Western Expansion and the Civil War Era (1830-1865)
1/178
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
179 Terms
What term did John Lewis O'Sullivan use to describe the idea of America's right to expand?
Manifest Destiny.
What religious aspect is associated with Manifest Destiny?
America is viewed as a promised land.
What racial aspect is linked to the concept of Manifest Destiny?
The belief in the superiority of the Anglo-Saxon race.
Who painted 'American Progress' in 1872?
John Gast.
By 1860, how many Americans had crossed the Mississippi River?
4.3 million.
What was the Oregon Trail?
A 2,000-mile journey from Missouri to Oregon, taking about six months.
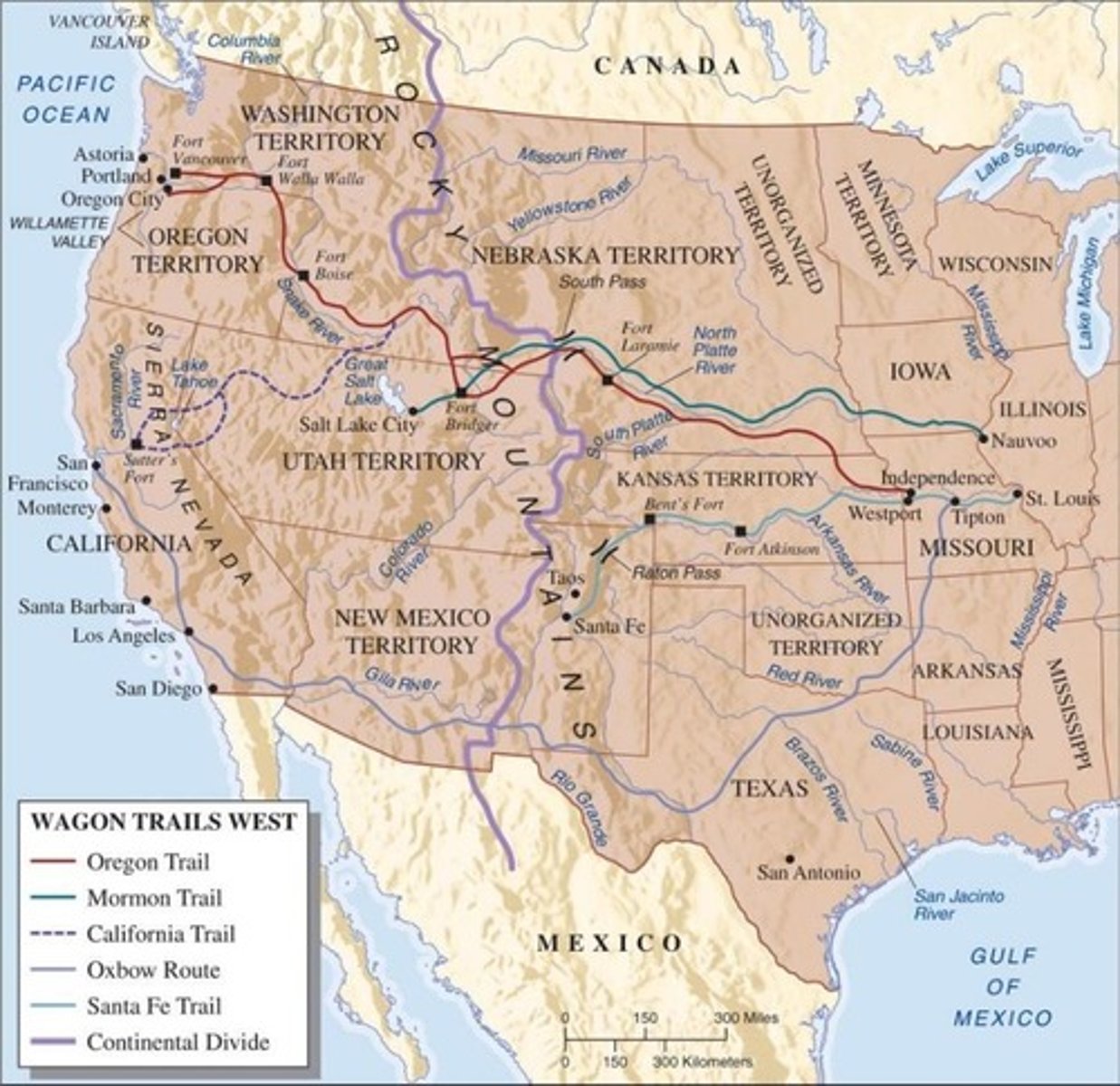
What was the population of Native Americans on the Great Plains by 1840?
Two-thirds of Native Americans lived on the Great Plains.
When did Mexico gain independence?
1821
What agreement did Great Britain and the U.S. reach in 1818 regarding Oregon Country?
They agreed to joint occupation.
What caused 'Oregon Fever' in the 1830s?
Rich soil attracted migrants to Oregon.
What was the population of California in 1840?
10,000 Hispanics and 800 Americans.
What law did Spain enact in 1820 regarding colonists?
It allowed colonists of any religion to settle in Texas.
Who was Stephen F. Austin?
An empresario who led the first successful colonization of Texas.
What was the 'Law of 1830' in Mexico?
It outlawed immigration from the USA and banned slave imports.
What significant event occurred in 1835 regarding Texian rebellion?
Texians and volunteers rose up against the Mexican nation.
What happened at the Alamo in February 1836?
Santa Anna's troops fought against Americans for 12 days.
