Dan Duhon Midterm - Biology 1 Honors
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
What is the term for the engulfing of large particles or cells from the surrounding by the cell membrane?
phagocytosis
Which type of endocytosis involves the cell engulfing fluid droplets from its surroundings?
Pinocytosis
The second law of thermodynamics states that the universe tends toward
disorder
Which of the following is NOT a function of the membrane proteins?
Transport, Hydrophobic Interactions, Cell to cell adhesion, attachment to the cytoskeleton
Hydrophobic interactions
Singer and Nicolson gave us the ___________.
Fluid Mosaic Model
In the absence of oxygen, what process follows glycolysis?
Fermentation
Which of the following molecules can move through the cell membrane by facilitated diffusion with the help of specific protein channels?
Large proteins, glucose, water, oxygen
Large proteins
Which of the following membrane transport process requires the binding of a specific molecule to a receptor on the cell membrane?
Facilitated diffusion, osmosis, receptor mediated diffusion, signal transduction
Receptor Mediated Diffusion
What is the role of aquaporins in the cell membrane?
Facilitating the transport of water
Which type of membrane transport is responsible for the movement of sodium and potassium ions to create an unequal distribution of ions?
osmosis
What happens to a cell placed in a hypertonic solution?
It gains water and swells
In which direction does active transport move ions across the cell membrane in the sodium-potassium pump and how many?
two potassium ions into the cell, and pumps three sodium ions out of the cell
What is the term for the engulfing of small liquid droplets from the surrounds by the cell membrane?
Pinocytosis
Which of the following membrane transport process is responsible for the secretion of hormones from cells?
facilitated diffusion, exocytosis, osmosis, active transport
exocytosis
Which type of molecule forms the hydrophobic tail of the phospholipid bilayer in the cell membrane?
lipids
What is the role of transport proteins in the cell membrane?
facilitate the movement of specific ions or molecules across the membrane
Which of the following processes involves the movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane?
facilitated diffusion, active transport, osmosis, pinocytosis
osmosis
What is the main function of cholesterol in the cell membrane?
enhance membrane fluidity
Which of the following is a function of the carbohydrate chains on a cell membrane?
structural support, storing energy, identifying cell type and facilitating cell-cell recognition, assisting active transport
Identifying cell type and facilitation cell-cell recognition
what is the term for the process by which a cell engulfs liquid droplets from the surroundings?
pinocytosis
Which of the following is an example of a hypertonic solution?
a solution with a LOWER solute concentration that the cell, a solution with a HIGHER solute concentration than the cell, a solution with the SAME solute concentration as the cell, a solution with a VARIABLE solute concentration
a solution with a HIGHER solute concentration than the cell.
Which type of membrane transport involves the release of large molecules from the cell using vesicles?
exocytosis
Which of the following is an example of a function served by proteins in the cell membrane?
storing genetic information, catalyzing chemical reactions, storing energy, providing mechanical support
catalyzing chemical reactions
What is the primary function of the sodium-potassium pump in the cell membrane?
transporting sodium ions into the cell and potassium ions out of the cell
Which of the following best describes the role of the cell membrane in maintaining homeostasis?
prevents the entry of all substances into the cell, regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell to maintain homeostasis, constantly release of all cellular contents, it has no role on homeostasis
regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell to maintain homeostasis
Which molecule can freely pass through the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane by simple diffusion?
oxygen
What is the term for the tendency of molecules to spread out evenly in a space to reach equilibrium?
simple diffusion
Atoms tend to __________ a valence shell
fill
Which of the following is NOT a property of water?
cohesion, surface tension, meniscus, adhesion
meniscus
Which of the following is a weak bond?
elicit, hydrogen, covalent, ionic
hydrogen
The outer electron shell or orbit of an atom is called the _________ shell.
Valence
What is the buffer system in your blood?
Carbonic acid
The _________ of an object is the amount of energy needed to raise one gram of water one degree Celcius.
Specific heat
The strand of the DNA molecule are held together by _______ bonds
hydrogen
Bases have a LOWER or HIGHER pH than acids?
Higher
Which of the following is NOT non-polar?
fats, oils, salt, waxes
salt
What is less dense at _______ degrees C
0
____________ means "water loving".
hydrophilic
Where is the majority of negative charge on a water molecule?
