DPT 745 Week 4 Lecture Notes Pt. 2
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
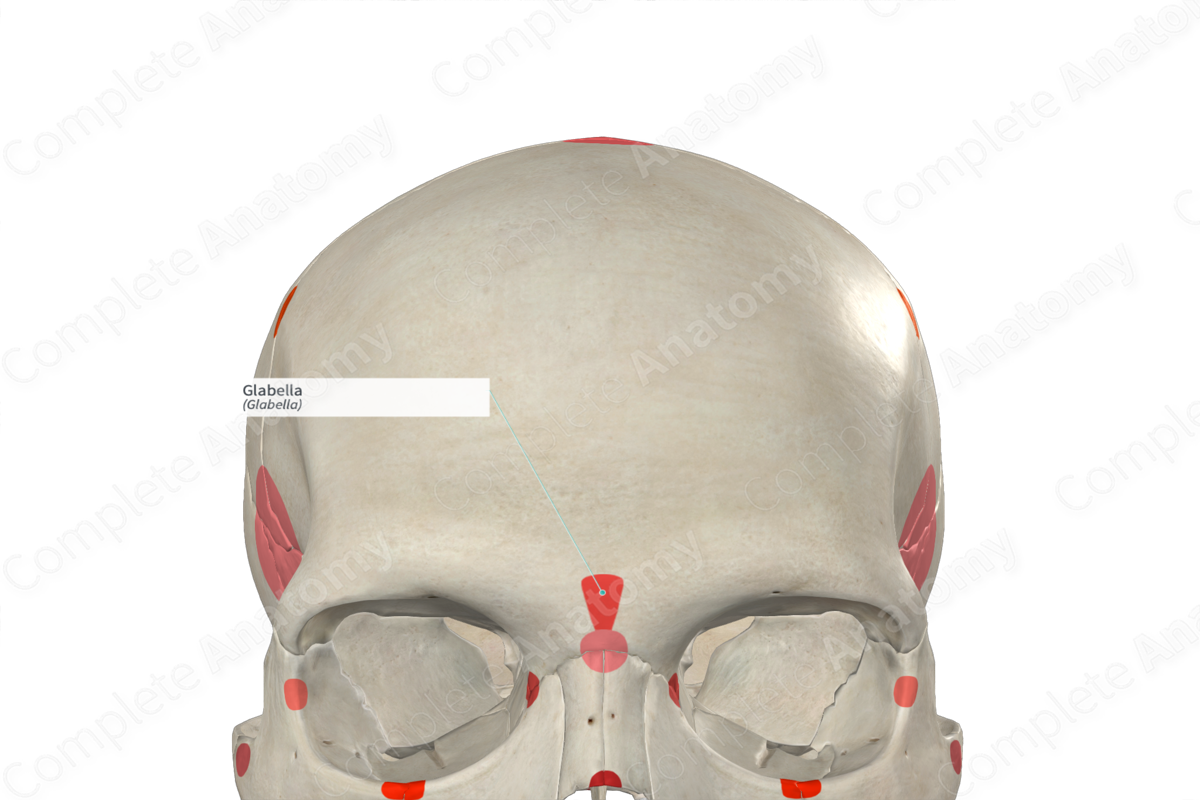
Glabella
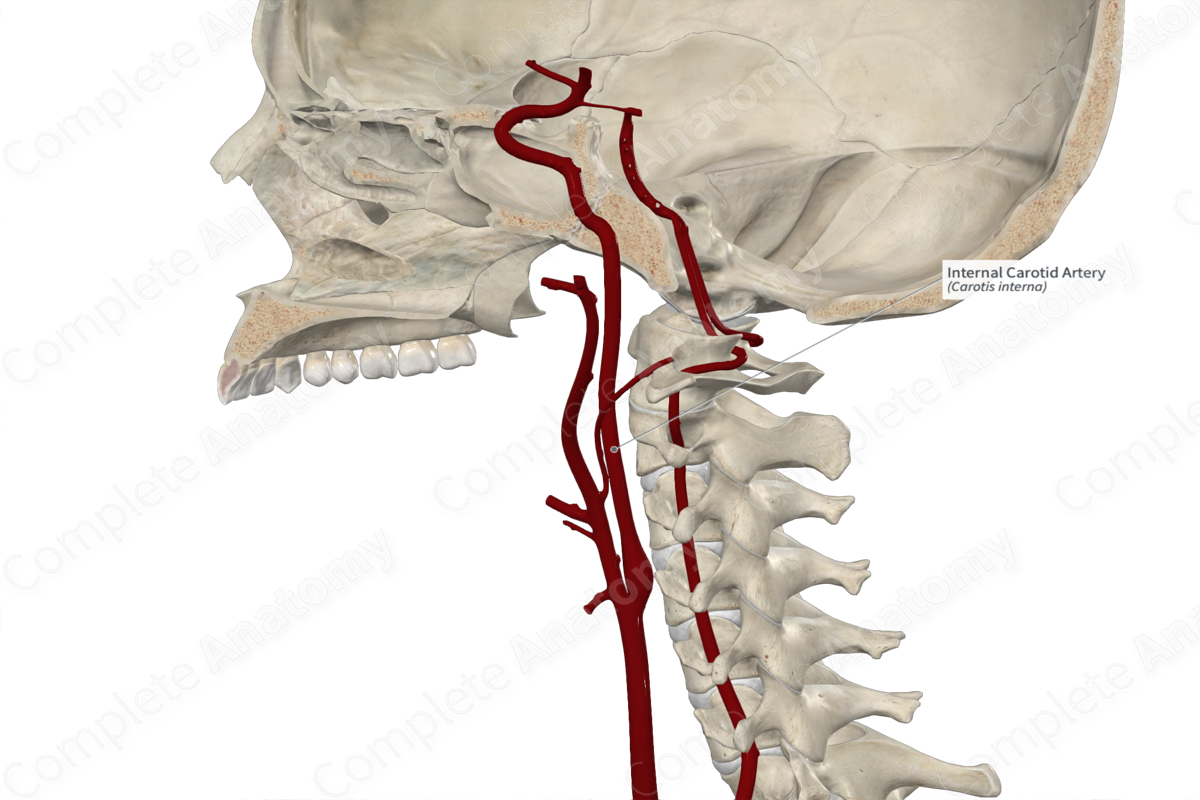
Internal carotid artery
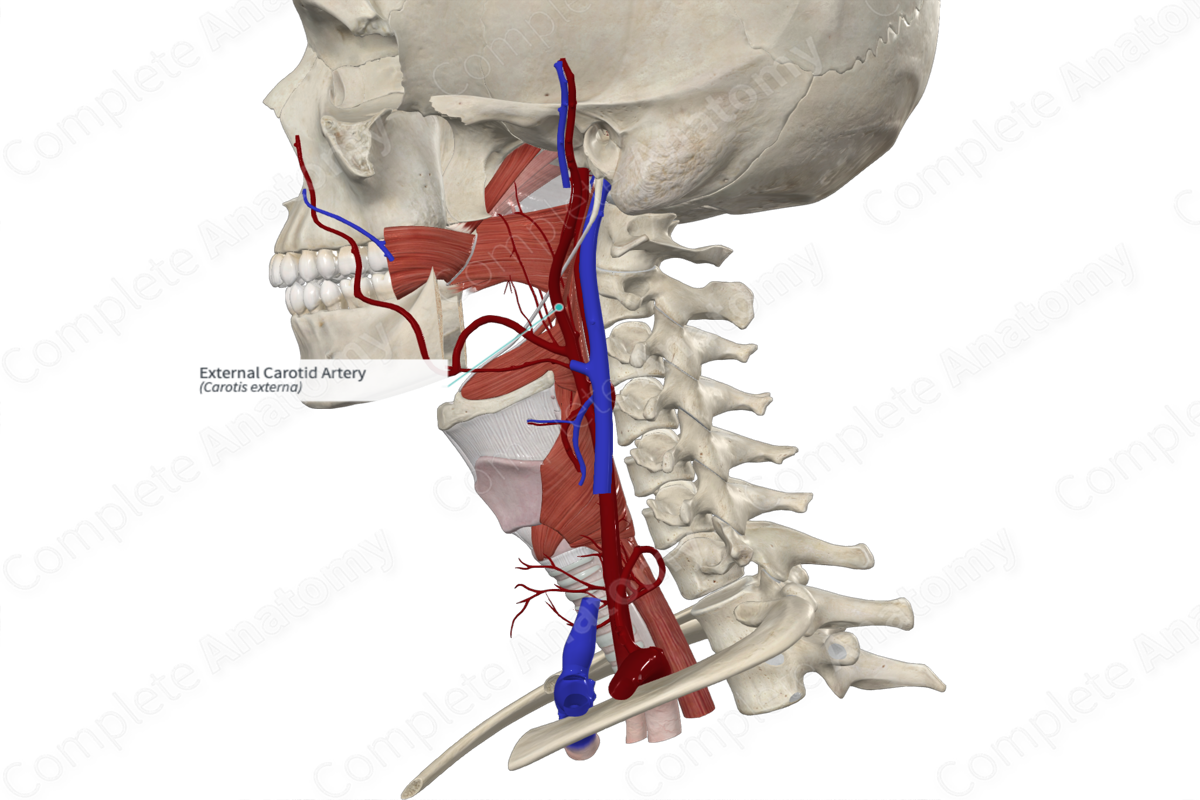
Common carotid artery
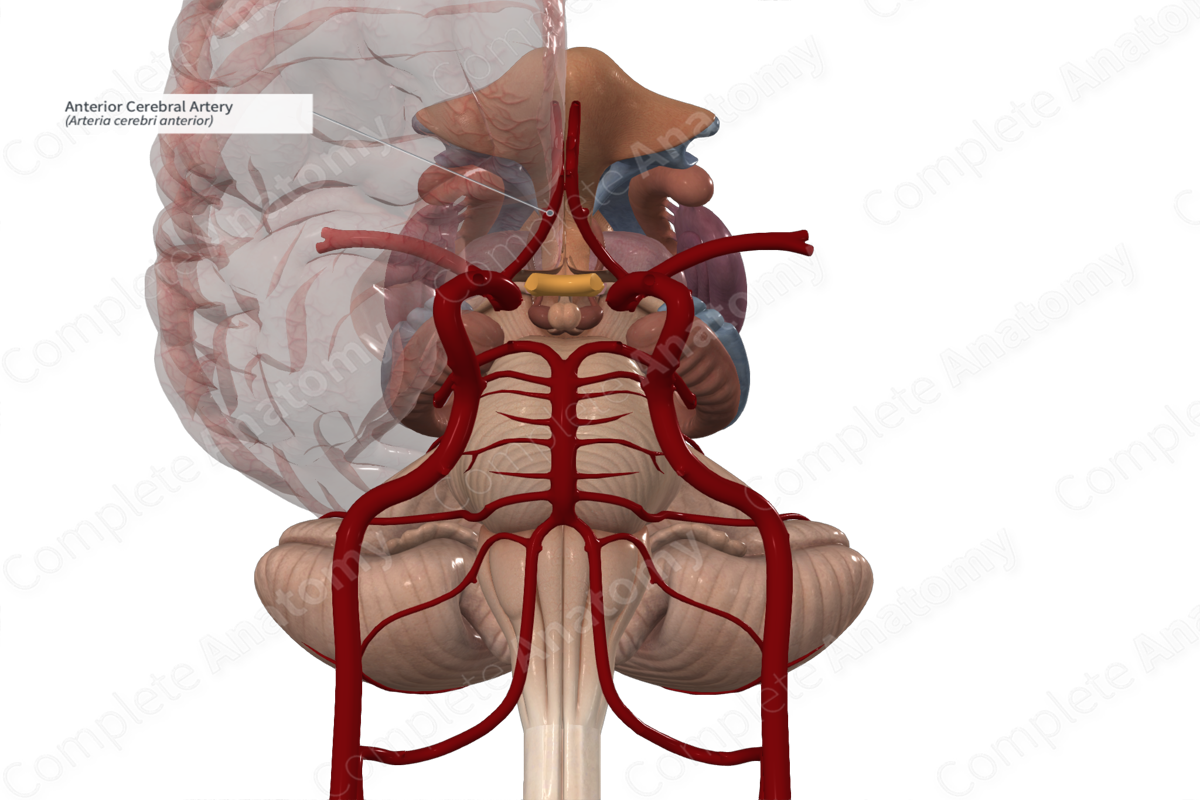
Anterior cerebral artery
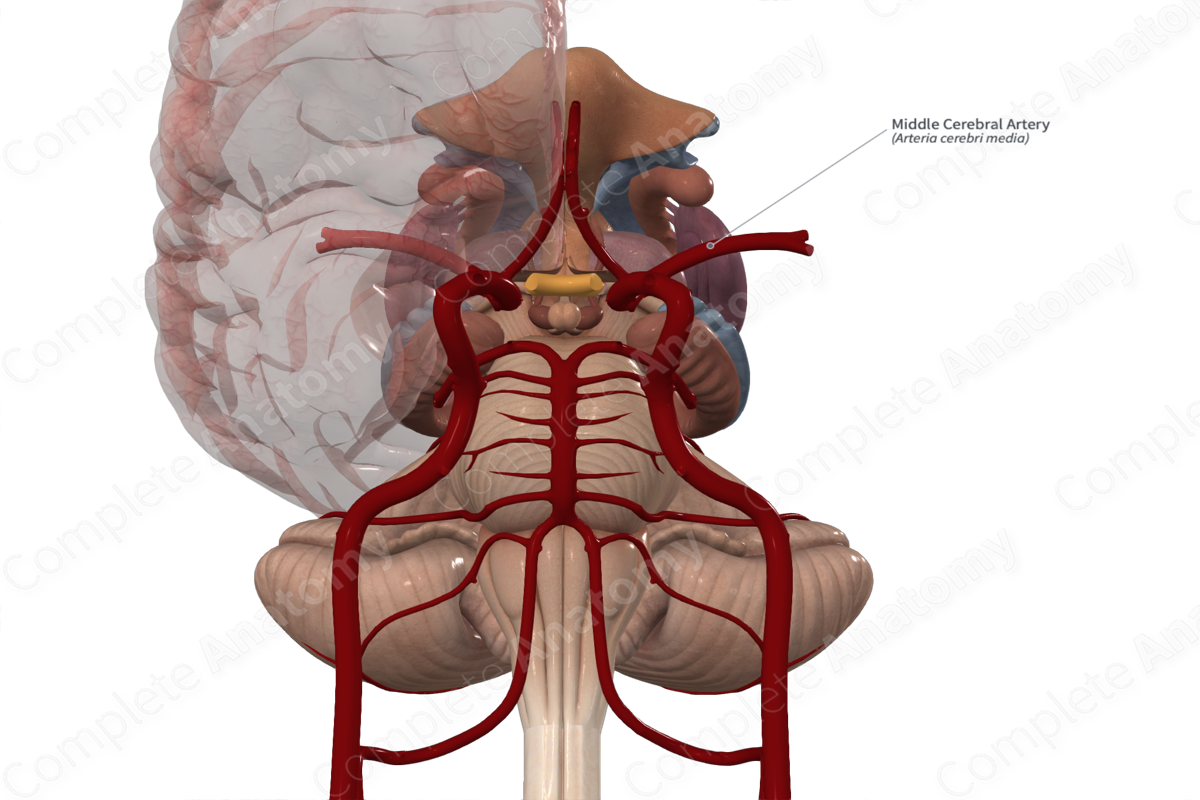
Middle cerebral artery
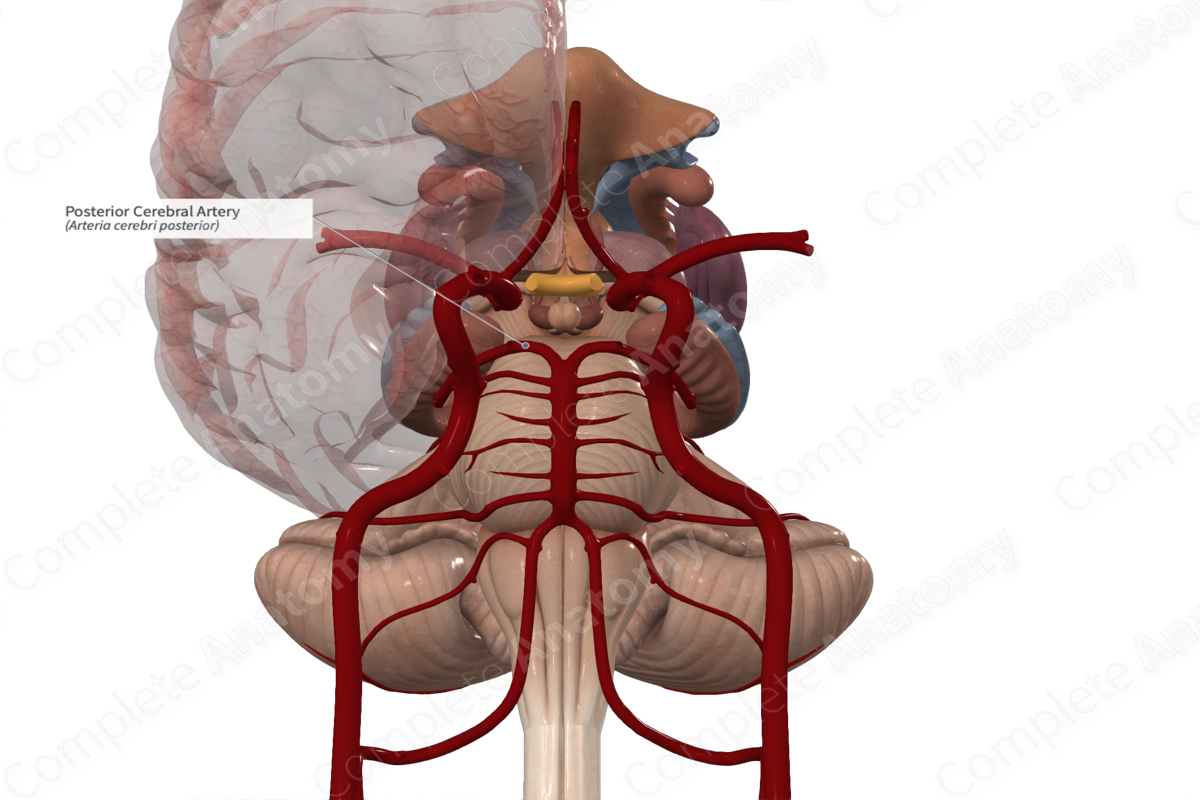
Posterior cerebral artery
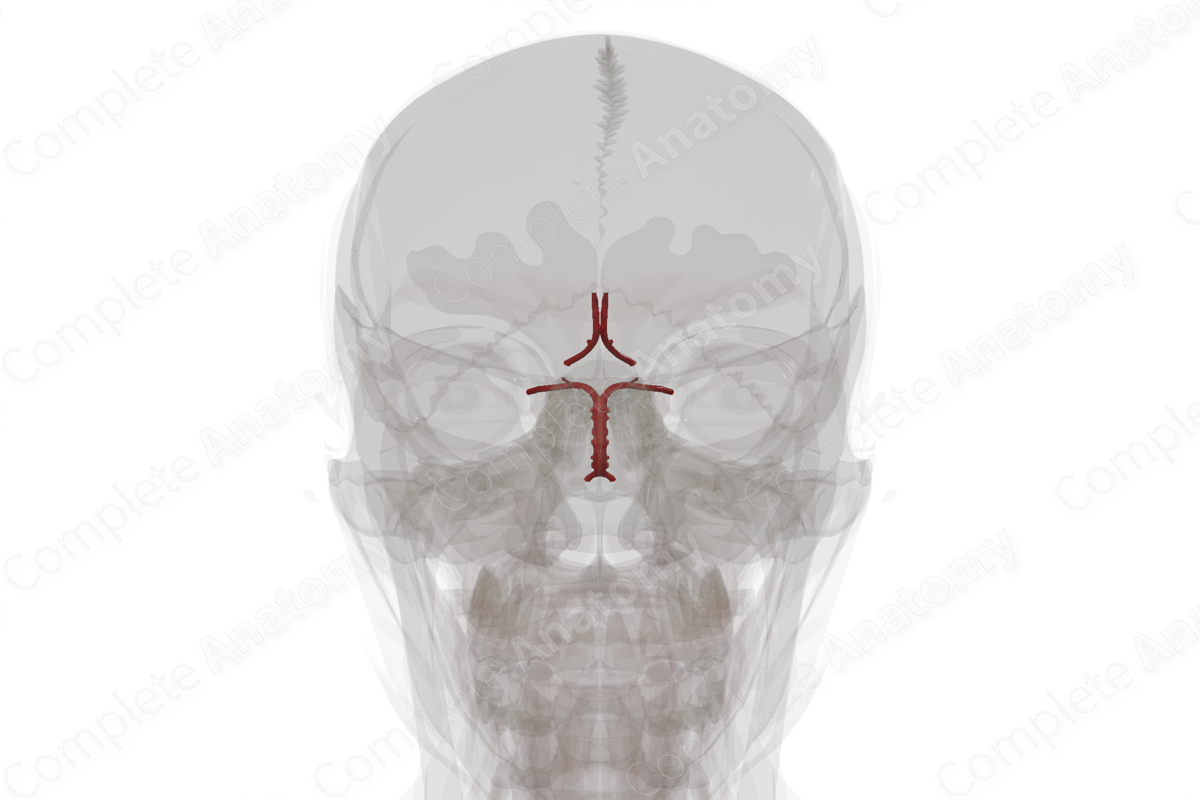
Cerebral arterial circle
Basilar artery
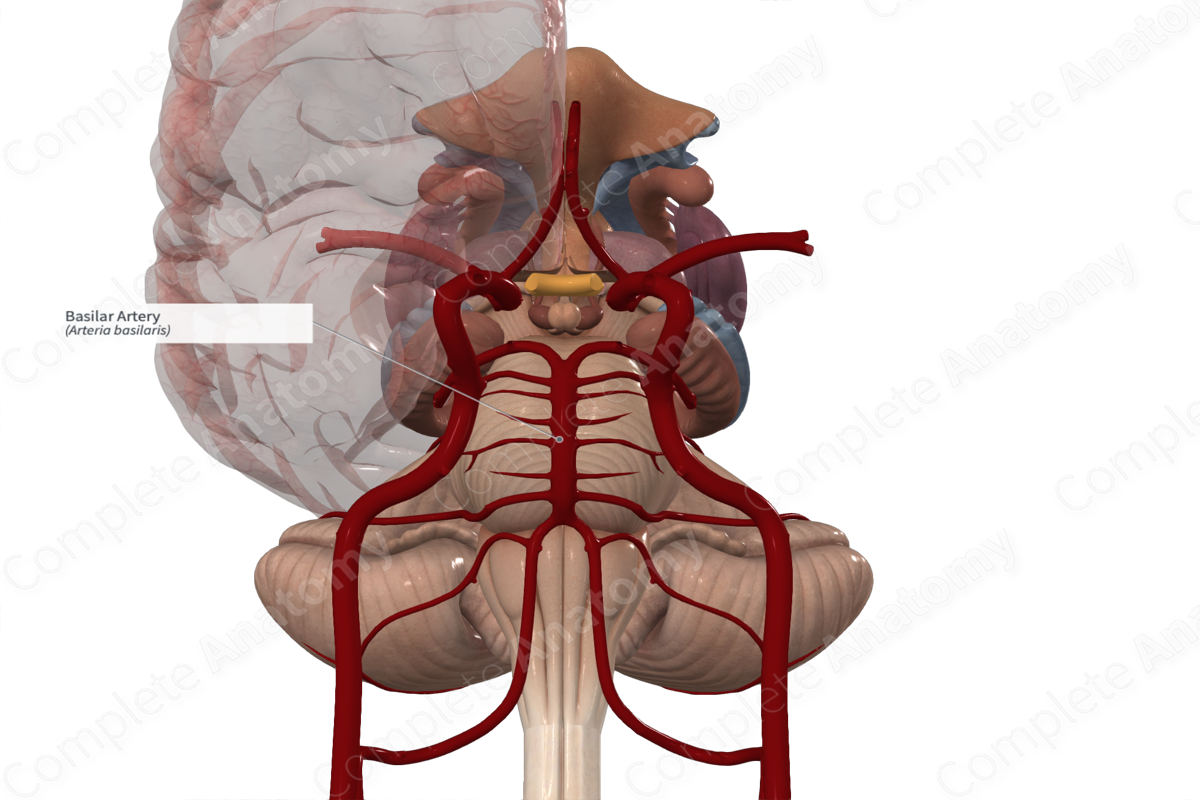
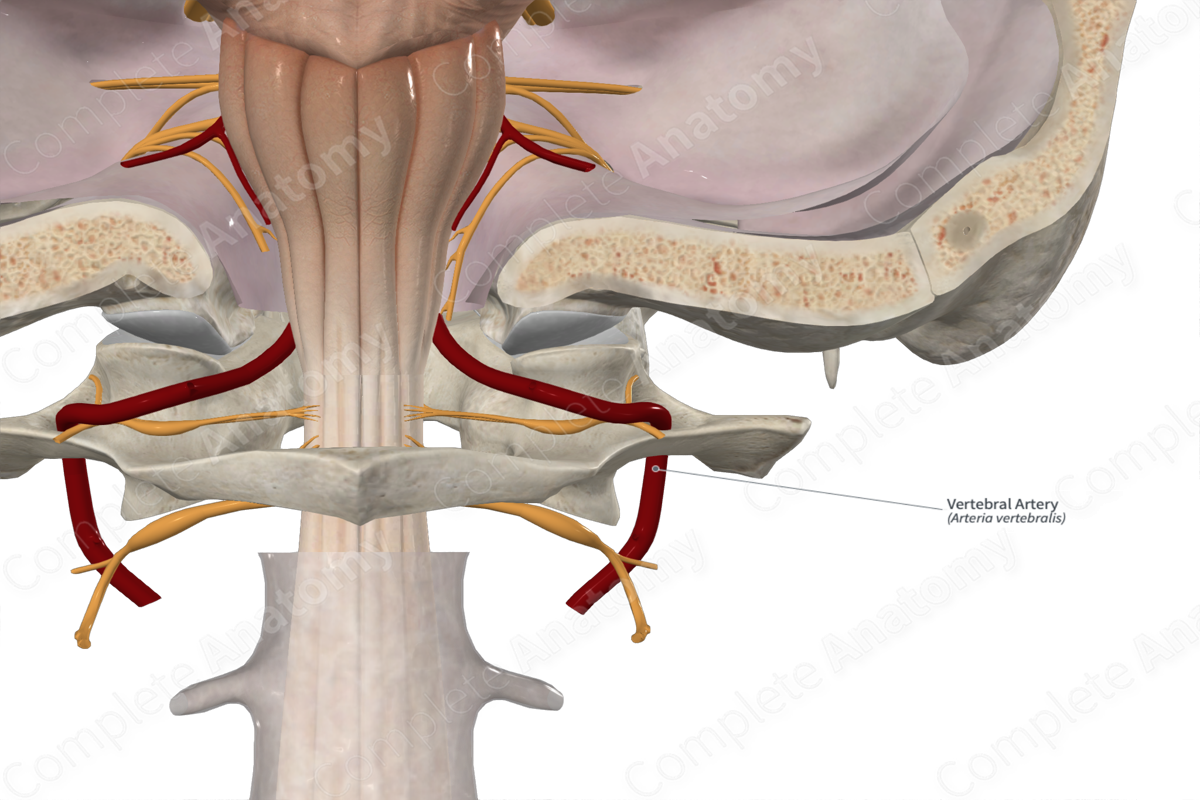
Vertebral artery
longitudinal
4
Brain
• The cerebrum includes the cerebral hemispheres and basal ganglia. The cerebral hemispheres, separated by the falx cerebri within the _____ cerebral fissure, are the dominant features of the brain
• Each cerebral hemisphere is divided for descriptive purposes into ___ lobes, related to the overlying bones of the same name
median
central
Brain
• From a superior view, the cerebrum is essentially divided into quarters by the _____ longitudinal cerebral fissure and the coronal central sulcus. The _____ sulcus separates the