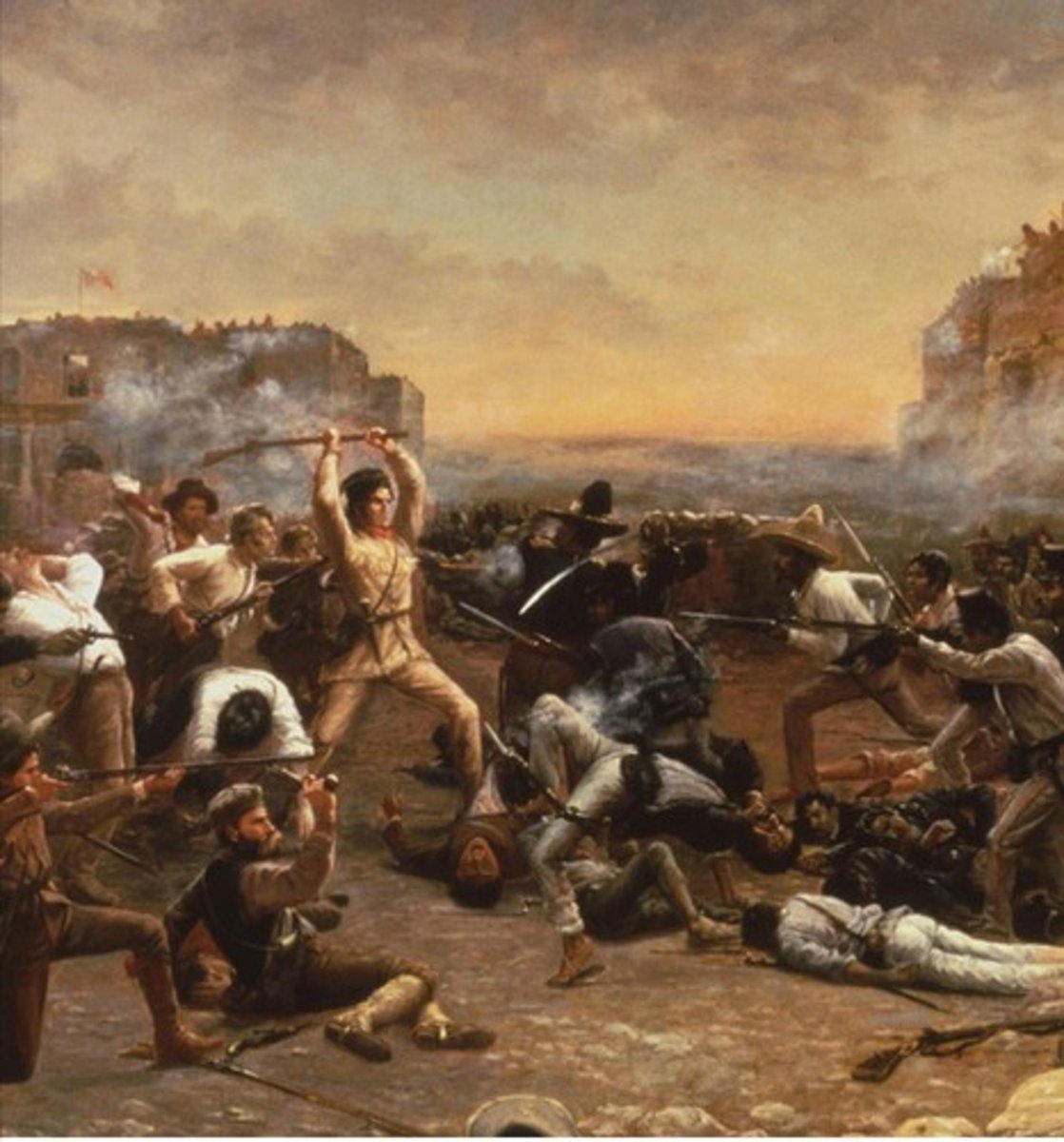

Who led the Texian army during the Battle of San Jacinto?
Sam Houston.
What was the outcome of the Battle of San Jacinto?
630 Mexicans were killed, and 700 surrendered; only nine Texian deaths occurred.
What was the southern boundary of the Republic of Texas as per the treaty?
The Rio Grande.
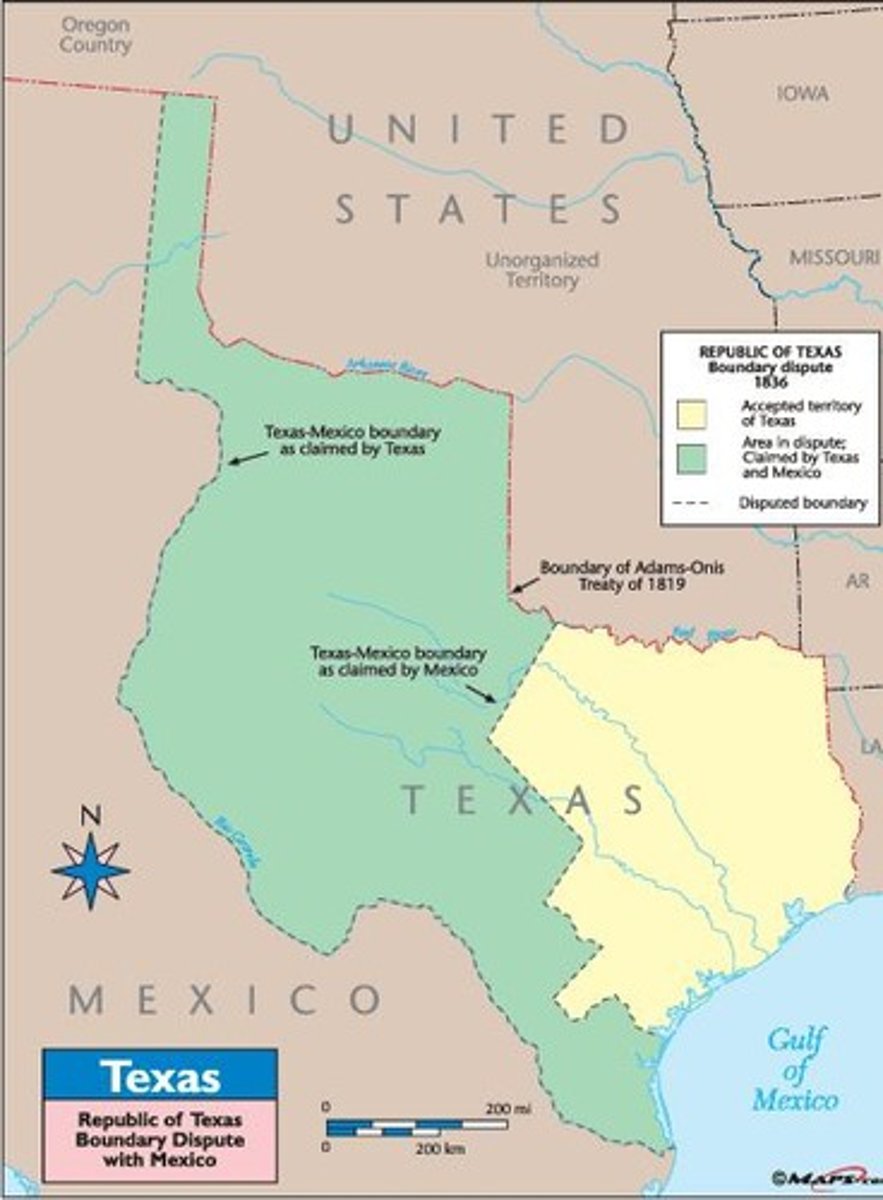
What was one of the policies of the Republic of Texas regarding slavery?
