MCAT: Foundation 5
1/1646
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
1647 Terms
Arrhenius acid
substances that dissociate in water to give H3O+ ions
3:2:2:2
butyl integration HNMR
1:2:3:3
isobutyl integration HNMR
1:1:1:1
tertbutyl integration HNMR
Arrhenius base
substances that dissociate in water to give OH- ions
greater degree than weaker acids
stronger acids dissociate at a
weaker acids
stronger acids dissociate more than
conjugate acid
when a base accepts a proton, it becomes an acid capable of returning that proton
conjugate base
when an acid donates a proton, it becomes a base capable of accepting that proton back
a weaker acid and a weaker base
the acid-base equilibrium favors
larger the pKa
the weaker the acid the
the larger the pKb
the weaker the base the
pKa electronegativity effect
the more electronegative element bears a negative charge more easily, giving a more stable conjugate base and a stronger acid
as size increases so does the acidity
pKa size effect
stabilize the conjugate base and increase acidity more than a single group
multiple electron withdrawing groups can
hybridization on acidity
as the hybridization decreases the acidity increases
resonance on pKa
more delocalized more acidic
lewis bases
electron pair donor (nucleophile)
nucleophile
donates electrons to a nucleus with an empty orbital, An electron-pair donor
lewis acids
electron pair acceptor (electrophile)
electrophile
accepts a pair of electrons
alkanes
single bonds between the carbons, all carbons are sp3, no functional groups
cycloalkanes