frontal lobes (anteriorly) from the parietal lobes (posteriorly). In a lateral view, these lobes lie superior to the transverse lateral sulcus and the temporal lobe inferior to it. The posteriorly placed occipital lobes are separated from the parietal and temporal lobes by the plane of the parieto-occipital sulcus
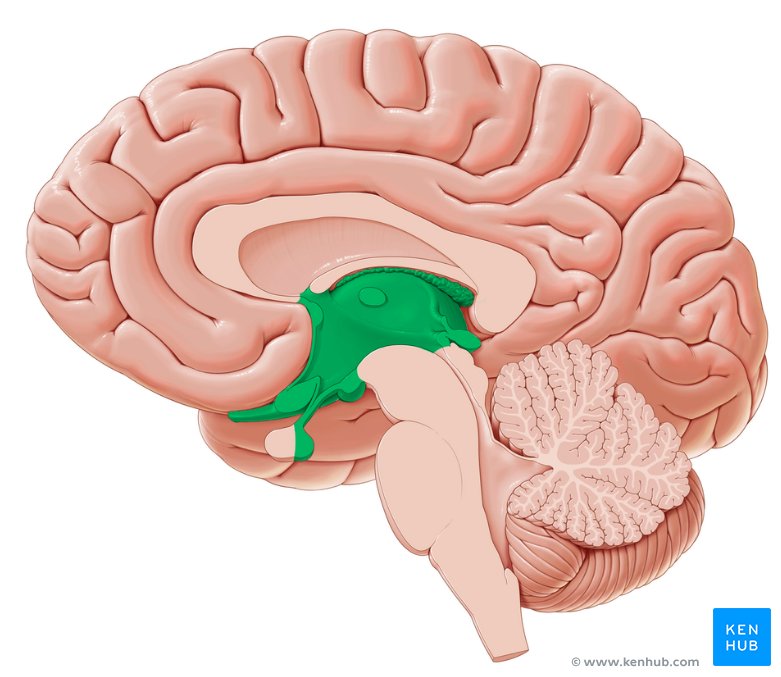
Diencephalon
Composed of the epithalamus, thalamus, and hypothalamus and forms the central core of the brain
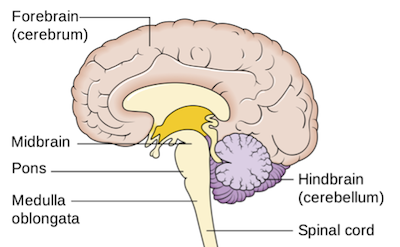
Forebrain
Responsible for voluntary actions, thinking, and processing
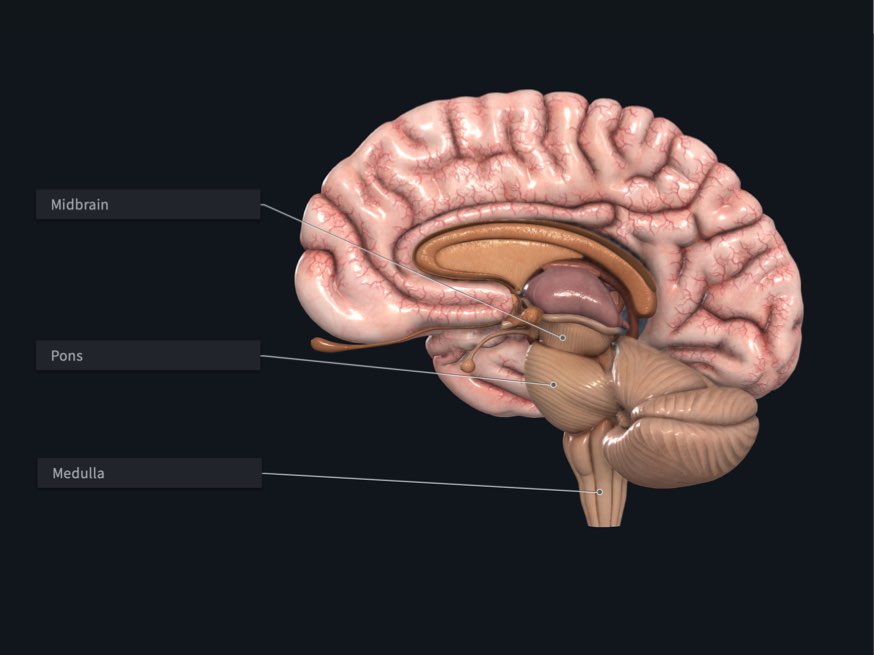
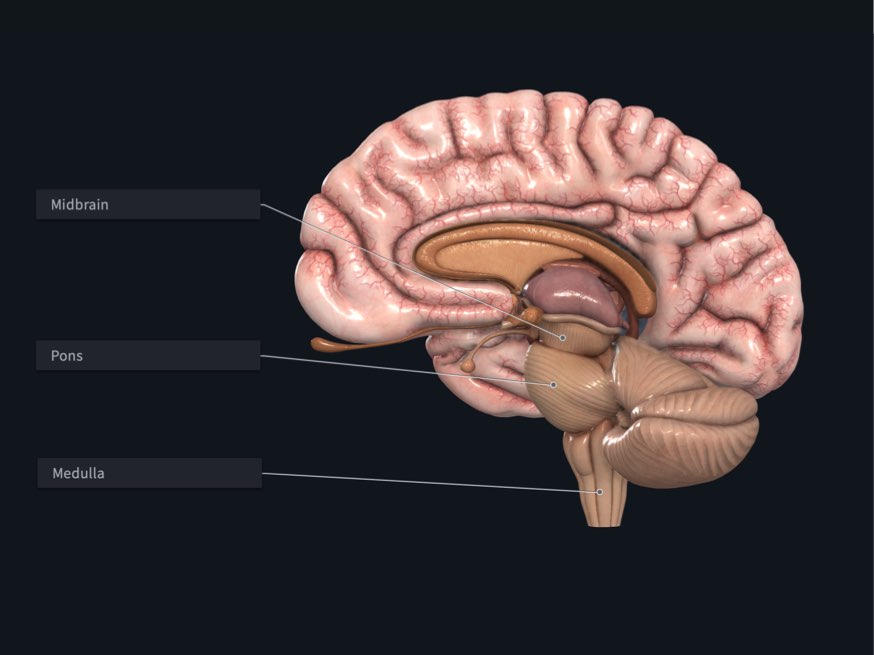
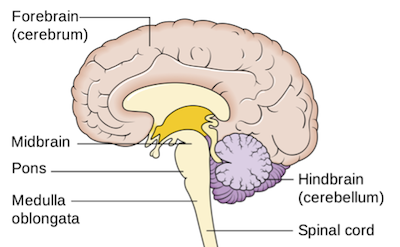
Midbrain
The rostral part of the brainstem, lies at the junction of the middle and posterior cranial fossae. CN III and IV are associated with the midbrain
Coordinating visual and auditory reflexes, motor control, and arousa
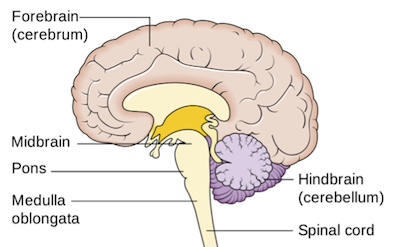
Hindbrain
Regulating vital bodily functions, coordinating movement, and maintaining balance
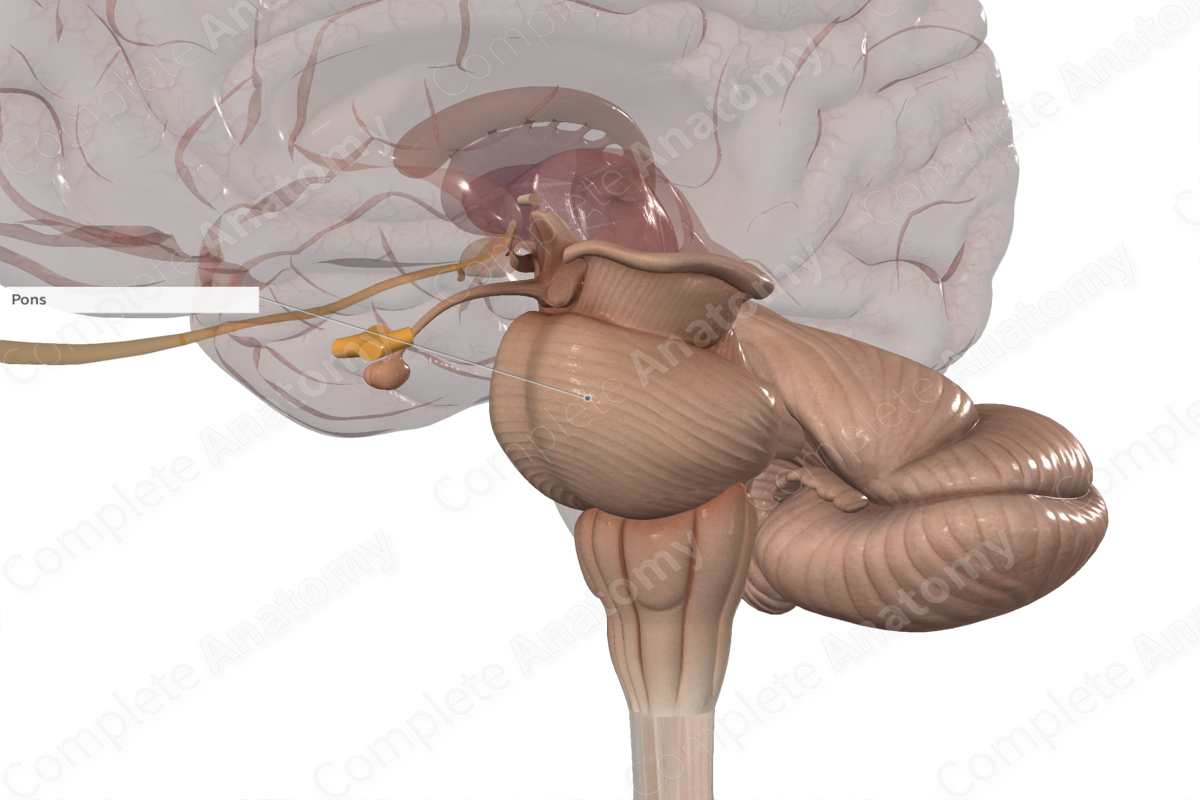
Pons
The part of the brainstem between the midbrain rostrally and the medulla oblongata caudally.