It legalized slavery and banned free blacks.
Who became the first president of the Republic of Texas?
Sam Houston.
What was one of the concerns of Andrew Jackson regarding Texas annexation?
The potential for adding a slave state and possible war with Mexico.
What was the Pre-Emption Act of 1841?
It permitted squatters on federal land to purchase land at a low price.
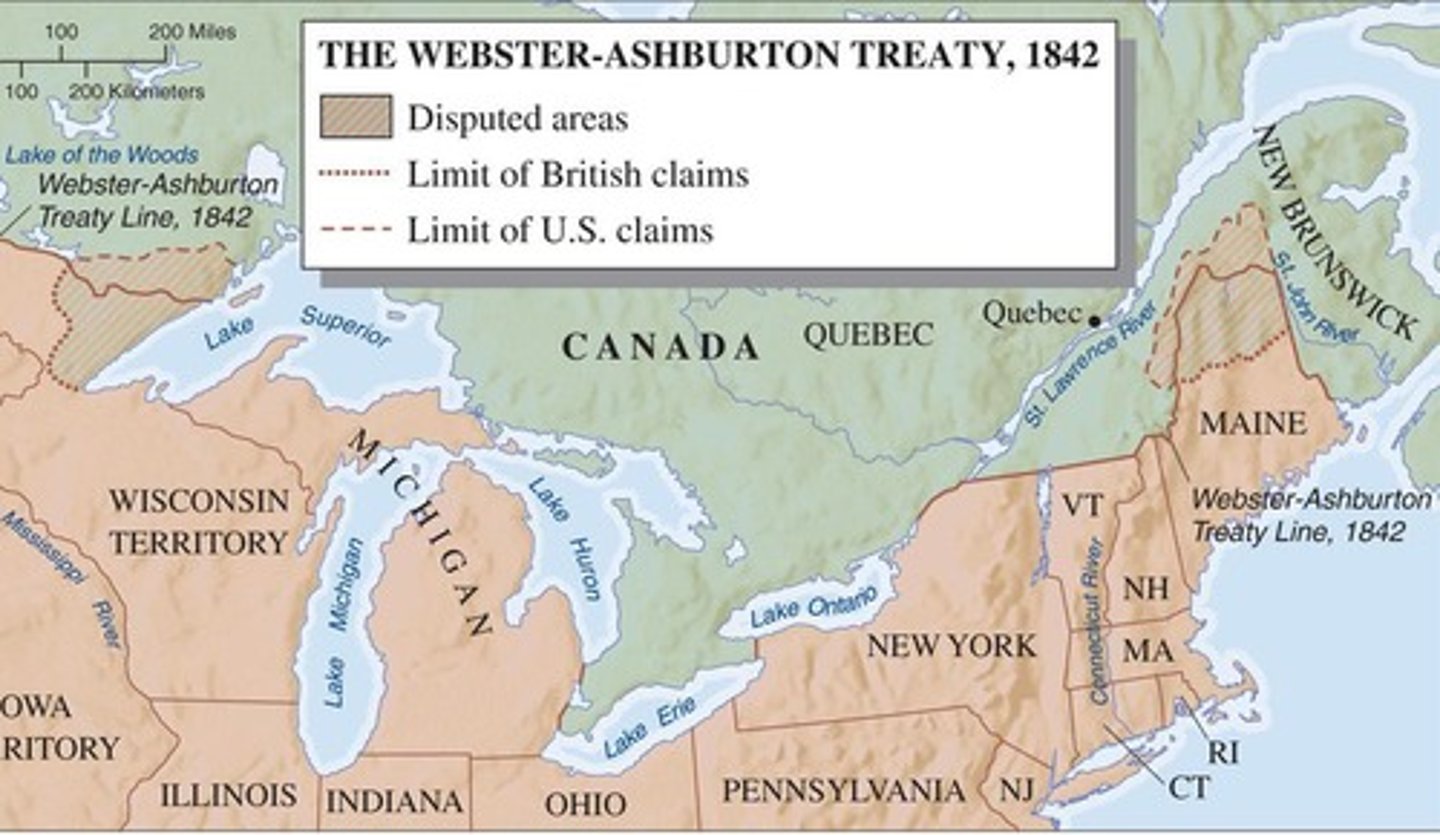
What treaty was signed in 1842 regarding the boundary between Maine and New Brunswick?
