Genetic Disorders of the Genitourinary System
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
What is the pathogenesis of Alport Syndrome?
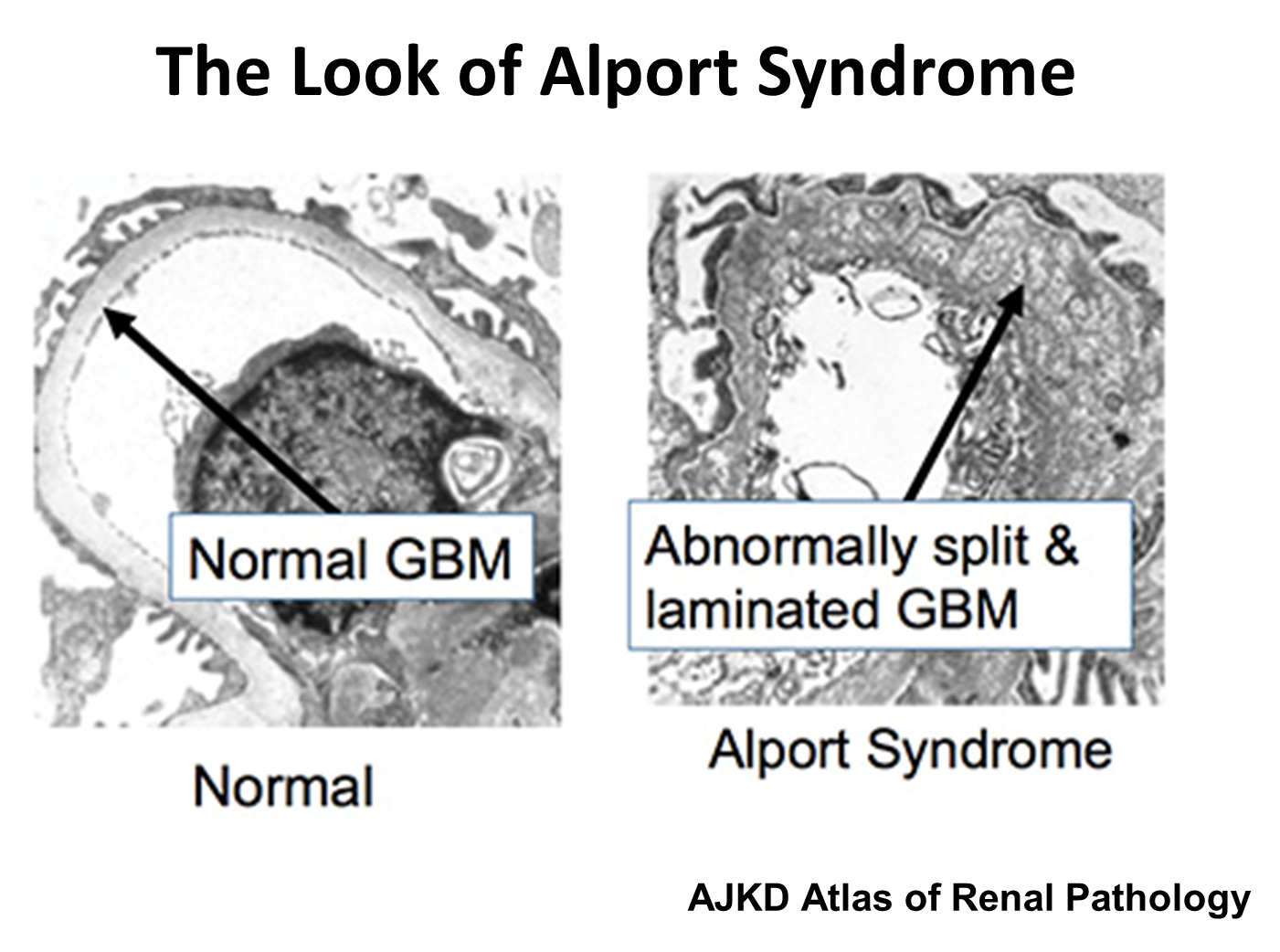
Alport Syndrome is an inherited condition caused by X-linked mutation in COL4A5 causing issues with subunit five on Type IV collagen found in the basement membranes kidneys, skin, eyes and inner ear
1) Podocytes typically bind to the 345 heterotrimer on the glomerular basement membrane
→ in Alport Syndrome, the subunit five is abnormal leading to the breakdown of the collagen chain
→ this creates episodes of repair and degradation
2) Causes a glomerular basement membrane that is described as basket weaving
→ abnormally split and laminated
What are the clinical manifestations of Alport Syndrome?
