Metal Bending Assessment - Mechanical Properties of Materials Lecture
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Define Strength.
the ability of a material to resist forces
we often make choices on the strength of the materials we use of fabrication
to compare the strengths of different materials, we must first understand stress
Define Stress.
relates to both magnitude of applied forces and amount of material resisting the force
σ = amount of stress
F = applied force in pounds
A = cross-sectional area in square inches
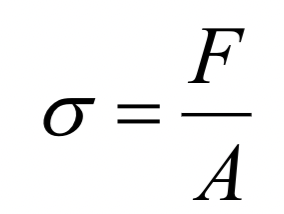
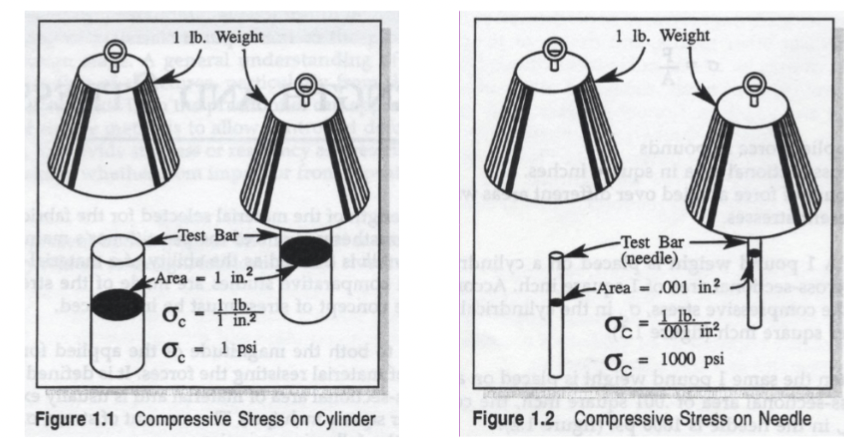
Will the same amount of force applied over different ares cause radically different stresses?
yes!
What are the four types of stress?
tensile
compressive
shear
flexural
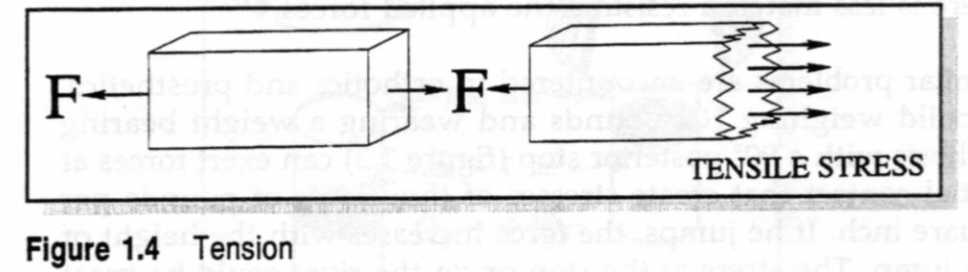
Tensile Stresses
act to pull apart an object
occur parallel to the lines of force but perpendicular to the area in question
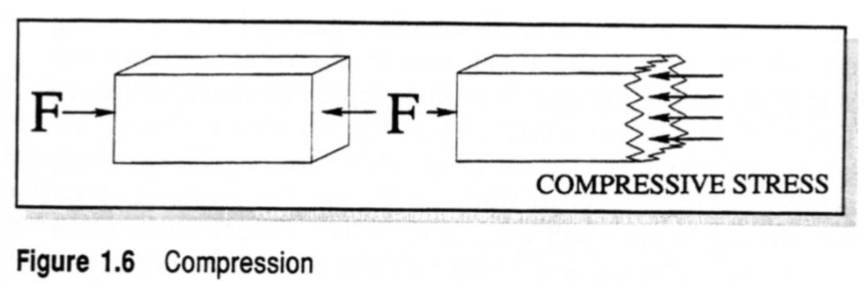
Compressive Stresses