The Webster-Ashburton Treaty.
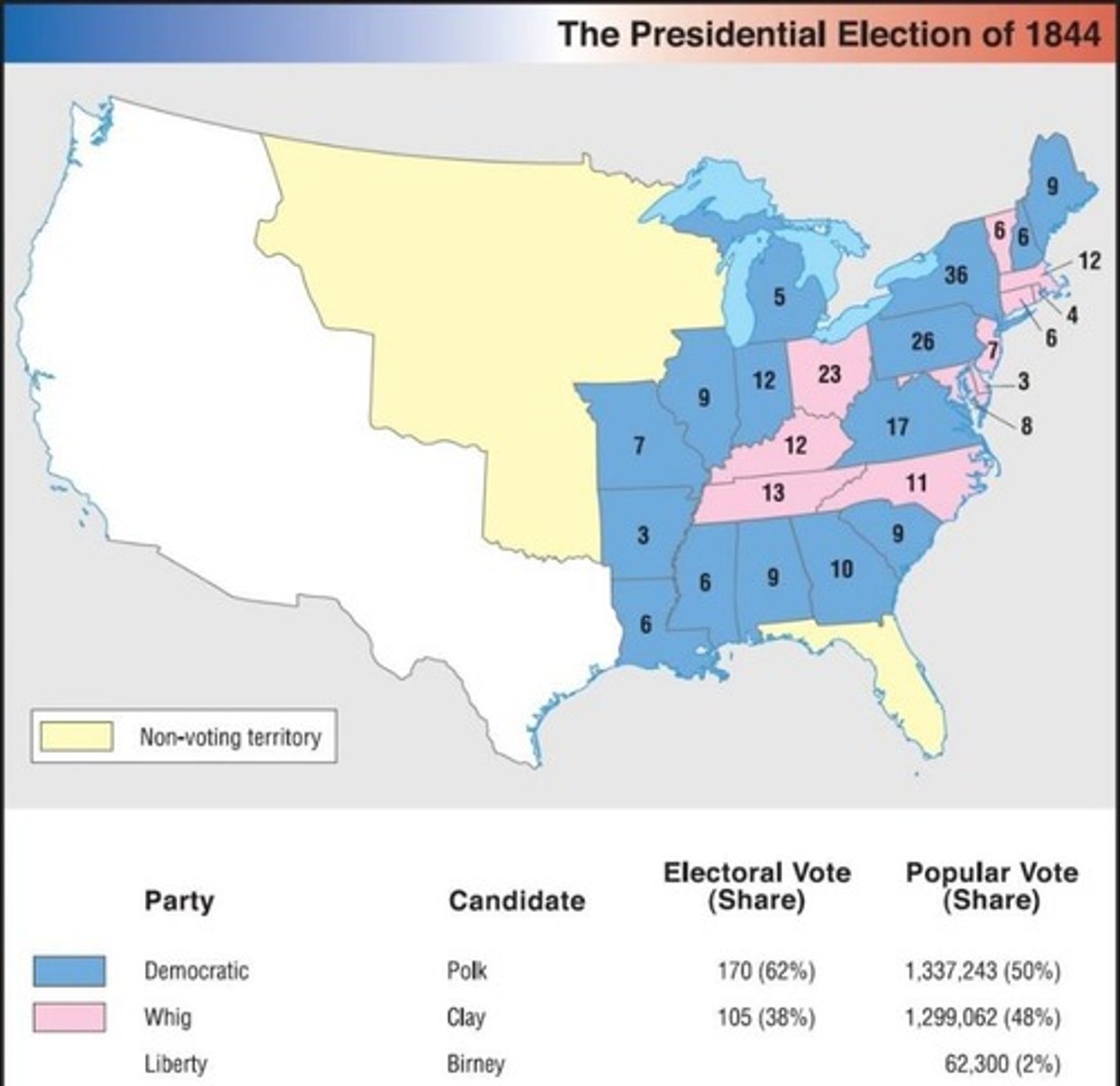
Who won the 1844 Presidential Election?
James Polk (Democrat) defeated Henry Clay (Whig).
What were the three main territorial acquisitions sought by President Polk?
1) Independent Treasury (no national bank), 2) Oregon Territory, 3) California from Mexico.
What treaty secured the U.S. claim to the Pacific Northwest south of the 49th parallel?
The Buchanan-Pakenham Treaty, signed on June 12th, 1846.