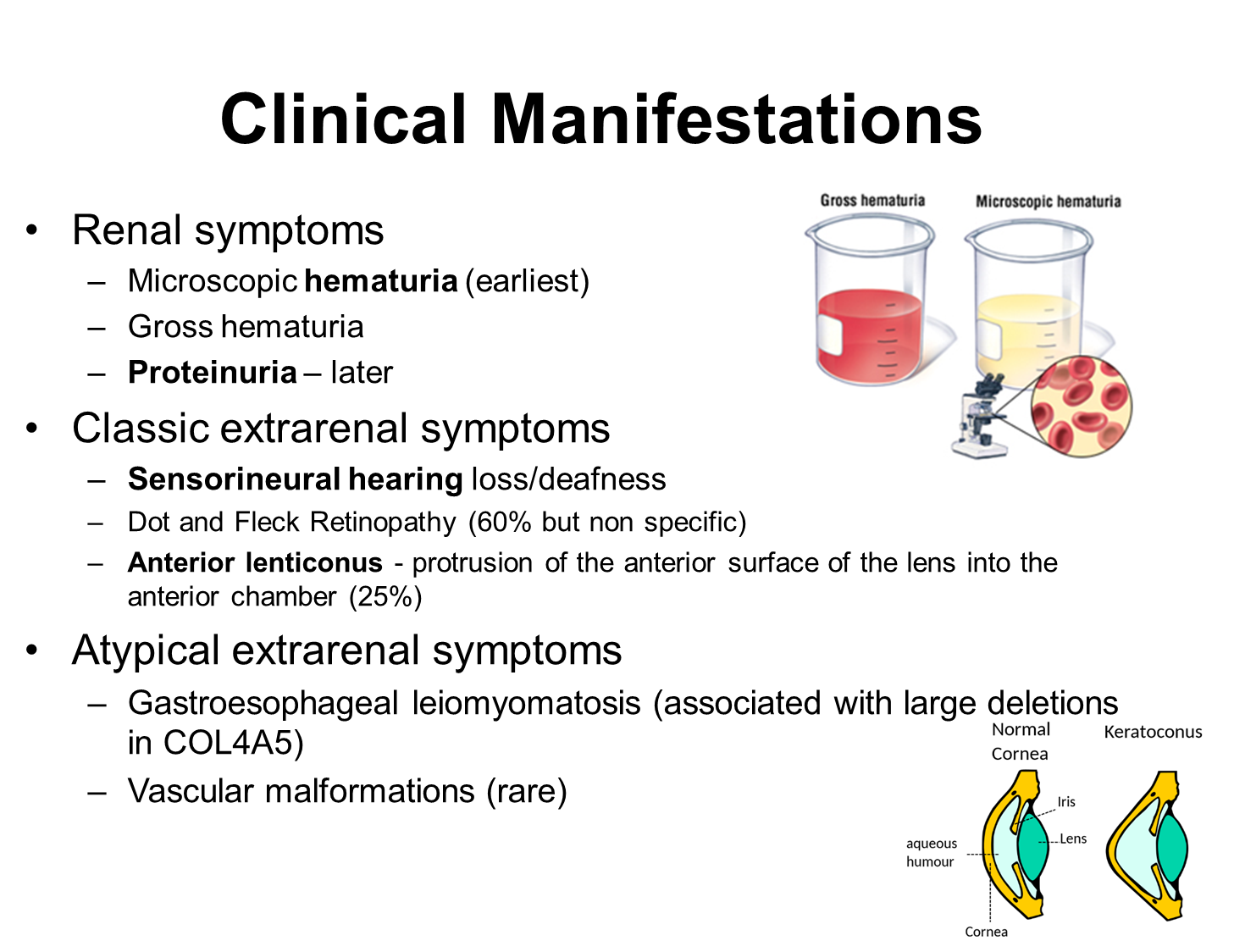
Alport Syndrome has renal and extrarenal manifestations
1) Renal Symptoms
→ microscopic hematuria is the earliest manifestation
→ proteinuria often occurs later on
2) Classic Extra-renal symptoms
→ sensorineural hearing loss or deafness
→ anterior lenticonus or protrusion of the anterior surface of the lens of the eye
What is the main management for Alport Syndrome
Alport Syndrome is mainly treated via the usage of ACE inhibitors even in patients with normal GFR and blood pressure
What is HNF1b Renal Disease
Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 1b (HNF1b) Renal Disease is caused by a mutation in MODY5 causing mutated hepatocyte nuclear factor 1b or transcription factor 2
HNF1b is used in epithelial cell differentiation and results in both renal and extra-renal manifestations
1) Renal