Lies in the anterior part of the posterior cranial fossa. CN V is associated with the pons
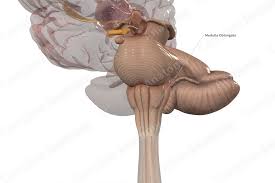
Medulla oblongata
The most caudal subdivision of the brainstem that is continuous with the spinal cord. The medulla lies in the posterior cranial fossa. CN IX, X, and XII are associated with the medulla, whereas CN VI–VIII are associated with the junction of the pons and medulla
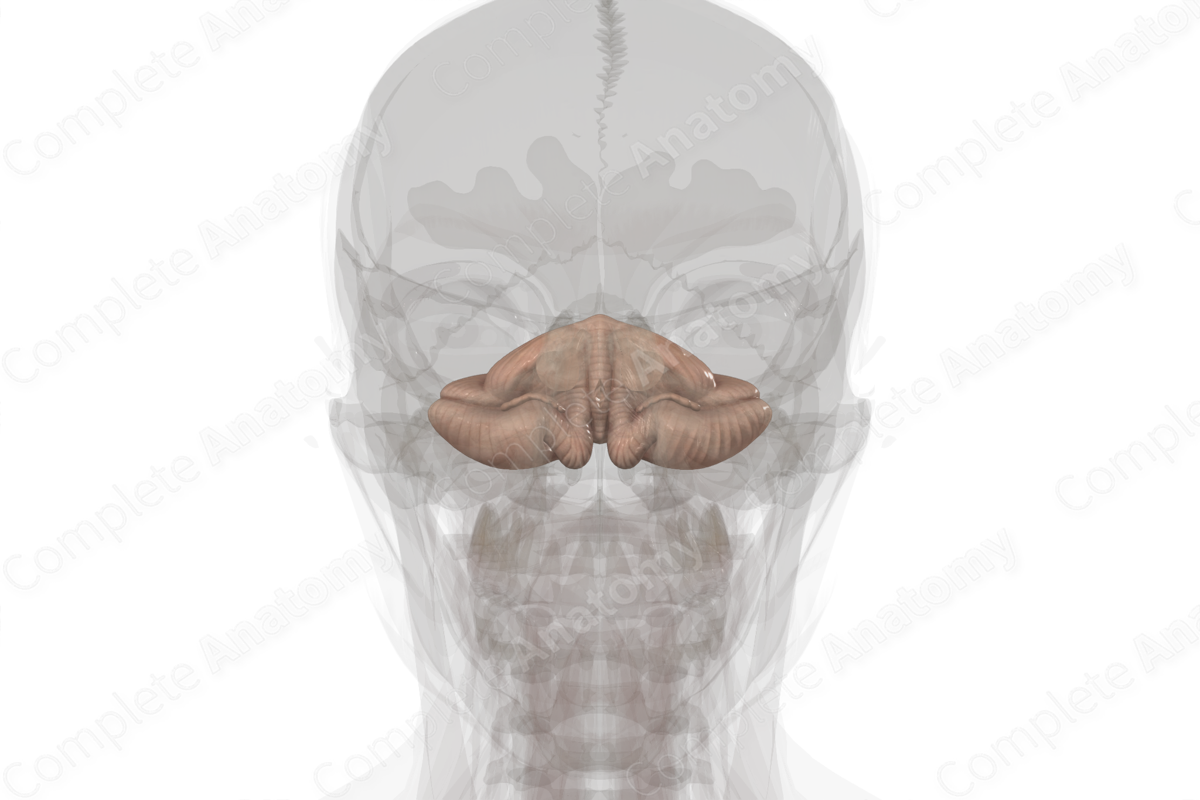
Cerebellum
Large brain mass lying posterior to the pons and medulla and inferior to the posterior part of the cerebrum. It lies beneath the tentorium cerebelli in the posterior cranial fossa. It consists of two lateral hemispheres that are united by a narrow middle part, the vermis
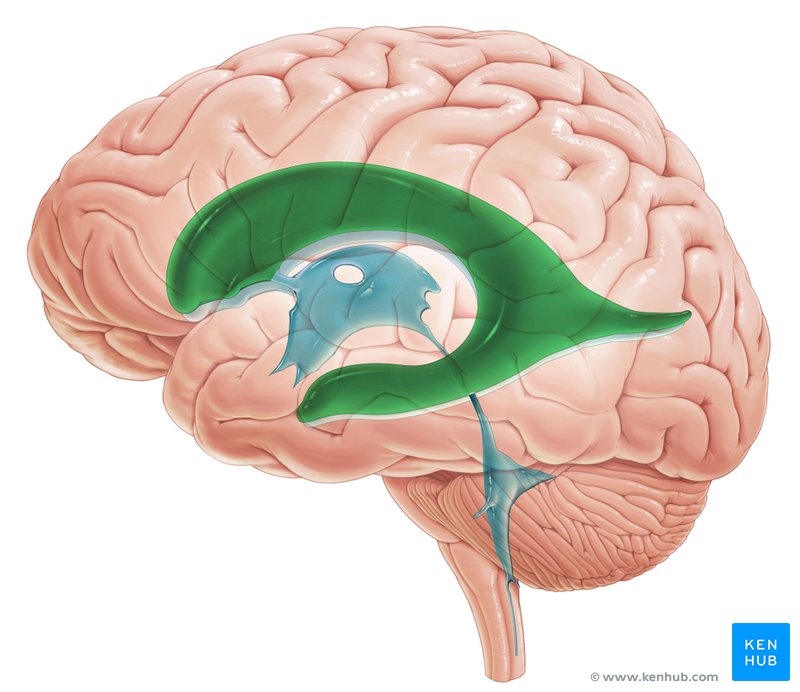
Lateral ventricles
Tthe 1st and 2nd ventricles, are the largest cavities of the ventricular system and occupy large areas of the cerebral hemispheres.
3rd ventricle
Each lateral ventricle opens through an interventricular foramen into this space; The ___ ventricle, a slit-like cavity between the right and the left halves of the diencephalon, is continuous postero-inferiorly with the cerebral aqueduct, a narrow channel in the midbrain connecting the 3rd and 4th ventricles
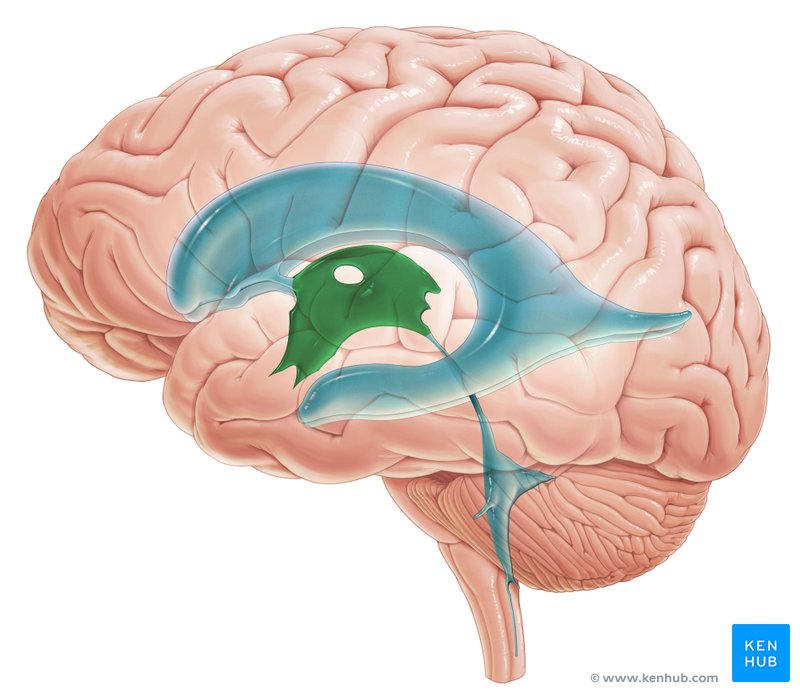
4th ventricle
The pyramid-shaped ___ ventricle in the posterior part of the pons and medulla extends inferoposteriorly.
• CSF drains into the subarachnoid space from the 4th ventricle through a single median aperture and paired lateral apertures. These apertures are the only means by which CSF enters the subarachnoid space. If they are blocked, CSF accumulates and the ventricles distend, producing compression of the substance of the cerebral hemispheres.
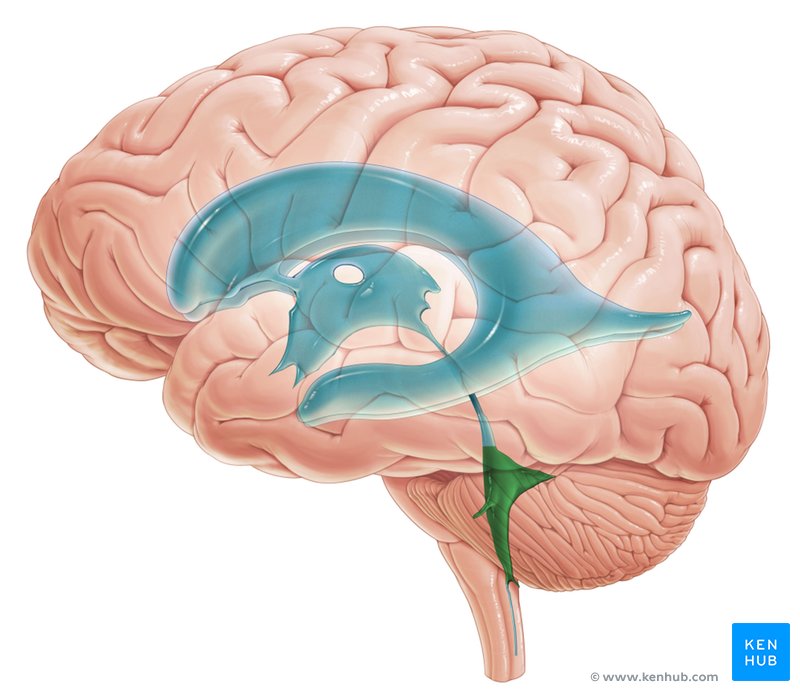
Cerebral aqueduct
Connects the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle, allowing CSF to flow between these two chambers of the brain.
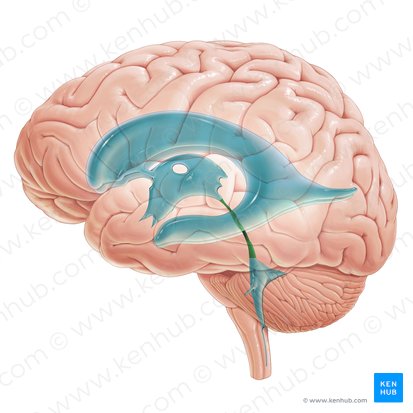
3rd
4th
apertures
Circulation of CSF
1. CSF leaves the lateral ventricles through the interventricular foramina and enters the ___ ventricle.
2. From here, CSF passes through the cerebral aqueduct into the ___ ventricle.
3. CSF leaves this ventricle through its median and lateral _____
• Some enters the subarachnoid space, which is continuous around the spinal cord and postero-superiorly over the cerebellum.
• Most CSF from the various subarachnoid cisterns flows superiorly through the sulci and fissures on the medial and supero-lateral surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres.
