Anatomy Finals
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
levels of organization from simplest to most complex
molecule
cell
tissue
organ
organ system
organism
superior v. inferior:
Superior:(ABOVE) Toward the head ex. Stomach
Inferior: (BELOW)Toward the feet ex. Pelvis
anterior v. posterior:
Anterior: (INFRONT) Toward the front ex. Sternum (breast bone)
Posterior: (BEHIND/BACK) Toward the rear ex. Brainsten
medial v. lateral
Medial: TOWARD the MIDLINE ex. The big toe is a medial (to the small toe)
Lateral: TOWARD the OUTSIDE/LEDGE ex. The ear is lateral to the nose
proximal v. distal
Distal: TOWARD the END of a LIMB ex. The wrist is distal (to the elbow)
Caudal: AWAYFROM the HEAD, same as inferior. (FEET)
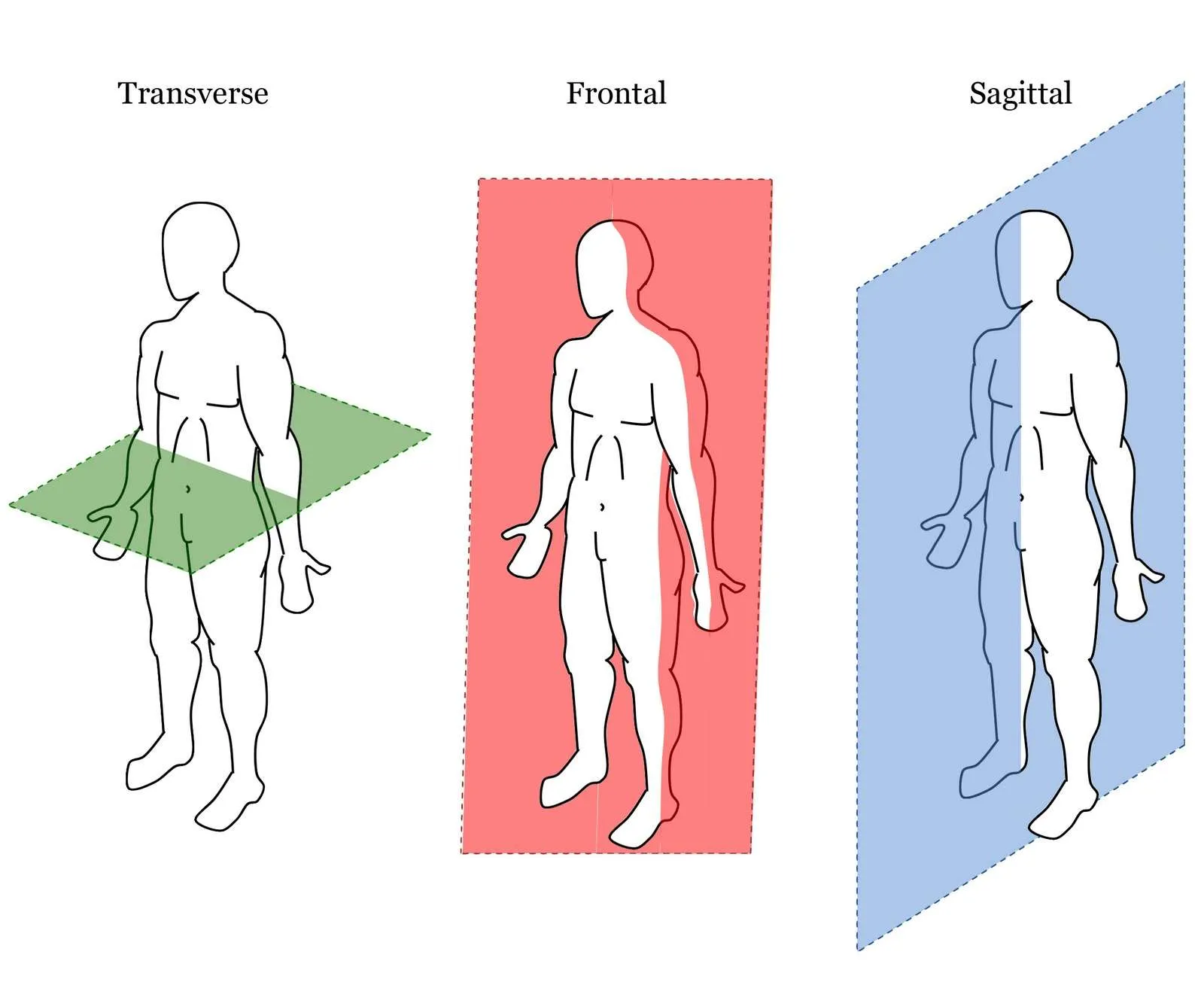
sagittal (or longitudinal)
frontal (or coronal)
transverse
Receptor
takes information from the body about variables. Responds to changes in the environment and sends information to the control center.
Effector
takes action in the body to change variables. Provides a means for response to the stimulus.
control center
determines whether variables above/low set point, analyzes the information whether action is required or appropriate response.
CNS v. PNS
(CNS): consists of the brain and spinal cord. Incoming sensory information and issue instructions based on past experience and current conditions. They send the information out to the body.
(PNS): part of the nervous system outside the CNS. Consists nerves that extend from the brain and spinal cord. Spinal nerves carry impulses to and from the spinal cord. Cranial nerves carry impulses to and from the brain.
somatic v. autonomic:
The somatic nervous system - allows us to voluntarily control our skeletal muscles, referred to as the voluntary nervous system.
autonomic nervous system - involuntary. Referred to as the involuntary nervous system has 2 parts - the sympathetic and parasympathetic, which brings the opposite effects. One stimulates and the other inhibits. Cardiac, smooth muscle, and glands.
parasympathetic v. sympathetic:
Parasympathetic conserves energy and promotes rest, while sympathetic activates the fight or flight response.
Muscle Types
Skeletal | Cardiac | Smooth | |
where found in the body? | everywhere | heart | organs |
appearance? | striated | striated | not striated (smooth) |
control of contraction? | voluntary | involuntary | involuntary |