Oxygen
True or False: All life on Earth occurs in water.
True
Water is reffered to as the ________
Universal Solvent
Which of the atoms in a water molecule have a positive charge?
Hydrogen
______ means "water fearing".
Hydrphobic
A solution of koolaid has a pH of 5.4. a student adds an alka-seltzer to the solution and stirs in. After the addition of the alka-seltzer, the pH is measured to be 8.4. What was released by the alka-seltzer to cause this change?
a base
The number of protons in an element determines its
atomic number
Water is a ________ molecule.
Polar
True or False: Compared with other substances, water requires more heat to increase its temperature.
True
pOH measures ________
The concentration of hydroxide ions in solution.
What is the basic structural unit of the cell membrane?
Phospholipids
Which of the following is found in the middle of the cell membrane?
ATP, Starch, fatty acids, hemoglobin
fatty acids
What type of membrane proteins span the entire lipid bilayer and are involved in the transport of substances across the membrane?
integral proteins
Which of the following types of membrane transport does not require energy expenditure and relies on the concentration gradient?
facilitated diffusion
Which of the following is a type of passive transport?
Sodium-potassium pump, osmosis, ATP synthase, exocytosis
osmosis
Which direction does water move during osmosis?
from a hypotonic solution to a hypertonic solution
Which type of transport moves molecules against their concentration gradient and requires energy in the form of ATP.
active transport
What is the role of ATP in active transport?
Pump ions or molecules across the cell membrane against their concentration gradient
Which organelle is responsible for the synthesis of lipids that are incorporated into the cell membrane?
endoplasmic reticulum
How many amino acids are essential?
20
Which of the following is NOT a function of proteins in our bodies?
Structural, cushioning our organs, enzymatic activity, contraction
cushioning our organs
Which of the following is the empirical formula for a carbohydrate (all numbers are subscripts)
COOH, C6H12O6, CH2O, C2H4NO2R
CH2O
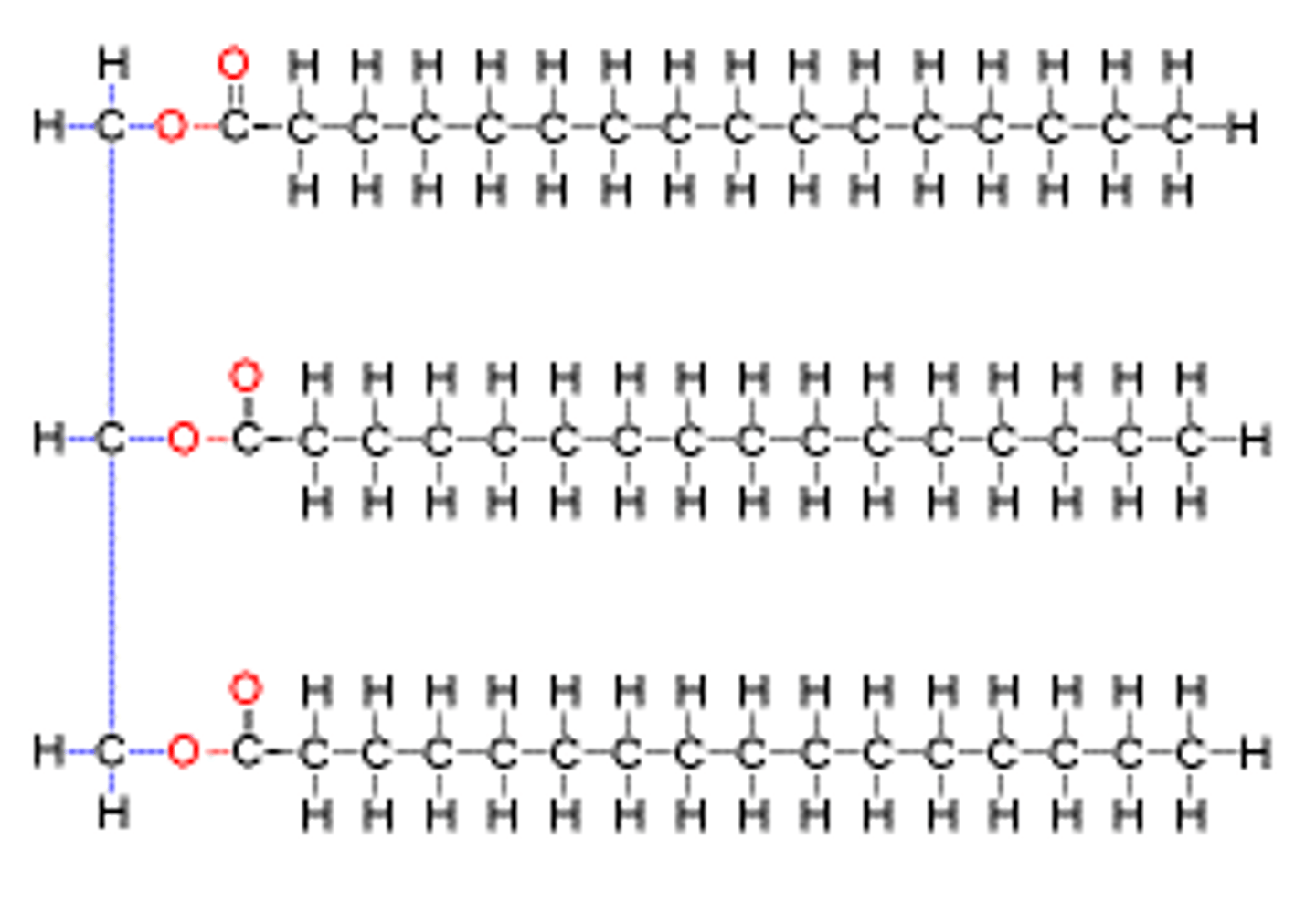
This molecule is a
