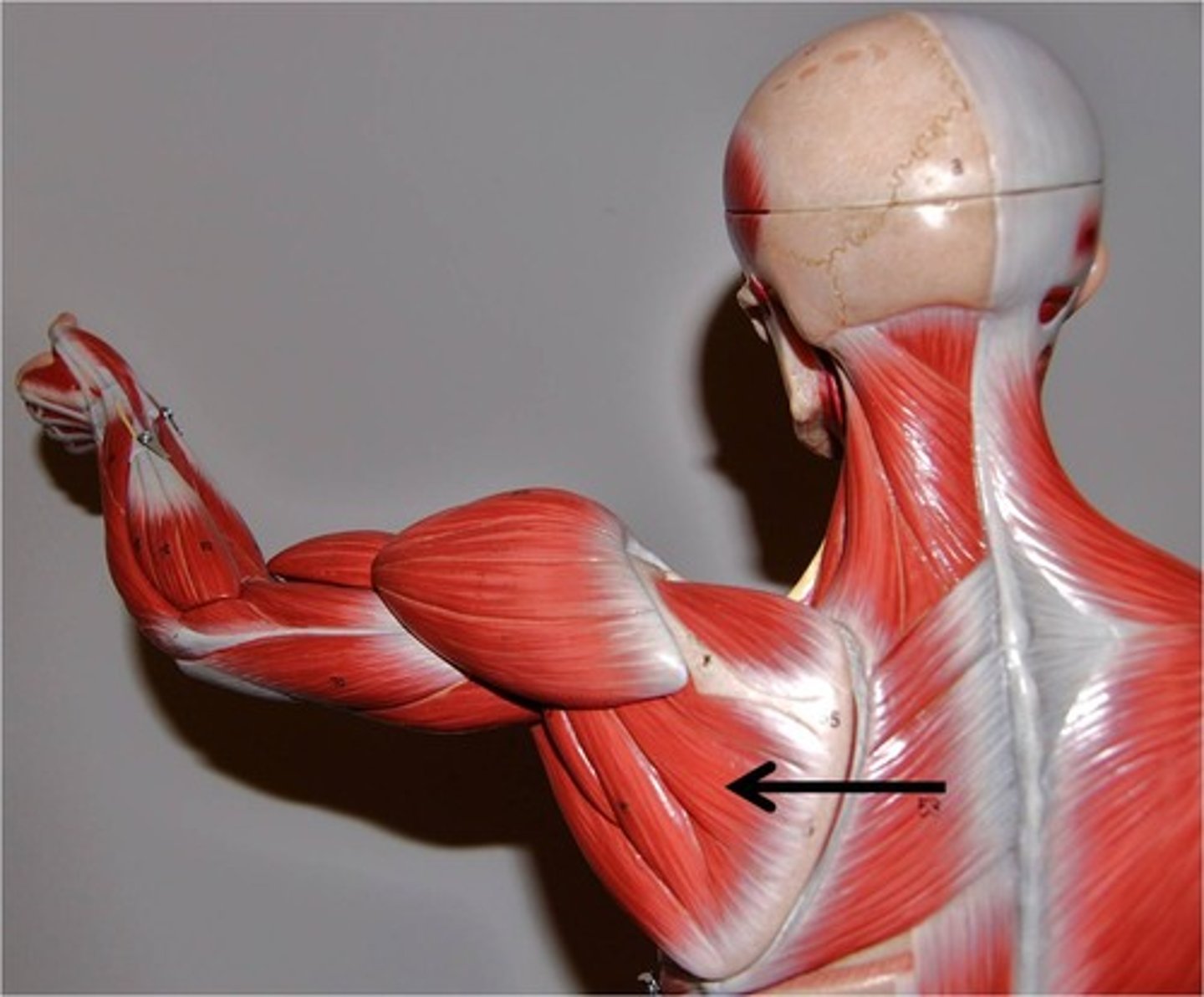
Teres minor
Small, elongated muscle; lies inferior to infraspinatus and may be inseparable from that muscle; a rotator cuff muscle
A-rotates arm laterally
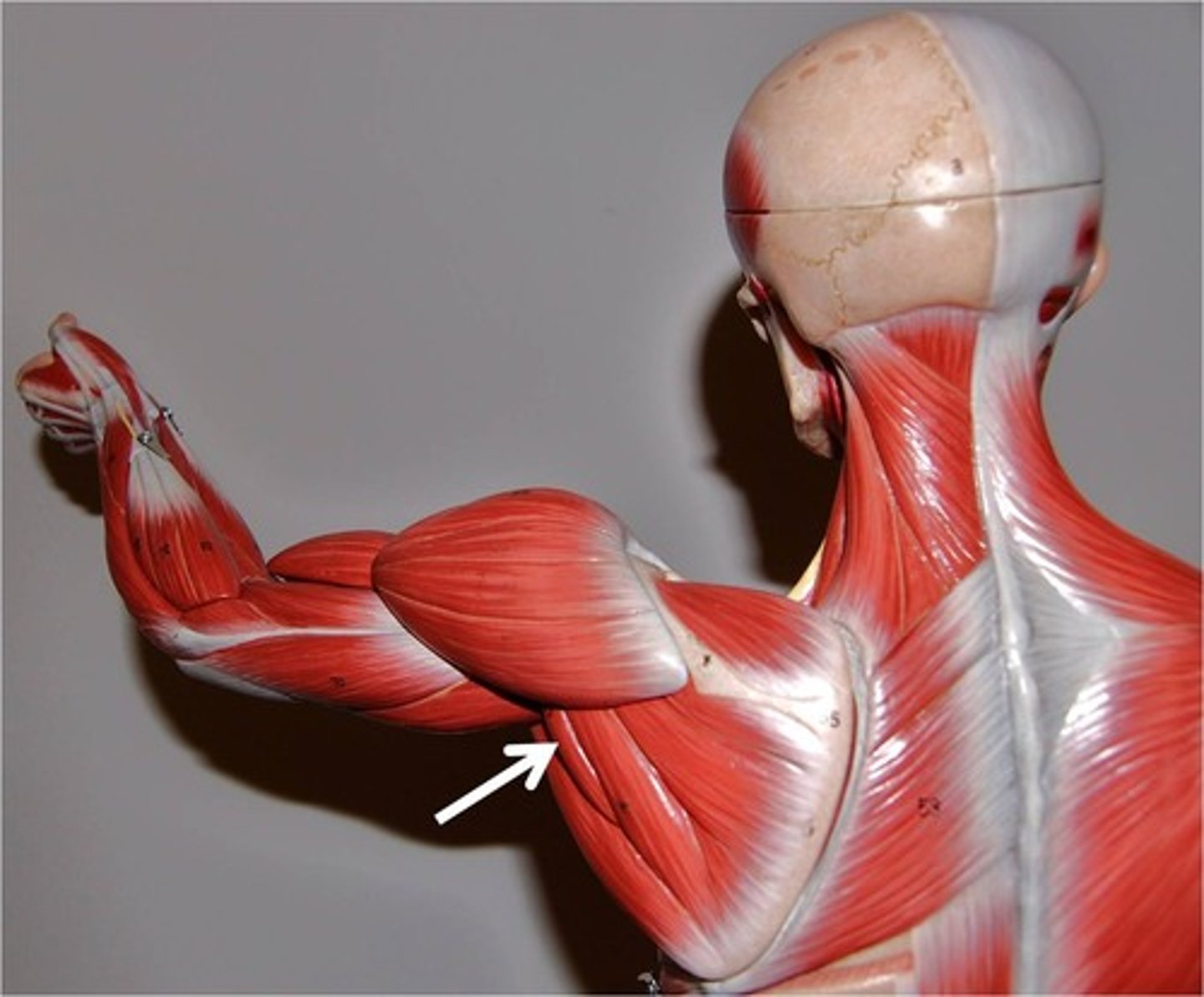
teres major
Thick, rounded muscle; located inferior to teres minor; helps form posterior wall of axilla along with latissimus dorsi and subscapularis
A-extends, medially rotates, and adducts arm; synergist of latissimus dorsi