act to squeeze or compress objects
compressive stresses also occur parallel to the lines of force and perpendicular to the cross-sectional area
Shear Stress
act to scissor or shear the object, causing the planes of the material to slide over each other
occur parallel to applied forces and cross-sectional area
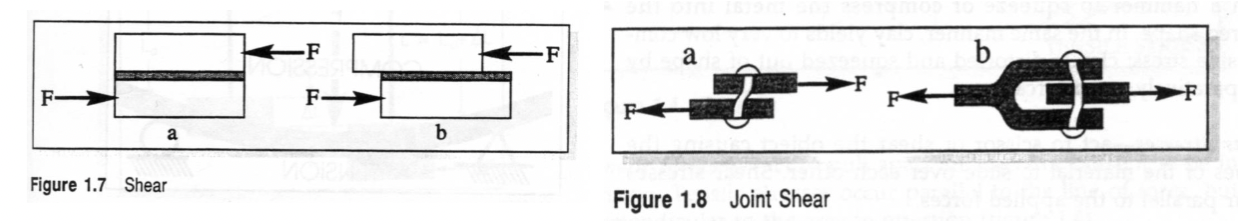
Flexural Stress
bending stresses
combination of tension and compression stresses
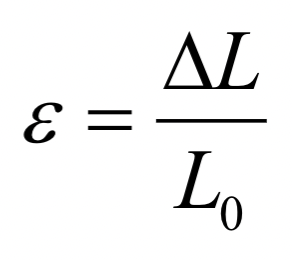
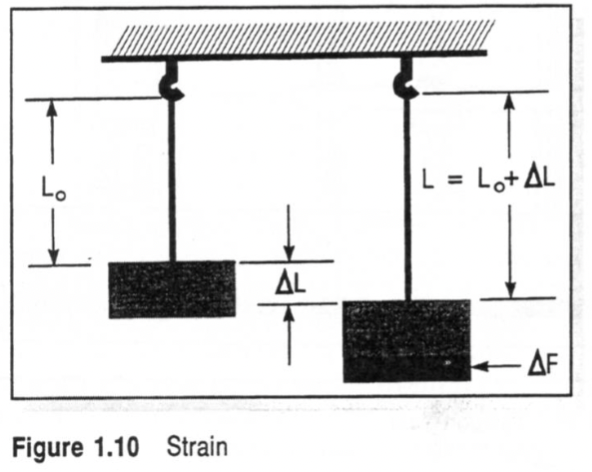
What is Strain?
material subjected to sufficient stress will deform or change shape
lengthening or shortening due to stress is called experiencing strain
ε = strain
ΔL = change in length
L0 = original length
strain is dimensionless
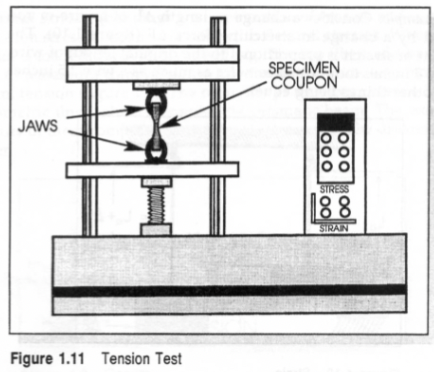
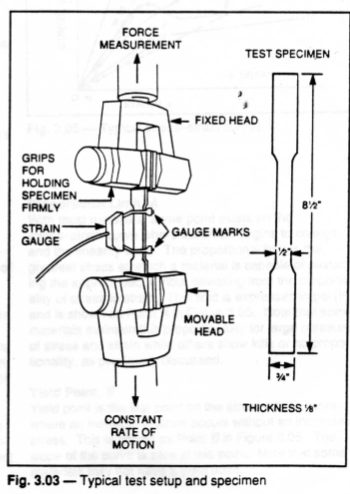
Tension Test
specimen size and testing conditions standardized
how hard is it to pull apart?
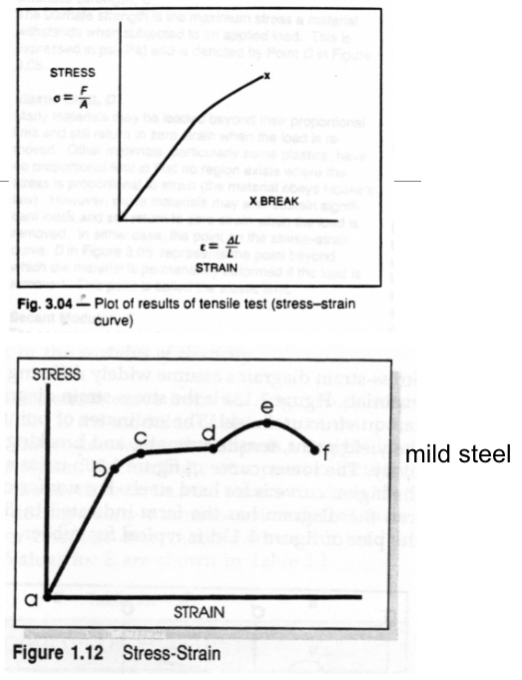
What effects the shape of the stress-strain curve?