Lipid
Which of the following is a purine?
Thymine, guanine, uracil, cytosine
guanine
Which of the following is a function of nucleic acids?
Carrying the genetic information, fighting diseases, energy, building carbohydrates
Carrying the genetic information
Which of the following might denature a protein?
excessive heat, exposure to light, exposure to bacteria, none of these
excessive heat
What is the difference between a saturated and unsaturated fatty acid?
an unsaturated fatty acid has double bonds
Which of the following is NOT true of lipids?
they make of most of the cell membranes, they are soluble in water, they store energy, they are large
they are soluble in water
Which of the following is a simple sugar (monosaccharide)?
starch, cellulose, fructose, chitin
fructose
how many electrons does carbon have in its valence orbital?
4
Which of the following is NOT included in every amino acid?
amino group, carboxyl group, glucose, alpha carbon
glucose
Proteins are long chains of ________ strung together.
amino acids
Which of the following is the most abundant enzyme in the world?
RUBISCO
Which of the following elements is NOT a major component of carbohydrates?
Nitrogen, oxygen, carbon, hydrogen
Nitrogen
What is the major role of carbohydrates in the cell?
provide energy
Which of these is NOT a monomer?
Fatty acid, lipids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids
carbohydrates
when two amino acids are joined together, what are the products?
a dipeptide and water
When two glucose monomers are joined by a covalent bond, the resulting disaccharide is ___________
maltose
The pH of pure water is
7
The property that permits water molecules to stick to other water molecules is called
cohesion
When the shared electrons are not equally distributed around the bonded atoms, this creates a ________ covalent bond
polar
Which type of solute will dissolve in water?
polar
These bonds are formed as a result of atoms sharing electrons to fill their valence shells.
Hydrogen
Which of the following types of bonds are the strongest?
Covalent
These bonds are formed when one atoms gains an electron and another atom loses an electron to create positive and negative charges which attract each other.