4. CSF also passes into the extensions of the subarachnoid space around the cranial nerves, the most important of which are the subarachnoid space extensions surrounding the optic nerves (CN II)
Interventricular foramina
Small openings located in the brain that connect the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle
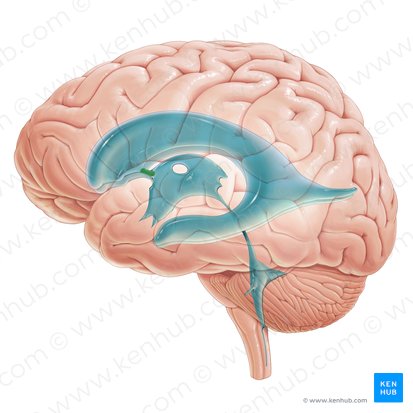
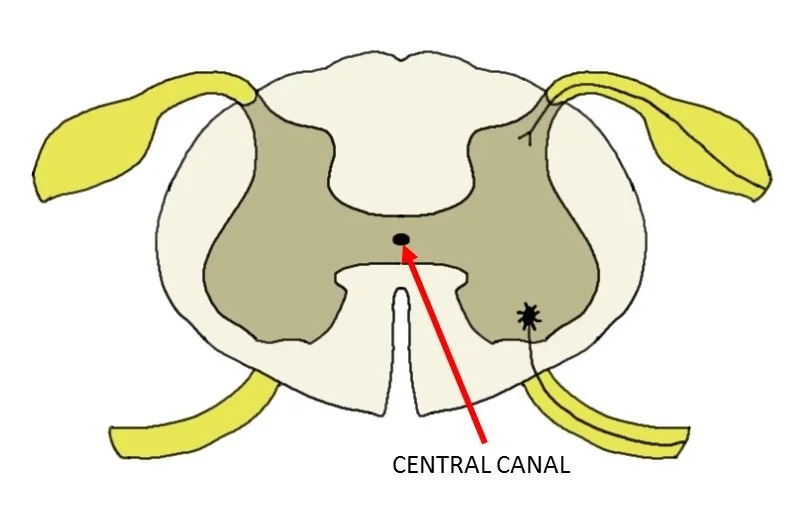
Central canal of spinal cord
a fluid-filled channel that runs through the center of the spinal cord, connecting to the brain's ventricular system
Choroid plexus
Where CSF comes from
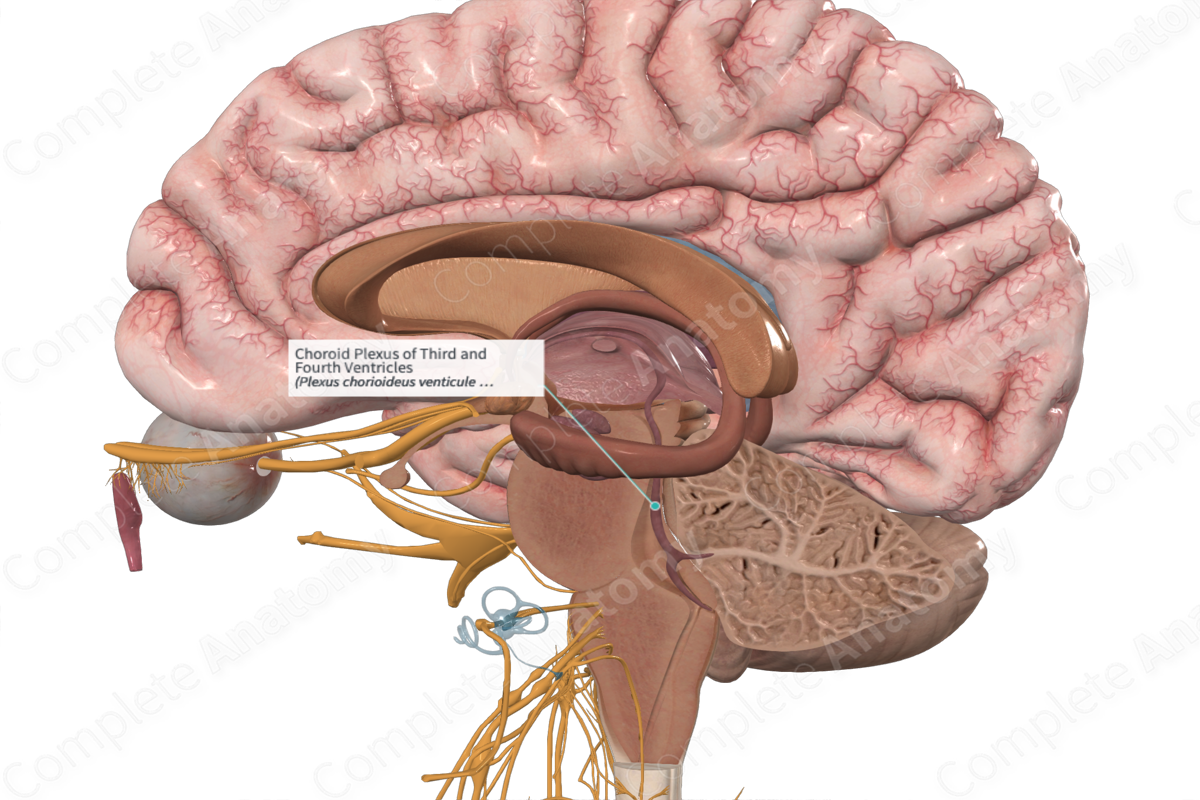
choroid
• Secretion of CSF
– CSF is secreted mainly the _____ plexuses in the lateral, 3rd, and 4th ventricles. The choroid plexuses are invaginated into the roofs of the 3rd and 4th ventricles and on the floors of the bodies and inferior horns of the lateral ventricles
granulations
• Absorption of CSF
– The main site of CSF absorption into the venous system is through the arachnoid _____. CSF enters the venous system through two routes:
(1) most CSF enters the venous system by transport through the cells of the arachnoid granulations into the dural venous sinuses, and …
(2) some CSF moves between the cells making up the arachnoid granulation
pressure
• Functions of CSF
– Along with the meninges and calvaria, CSF protects the brain by providing a cushion against blows to the head. The CSF in the subarachnoid space provides the buoyancy that prevents the weight of the brain from compressing the cranial nerve roots and blood vessels against the internal surface of the cranium
– Changes in intracranial _____ occur from time to time and are mitigated by the displacement or replacement of CSF
Connective
Epicranial
Loose
Periosteum
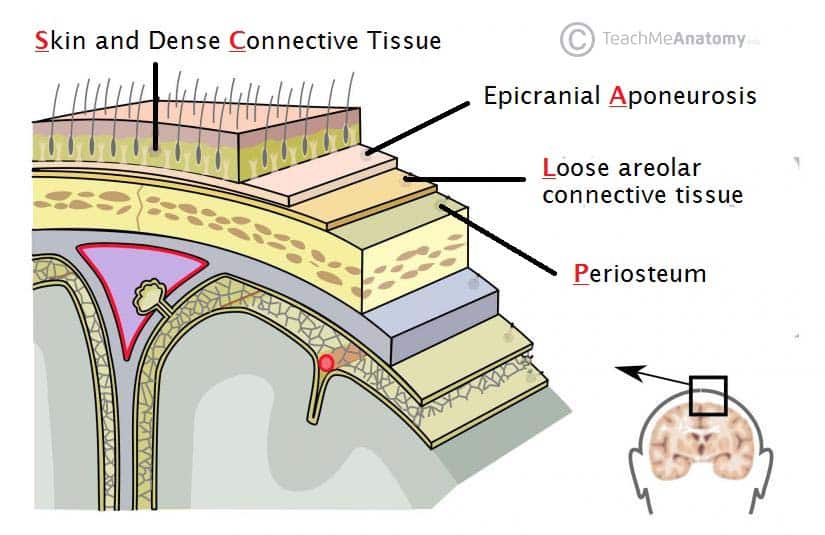
SCALP
• Five layers of tissue (SCALP)
– Skin
– _____ tissue – contains a large number of blood vessels
