Oogenesis, Folliculogenesis, and Egg Maturation
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Animal Science Oogenesis
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Ovary Two Major Functions
Oogenesis/Folliculogenesis and Steroidogenesis
Oogenesis
Produce fertilizable ova (pre-natally)
Steroidogenesis
Produce steroid hormones that maintain repro tract, facilitate migration of early embryo, and assist in successful implantation
Folliculogenesis
Growth of the ovarian follicle (contains the oocyte)
Female - XX Chromosome Pair (d35-36)
No SRY Protein → Ovaries develop → No AMH → Paramesonephric ducts become the oviducts, uterus, cervix, and part of vagina → Complete female repro tract
2 Prenatal Stages of Oocyte Maturation
Mitotic division (oogonia)
Nuclear Arrest (Primordial follicles)
2 Postnatal phases of Oocyte maturation
Cytoplasmic growth
Resumption of meiosis
Day 150 - Meiotic Arrest
Resulting in a fixed number of primordial follicles (ovarian reserve)
Cortex
Contains ovarian structures (follicles and corpus lutea) and is where ovulation occurs
Medulla
Contains the lymphatics, nerves, and vasculature
Primordial Follicle
Single layer flattened follicular cells, fixed # at birth
Primary Follicle
Single layer granulosa cells
Secondary Follicle
>2 layers granulosa cells, no antrum, zona pellucida
Tertiary Follicles
Multiple layers granulosa cells, antrum
Theca externa
Connective tissue (Tissue support), blood vessels end
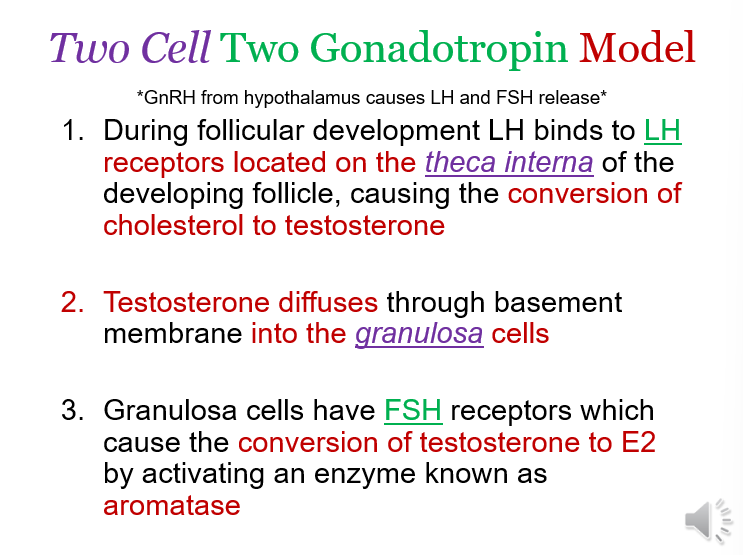
Theca interna
Bind LH → testosterone
Granulosa cells
Bind FSH → estrogen + follicle development
Zona pellucida
Separates oocyte from granulosa cells
______ days from activation to preovulatory
90
_____ from prenatal to preovulatory (large antral) size
42
______ days early antral to preovulatory (follicular wave)
10-13
Recruitment
A cohort of small antral follicles begin to grow and produce estrogen
Selection
One follicle selected to become dominant follicle (potentially ovulatory) from the cohort of previously recruited antral follicles
Dominance
Dominant follicle produces increasing amount if estrogen and inhibin
Dominant follicles exert ______ ______ on other antral follicles from the cohort
Inhibitory effects
GnRH - Hypothalamus
Causes release of gonadotropins
LH - Anterior Pituitary Gland
Estrogen production; Causes ovulation
FSH - Anterior Pituitary Gland
Estrogen production; Granulosa cell mitosis and follicular fluid production to form antrum
E2 - Ovarian Follicles
many - mating behavior
P4 - Ovarian Corpus Luteum
Pregnancy Maintenance
GnRH, LH, FSH critical roles in:
Steroidogenesis, growth, maturation, ovulation, and luteinization of the dominant follicle
FSH plays a major role in _____ ______ and stimulates granulosa cell mitosis and ______ _____ ______
Antrum Formation
Follicular Fluid Formation