histology of the kidney
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
what is the filtrate flow from the kidney to the urethra
kidney → ureter → urinary bladder → urethra
what 5 structures are included in the cortex of the kidney
renal corpuscles
proximal tubules
loop of Henle
distal tubules
collecting ducts
what 4 structures are included in the medulla of the kidney
renal pyramids
collecting ducts
thick and thin limbs of loop of Henle
medullary rays
medulla structures all represent invasion of…
ureteric bud tissue in the metanephric kidney tissue
the loop of Henle can also be referred to as…
loop of the nephron
when filtrate enters the collecting tubule, it is now called…
urine
what are the two parts of the collecting tubule
connecting tubule
collecting duct
what and where is the connecting tubule
an initial arching which drains a single nephron; will lead to the collecting duct
what is a collecting duct
drains many nephrons and will extend uninterrupted through both the cortex and the medulla carrying the urine down the renal papilla to the minor calyx
what are the two types of nephrons
cortical nephron
juxtamedullary nephron
main funx of the cortical nephron
reabsorption of water and small molecules
main funx of the juxtamedullary nephron
concentrates urine
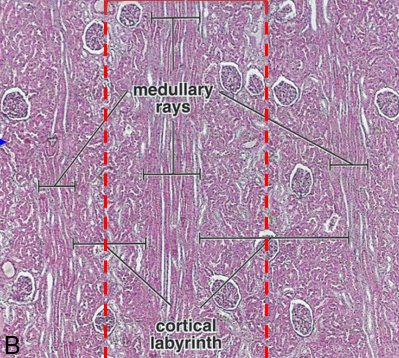
what are medullary rays