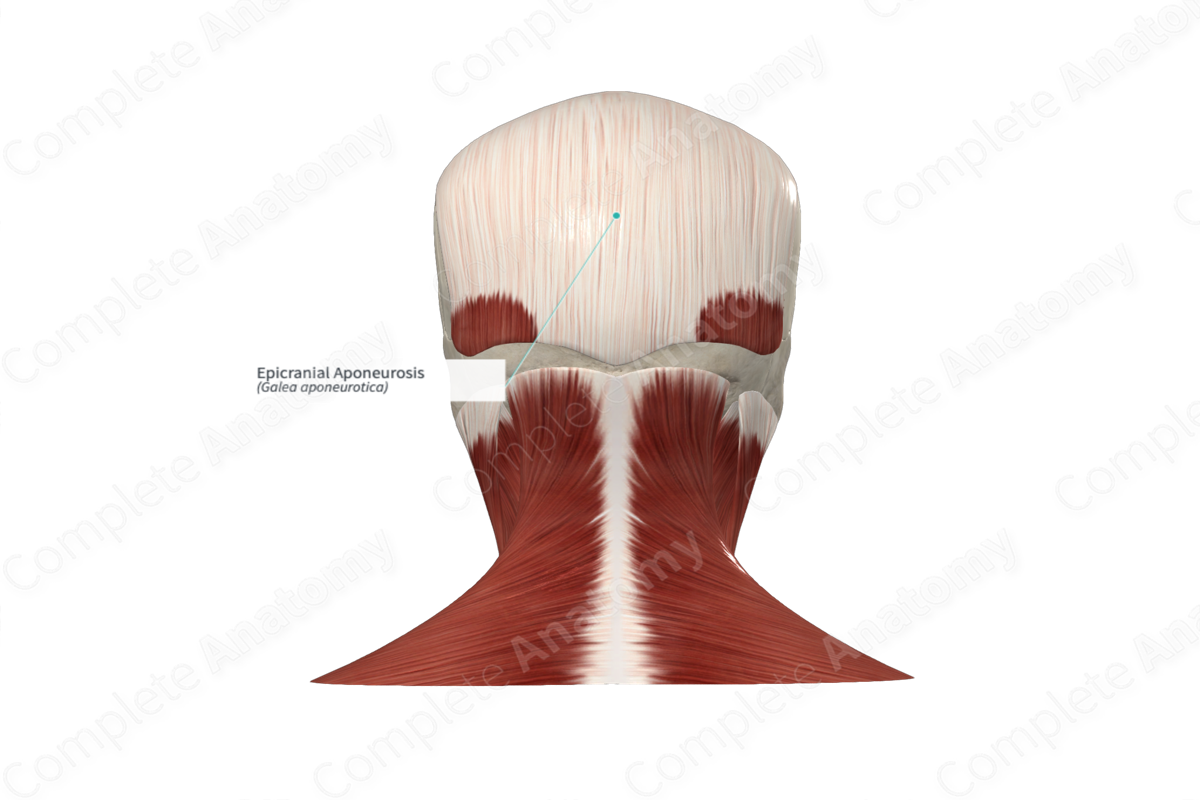
– _____ Aponeurosis – strong membranous tendon connecting the anteriorly placed frontalis muscle and the posteriorly placed occipitalis.
– _____ connective tissue – allows the outer three layers to move freely over the skull.
– _____ of the cranium.
Epicranial aponeurosis
Frontal belly of occipitofrontalis
AKA frontalis muscle
A muscle located in the forehead region of the human skull. It plays a crucial role in forming facial expressions, particularly those conveying surprise or shock.
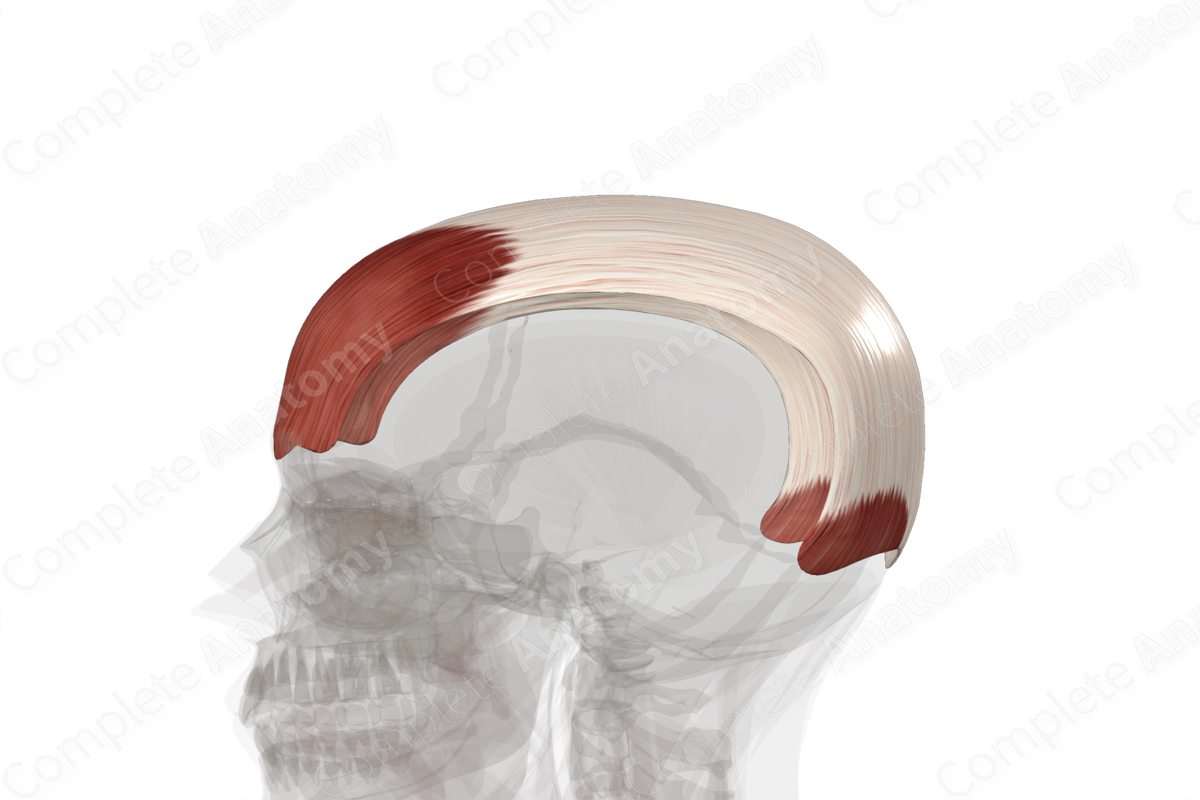
Occipital belly of occipitofrontalis
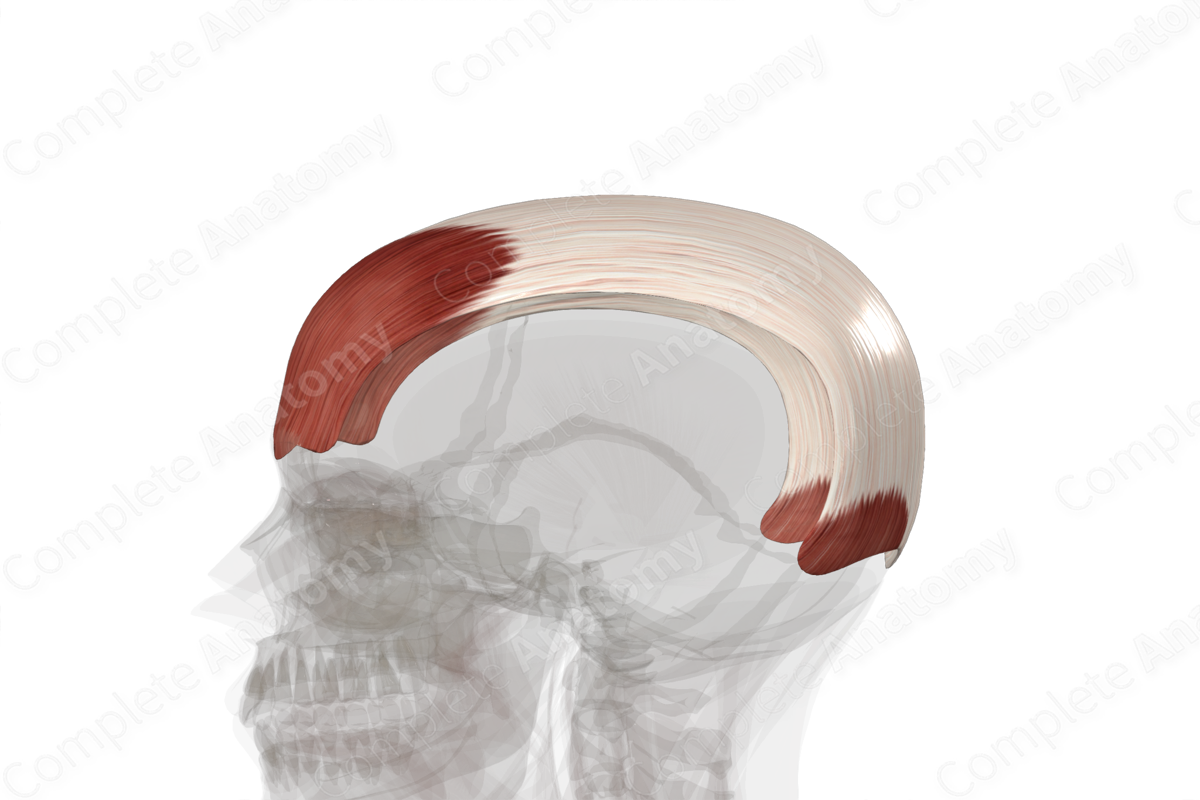
AKA occipitalis muscle
A component of the occipitofrontalis muscle, also called the epicranius muscle. The occipitofrontalis muscle is a broad muscle covering the superior and posterior parts of the skul
Face
ears, hairline, chin
The _____
• the anterior aspect of the head bounded posteriorly by the _____, superiorly by the _____, and inferiorly by the _____
• Encompasses the ears, eyes, nose, and mouth
7
Temporal
Zygomatic
Buccal
Mandibular
Cervical
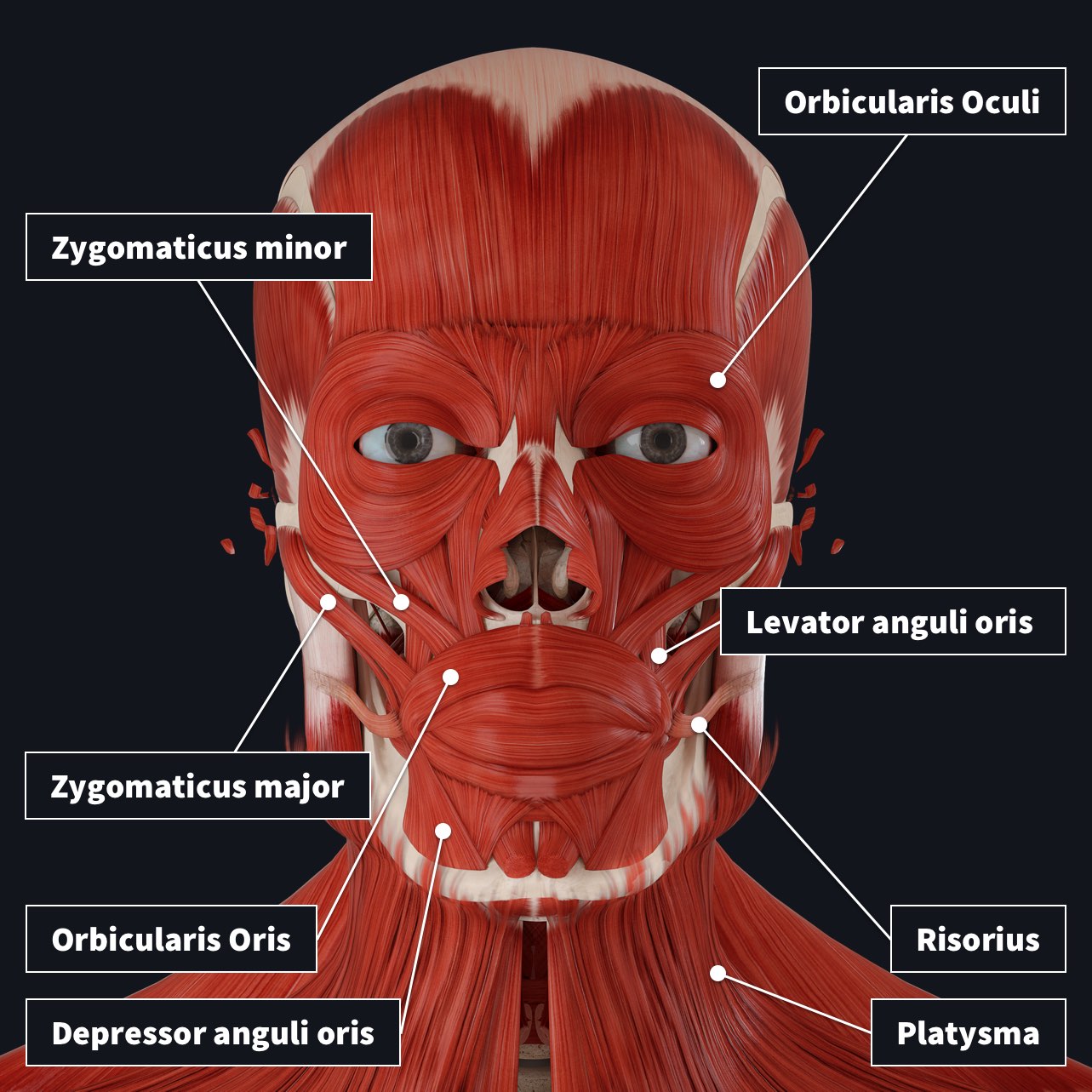
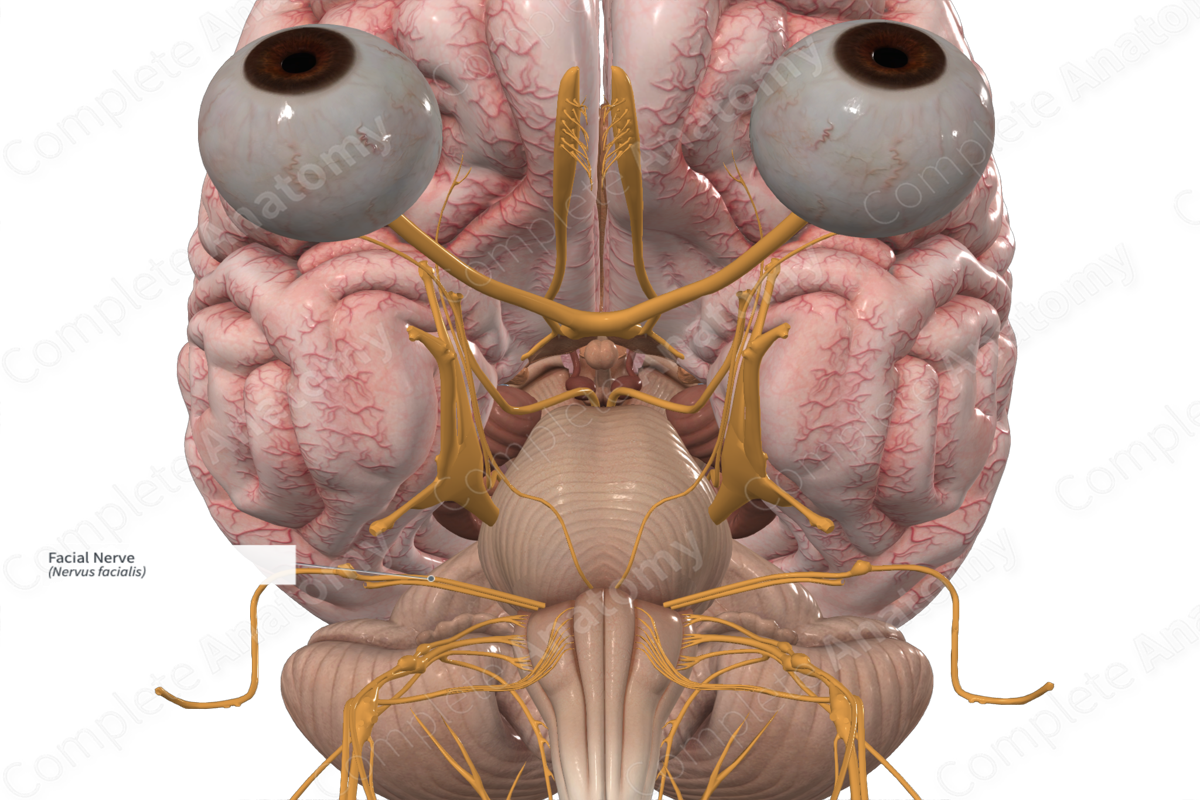
Motor Innervation of Face
• Cranial nerve ___ - facial nerve
– Exits the stylomastoid foramen and enters the parotid gland. Within the gland it divides and gives rise to five major branches
– _____ – to orbital and forehead
– _____ - to zygomatic, orbital, infraorbital regions
– _____ - to cheek and upper lip
– Marginal _____ – lower lip and chin
– _____ – to neck for innervation of platysma
Stylomastoid foramen
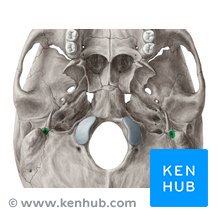
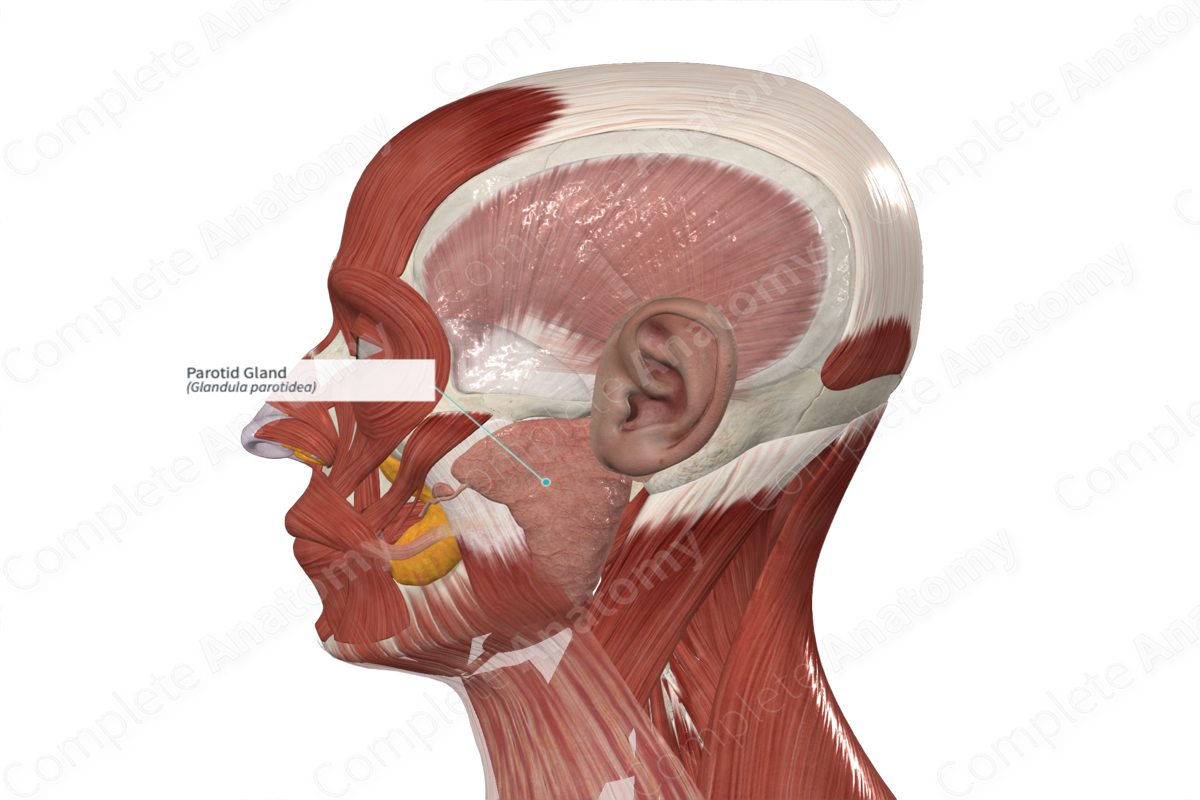
Parotid gland
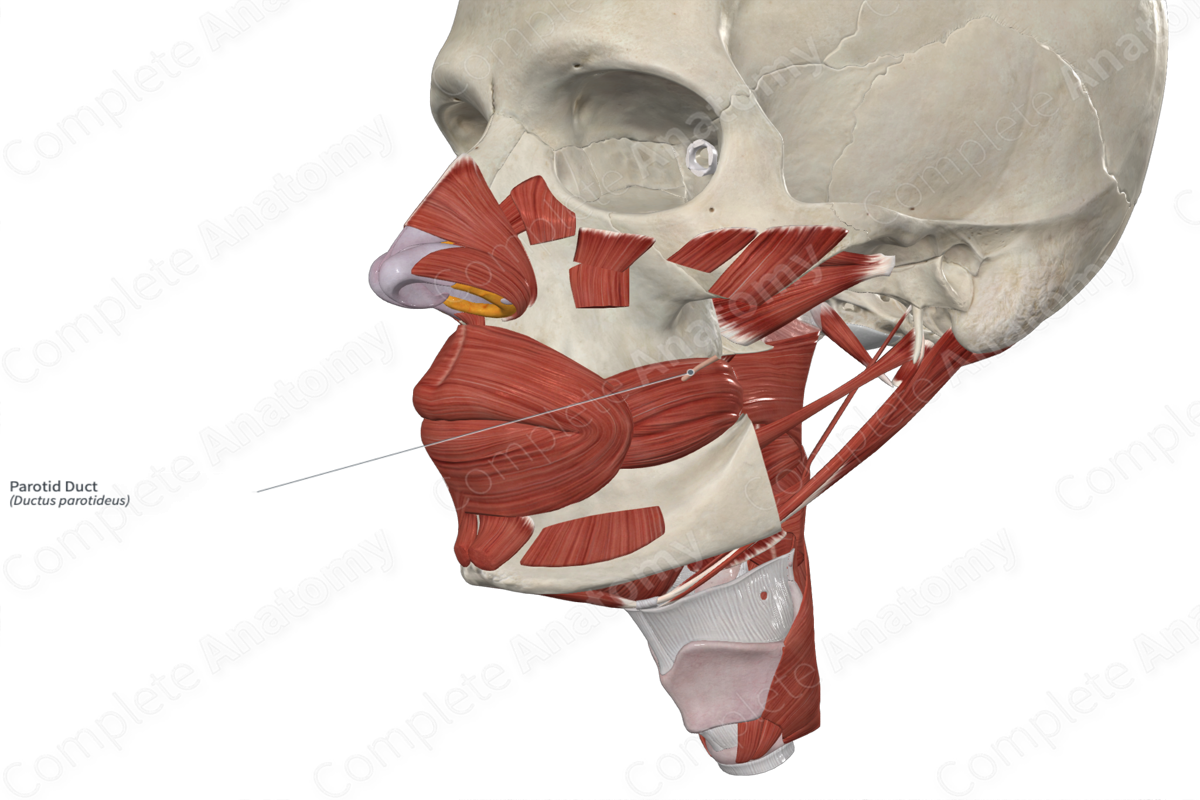
Parotid duct
Pierces buccinator
5
Sensory Innervation of Face
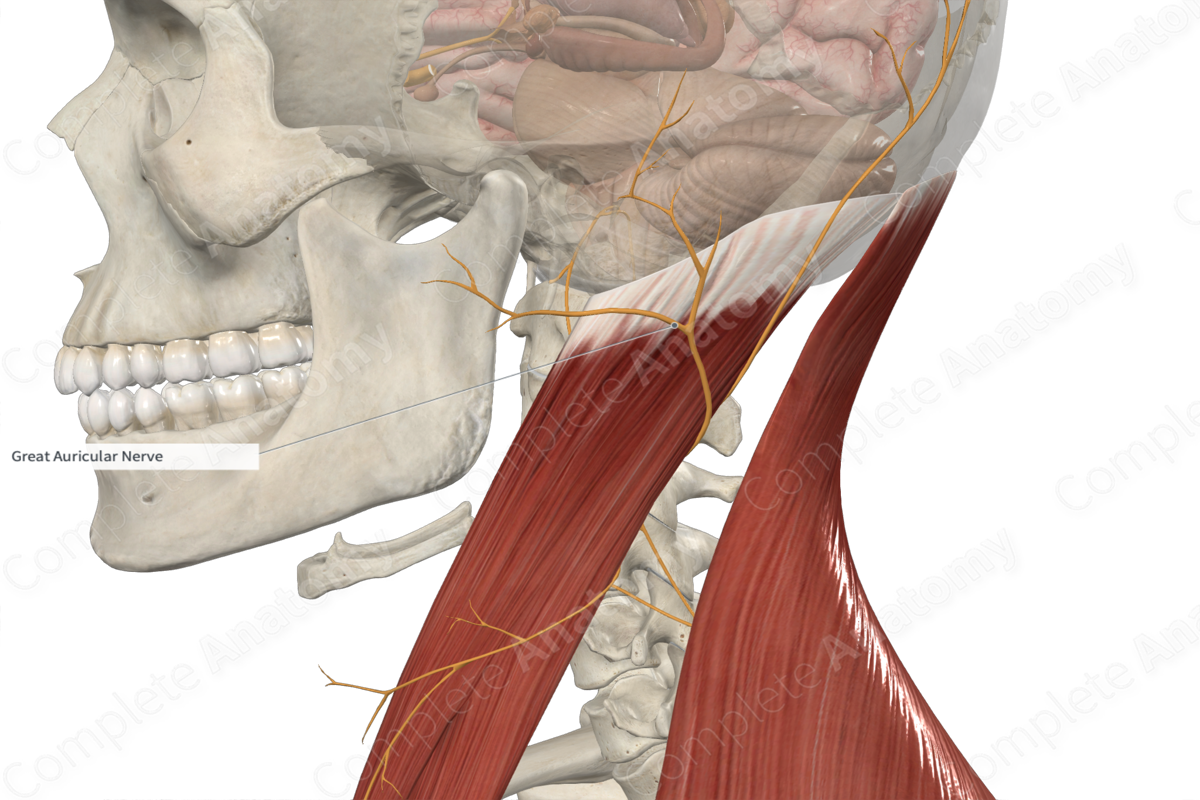
• Sensory innervation occurs via the 5th cranial nerve and the great auricular nerve from the cervical plexus.