Ionic
_________ determines the chemical behavior (reactivity) of an atom.
electrons
An unequal distribution of charges within a covalently bonded molecule.
polarity
The substance that is dissolved in a solution is the ___________
solute
Of the three types of bonds we discussed, which is the weakest?
hydrogen
Which of the following is NOT one of the four elements that make up 95% of living matter?
phosphorous
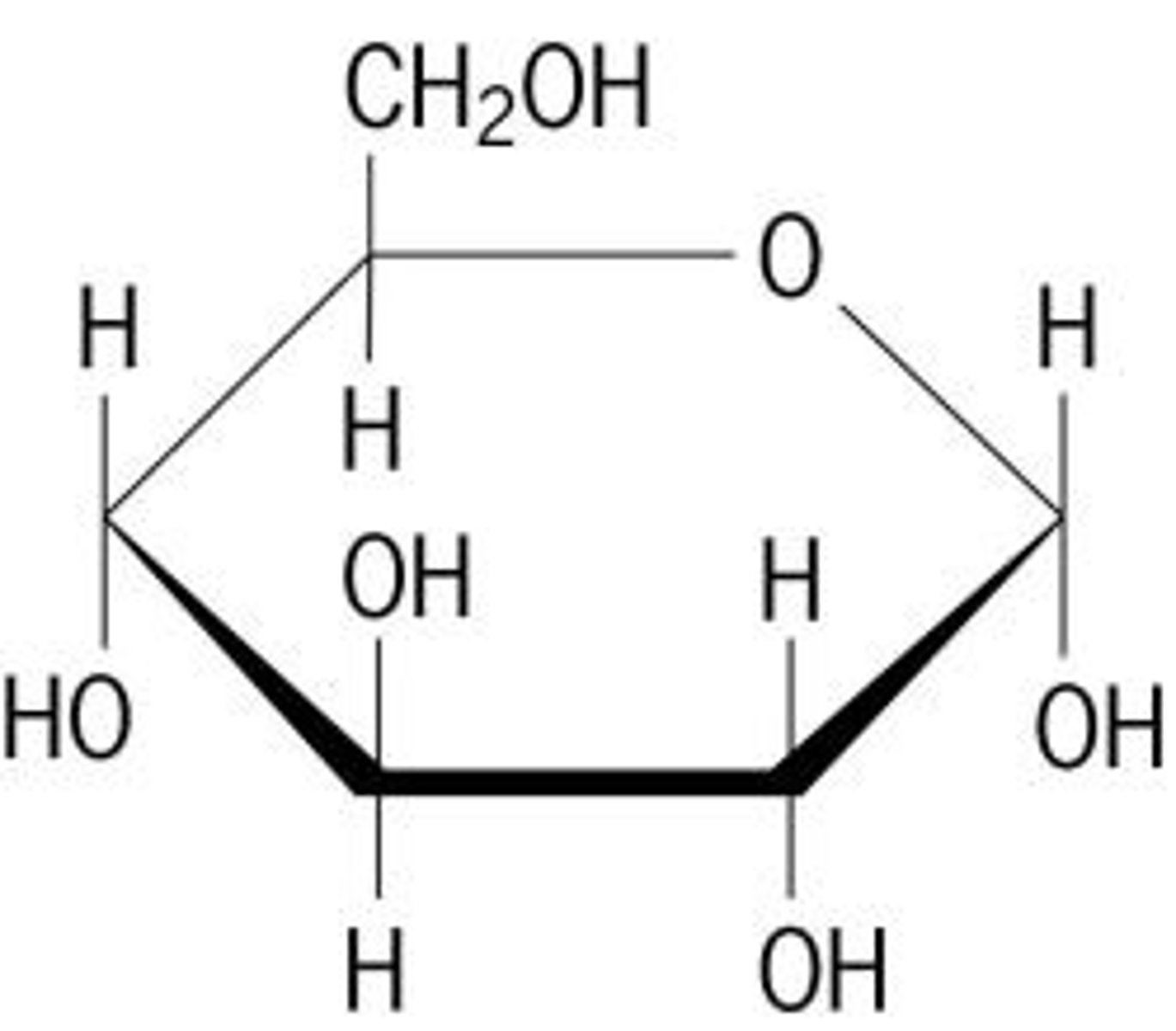
This macromolecule is a(n)
carbohydrate
Saturated fats are usually
solid at room temperature
What is the process that form macromolecules?
dehydration synthesis
Large, nonpolar organic molecules that includes waxes and store more energy per gram than other organic compounds.