→ prenatal polycystic kidney disease
→ chronic tubular interstitial nephritis
→ hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia
2) Extra Renal
→ Diabetes at less than 10 years of age
→ can also develop diabetes following after transplantation
What is Nail Patella Syndrome?
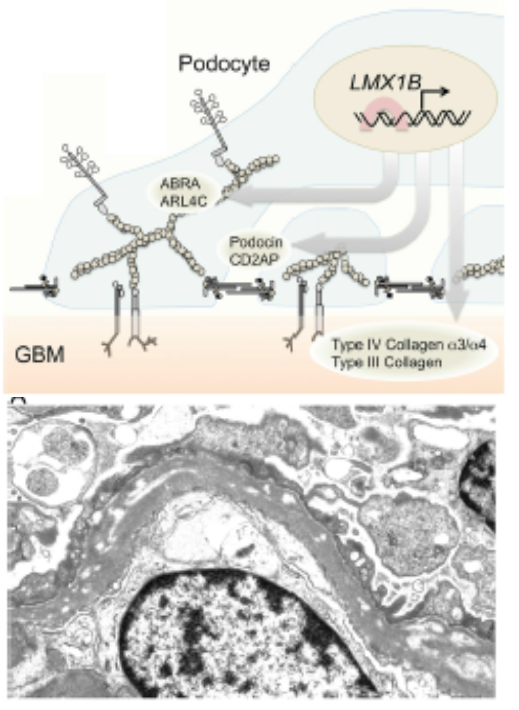
Nail Patella Syndrome is a disease caused by a mutation in LMX1B which is a DNA-binding transcription factor involved in inducing podocyte binding to the glomerular basement membrane
1) Patients often have a wide variety of extra-renal manifestations such as hypoplastic or absent kneecaps and nails
→ can also have elbow abnormalities as well as iliac horns at their hips
2) Kidney manifestations are less common, but include proteinuria and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
What is Multicystic Dysplastic Kidney?