• ___th cranial nerve - supplies the face
– ophthalmic division
– maxillary division
– mandibular division
• Great auricular nerve - supplies the areas anterior, inferior and posterior to the ear.
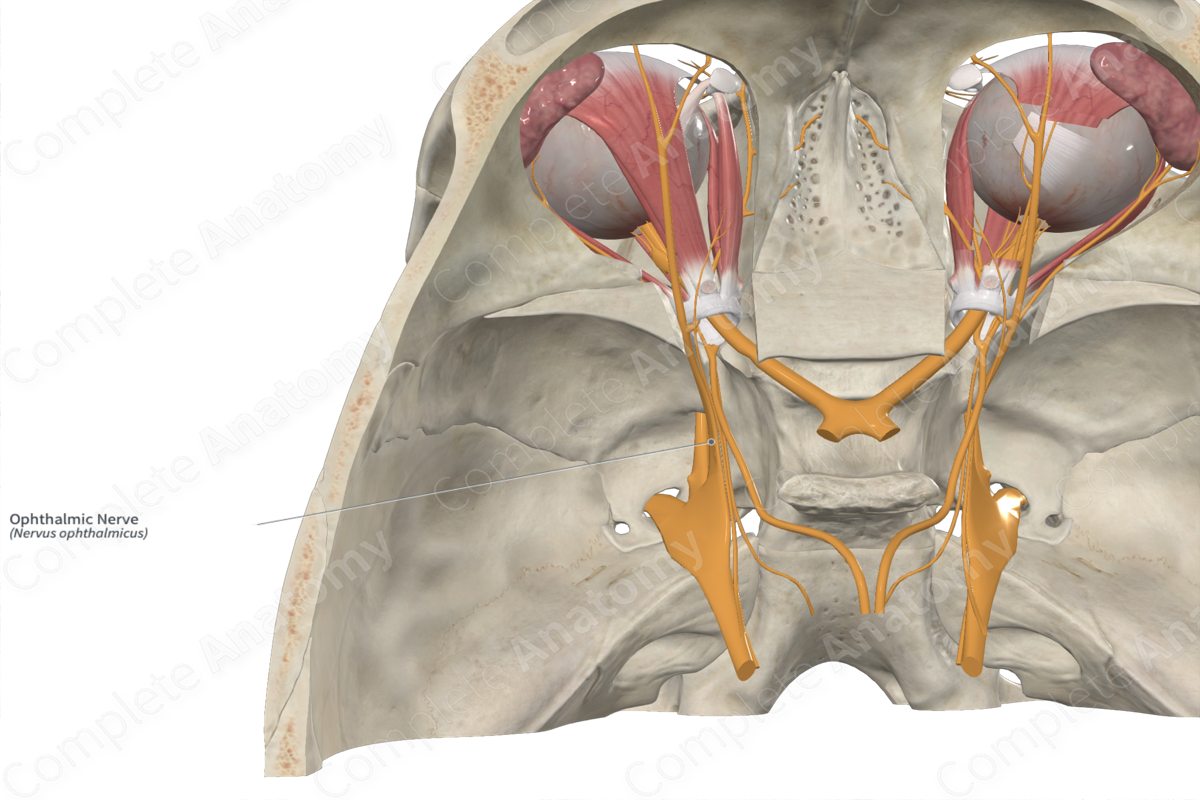
Opthalamic nerve (CN V1)
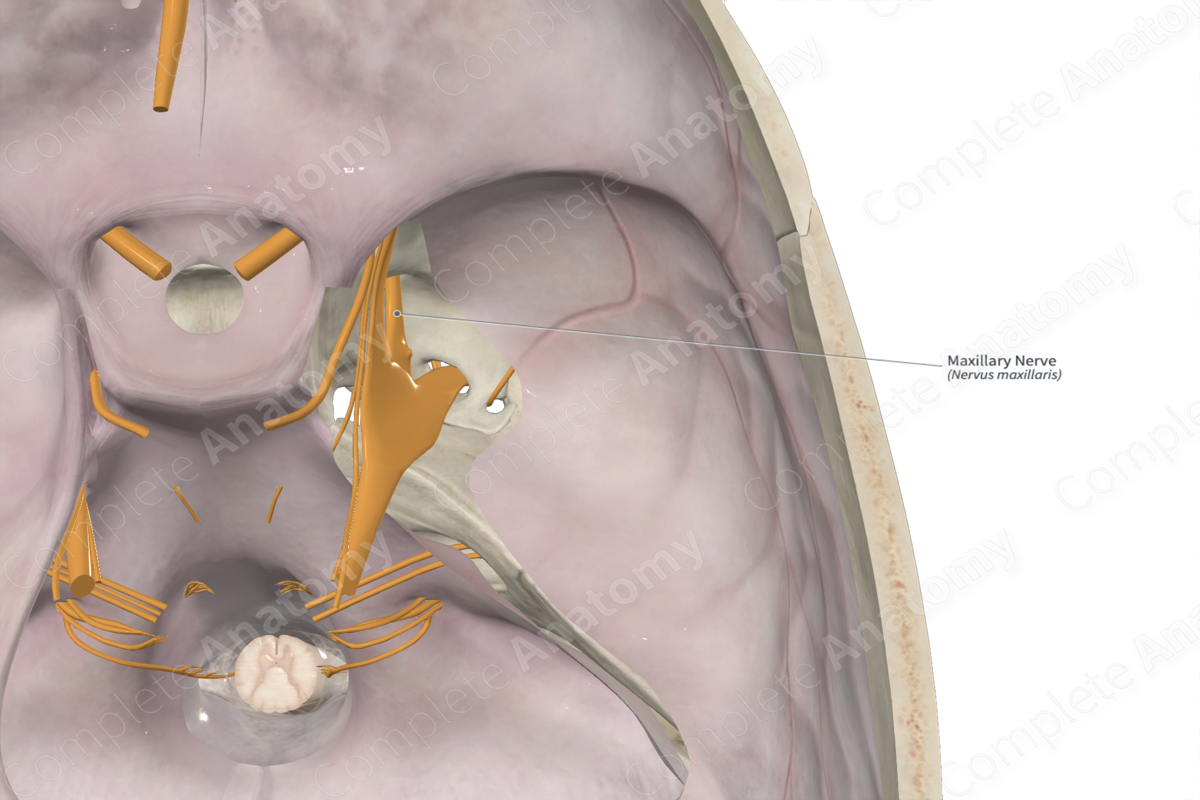
Maxillary nerve (CN V2)
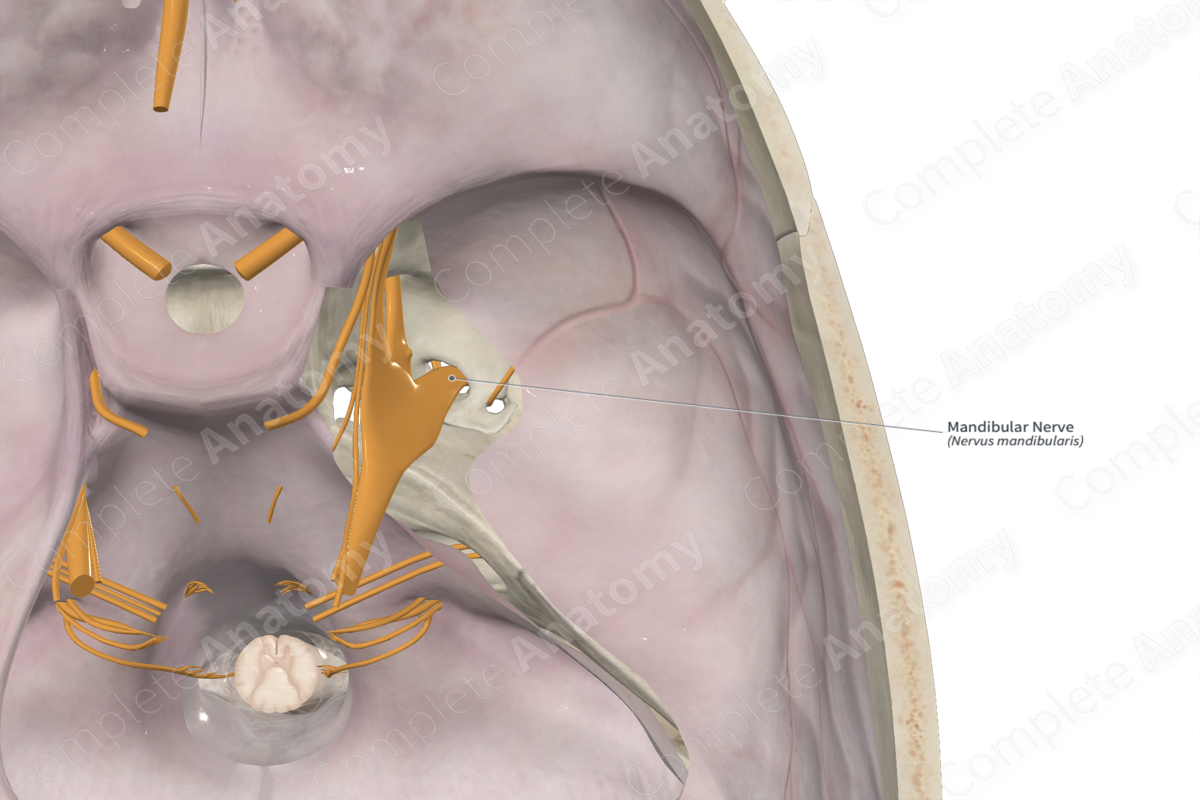
Mandibular nerve (CN V3)
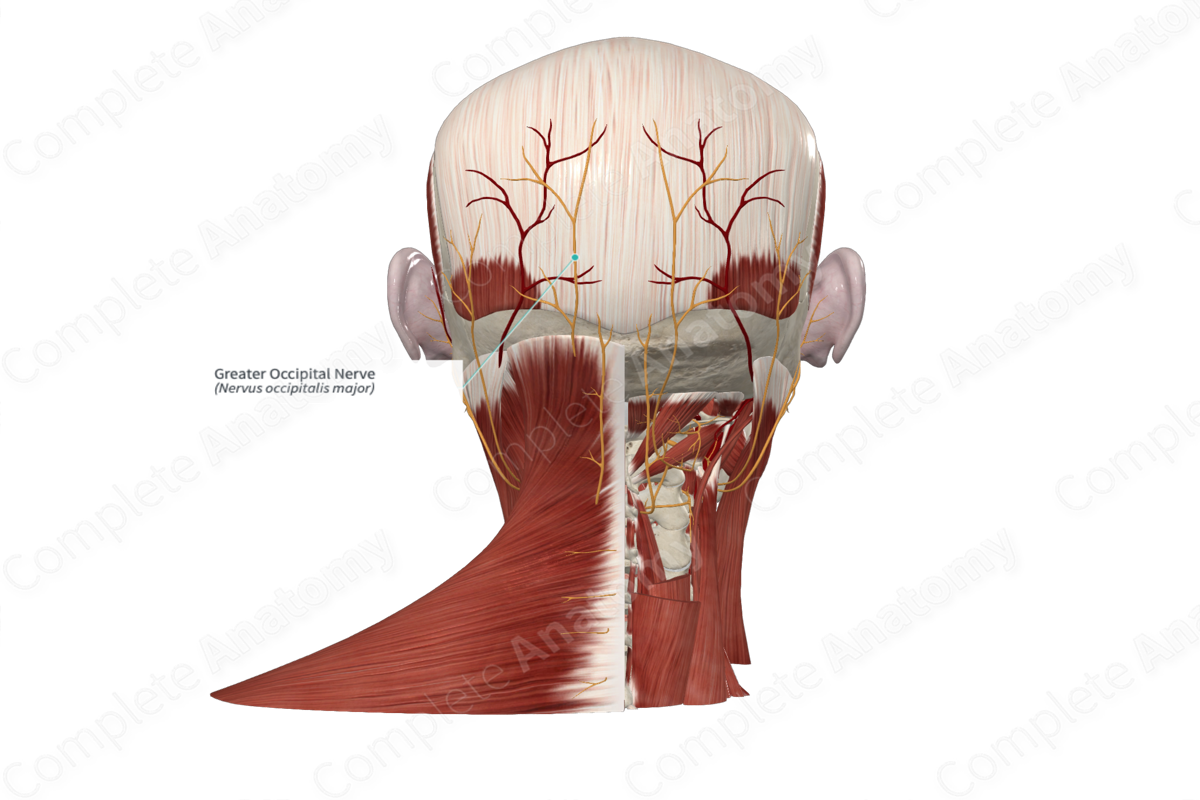
Greater occipital nerve (C2)
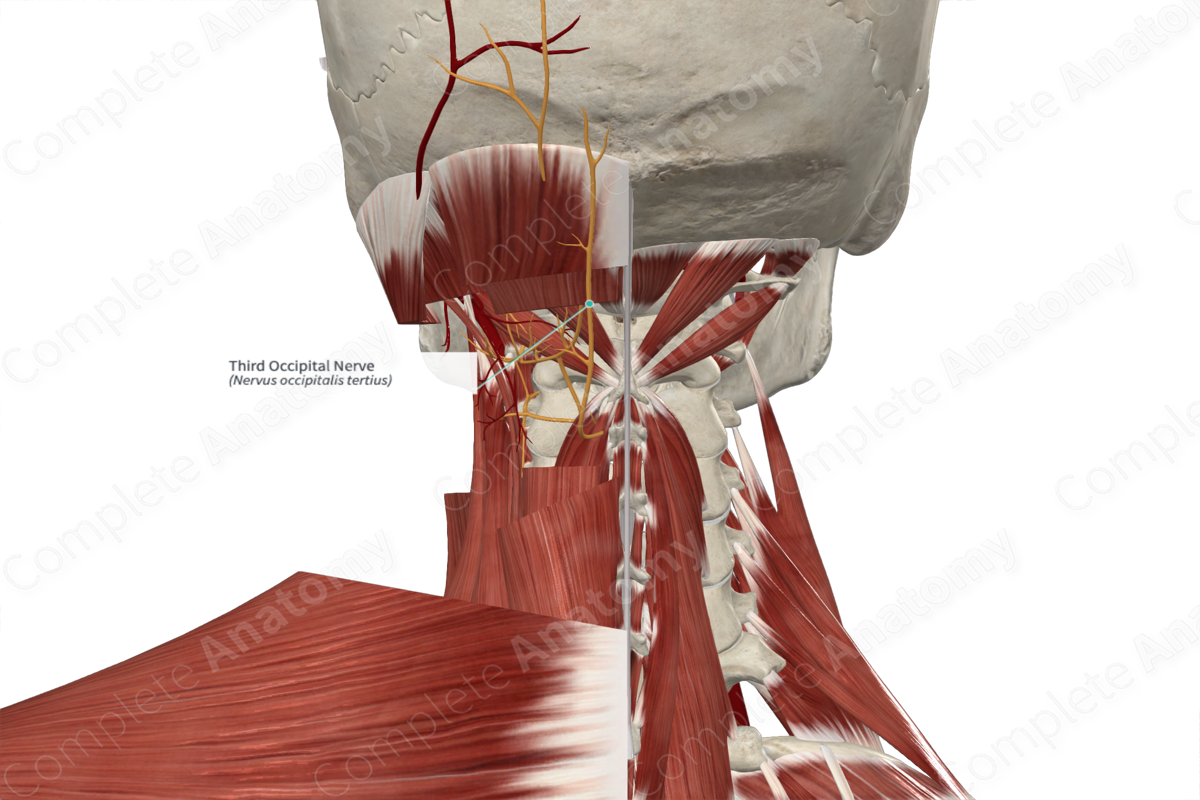
Third occipital nerve (C3)
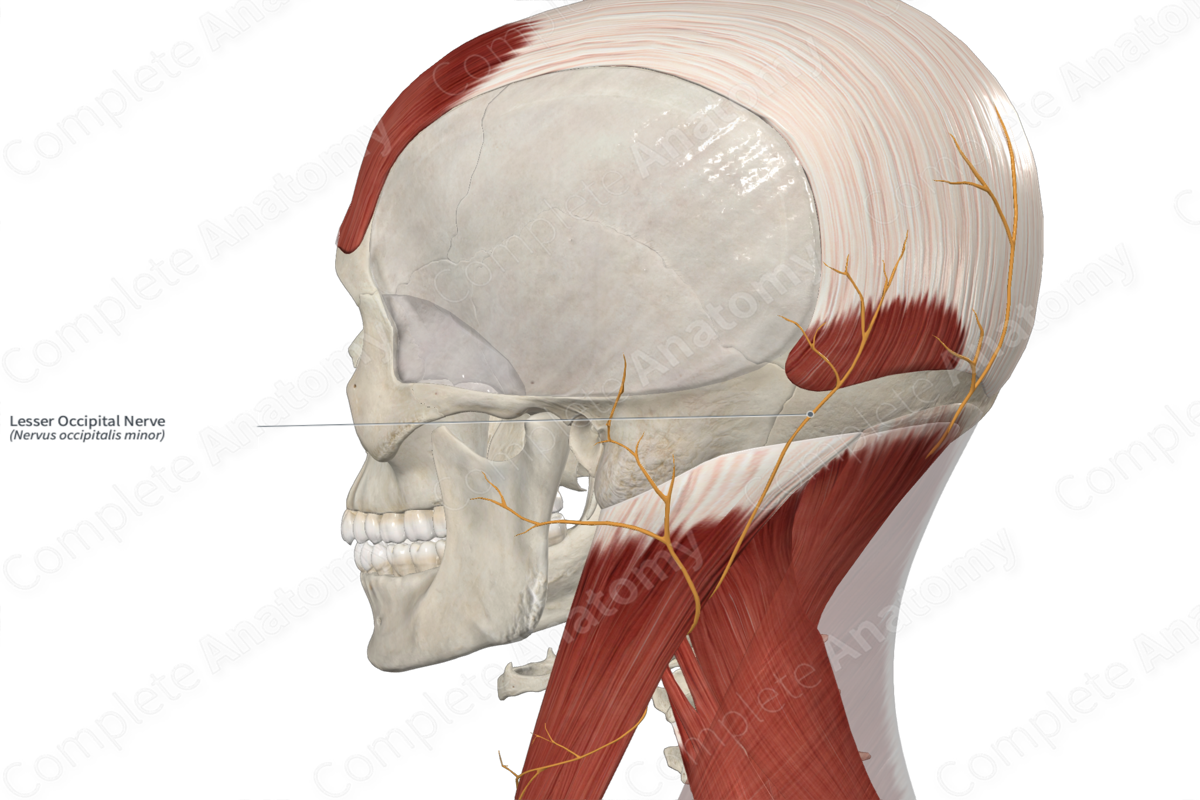
Lesser occipital nerve (C2-3)
Great auricular nerve (C2-3)
Facial
temporal
transverse
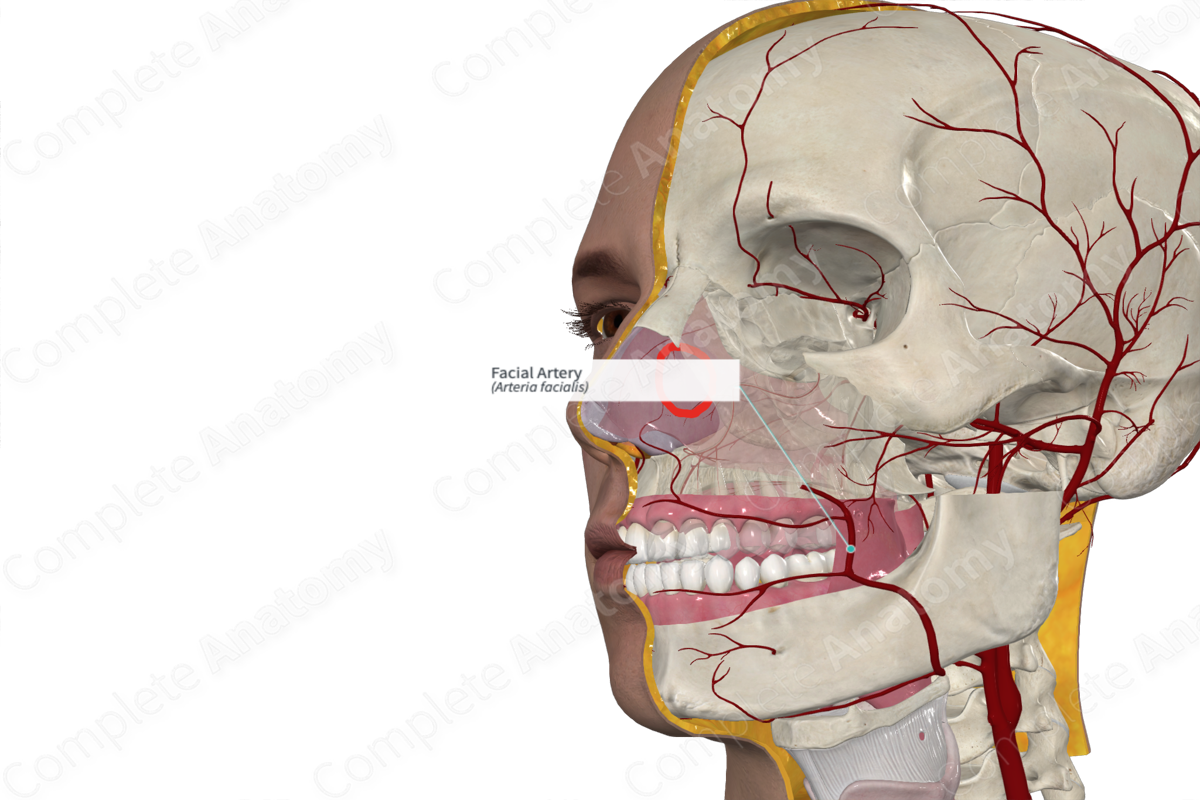
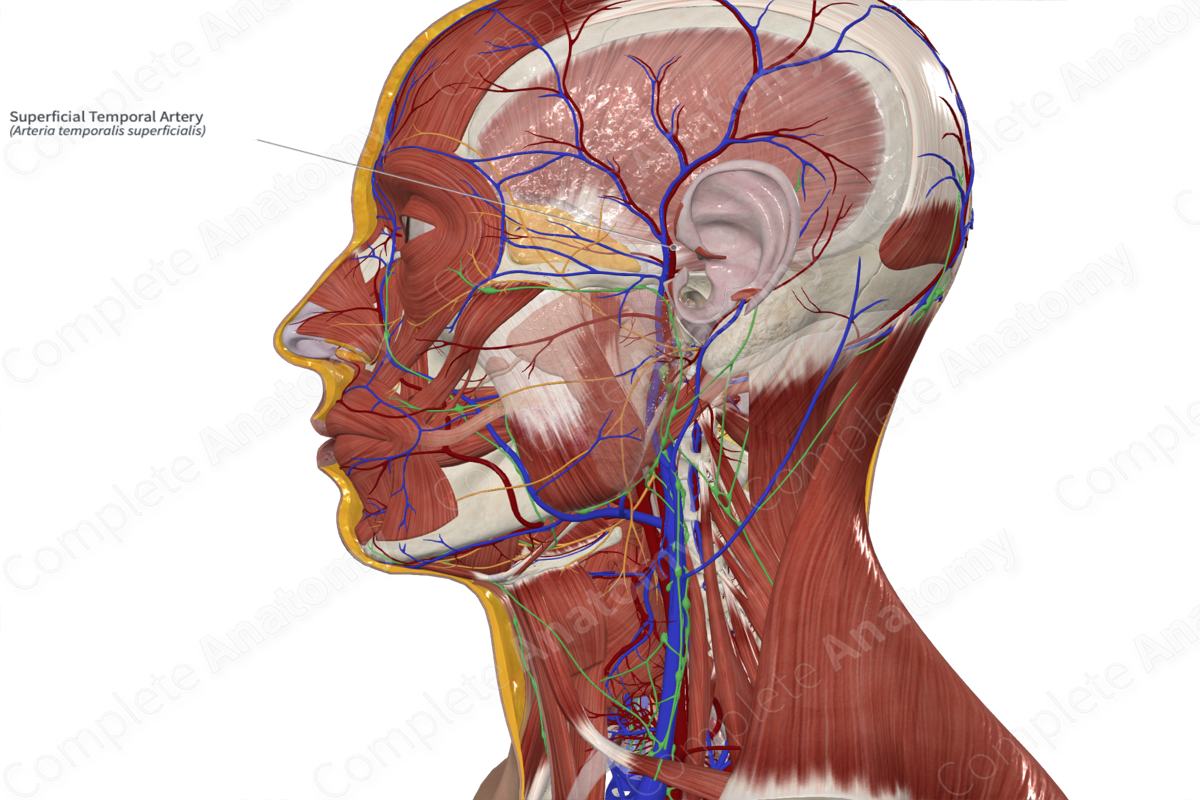
Arterial Supply of Face