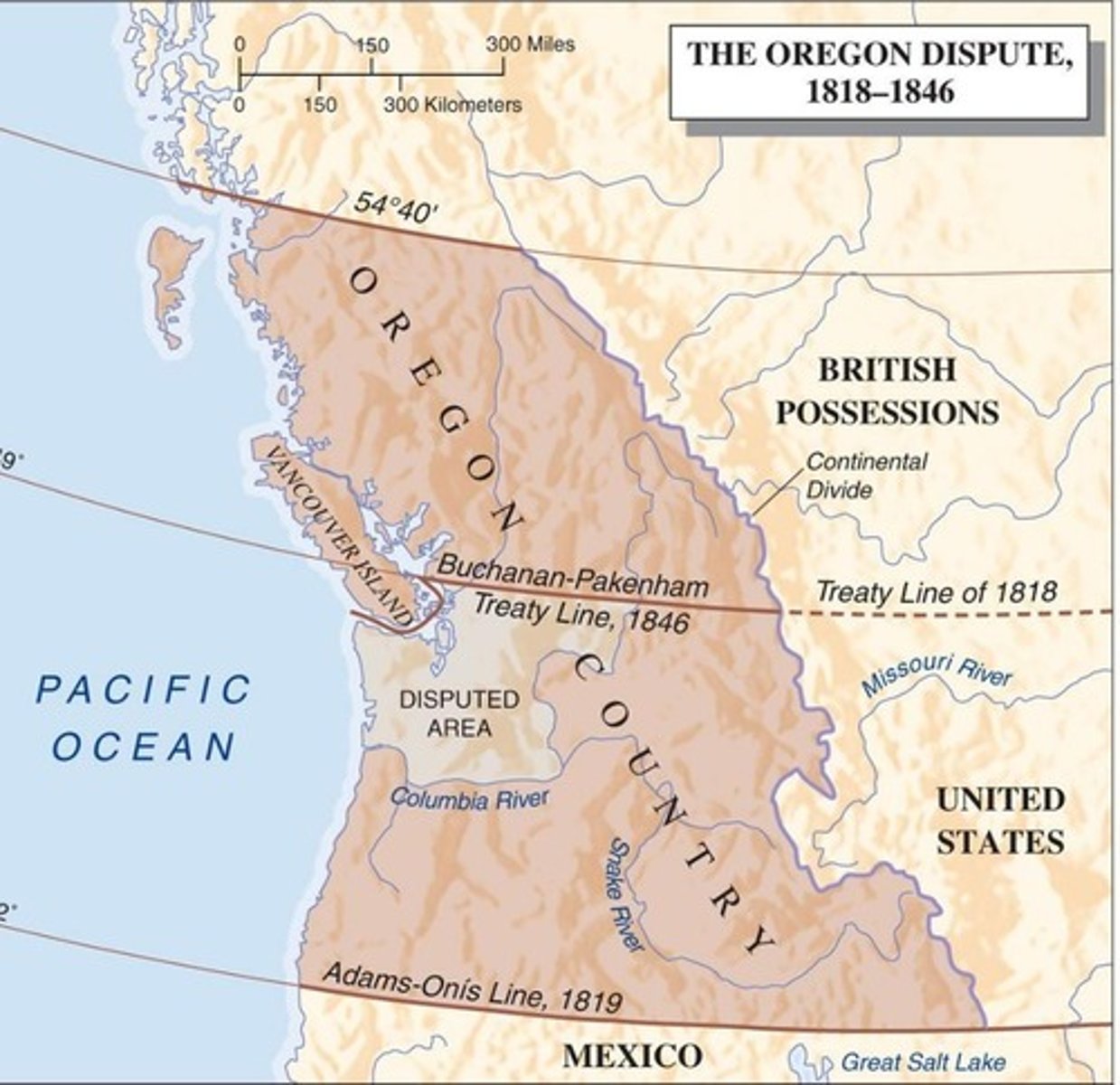
What event marked the end of diplomatic relations between Mexico and the USA?
Mexico ended diplomatic relations with the USA on March 6th, 1845.
What was the recognized northern boundary of Mexico prior to Texas independence?
The Nueces River.
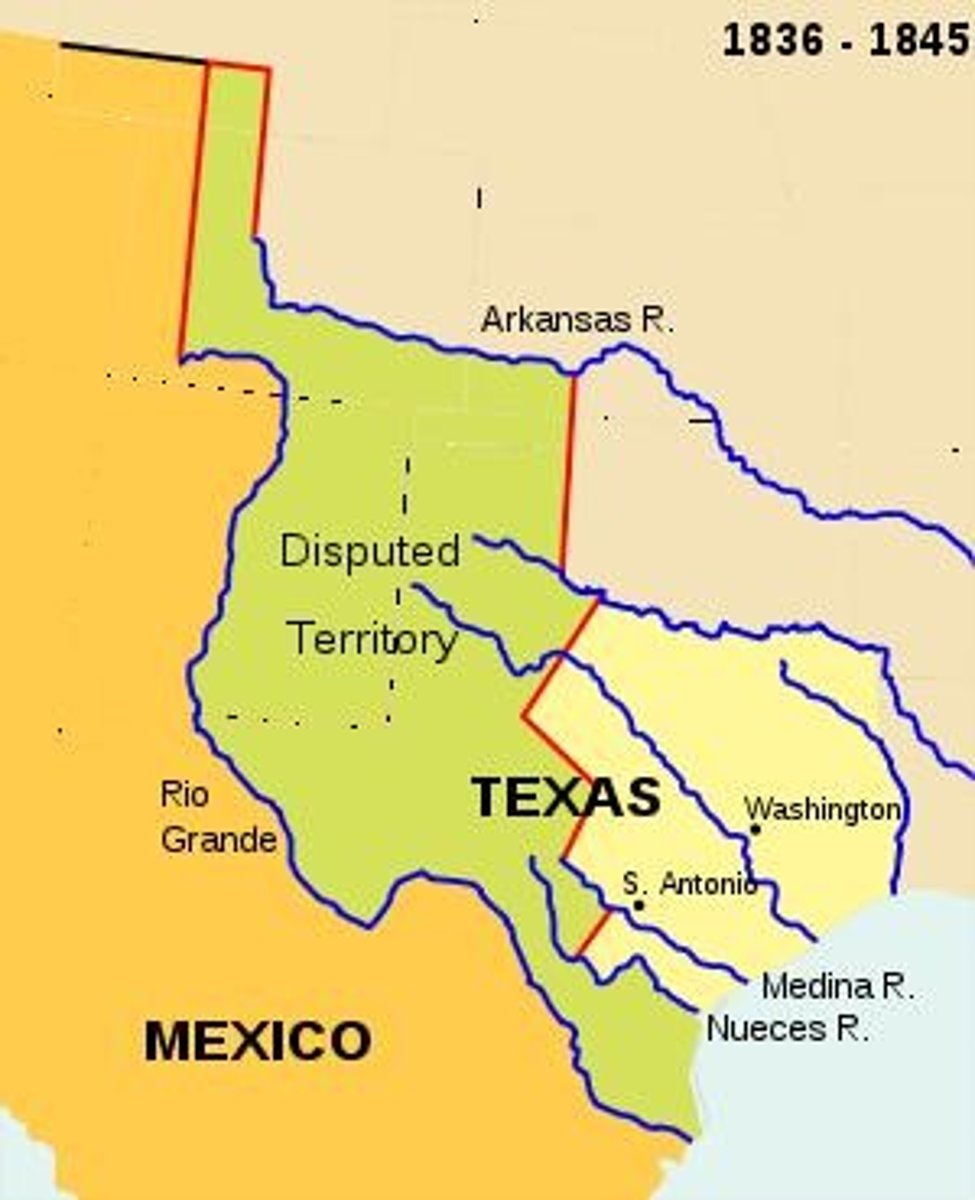
What was the new border of Texas after its independence?