composition
heat treatment
prior history of plastic deformation
strain rate - how fast it deforms
temperature
state of stress
When stress is linearly proportional to strain, strain is _______.
elastic
If the strain is elastic, the stressed part will [ return, not return] to original shape?.
return
In Plastic Deformation, the material _______ deformed after the stress is removed.
remains
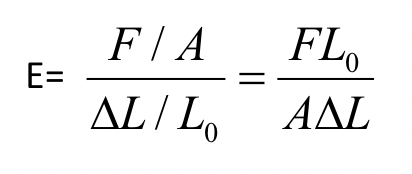
Hooke’s Law
σ=εE OR E =σ/ε
σ = stress in psi
ε = strain in inch/inch
E = Young’s modulus, or modulus of elasticity
the modulus E, is the slop of the initial straight line portion of the stress-strain curve
Combines equations for stress, strain, and modulus where F, L0, and A are constants, shows the linear relationship between F and ΔL
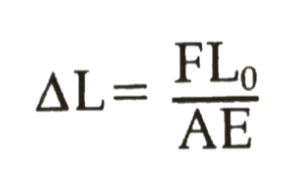
If there is 2x force put on a material. . .
you get 2x the amount of length change
Proportional Limit
slope begins to change and linearity ends. permanent change in shape starts
Yield Point
first point where increase in strain appears without increase in stress. Not all materials have a yield point.
Tensile Strength
maximum tensile force (e) divided by original cross-sectional area
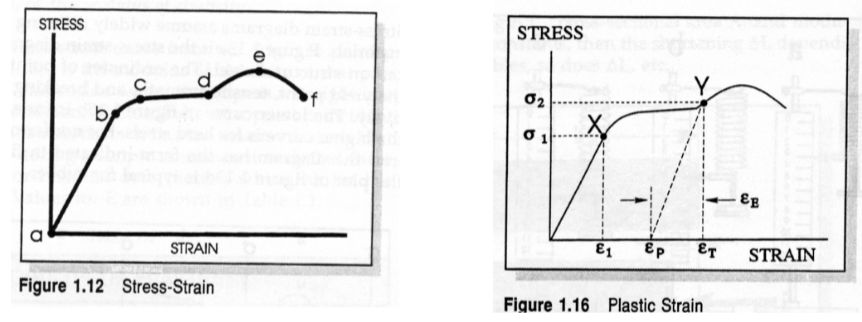
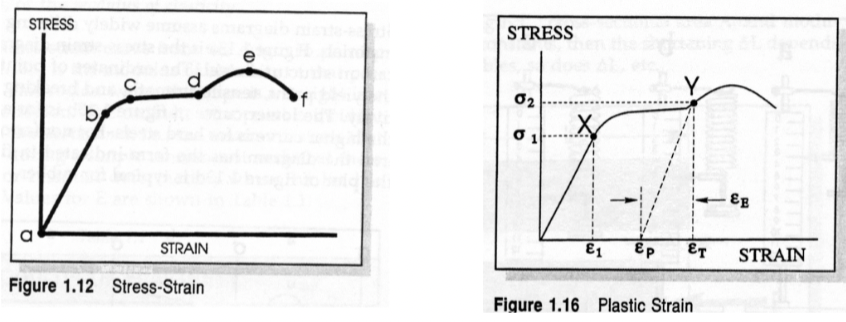
Toughness
area under the curve to the point of maximum stress (a-b-c-d-e), the ability to withstand shock loads before rupturing
Plastic or Permanent Strain (εp)
permanent strain when load removed
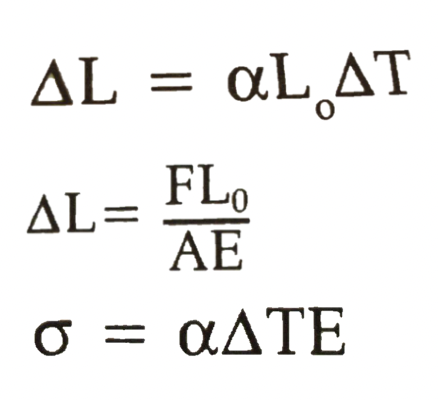
Thermal Stress
when a material is subjected to a change in temp, its dimensions will change. If the material is constrained by neighboring structures, stress is produced.
