Parasitology 11 Schistomiasis
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Flukes
attach to host with ventral and oral sucker
absorb nutrients through tegument
blind gut
professional excreters
varied reproductive strateg
What are the blood flukes?
Schistosoma hematobium/mansoni/japonicum
Vector for Schisostoma hematobium/mansoni/japonicum
Snails
The main definitive host for Schistosoma spp. (except what species?) is humans.
S. japonicum
What is the intestinal fluke?
Fasciolopsis buski
What is the liver fluke?
Clonorchis sinensis
What is the lung fluke?
Paragonimus westermani
Blood fluke (Schistosoma) life cycle
eggs hatch and release miracidia
miracidia penetrate snails
form sporocysts in snails
snails release cercariae
cercariae penetrate skin of human, losing tail
cercariae become schistosomulae
circulate and migrate to blood in liver to mature into adults
paired adult worms lay eggs, exiting in feces or pee
What blood flukes exit in urine?
Schistosoma haematobium
What blood flukes exit in feces?
Schistosoma mansoni and Schistosoma japonicum
1 miracidium releases how many cercarie?
4000
T/F: Snails release cercaria when sun comes up
True
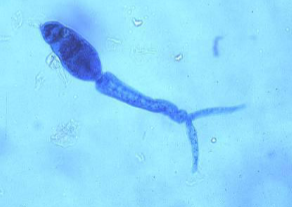
What is this?
Schistosoma cercaria
T/F: Miracidium is only seen in water.
True
What is this?
Schistosoma miracidium
How are male and female Schistosoma worms different in their tegumental surfaces?
Male: Tubercules
Female: Papillae
How does Schistosoma avoid the immune system?
attaching host serum proteins to their tegument
Treatment against Schistosoma?
Praziquantel to disrupt tegument
Where do adult worms of Schistosoma mansoni live in?
inferior mesenteric veins of large intestine
Where do adult worms of Schistosoma japonicum live in?
superior mesentric veins of small intestine
Transporting to what organ leads to egg death and human disease for Schistosoma?
liver
Schistosoma eggs in liver lead to what
pipe stem fibrosis
chronic exposure promots Th2 cell mediated immune response
granulomatous response
periportal liver fibrosis and cirrhosis
hepta-splenic schistosomiasis
Katayama fever
what is it?
caused by what?
symptoms?
immunoallergic reaction against schistosoma egg antigens
S. japonicum and S. mansoni
shaking chills, hives, shock
What does Schistosoma hematobium target?
urinary bladder
S. hematobium pathology
bladder fibrosis
obstructive uropathy
increased risk of bladder cancer
Schistosoma diagnosis
eggs in stool or urine
mucosal scrape or biopsy if negative
antigens and NAATs are being developed
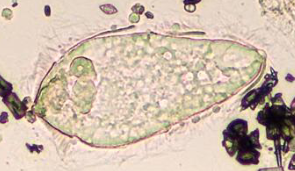
Which species
Schistosoma mansoni
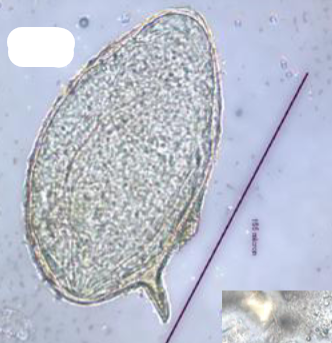
Which species
Shistosoma japonicum
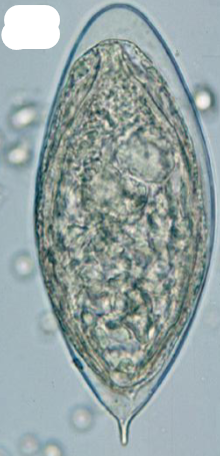
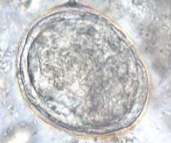
Which species
Shistosoma hematobium
Treating Katayama Fever
short course of corticosteroids
praziquantel INEFFECTIVE against EGGS/LARVAE
Treating post-acute to chronic illness
target adults with praziquantel
manage impacts of granulomas
Swimmer’s itch
caused by Austrobilharzia variglandis
grow in ducks, then infect humans swimming