lipids
Phospholipids are made of _____________
a phosphate head and two fatty acid tails
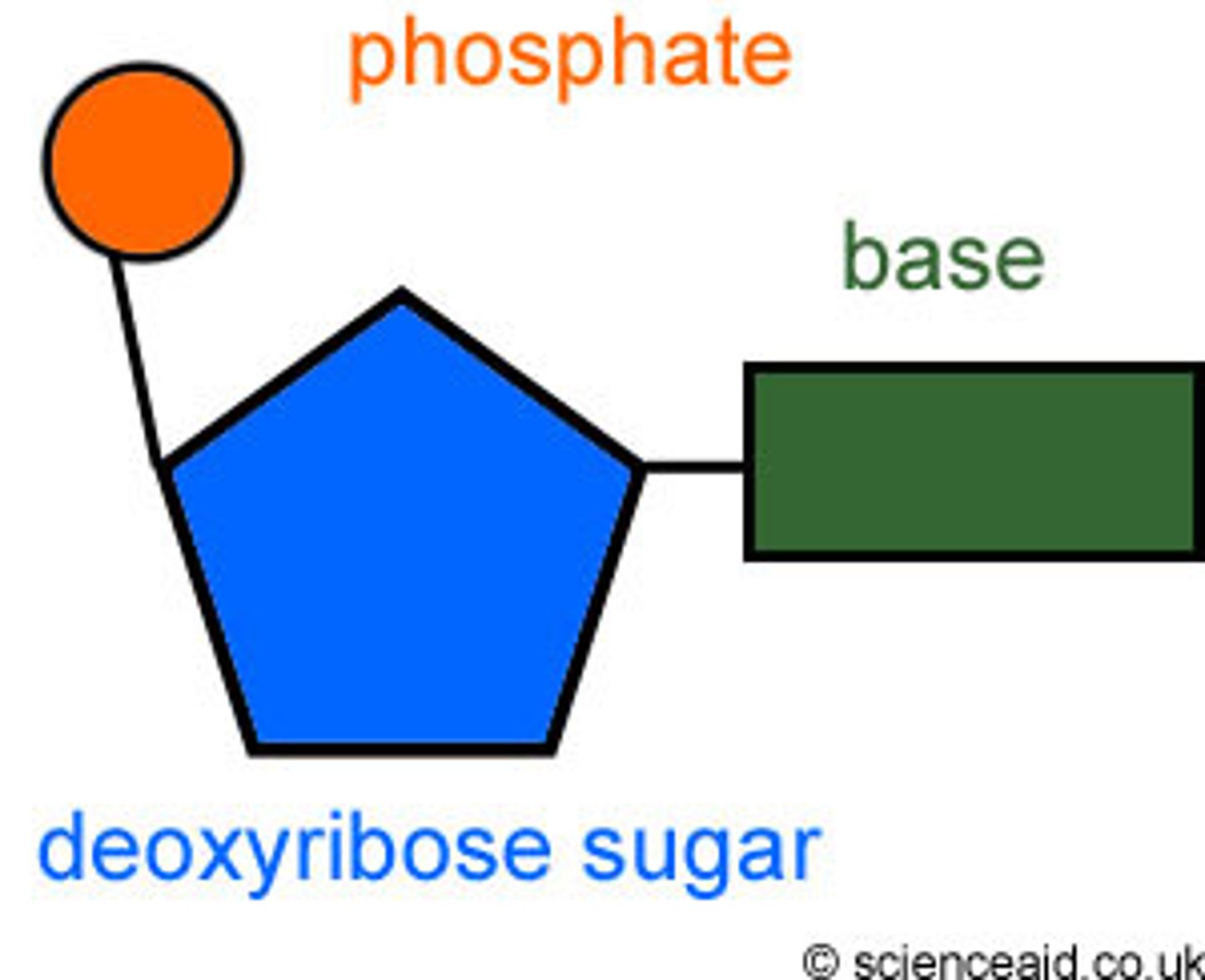
Which macromolecule is made of this monomer?
nucleic acid
What is the function of the enzyme RUBISCO in the Calvin cycle?
Carbon fixation
Which color of light is least effective for photosynthesis?
Green
What is the role of the ETC in photosynthesis
ATP synthesis and NADPH production
In what part of the plant cell does photosynthesis primarily occur?
chloroplast
What is the function of the ATP produced during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis?
glucose synthesis
In which part of the chloroplast are the pigments responsible for light absorption located?
thylakoid membrane