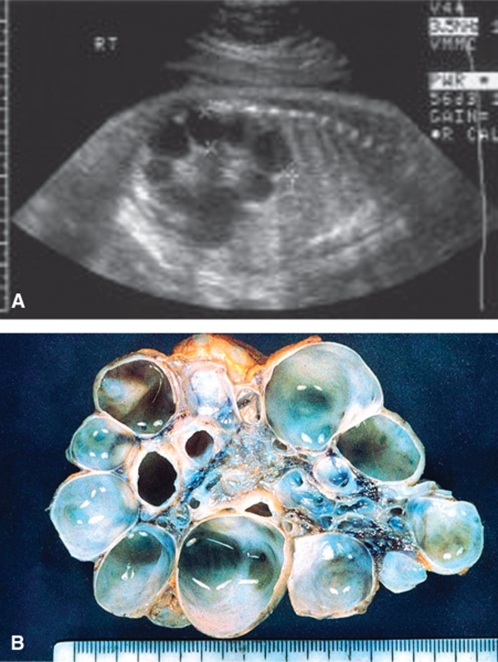
The most common flank mass in neonates where the kidneys fail to develop and instead form fluid filled pockets
1) Kidneys will lack function or blood flow, and upon ultrasound, large fluid filled pockets are able to be imaged
→ disease is associated with genetic mutations in genes involved in cellular migration
What are the three classes of congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract?
CAKUT or Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract are divided into three classes. An extremely common birth defect
1) Parenchymal Malformation
→ issues with the functional tissue, or the parenchymal tissue of the kidney
2) Embryonic Migration
→ issues with the migration of the ureteric bud to its proper position
3) Defects of Plumbing
→ some kind of obstruction or other issue, with the most common being posterior urethral valve
What is Posterior Urethral Valve?
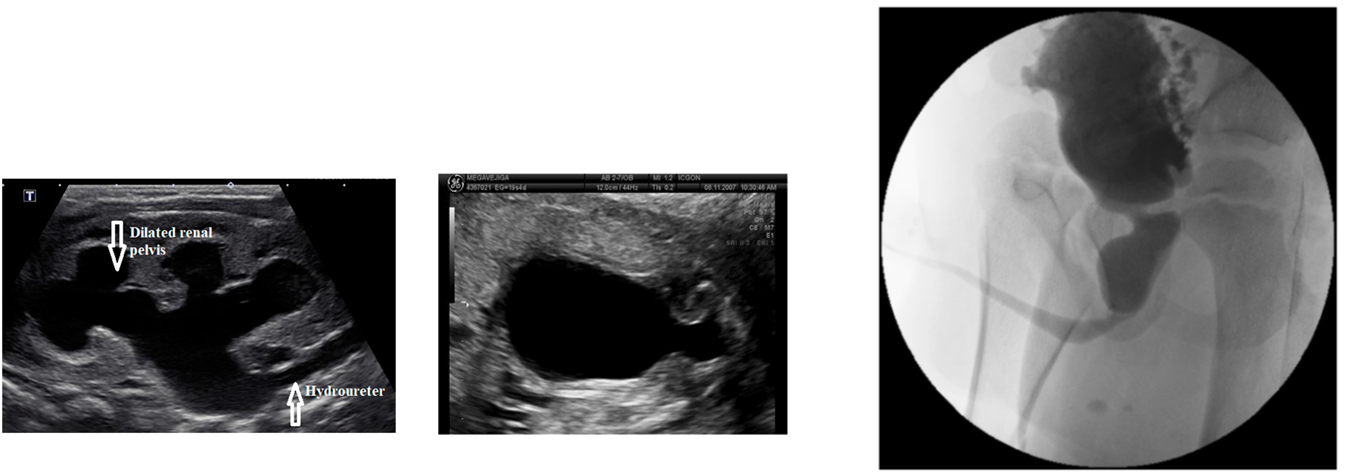
Posterior Urethral Valve is the most common urinary tract obstruction and is a obstructive CAKUT or congenital abnormality of the urinary tract
1) Extra piece of tissue in the urethra at the level of the prostate develops, causing obstruction
→ because of this, it only occurs in men
2) On ultrasound there will be large and distended bladder and proximal urethra
What is Duplex Kidney and Horseshoe Kidney
Both of these are cell-migration CAKUT
1) Duplex Kidney
→ 2 ureteric buds on the same side, resulting in a single kidney having two ureters
→ can cause obstruction due to the ureters curling around each other and reflux at the bladder
2) Horseshoe Kidney
→ fusion of kidneys at the midline as the kidneys migrate upward
→ typically caught at the inferior mesenteric artery