sp3 carbons form a ring
alkene
hydrocarbons that contain carbon-carbon double bonds and ends in (-ene) sp2
cycloalkene
double bond in a carbon ring
alkynes
hydrocarbons that contain carbon-carbon triple bond
aromatic hydrocarbons
derivatives of benzene (arenes)
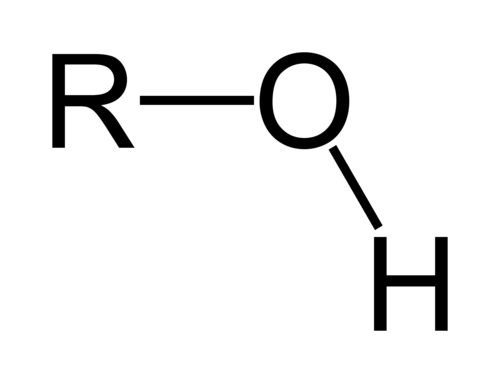
alcohols
contain the hydroxyl group (-OH) as the functional group
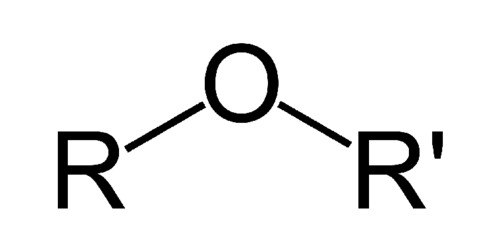
ethers
contains two alkyl groups bonded each to oxygen
aldehydes
a double bond with oxygen (carbonyl group) and a single bond with another element
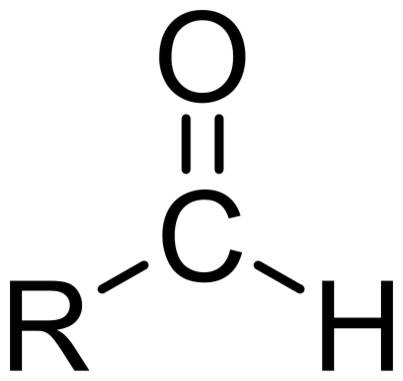
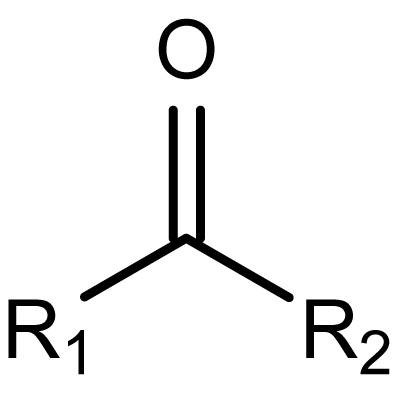
ketone
an organic compound with a carbonyl group attached to two carbon atoms
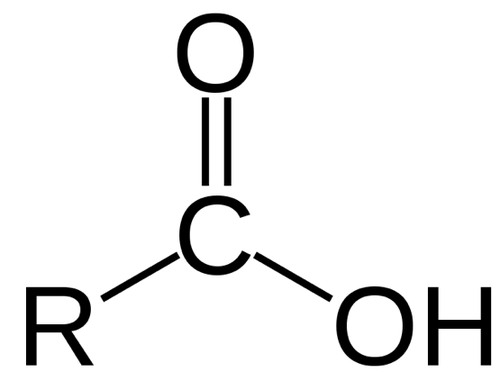
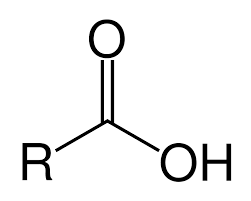
carboxylic acid
contain the carboxyl group, each derivative contains a carbonyl group and a bond with an electron-withdrawing group
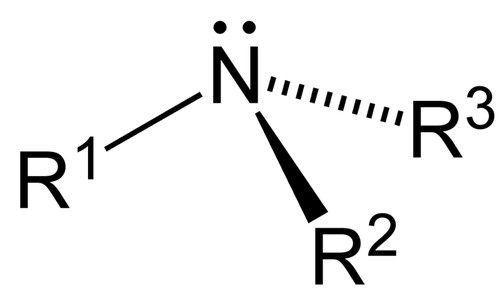
amine
alkylated derivatives of ammonia
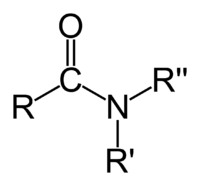
amides
carboxylic acid derivative with a nitrogen attached to the carbonyl group
nitriles
contain the cyano group

ester
C=O(O)R
alkyl halide
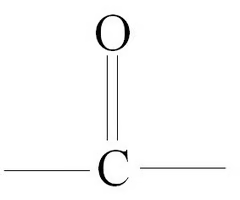
carbonyl
carboxyl
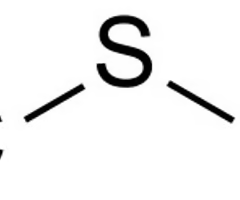
sulfide
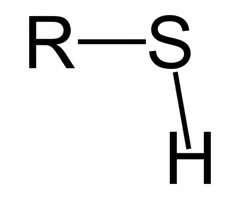
thiol
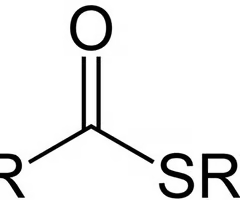
thioester
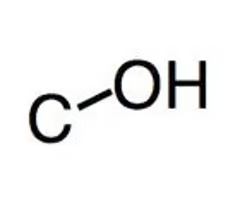
hydroxyl
isopropyl group
2 branches
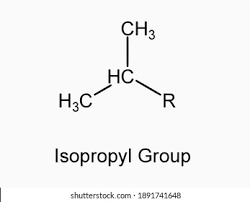
brønsted–lowry acid
proton donator