• _____ artery - primary supplier, arises from the external carotid. It gives rise to multiple branches
• Superficial _____ artery - terminal branch of the external carotid. It gives rise to the _____ facial artery.
Facial artery
Superficial temporal artery
Facial nerve (CN VII)
Transverse facial artery
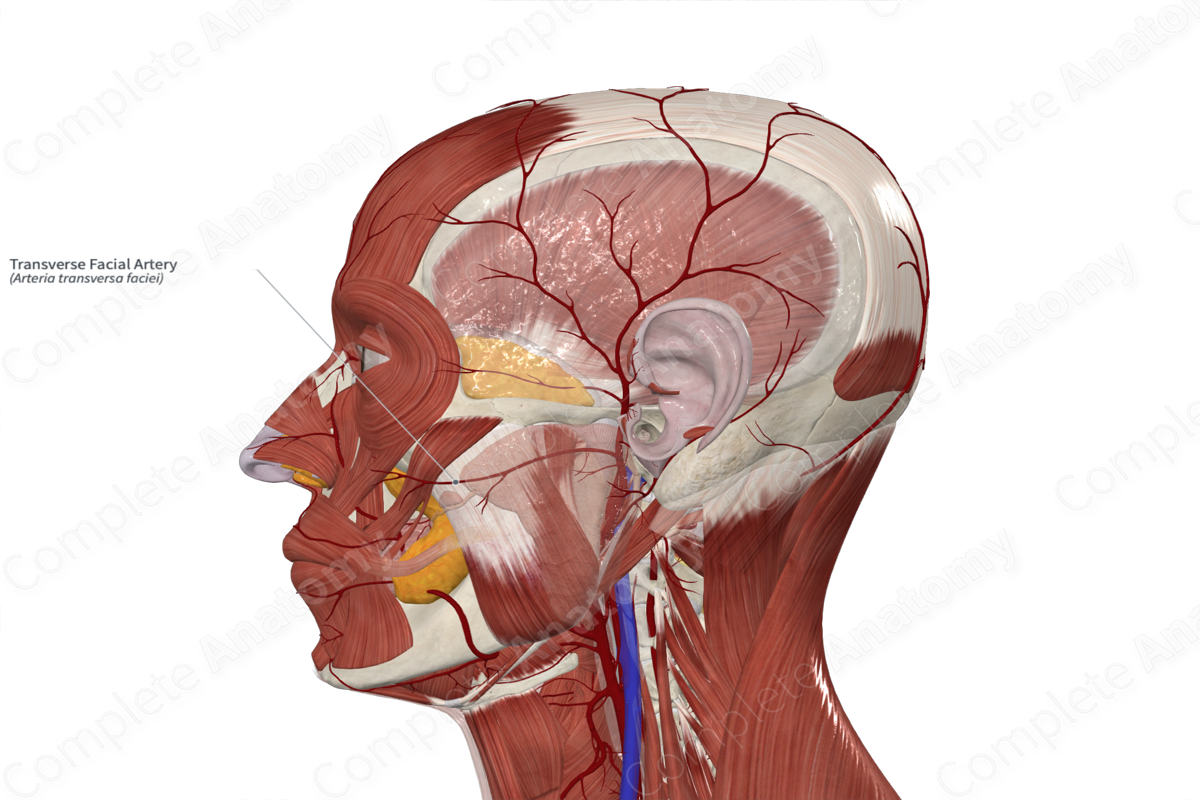
Facial
temporal
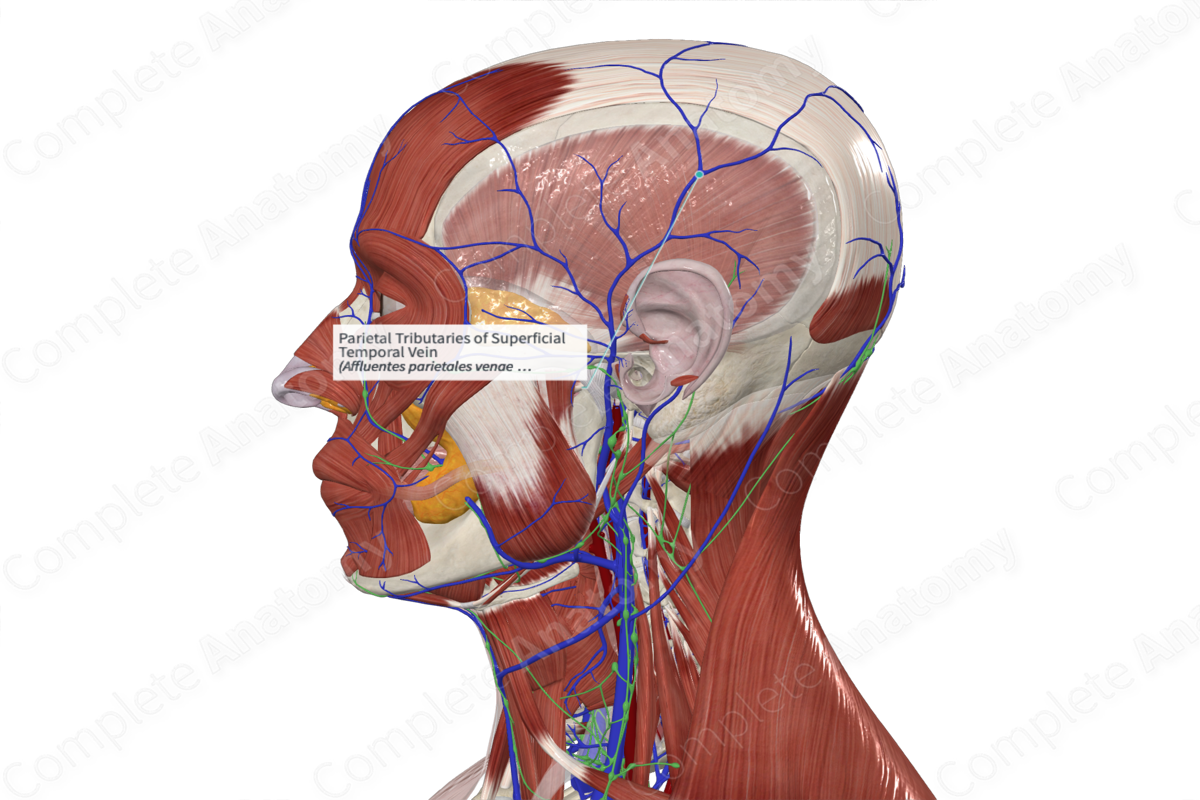
Venous drainage of Face
• _____ Vein: primary drainage
– Joined by the Anterior division of the retromandibular vein
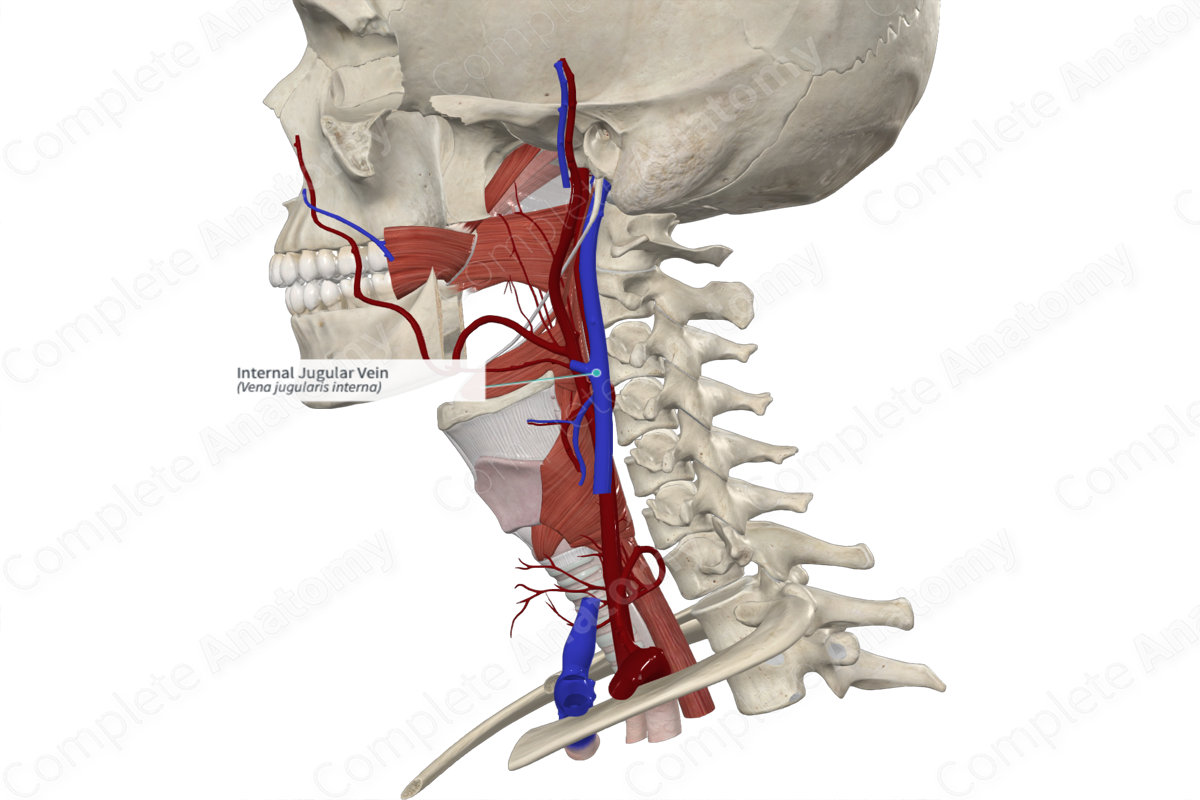
– Drains into internal jugular vein
• Superficial _____ vein - comes from the forehead
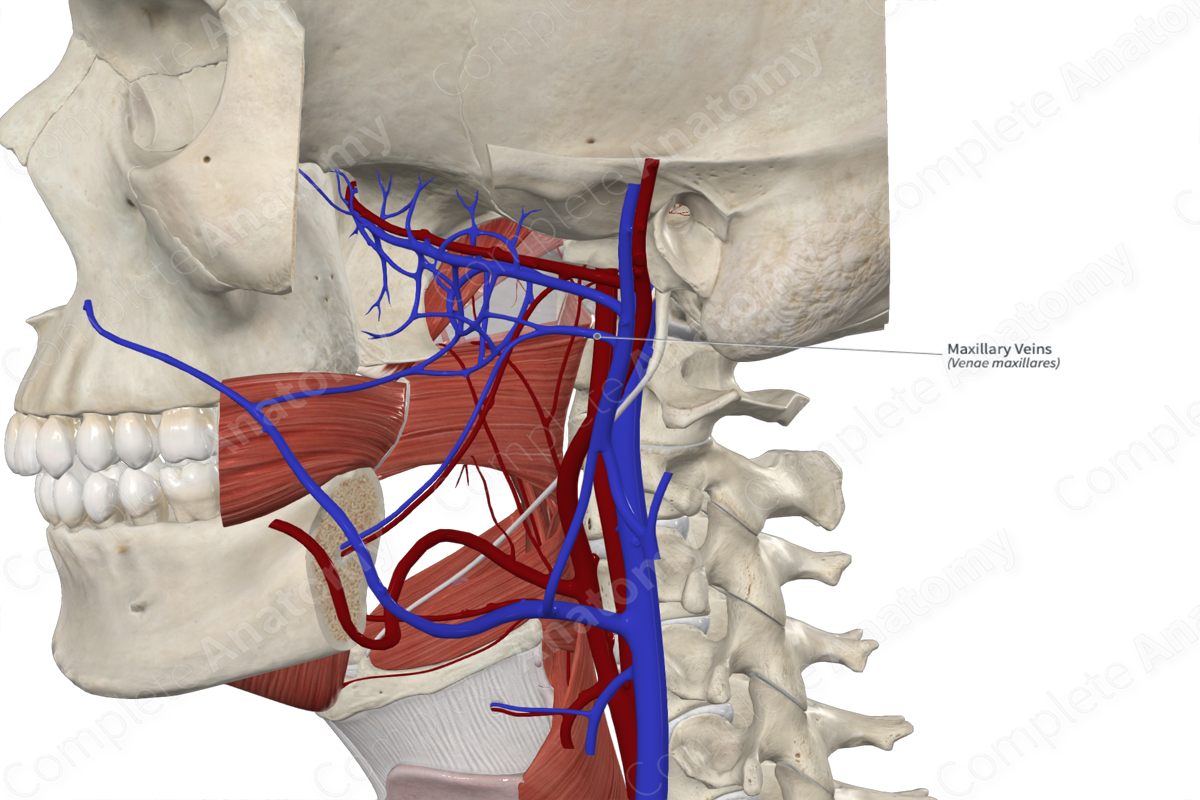
– It is joined by the Maxillary vein
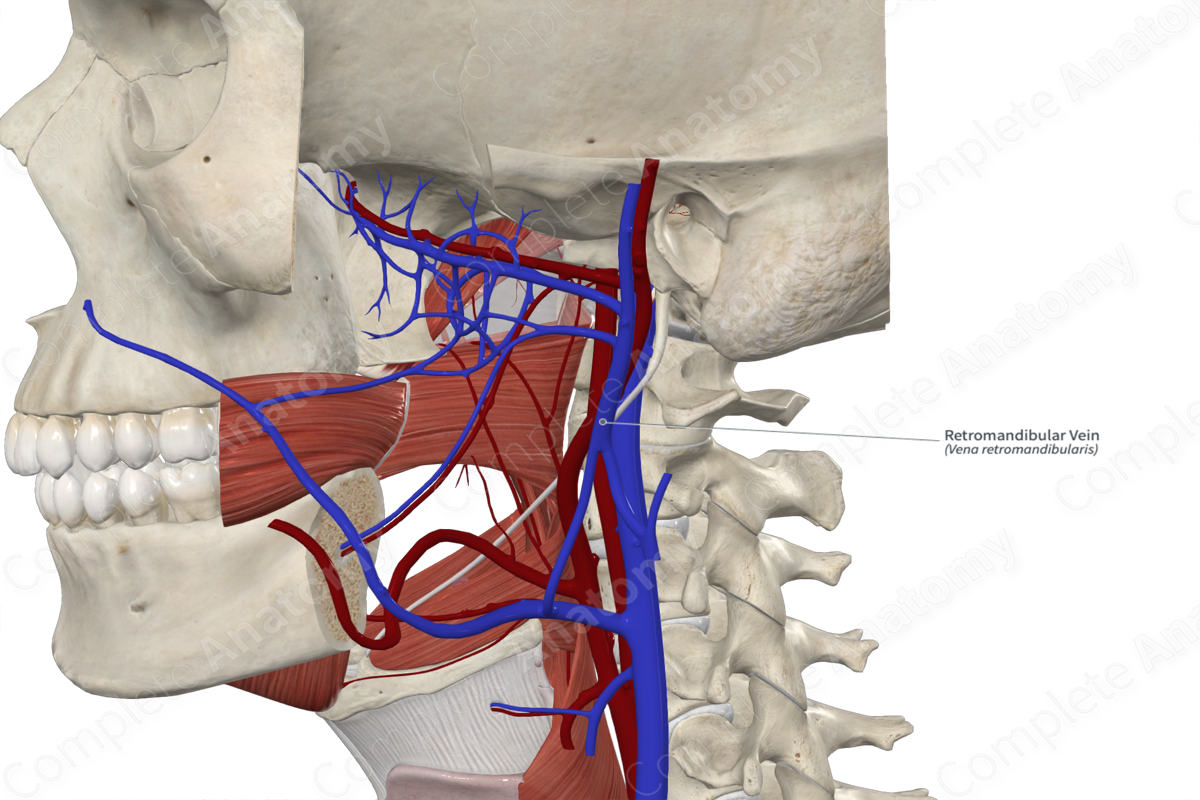