Plastics have a _________ coefficient of thermal expansion.
higher
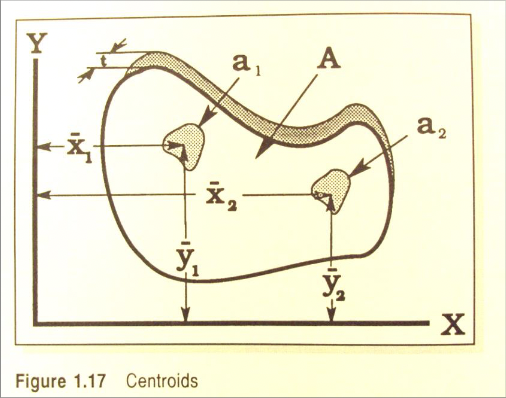
Centroid
The centroid of an area is defined as the point of application of the resultant of a uniformly force acting on the area.
The center of gravity and centroid of two identically shaped objects will be the same if the density is uniform in each object.
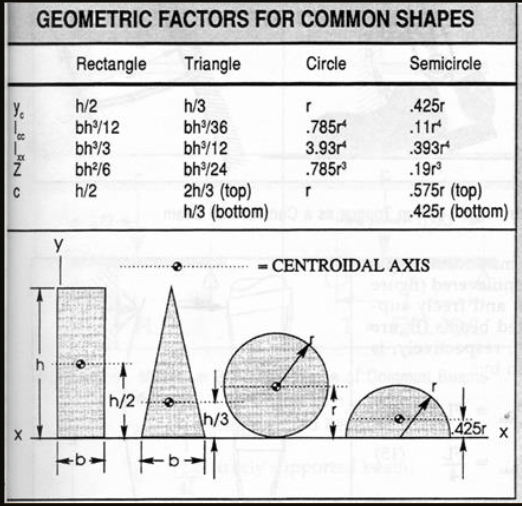
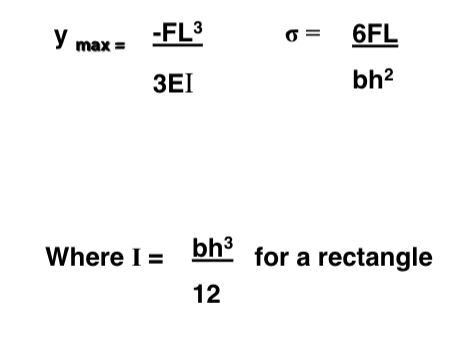
Second Moment of Inertia (second moment of area, area moment of inertia)
is a property of a shape that is used to predict its resistance to bending and deflection.
for a rectangle L = bh^3 /12