appear as streaks in the cortex running toward the medulla; each ray consists of one collecting duct plus the parallel loops of the many nephrons that empty into that duct
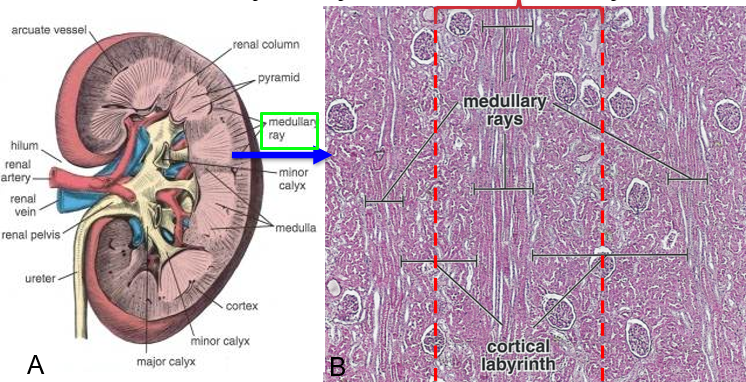
what is a cortical labyrinth
substance between medullary rays; has renal corpuscles and the associated convoluted tubules of the nephrons that empty into the collecting duct of a ray
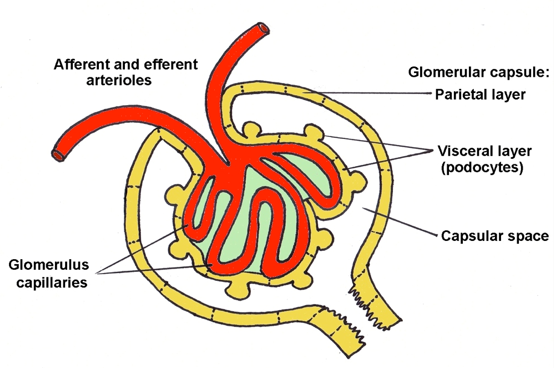
______________ + _____________ = the renal corpuscle
glomerulus (capillary tuft) + glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule enclosing it
at what pole do arteriole enter and leave at the renal corpuscle
vascular pole
what pole is the proximal convoluted tubule start in the renal corpuscle
urinary/tubular pole
what are the three major layers of Bowman’s capsule
outer parietal layer
inner visceral layer
intervening capsular space
histologically, what is the outer parietal made out of
simple squamous epithelium
histologically, what is the inner visceral layer of Bowman’s capsule made out of
octopus-shaped cells called podocytes (on the glomerulus capillaries)
in order, how is blood filtered from the glomerular capillaries to Bowman’s space
through fenestrae in the endothelial cells
through the basement membrane
through filtration slits between pedicels of the podocytes
what is the capillary tuft of the glomerulus supported by
mesangial cells and ECM = mesangium (green)
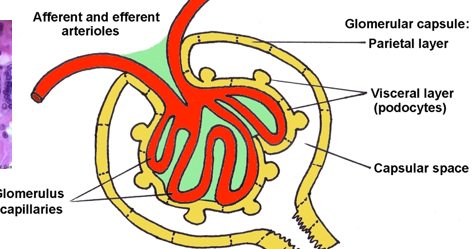
