Preformulation and Stability: Physical-Chemical Properties in Drug Development
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What is preformulation?
The investigation of physical and chemical properties of a new drug substance alone or in combination with excipients.
What is the main objective of preformulation?
To formulate stable and effective dosage forms.
List three specific objectives of preformulation.
To increase drug stability, improve drug bioavailability, and reduce drug-excipient incompatibility.
What physical properties are investigated during preformulation?
Physical description, particle size, crystalline structure, melting point, and solubility.
What are the common forms in which drugs can be used therapeutically?
Solids, liquids, and gases.
What challenges do liquid drugs face in dosage form design?
Volatility, difficulty in tablet formulation, and stability issues.
What is the significance of particle size in drug formulation?
It affects dissolution rate, bioavailability, content uniformity, taste, texture, color, and stability.
What is polymorphism in materials science?
The ability of a solid material to exist in more than one form of crystal structure.
How does polymorphism affect drug substances?
It influences physicochemical properties, including melting point and solubility.
What are the two types of incompatibility with excipients?
Physical incompatibility and chemical incompatibility.
What is physical incompatibility?
Mixing of two substances that affects their physical properties like solubility and appearance.
What techniques are used to determine crystal properties in preformulation?
Hot stage microscopy, thermal analysis (DSC), infrared spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction (XRD).

What is the melting point of a drug substance indicative of?
It can indicate the purity of the chemical substance.
What is the heat of vaporization?
The amount of heat absorbed when 1 g of drug substance vaporizes.
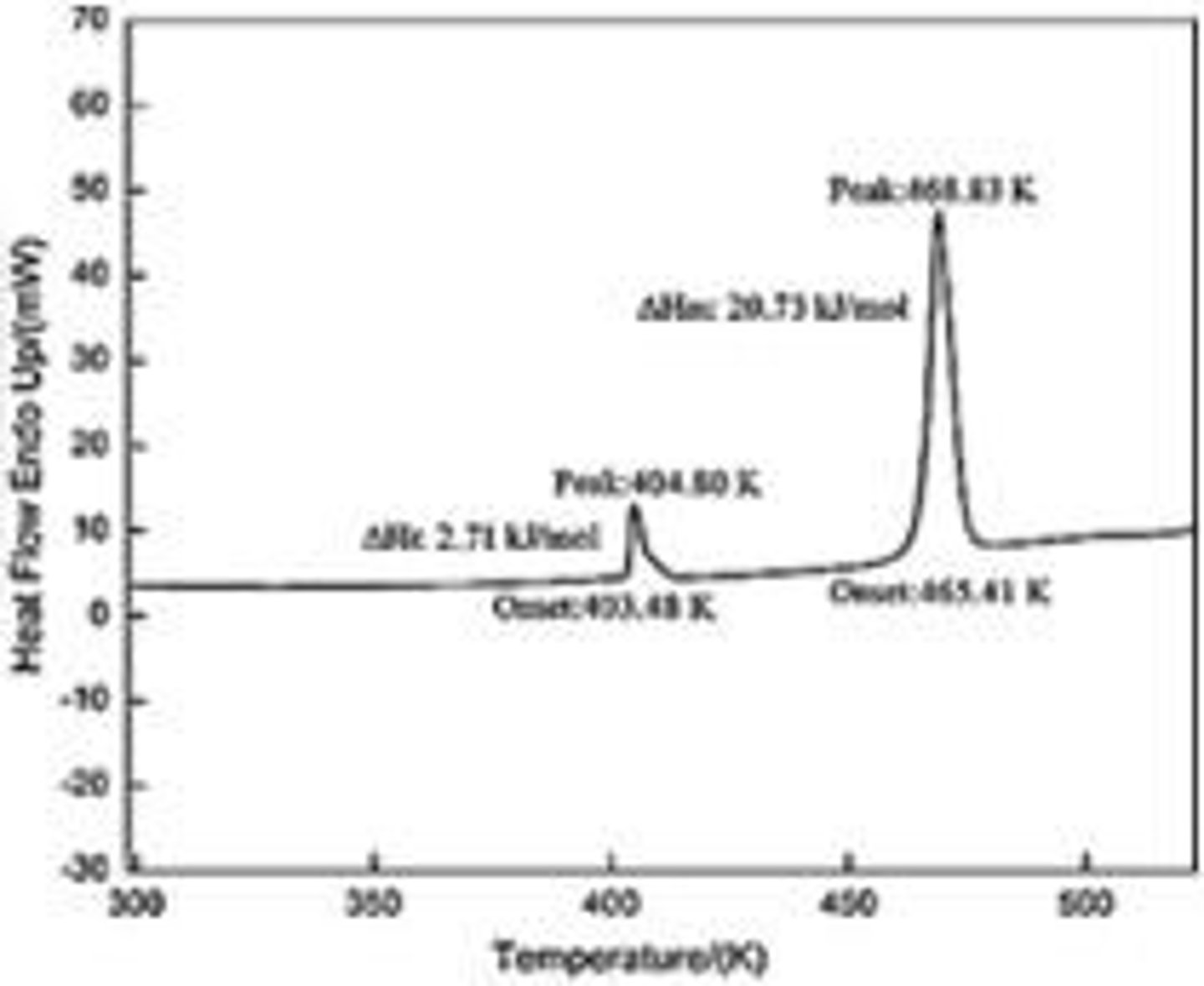
What is the role of differential scanning calorimeters (DSC) in preformulation?