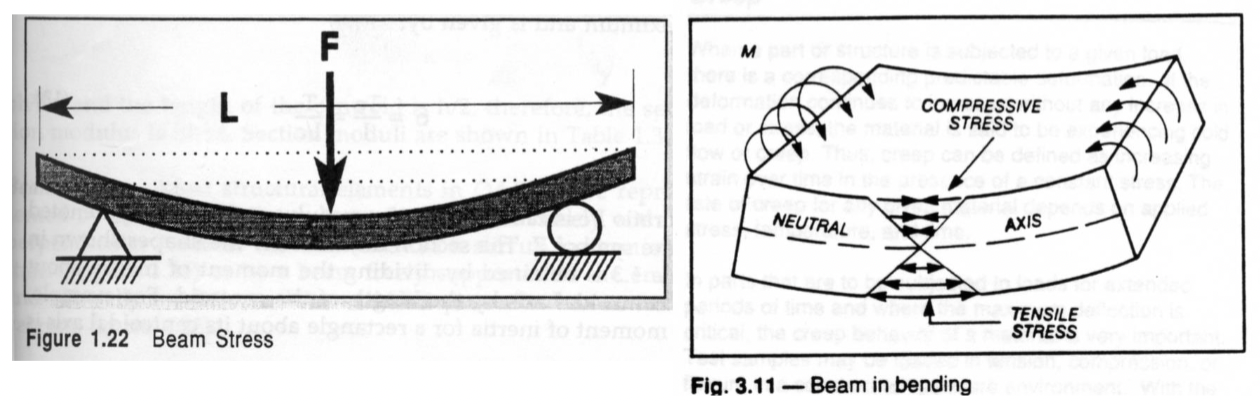
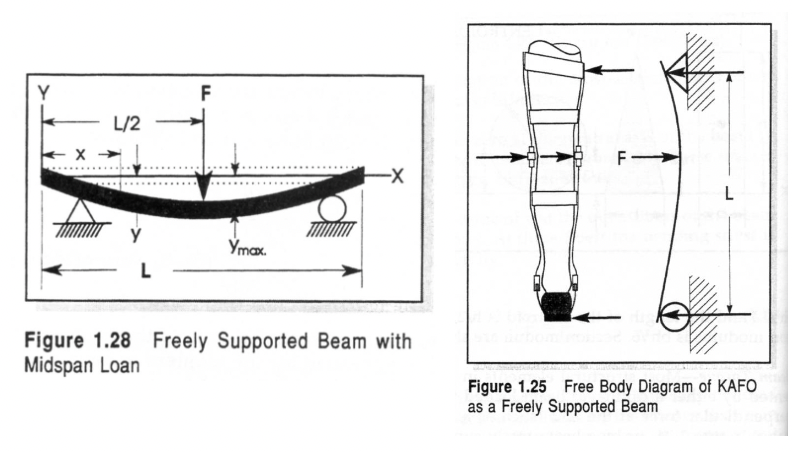
Stresses in Beams
there is a difference
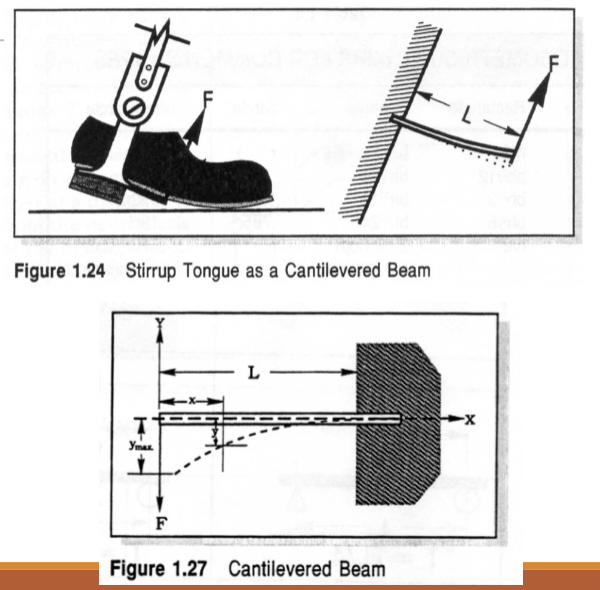
Cantilevered Beam
One end of the beam is fixed.
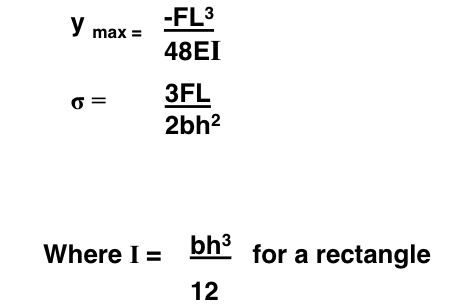
Freely Supported Beam
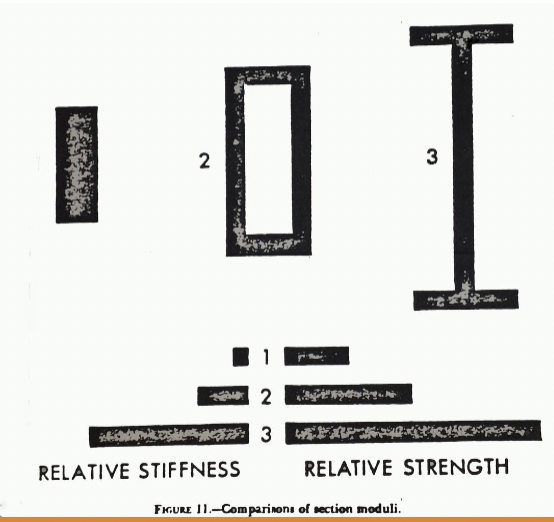
Comparisons of Section Moduli
these are the same materials and everything, the only difference is the configuration
Most materials exhibit a linear behavior at least initially on their stress-srain curve describe by ________ Law.
Hooke’s
When subject to flexural stress the amount a beam bends is influenced by its ______.
shape