brønsted–lowry base
proton acceptor
as atomic mass increases
Frequency decreases…
as bond energy increases
Frequency increases…
sp3 carbon-carbon single bond stretch
1000-800 cm-1
sp2 carbon-carbon double bond stretch
1650-1600 cm -1
sp carbon-carbon triple bond stretch
3300 cm -1
Alcohol O-H stretch
(3300 cm-1) broad with a rounded tip
Acids O-H stretch
(2500-3300 cm -1) very broad
Primary amine (RNH2) stretch
(3300 cm-1) broad with two sharp spikes
Secondary amine (R2NH) stretch
(3300 cm -1) broad with one sharp spike
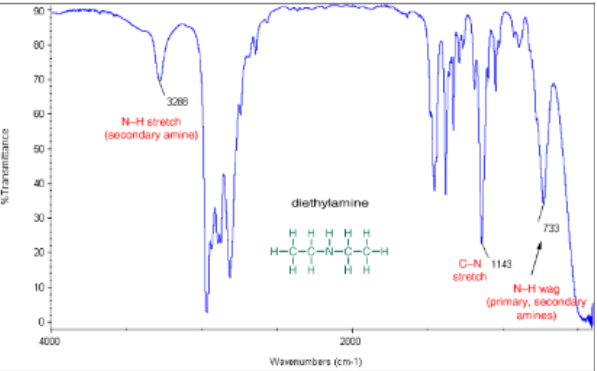
Tertiary amine (R3N) stretch
no signal because no H-bonds
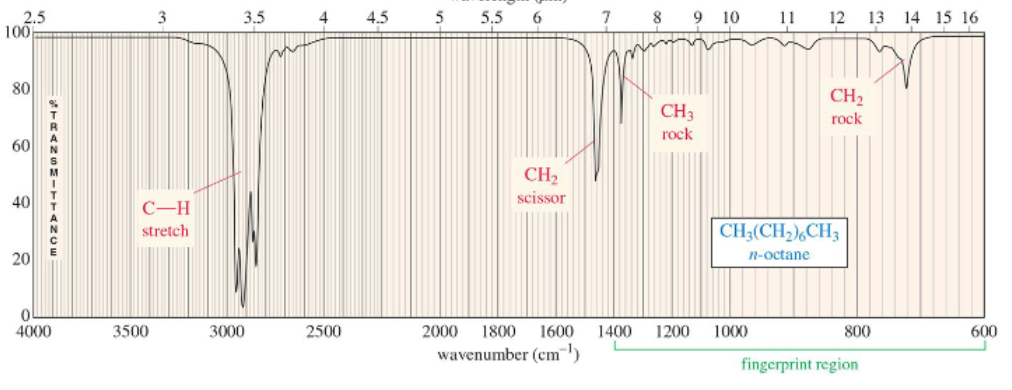
alkane IR
only C-H and C-C bending frequencies
C-H stretch
broad band between 2800 and 3000 cm–1, present in almost all organic compounds
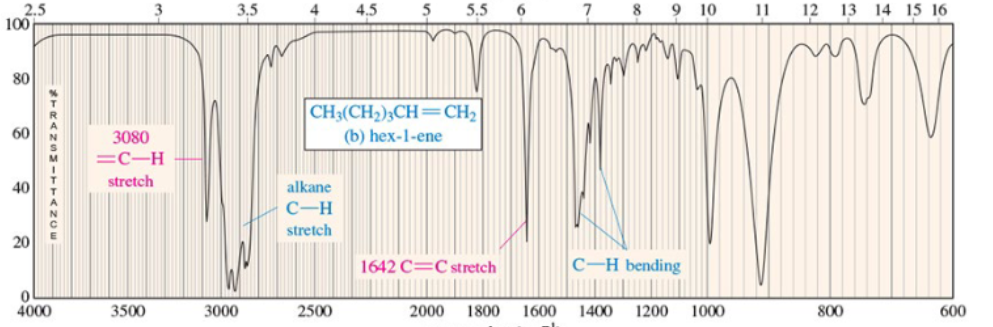
Isolated C=C frequency
1640-1680 cm -1
Conjugated C=C frequency
1620-1640 cm -1
aromatic C=C frequency
approx. 1600 cm-1
unsymmetrical
for a C=C signal the signal must be…
benzene common frequency
1619 cm -1
unsaturated =C-H
just above 3000 cm -1
unsaturated -C-H
just below 3000 cm -1
fingerprint region bonds
C-C, C-O, C-N (indetectable)
C=C stretch
1600-1690 cm -1
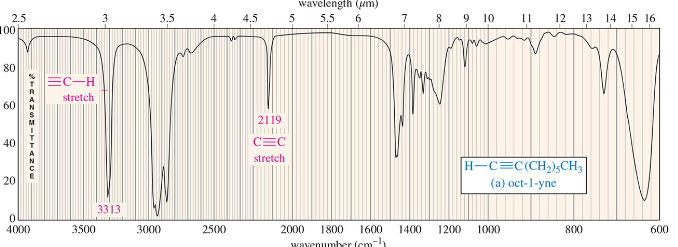
internal alkyne stretch
no detectable signal due to symmetry
external alkyne stretch
just below 2200 cm -1
carbon-nitrogen triple bond stretch (nitrile)
(2200 to 2300 cm–1) intense and sharp absorption
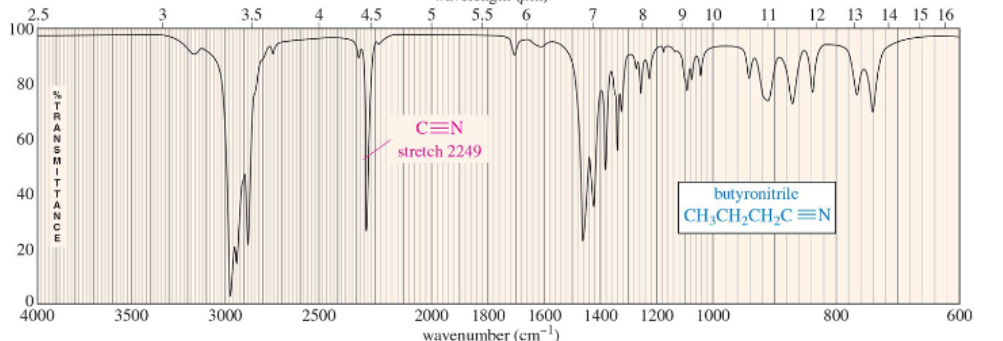
so nitriles produce stronger absorptions than alkynes.