– Together they form the retromandibular vein
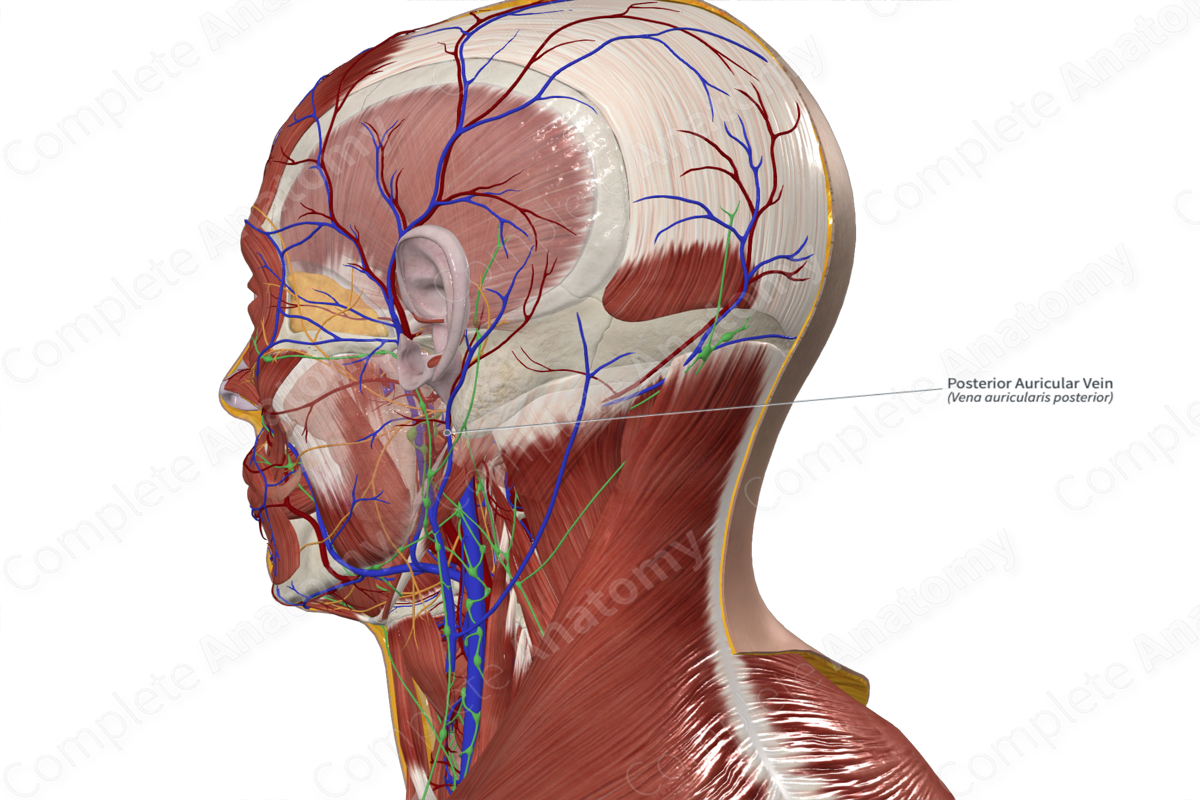
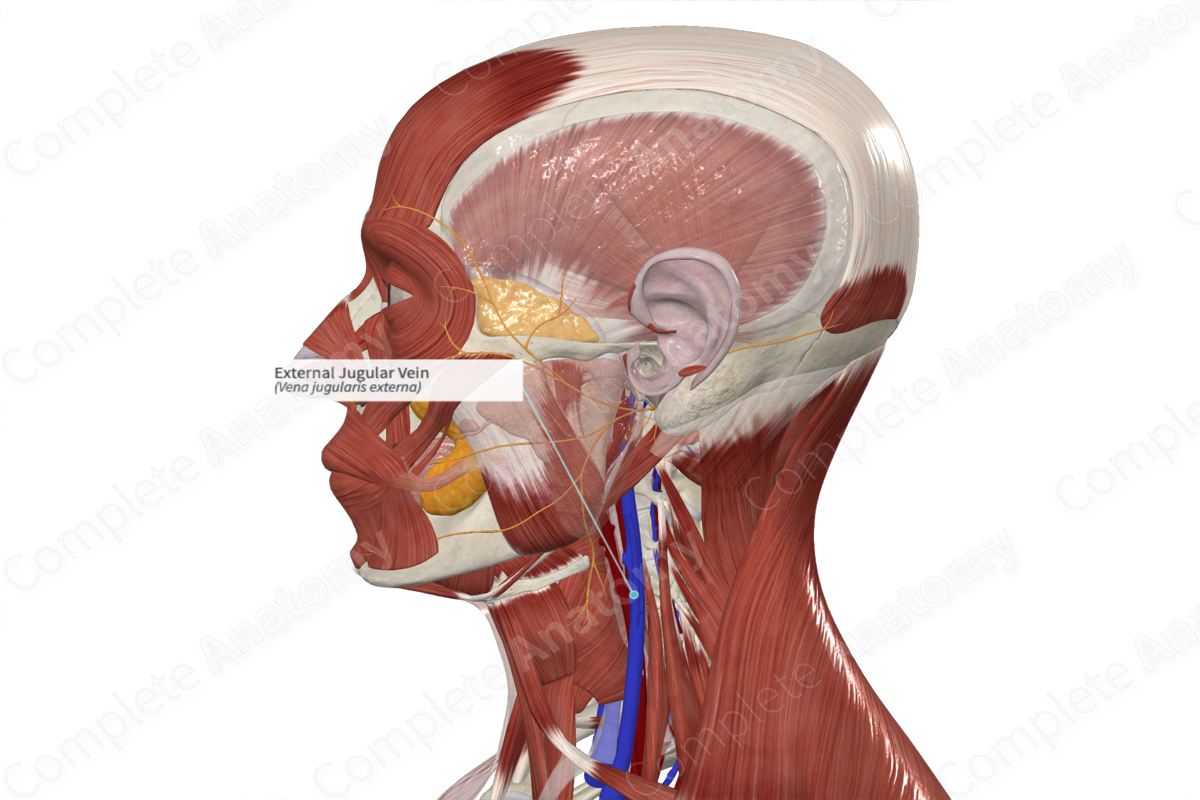
– Retromandibular and posterior auricular vein form the external jugular vein
Superficial temporal vein
comes from the forehead
– It is joined by the Maxillary vein
– Together they form the retromandibular vein
– Retromandibular and posterior auricular vein form the external jugular vein
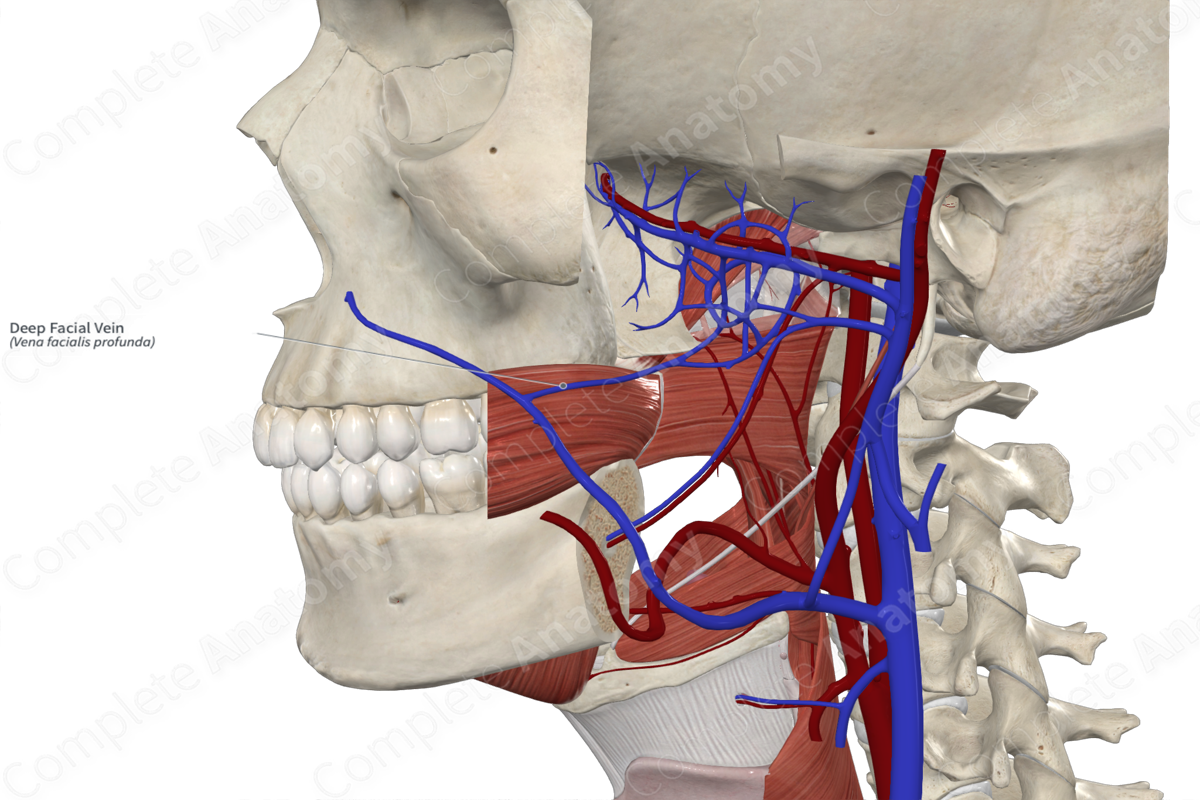
Facial vein
Primary drainage
– Joined by the Anterior division of the retromandibular vein
– Drains into internal jugular vein
Retromandibular vein
Maxillary vein
Posterior auricular vein
External jugular vein
Internal jugular vein
Ecchymosis
Extravasation of blood under the skin