They measure temperatures and heat flows associated with thermal transitions in a material.
What is the importance of vapor pressure in drug formulation?
It is crucial for the operation of implantable pumps and aerosol dosage forms.
What are the advantages of liquid drugs in therapy?
They can be beneficial for large doses taken orally and for topical applications.
What is melting point depression?
The phenomenon where the melting point of a material decreases with a reduction in its size, prominent in nanoscale materials.
What is the significance of purity in drug substances?
Impurities can affect drug stability, cause unexpected reactions, and may be toxic.
How can impurities be detected in drug substances?
Through melting point measurement, thermal analysis, and chromatographic techniques.
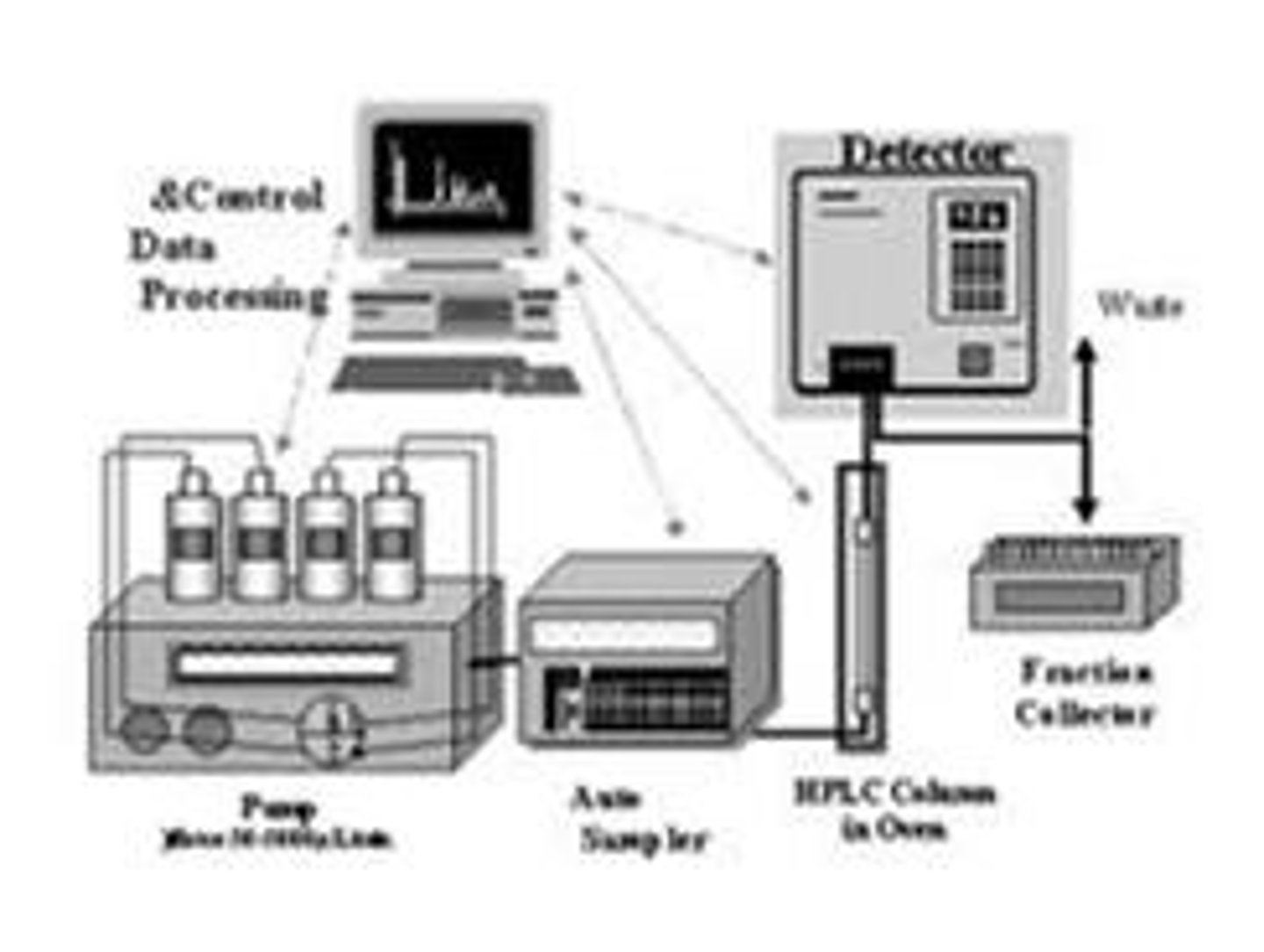
What is the role of chromatography in preformulation?
