AP Computer Science A - Primitive Types (Unit 1) Test Review
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
it is a javadoc comment
What does */ mean?
-it is an inline comment
-for example, it could be something like: double sum; // we defined the double variable sum
-in the example above, everything after // was the inline comment
What does // mean?
Class
where the program lives in memory
public class ______________________;
What is the class header in Java?
the class body
What is below the class header?
methods
What goes inside the class body?
public static void main(String[] args);
What is the main method header?
they tell something to happen
What do methods do inside classes?
a class is like your house and the method is like the power in your house
What is an analogy that can be used to relate classes to methods?
it is an "at author tag"
What does @author mean?
System.out.println(); and System.out.print();
-a method inside the main method
-inside the parentheses, you put in a parameter/argument to get some output after the method acts on it

no, the spacing is just for readibility
-meaning that you can have single spaced or double spaced lines
Does spacing between lines matter when writing code? What is the spacing for?
1. it receives your code (the source code file)
2. it compiles (translates it to the computer)
3. now it has the bytecode file (a bunch of 0's and 1's)
4. now it executes (runs) the code
What are the four steps to a program running, in Java?
it receives you source code file (the code you wrote)
What is the first step in Java running a code?
it compiles the code (checks your code for any errors and then translates it to a bunch of 0's and 1's)
What is the second step in Java running code?
it gets the bytecode file (the code that only has 0's and 1's)
What is the third step in Java running code?
it executes the code (runs the code)
What is the fourth step in Java running code?
Compiling
-the second step in Java running your code
-basically, the computer checks for errors, and if there are no errors, then it converts your program to 0's and 1's
Execute
-the fourth and final step of Java running your code
-basically Java will follow all the commands and directions that you gave it in the code, and it will run your code
double quotations " "
What must we put all strings in?
string data type variables
What can strings be stored inside?
we can concatenate the two strings or the string and the variable
What can we do if we want to combine two or more strings or if we want to combine a string with something that is inside a variable?
-System.out.print();
-System.out.println();
What are the two methods used to print things in Java?
System.out.print(); prints code without forcing a new line, but when you use System.out.println();, Java forces a new line after it executes the print statement
How is System.out.print(); different from System.out.println();?
it adds a tab
What does the shortcut, /t, do?
it adds a new line
What does the shortcut, /n, do?
-compile-time error: incorrect syntax like spelling errors, no parentheses, etc.
-run time error: a problem during program execution that causes the program to terminate/stop
-logical error: the program runs but produces incorrect results (for example, if you used a wrong formula, etc.)
What are the 3 major types of errors when coding in Java?
Compile time error
incorrect syntax like spelling errors, no parantheses, etc.

Run time error
a problem during program execution that causes the program to terminate/stop

Logical error
the program runs but produces incorrect results (for example, if you used a wrong formula, etc.)
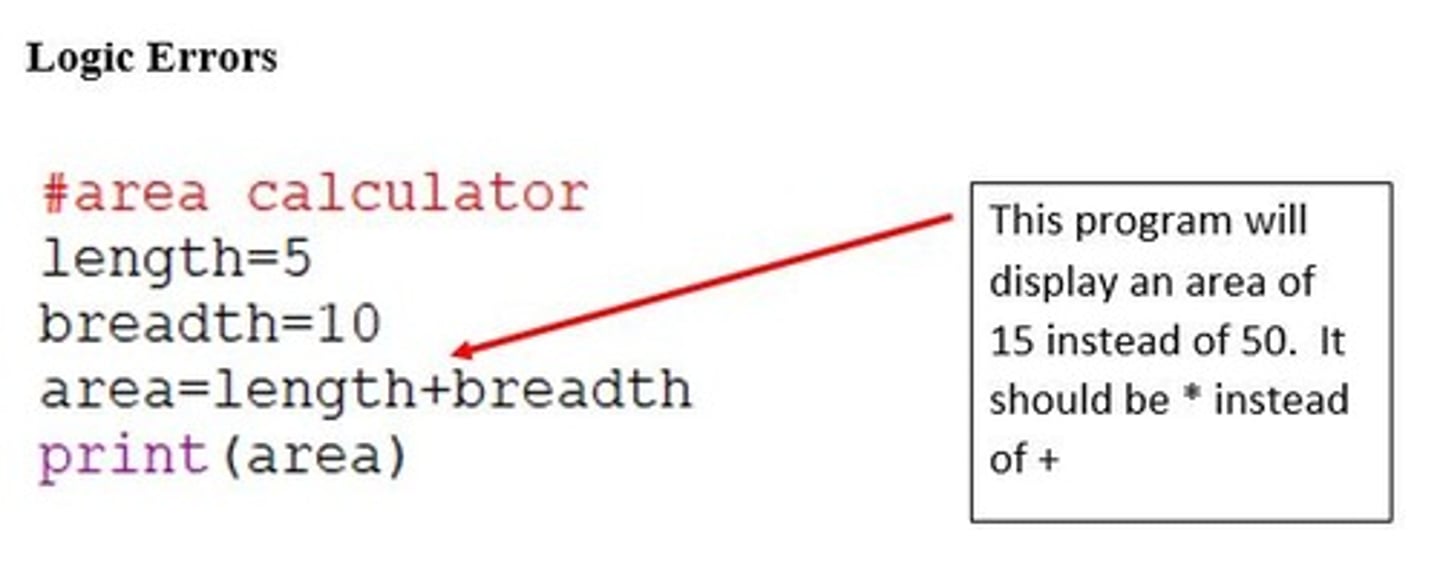
-not having a semicolon ; after each line
-if DOUBLE quotes are not placed around strings
-if you forget to put brackets {} at the very start and the very end of the entire code
What are some common errors in Java?
a semicolon ;
What do you need to put after each line of code?