what is the mesangium
an extra-cellular matrix of collagen IV, proteoglycans, and glycoproteins that support the capillary loops
where are podocytes found
they surround glomerulus capillaries- they form the simple epithelium of the inner visceral layer
what are podocytes
have primary processes and secondary processes that aid in filtration
what are the primary processes of podocytes known as
arms
what are the secondary processes of podocytes known as, what is their funx
pedicels- interdigitate to give support for capillaries and form filtration slits
filtrations depends on what three things…
high blood pressure (45 mm hG)
fenestrated capillaries
membrane channels- aquaporins
peritubular capillaries receive _________ molecules and give up ______________ molecules
reabsorbed; secreted
describe histologically what the proximal convoluted tubules look like
cuboidal cells that are large and stained pink, are wider than the DCT and have fewer nucelli
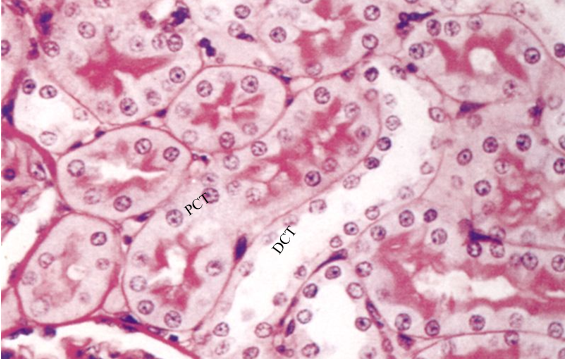
how does the PCT cells inc the apical surface area
have densely packed microvilli that form an apical brush border and almost obliterate the tubule lumen → gives them a fuzz-filled appearance in histological sections
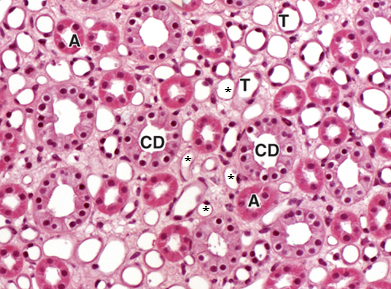
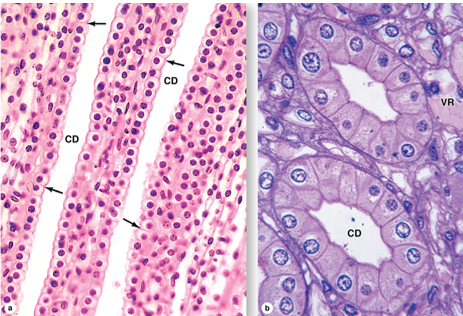
CD
collecting ducts
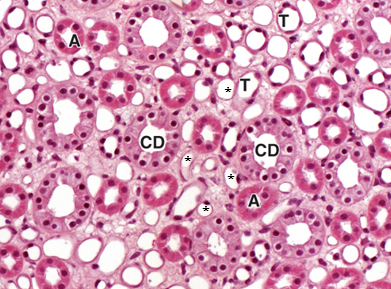
A
thick-walled ascending limb
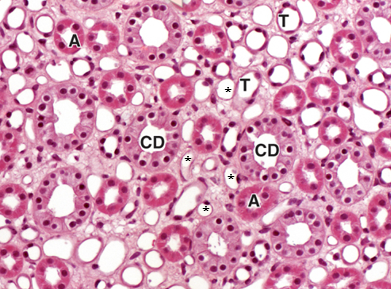