It is used to analyze organic-related impurities in drug substances.
What is the impact of particle size on flow characteristics?
Particle size affects flow characteristics and sedimentation rates.
What is the preferred dosage form among physicians and patients?
Tablets or capsules, as they are generally tasteless and accurately dosed.
What are the common forms of dosage in the pharmaceutical market?
Tablets and dry-filled capsules constitute around 70% of dosage forms.
What is chemical incompatibility in pharmaceuticals?
A chemical reaction such as reduction, oxidation, or hydrolysis that can lead to effervescence or color change.
What is solubility in the context of drug substances?
A physicochemical property that refers to the ability of a drug to dissolve in solution, crucial for therapeutic effect.
What are some methods to increase drug solubility?
Chemical modification, decreasing particle size, adjusting pH, adding cosolvents, and forming complexes.
How does particle size affect drug solubility?
Smaller particle sizes can lead to increased solubility and dissolution rates.
What is dissolution rate?
The time it takes for a drug to dissolve in fluid, which affects absorption and bioavailability.
What factors can affect the dissolution rate?
Particle size, the solubility of the drug, and the use of highly water-soluble salts.
What is the significance of drug stability?
Ensures uniformity of dose, maintains active ingredient availability, and prevents degradation or toxicity.
What are the types of drug stability?
Chemical, physical, microbiological, therapeutic, and toxicological stability.
What is hydrolysis in the context of chemical instability?
A destructive process where drug molecules interact with water, leading to breakdown products.
How can hydrolysis be inhibited?
By decreasing water content, limiting environmental exposure, and controlling pH.
What is photolysis?
Decomposition of substances due to light exposure, which can be prevented by protective packaging.
What are common pathways of physical instability?
Polymorphs, crystallization, precipitation, vaporization, and adsorption.
How does pH affect drug stability?
Rates of reactions can vary with pH, and optimal pH can maximize stability.
Why is light a concern for drug stability?
Light can act as a catalyst, increasing the rate of some chemical reactions.
How does air affect drug stability?
Oxygen can induce degradation through oxidation, which can be minimized by proper packaging.
What is the role of solvents in drug stability?
Solvent effects can complicate stability; some drugs may be unstable in certain solvents.
Why is particle size important in drug formulation?
Smaller particle sizes can enhance reactivity, solubility, and stability, affecting dissolution rates.
What is ionic strength and its significance?
The concentration of electrolytes that can affect reaction rates in drug formulations.
What does microbiological stability entail?
Ensuring that a formulation is free from microbiological contamination and meets sterility standards.
What are some consequences of chemical instability?
Decreased therapeutic activity, degradation of active ingredients, and potential production of toxic substances.
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation used for?
To determine the pH-dependent solubility of weak acids and bases.
What is the importance of the Arrhenius equation?
It relates temperature to the rate of chemical reactions, helping predict stability over time.
What are the effects of temperature fluctuations on drug stability?
They can cause crystallization and alter particle size distribution in suspensions.
What is the significance of using amber containers for pharmaceuticals?
They protect light-sensitive drugs from photolysis, extending shelf life.
What is the role of preservatives in drug formulations?
To prevent microbiological contamination and maintain product stability.