Nitrile bonds are more polar than carbon–carbon triple bonds…
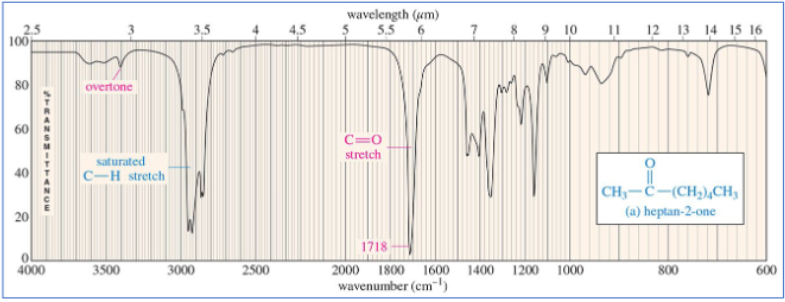
common C=O stretch
1710 cm –1, usually strongest signal in IR
ketone C=O stretch
around 1710 cm-1
ketone IR
C=O around 1710 cm-1 and saturated C-H just below 3000 cm-1
aldehyde IR
C═O stretch around 1720 cm –1 and two different stretch bands for the C-H bond at 2720 and 2820 cm –1
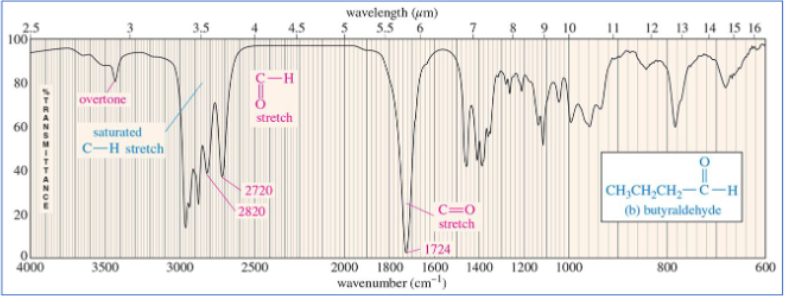
aldehyde C=O
1725 cm -1
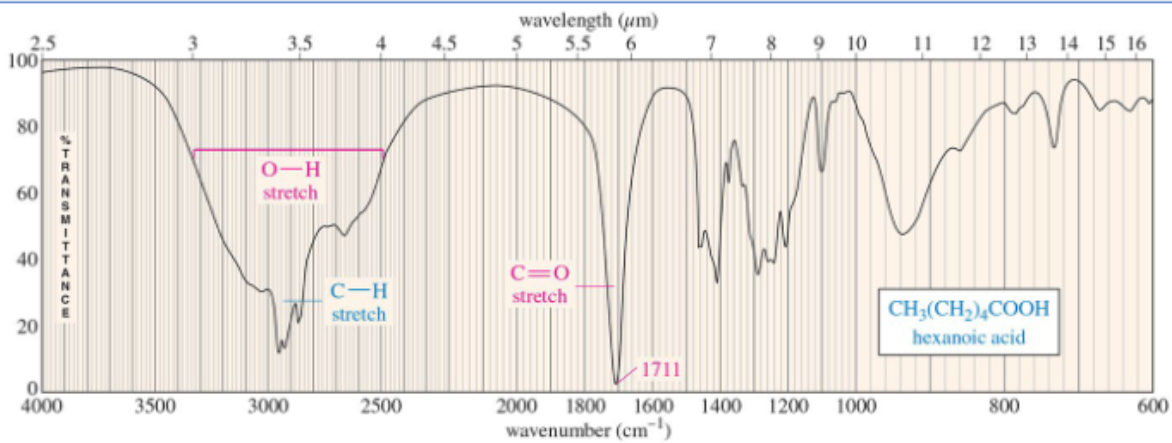
carboxylic acid C=O
1710 cm-1
carboxylic acid IR
O-H absorbs broadly (2500-3500 cm-1) due to strong hydrogen bonding and C=O around 1710 cm-1, need both peaks
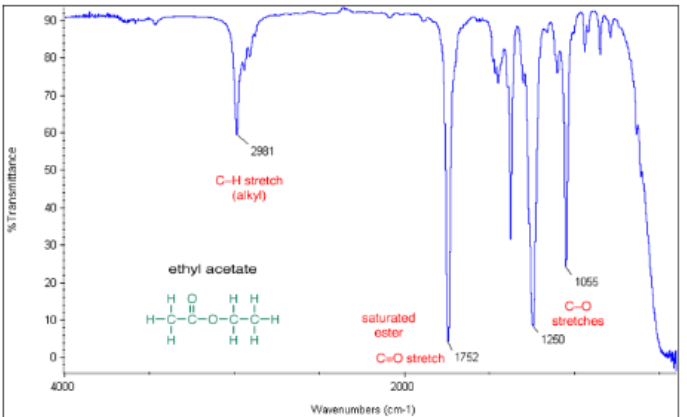
saturated aliphatic carboxylic ester C=O
from 1750-1735 cm -1
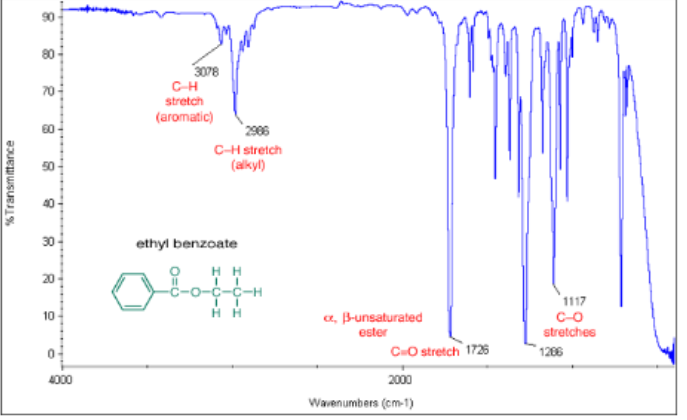
α, β-unsaturated carboxylic ester C=O
from 1730-1715 cm -1
α, β-unsaturated carboxylic ester IR
C=O from 1730-1715 cm -1 and numerous C-O peaks and two alkyl C-H peaks
saturated aliphatic carboxylic ester IR
C=O from 1750 to 1735 cm-1 and a few C-O peaks with one alkyl C-H peak
ether IR