T
thin-walled descending limb
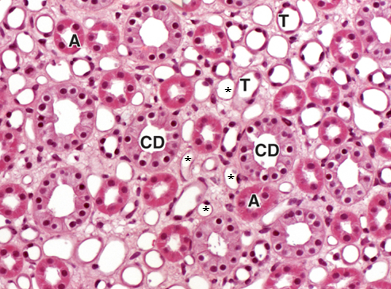
*
vasa recta capillaries
describe what the distal convoluted tubules look like histologically
have fewer and shorter microvilli, lack brush border, fewer mitochondria- less acidophilic than PCT → lighter pink, higher number of nuclear profiles
brush border or no- is it PCT or DCT
no brush border- DCT
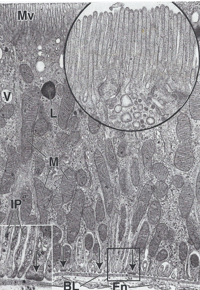
brush border or no- is it PCT or DCT
brush border- PCT
what are the collecting ducts lined by
simple cuboidal epithelium changing to columnar in larger ducts; epithelial cells have round apical surfaces and distinct intercellular boundaries that can be seen w a light microscope
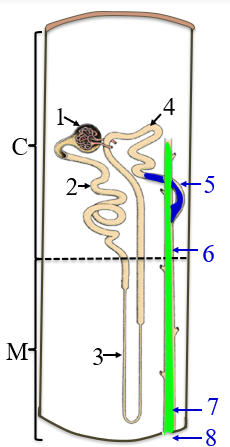
1
renal corpuscle
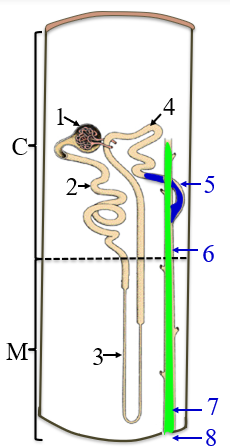
2
PCT
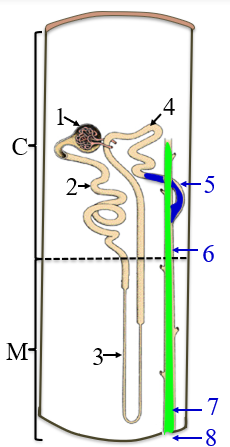
3
the loop of henle/nephron
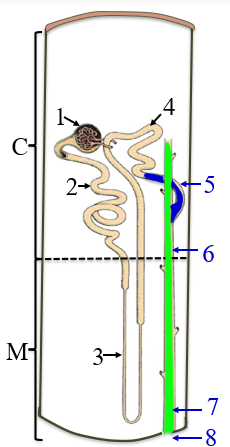
4
DCT
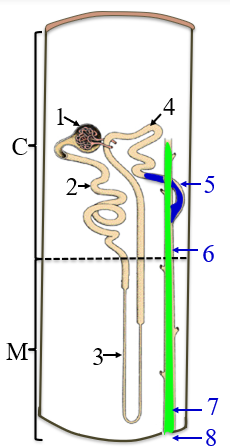
5
collecting tubule
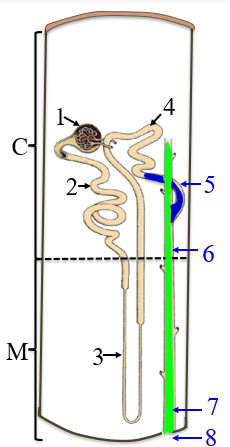
6
collecting duct
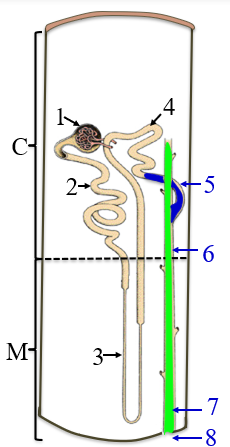
7
papillary duct
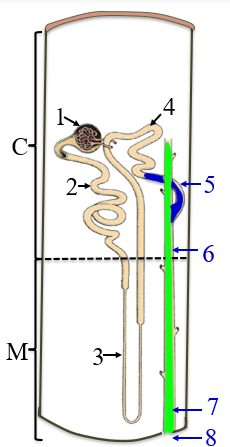
8
minor calyx
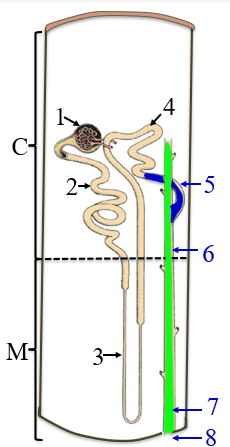
C
the cortex
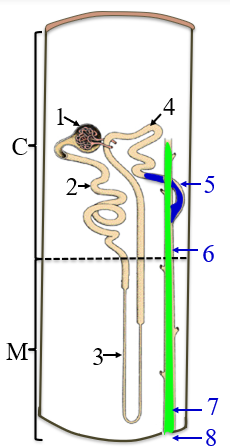
M
medulla
what are the two types of epithelial cells in the collecting ducts
dark cell- intercalated
light cell- principal
funx of dark/intercalated cell in the collecting duct