brackets {}
What must be placed at the very beginning and end of the code?
Debugging
fixing errors in your programming
-numbers (1, 2, 3, etc.)
-letters (a, b, c, etc.)
-symbols (#, $, %, etc.)
What can strings contain, as long they are in double quotes?
they manage data
What do programs do?
in memory
Where is data stored?
slots
What does the computer's memory has, that tells us the address of data?
Variables
the names of each slot of the computer's memory that holds data from the program
its data type, its name, and its value
What does each variable have?
yes
Can the value of a variable change throughout the code?
-the variable's data type is String
-the name is quote
-the value is "Don't quit"
In the following declaration and assignment of the variable, what is the variable's data type, what is its name, and what is its value?:
String quote = "Don't quit";
the assignment operator, that sets the value of a variable
What is = in Java?
we can define it like this:
int fortniteWins
and then we can set it to a value like this:
int fortniteWins = 20
How do we define a variable and then set its value?
it gets some default value that is determined by its data type
If no value is set, then what value does a variable get? Why is this value determined by?
yessir
Can you declare multiple variables of the SAME data type on the same line?
no
Can you set the values of multiple variables of any data type (whether they have the same data type of not), on the same line?
nope
Can you declare multiple variables of DIFFERENT types on the same line?
-the name must be unique and cannot be a copy of some method in Java or something
-it cannot begin with a number
-the names are case sensitive (upper vs lower case)
-use camelCase style for longer name, where the first word is all lower case and then all the words afterwards start with a capitalized letter
What are the rules for writing variable names?
Concatenation
-values can be combined by using the + operator
-for example, String name = "Naruto"
System.out.print("My name is " + name)
-in this example, we ____________ the string, "My name is " with the variable name
-we never put variables in quote when ________________
never
Do we ever put variables in quotes when concatenating?
Scanner
a class that allows us to read text from a given input
import java.util.Scanner;
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(" ")
String input = scan.nextLine
-"scan" is the name of the scanner, "new Scanner" initiates a new scanner object, and "(System.in)" lets the user input into the console
-when we use the print method, we essentially let the user input something into the console
-In String input = scan.nextLine();, we are checking for what the user inputted into the console and then storing that in the variable, input
How do we use the scanner class?
-by doing something like this System.out.println(variable1 + " " + variable2);
-as you can see, we purposefully put a space between the two double quotes to create a space between the two variables
When we concatenate, how we put spaces between two variables?
-int
-byte
-short
-long
-double
-float
-char (a single letter)
-boolean
-we really only need to worry about double, int, and boolean
What are the 8 primitive data types?
reference data type
What type of data type are strings?
-128 to 127
What is the domain (range of input values) for a byte?
-32,000 to 32,000
What is the domain (range of input values) for a short?
-2 billion to 2 billion
What is the domain (range of input values) for an int?
-9 quintillion to 9 quintillion
What is the domain (range of input values) for a long?
6 to 9 significant figures
What is the domain (range of input values) for a float?
15 to 17 significant figures
What is the domain (range of input values) for a double?
-ints are 32 bit (take up less memory) and they CANNOT hold decimal values (only whole numbers)
-doubles are 64 bit (take up more memory), their values can either be decimals or whole numbers, and they add .0 to the output when a whole number is inputted
What is the difference between an int and a double?
double, since they are 64 bit, while ints are only 32 bit
Do ints or doubles take up more memory?
an int cannot hold a decimal value, but doubles can hold either decimals or whole numbers
Can an int hold a decimal value? What about a double?
Char
-16 bit
-it stores a single symbol using single quotes ' '
-it can store any symbol from the unicode character set
-English uses characters from a subset of unicode called ASC ||
-it can print special characters using the \u escape sequence, followed by the code
-without having to use the math class
-for example:
int number = 4;
int newNum = 4 * number;
System.out.print(newNum);
Basic expressions can be utilized without having to use what? What is an example of a basic expression?
for strings
What data type do we use scan.nextLine(); for?
for ints
What data type do we use scan.nextInt(); for?
for doubles
What data type do we use scan.nextDouble(); for?