The C—O stretch is in the fingerprint region around 1000–1200 cm –1, has C—O stretch but does not have a C═O or an OH stretch, then the compound
C-O stretch
1000 to 1300 cm-1
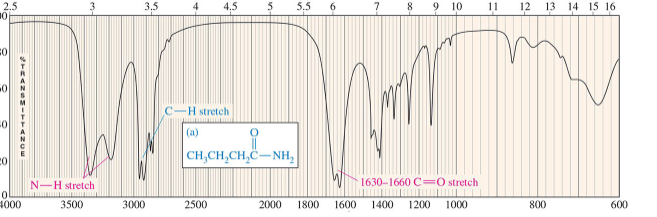
amide absorption
C═O at 1640 - 1680 cm –1, N-H absorptions around 3300 cm -1
MS fragmentation
The masses of the fragments and their relative abundance reveal information about the structure of the molecule, only positive signals are detected
radical ion
when a molecule loses one electron, it then has a positive charge and one unpaired electron
most common mass spectrometer
magnetic deflection
m/z
the exact radius of curvature of an ion's path depends on its mass-to-charge ratio (+1)
base peak
the tallest peak, 100% abundance most common fragmentation
M+ peak
molecular ion peak; corresponds to molecular weight
methyl m/z
15
ethyl m/z
29
propyl m/z
43
butyl m/z
57
pentyl m/z
71
benzene m/z
78
High Resolution MS
the exact mass of a compound can be found
isotopes are present in their usual abundance
MS with isotopes
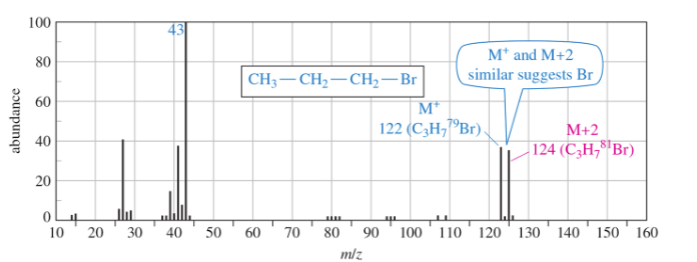
Br MS
79 Br (50.5%) and 81 Br (49.5%) M+ peak and an M+2 peak of equal height