secreted H into lumen and reabsorbs HCO3
funx of light/principal cells in the collecting duct
reabsorbs Na and secreted K
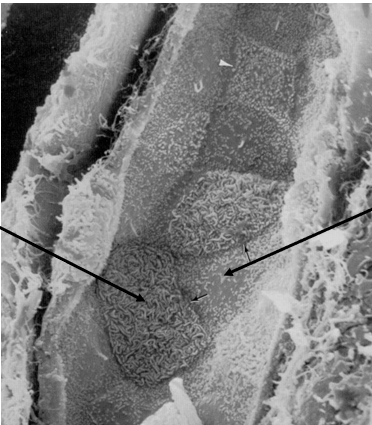
left arrow
dark/intercalated cell of the collecting duct
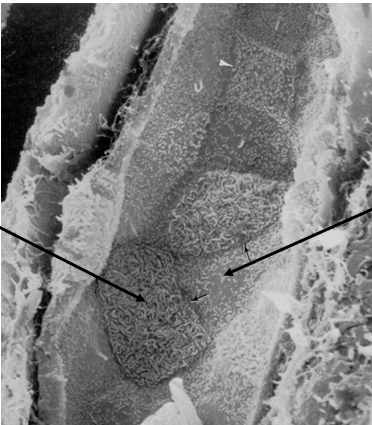
right arrow
light cell- principal cell
where is the juxtaglomerular apparatus located
against the afferet arteriole near the vascular pole of each glomerulus
what cells make up the JGA
macula densa
juxtaglomerular cells
extraglomerular mesangial cells
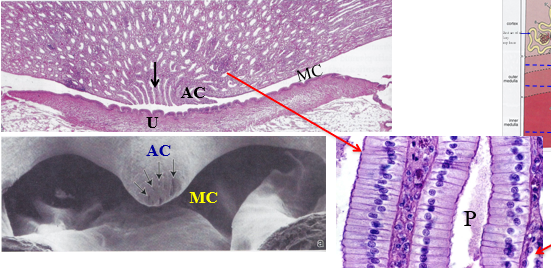
what “zone” is this
inner zone of the renal medulla
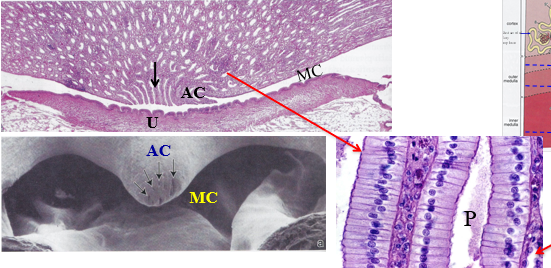
P
papillary ducts
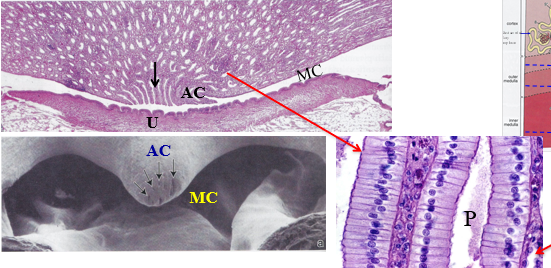
MC
minor calyx
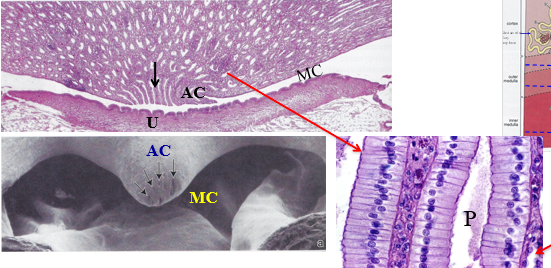
AC
area cribrosa of the renal papilla
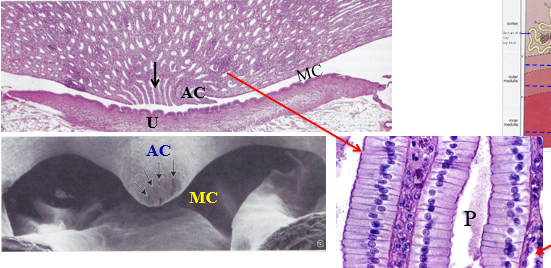
U
urothelium that lines the minor calyx
from the renal calyces through the urinary bladder, is the structure similar or different
similar
describe histologically how the structure from the renal calyces through the urinary bladder look
mucosal layer w transitional epithelium (urothelium) and lamina propria
transitional epithelium stretches
muscularis mucosae and submucosal layers are absent
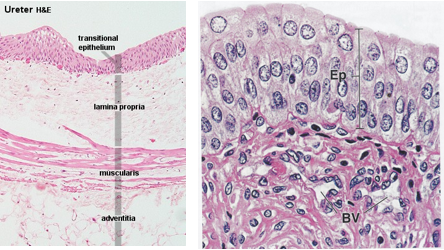
the urothelium has abundant ___________ and folds to allow for distension
elastin
describe the structure of the ureter