The border was pushed 150 miles south to the Rio Grande.
What were the main objectives of John Slidell's mission to Mexico?
1) Cancellation of Mexican debt from the Mexican Revolution, 2) Official recognition of the new border, 3) $30 million for California and New Mexico.
What incident sparked the Mexican-American War?
Mexican cavalry killed 11 and captured 47 U.S. soldiers on April 25th, 1846.
When did Congress declare war on Mexico?
May 13th, 1846.
What was Abraham Lincoln's contribution to the debate over the Mexican-American War?
He introduced the 'Spot Resolutions' in December 1847, questioning whether blood was shed on U.S. soil.
Who captured Mexico City during the Mexican-American War?
General Winfield Scott on September 14, 1847.
What were the territorial gains for the U.S. as a result of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo?
Texas north of the Rio Grande, California, New Mexico, and parts of Arizona, Colorado, Nevada, Utah, and Wyoming for $15 million.
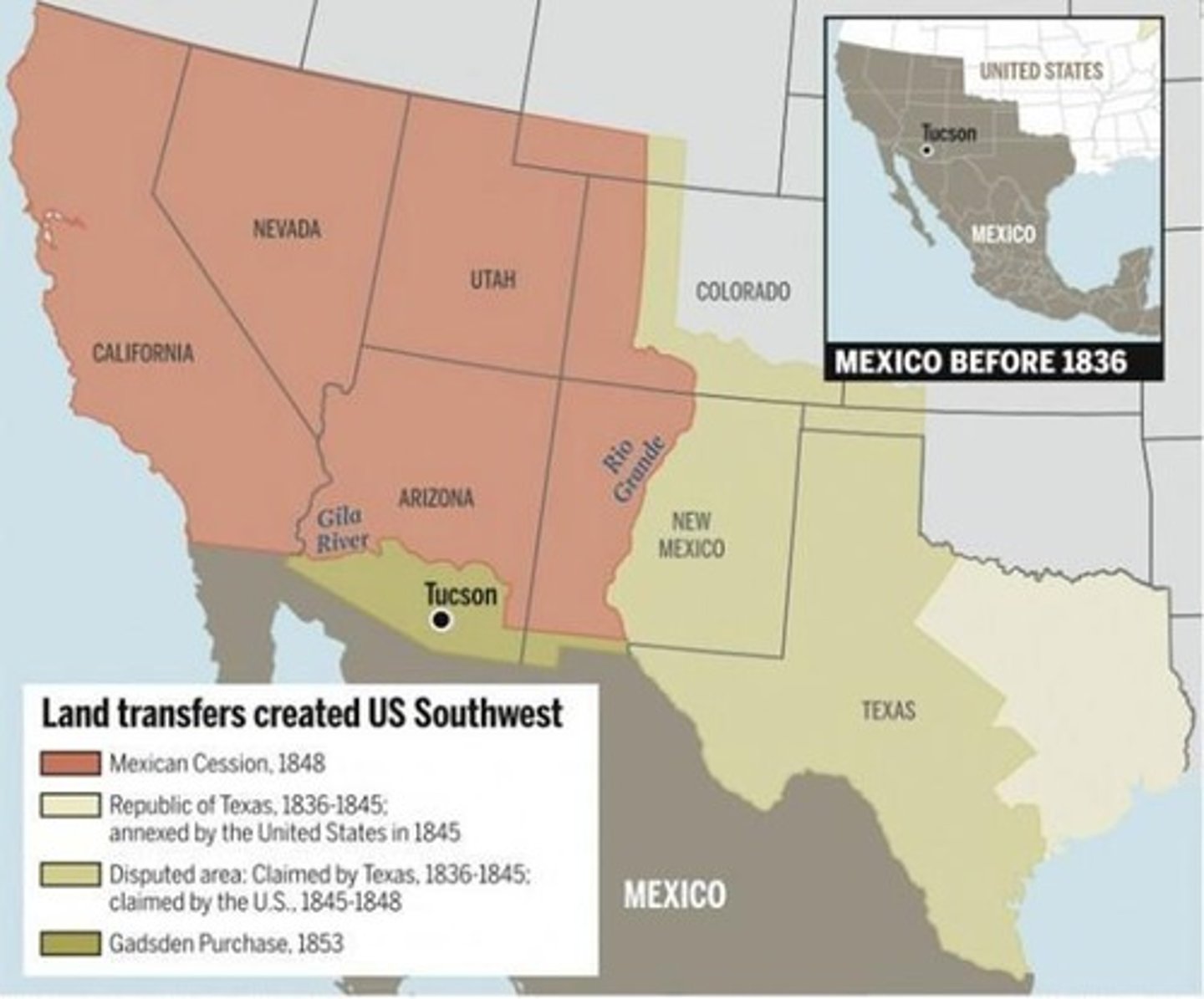
What was the casualty rate for American soldiers during the Mexican-American War?