-values of variables that have been locked in place using the final modifier, meaning that they cannot change later on
-these types of values cannot be changed by the user
-for example, you might want to use the final modifier for a number like pi when creating code that finds the area of a circle
What are final values?
-it goes through your datatypes and checks the domain of that variable/all the possible values you can store for that variable and also the functions that we can do with the data in the variable
-Java knows what the domain and functions are depending on the datatype
Before allocating memory for a certain variable, what does Java do?
a datatype of variables that can only hold integers (positive and negative whole numbers)
What is an int?
a datatype of variables that can hold either decimal values or integers
What is a double?
you can store numbers in strings, but you cannot use them for mathematical calculations (only for concatenation)
Can you store numbers in strings? Then can strings be used for mathematical calculations?
age
What is a variable that an int can be used to store?
rainfall
What is a variable that a double can be used to store?
street address
What is a variable that a string can be used to store?
-primitive data types have variables that hold the actual value that they are set to
-reference/class data types have variables that hold a reference to a memory location
How are primitive data types different fro reference data types?
a reference data type
What type of data type is a string?
-they ALWAYS START with a lower case letter
-for example:
int age;
-notice how the (i) is not capitalized
-another example:
double rainfall;
-notice how the (d) is not capitalized
How do names of primitive data types like int, double, etc, always start?
-they ALWAYS START with capitalized letters
-for example:
String name;
-notice how the (S) is capitalized
How do the names of reference data types like strings, always start with?
Java will concatenate the string stored in the variable with the number
What will happen if you put a plus sign (+), between a string variable that holds a STRING and some number?
Java will mathematically add the int/double with the other number and then once you output this, you see the sum of the int/double and the number
What will happen if you put a plus sign (+), between an int/double and some other number?
Boolean
-can only either a true value or a false value
-it is represented in memory as a single bit
-it is a primitive data type
-for example, we can set a value for this datatype like this:
boolean y = true
-in the example above, boolean is the data type, y is the name of the variable, and true is the value of the boolean variable
Bit
a binary value (either a 0 or a 1)
Integer.MIN_VALUE;
-tell us the minimum value in the domain of the integer data type
-we should get a value that is equal to around -2 billion
Integer.MAX_VALUE;
-tells us the maximum value in the domain of the integer data type
-we should get a value that is equal to around +2 billion
prevents the user (that's inputting into the console), from changing that primitive data type's variable's value
What does putting the word "final" before a primitive data type name (such as int), do?
-String, Integer, and Custom Classes
-don't confused Integer with int, because, one starts with an upper case "I" and the other with a lower case "i"
What are the three reference data types?
boolean, int, double, string
How would you arrange the following data types in terms of increasing memory required to store their values?: double, int, string, and boolean
Overflow
-when you add a number to the max value of some primitive data type's domain, and what happens is, the number wraps around and you are outputted the minimum value in the domain instead
-for example, adding 10 the maximum value in the domain of an int, which is 2 billion, would cause to be outputted the minimum value in the domain, which is around -2 billion (notice how the numbers wrapped around)
you'd get a run time error
What would happen if you previously defined the final value of an int or double (using the final modifier), and tried to add or subtract some number from that value, and then print it?
reference data types are data types that have variables that have been set values which cannot fit in the allocated memory spot given to them, so the reference data type directs Java to store the value of its variable in a location with plenty of space
What are reference data types?
variables that hold strings as values
What are string variables?
String literals
strings that are found inside the double quotes inside like the parentheses for the printing method

Modifier
-a word which we use before a variable declaration to modify its properties
-the modifier usually comes before the data type when declaring variables
-example: final
-example of the application of a modifier:
final double pi;
pi = 3.14
*
What operator do we use to do multiplication?
/
What operator do we use to do division?
+
What operator do we use to do addition?