hollow tubes of smooth muscle
urothelium can be from 3-5 layers
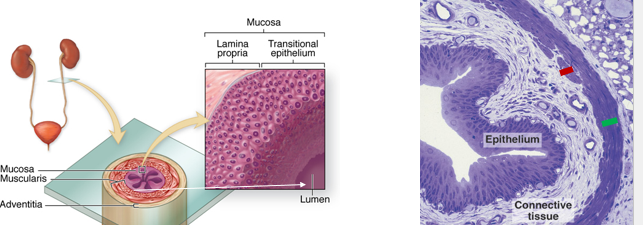
what are the layers of the urinary bladder wall
mucosa of urothelium and lamina propria
submucosa
muscularis
adventitia
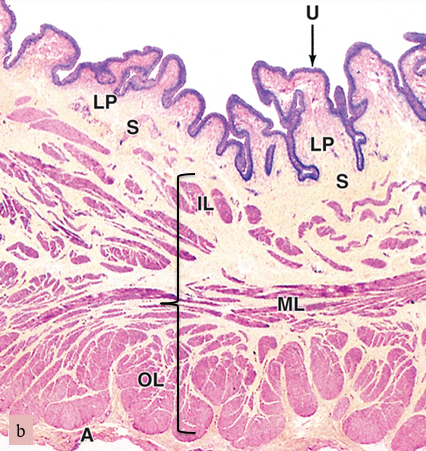
what are we looking at here
bladder
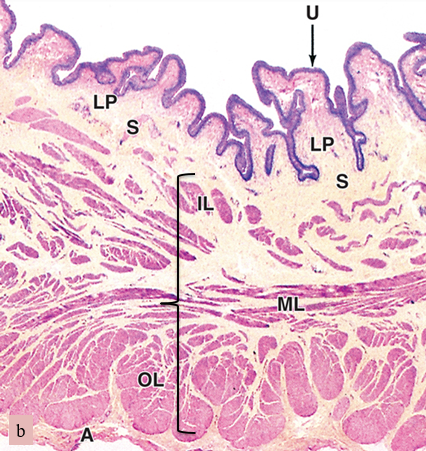
U
urothelium
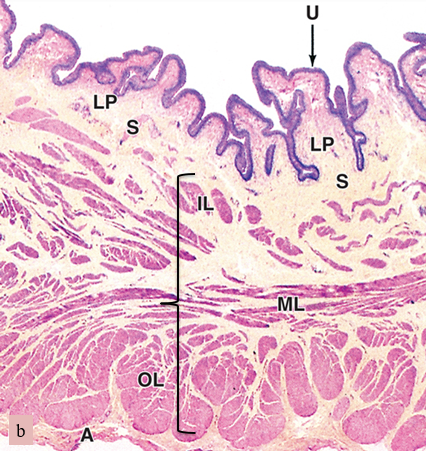
LP
lamina propria
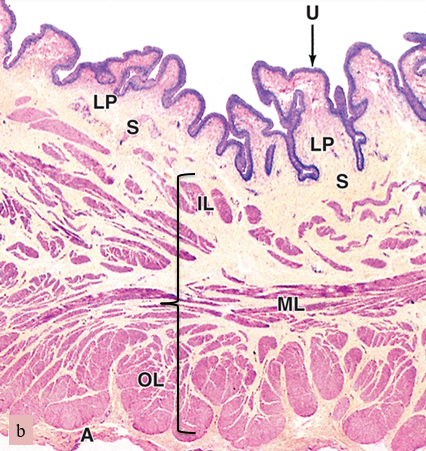
S
submucosa
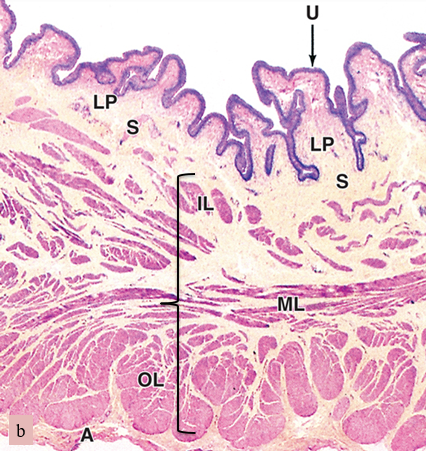
bracket
muscularis (smooth muscle)
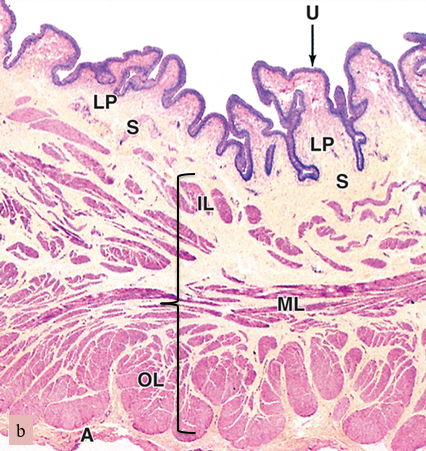
A
adventitia
the urothelium resists stretch and is impermeable to water, solutes and toxic agents, why is this important
prevents interstitial water in the bladder wall from diffusing into the hypertonic urine, and prevents urea and other toxins in urine from poisoning the bladder wall
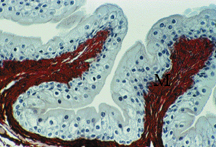
stretched or unstretched bladder
unstretched- is relaxed
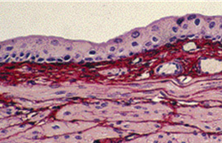
stretched or unstretched bladder
stretched- distended state
what is the urethra of a male lined by
pseudostratified columnar to stratified epithelium, becoming stratified squamous epithelium in the glans near the tip of the pp
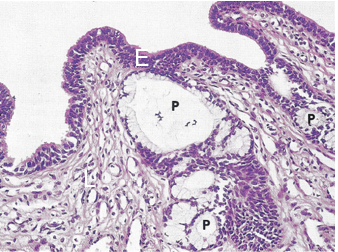
what is the urethra of a female lined by
transitional and pseudostratified epithelium, then stratified squamous toward the opening to the exterior- vulva