The highest casualty rate for any American war, with 110 out of every 1,000 dying, mostly from disease.
What was the Wilmot Proviso?
A proposal to allow slavery in Texas but not in former Mexican lands, which was defeated in the Senate.
What was Calhoun's argument regarding slavery?
He argued that the Bill of Rights guaranteed the right to slavery.
What was the concept of popular sovereignty proposed by Lewis Cass?
The idea that citizens should regulate their own affairs regarding slavery.
Who were the main candidates in the 1848 presidential election?
Lewis Cass (Democrat) and Zachary Taylor (Whig).
What was the Free Soil Party's stance in the 1848 election?
They aimed to prevent the expansion of slavery into the West.
Who was the presidential candidate for the Free Soil Party?
Martin Van Buren.
What significant discovery was made in California on January 24th, 1848?
Gold was found on John Sutter's property in Sacramento Valley.
How did the population of Americans in California change by the end of 1849?
It increased from 700 to 100,000 Americans.
What was the Compromise of 1850?
A series of resolutions aimed at balancing the interests of the North and South regarding slavery.
What were the key components of the Compromise of 1850?
1) California admitted as a free state, 2) Texas-New Mexico Act, 3) Utah Act, 4) Fugitive Slave Act, 5) Abolishment of public sale of slaves in D.C.
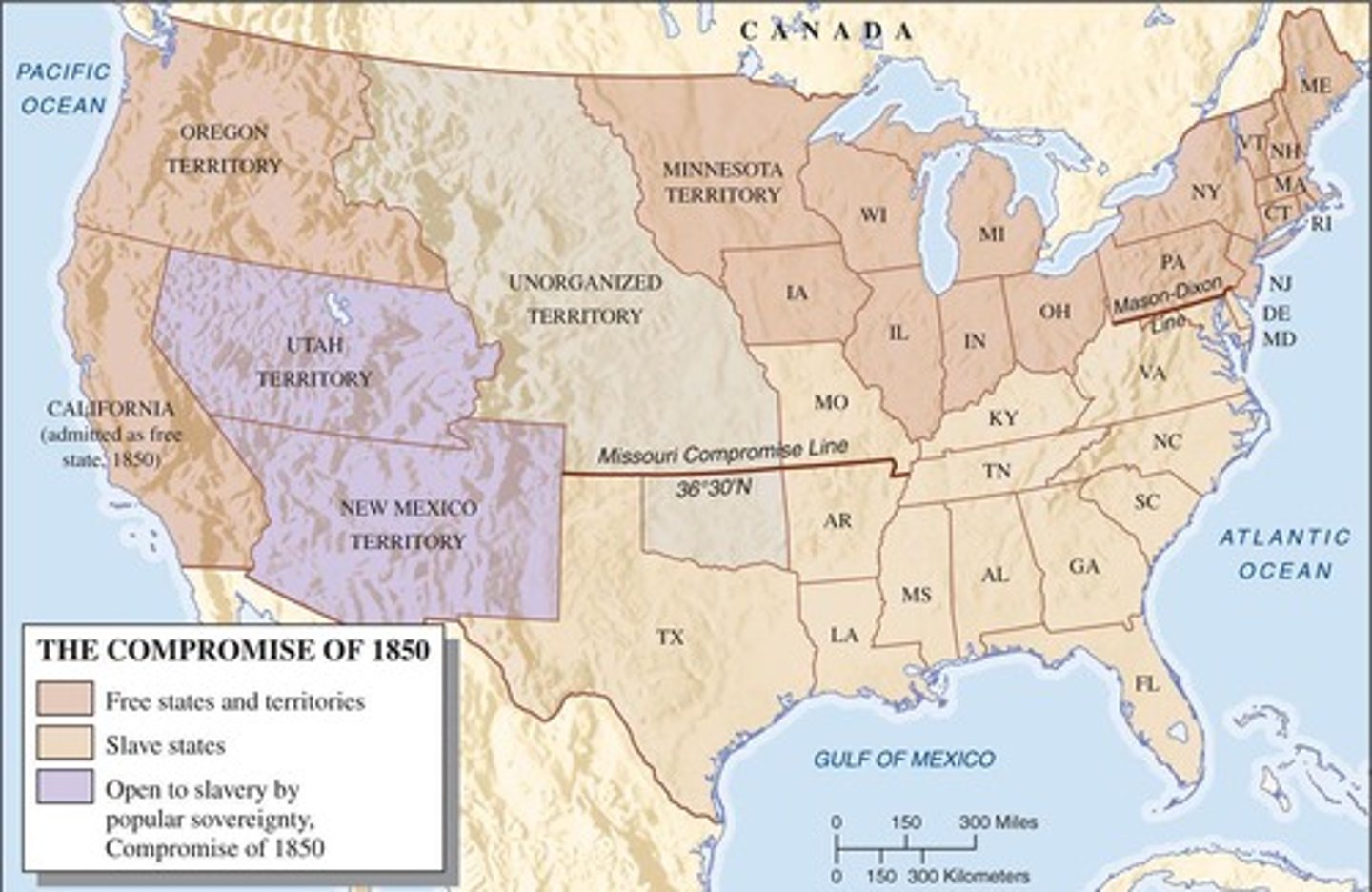
What principle determined the issue of slavery in Utah and New Mexico?
Popular sovereignty.
What was a consequence of the Fugitive Slave Act in the North?
It provided temptation to kidnap free blacks.
What could federal marshals compel citizens to do under the Fugitive Slave Act?
Assist in capturing runaway slaves.
How many slaves were returned under the Fugitive Slave Act by 1860?
Only 330 slaves were returned due to widespread opposition.
What was the reward offered for the capture of the runaway slave James Hart?
One hundred dollars if taken in Maryland, or one hundred and fifty dollars if taken out of state.
What is the title of the novel by Harriet Beecher Stowe that exposed the horrors of slavery?
Uncle Tom's Cabin.
How many copies of Uncle Tom's Cabin were sold in its first year?
300,000 copies domestically and 1 million in Great Britain.
What significant political event occurred in the 1852 election?
Democrats chose Franklin Pierce, and Whigs chose General Winfield Scott.
What did the Kansas-Nebraska Act of 1854 allow settlers to decide?
The issue of slavery in the new territory.
Who was the senator behind the Kansas-Nebraska Act?
Senator Stephen Douglas.
What was the impact of the Kansas-Nebraska Act on the Missouri Compromise?
It overturned the Missouri Compromise latitude line.
What violent conflict arose from the Kansas-Nebraska Act?
Bleeding Kansas.
What event involved John Brown and his sons attacking a pro-slavery settlement?
The attack on Pottawatomi.
What was the outcome of the Bleeding Sumner incident?
Congressman Preston Brooks assaulted Charles Sumner, worsening tensions in the Union.
Who were the candidates in the 1856 presidential election?
Democrats chose James Buchanan and Republicans nominated John C. Fremont.
What was the Supreme Court's ruling in Dred Scott v. Sanford?
Scott was not a citizen and could not petition the court for freedom.
What did Chief Justice Roger Taney state about black citizenship in the Dred Scott decision?
No black, free or slave, could claim U.S. citizenship.
What was the main topic of the Lincoln-Douglas debates?
The issue of slavery and popular sovereignty.
What did Abraham Lincoln argue about the future of the American government during the debates?
It could not endure permanently half-free and half-slave.
What was the significance of Minnesota's admission as a free state in 1858?
It increased paranoia in the South.
What was John Brown's plan in October 1859?
To cause a slave uprising in Virginia.
What event did John Brown and his followers plan in 1859?
They planned to cause a slave uprising in Virginia.
What was the outcome of John Brown's raid?
His plan failed, but he became a martyr for the abolitionist cause.
What significant political split occurred during the 1860 Presidential Election?
The Democrats split into Northern Democrats, who chose Douglas, and Southern Democrats, who chose John C. Breckenridge.
What was Lincoln's role in the 1860 Presidential Election?
He was selected as the candidate for the Republican Party.
What party did the border states form during the 1860 election?
The Constitutional Union Party, with John Bell as its candidate.
What percentage of the popular vote did Lincoln receive in the 1860 election?
39% of the popular vote.
What was the significance of the cartoon titled 'Prospect of a Smash Up' from 1860?
It depicted the Democratic Party about to be split by sectional differences and the rise of Republicans.
When did South Carolina pass the Ordinance of Secession?
On December 20, 1860.
What was President Buchanan's response to South Carolina's secession?
He declared it illegal but claimed no constitutional authority to compel South Carolina to rejoin.
What actions did secessionists take after South Carolina's secession?
They seized federal forts.
What happened on January 5, 1861, regarding Fort Sumter?
Buchanan attempted to resupply Fort Sumter, but the ship was forced back.
Which states seceded by February 1, 1861?
South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas.
What did the seceded states adopt on February 4, 1861?
A new constitution for the Confederate States of America, with Jefferson Davis as president.
What was the purpose of the Last Gasp Compromise proposed by Senator John C. Crittenden?
To permit slavery in the South beneath the Missouri Compromise line and guarantee slavery where it existed.
What was Lincoln's stance on slavery in his inaugural address?
He pledged not to interfere with slavery in any state where it existed.
What did Lincoln assert about the union of states in his inaugural address?
He stated that the union was perpetual and that states could not legally leave.
What actions did Lincoln take regarding federal forts in the South?
He pledged to defend federal forts and sent ships to resupply Fort Sumter.
What event marked the beginning of the Civil War?
The Confederate shelling of Fort Sumter on April 12, 1861.
What were some causes of the Civil War?
Strong abolitionist movement, Uncle Tom's Cabin, the Underground Railroad, Harper's Ferry, and Lincoln's election.
What was the population comparison between the Union and Confederacy?
Union population was 22 million, while the Confederacy had 9 million plus 3.5 million slaves.
What was the Anaconda Plan?
A three-pronged strategy to defend Washington D.C., pressure Richmond, and implement a Southern naval blockade.
What was Jefferson Davis's strategy for the Confederacy?
He wished for a prolonged defensive war and hoped for foreign intervention.
What was the significance of the First Battle of Bull Run?
It was the first major land battle of the Civil War, where Confederate forces under General Beauregard defeated Union forces.
What did Lincoln call for in terms of military recruitment?
He called for 500,000 volunteers to join the army.
What was the conscription policy in the South?
Rich Southerners could avoid conscription by finding a substitute or paying $500.
What event marked the beginning of the Civil War's spread into the Great Plains?
The Civil War spread into the Great Plains and beyond, with significant military leadership from both the Federals and Confederates.
Who led the Union forces in Kansas during the Civil War?
Major General David Hunter.
What was the significance of the Union victory in Boonville, Missouri in June 1861?
It prevented Missouri's secession from the Union.
What was Kentucky's initial stance in the Civil War, and how did it change?
Kentucky declared neutrality but became loyal to the Union after a Confederate invasion.
What was the outcome of the Battle of Shiloh in April 1862?
The Union Army suffered 13,047 casualties, while the Rebel Army had 10,699 casualties, leading to a Union victory.
What led to the fall of New Orleans in April 1862?
The city surrendered after a successful Union naval blockade led by David Farragut.
Who was appointed as the head of the Army by Lincoln during the fighting in the East?
General George McClellan.