Rheumatology 2
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
polymyositis, dermatomyositis, proximal, enzymes, mononuclear, necrosis
Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies
Includes ______________ (PM), _______________ (DM), and multiple types of myositis
Common clinical features
Progressive, symmetrical, ___________ muscle weakness, elevation of muscle ___________, muscle histology showing ___________ inflammatory cell infiltrates and muscle fiber ___________, and EMG abnormalities
T, myofibers, CD8, 1, necrosis
Polymyositis (PM)
Pathogenesis
Endomysial _ cells surround and invade ___________, macrophages, dendritic cells, and plasma cells
Clonally expanded ___-positive cytotoxic T cells invade muscle fibers that express MHC class _, which leads to fiber _________
microangiopathy, autoantibodies, complement, ischemia
Dermatomyositis
Pathogenesis
A ______________ affecting both skin and muscle
_____________ cause injury to endothelial cells, which activates the ___________ cascade, and leads to capillary injury and muscle _________
proximal, malar, Shawl, heliotrope, periungal, gottron, scalp
Dermatomyositis
S/S
Symmetric _________ muscle weakness
Dusky red rash in ______ distribution that mimics SLE
Facial erythema beyond the malar distribution
“_______ or V sign”
Periobital edema and purplish color over the eyelids (__________ rash)
_________ erythema and dilation of nailbed capillaries
_____________ sign: scaly patches over dorsum of PIP and MCP joints
______ involvement may mimic psoriasis
weakness, leg, arm, dysphagia, atrophy
Polymyositis (PM)
S/S
Symmetric proximal muscle __________
Gradual and progressive
Upper and lower ext, neck
___ weakness often precedes ___ weakness
Pain and tenderness of affected muscles
___________
Muscle ___________ and contractures late in disease
extramuscular, autoantibody, >, PM
Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies
Differing Features
Association with ___________ manifestations and ____________ profiles
Epidemiology for PM and DM
F _ M for PM and DM
Childhood or adult onset (__ rare in children
Peak incidence in 4th-6th decades
subacute, weakness, deltoids, hip, neck, mild, cancer
Clinical Features of PM and DM
___________ presentation (weeks/months)
Symmetric proximal muscle _________ (cardinal feature)
___________, ___ flexors, _____ flexors most commonly
Difficulty washing/combing hair, rising from a seated position, climbing stairs, lifting head off pillow
No pain to ____ myalgias only
Associated with ________ (DM > PM)
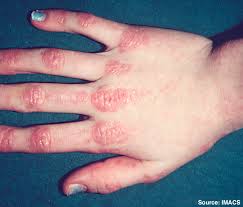
Gottron Papules
What DM skin finding is being described?
Erythematous/violaceous papules over bony prominences
Dorsal aspect of MCP and IP joints most common
Can scale and/or ulcerate
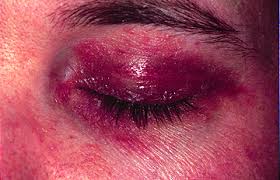
Heliotrope eruption
What DM skin finding is being described?
Erythematous/violaceous eruption on periorbital skin
± eyelid edema
shawl, V, nailfold, calcinosis cutis
Other Skin findings in DM
Photodistributed erythema (______ and _ sign)
Poikiloderma
__________ changes
Scalp involvement
____________ ________
dysphonia, reflux, interstitial, myocarditis
Extramuscular S/S of PM and DM
General
Fatigue, weight loss, hoarseness, ____________ (pharyngeal weakness), Raynaud’s
GI
Dysphagia, ________, dysmotility of the bowel
Pulm
Respiratory muscle weakness causing ventilator insufficiency, ____________ lung disease
Cardiac
___________, CHF, MI
MSK
Arthritis/arthralgias
DM
Which condition is more associated with the following cancers?
Ovarian
Lung
Pancreatic
Breast
Colorectal
Stomach
Lymphoma
Adeno > Squamous > Lymphoid
PM
Which condition is more associated with the following cancers?
Lung
Non-Hodgkins lymphoma
Bladder
muscle, CK, aldolase, ANA, muscle biopsy, endomysial, perifascicular
Diagnosis of PM and DM
Labs
Elevated _______ enzymes → __, LDH, __________
Autoantibodies
___ (80% of pts)
Myositis specific (30-40% of pts)
Myositis Associated
EMG
_______ ________ (Definitive Dx)
PM → __________ inflammation
DM → ____________ and perivascular inflammation
Anti-Jo-1, Anti-Mi-2, Anti-155/140, Anti-signal
Myositis Specific Antibodies
____-__-_ (antisynthetase)
PM or DM with Interstitial lung disease, arthritis, mechanic’s hands
____-__-_
DM with rash more than myositis
____-___/___
Cancer-associated myositis
____-_________
Severe, acute necrotizing myopathy
steroids, strength, function, year, decrease, methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine
Treatment of DM and PM
_________
Initial Treatment
Show to improve __________ and preserve muscle __________
High dose then taper over a _____ (depends on response)
Monitor muscle enzymes (should _________)
80% of pts improve with steroids
DMARD
______________ or azathioprine most often used
Sometimes added initially along with steroids
If fail steroids
Anti-malarial
_______________ useful for skin lesions
pain, stiffness, 50, >, unknown, GCA
Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR)
Symptom complex that includes ____ and __________ of the shoulder and hip girdles and proximal extremities
Epidemiology
Age > __ y/o (peak between 70-80 y/o)
F _ M
Pathogenesis
Mostly __________
Similar to ___
acute, bilateral, mornings, shoulders, ROM
Polymyalgia Rheumatic Symptoms
Aching/Stiffness
Can be _____/abrupt
__________
Severe in _________ (lasting > 1 hr)
__________, neck, hip girdle, torso
Limited ___
GCA
Ask/look for s/s of GCA
clinical, normal, US, MRI, steroids, quick, years
Polymyalgia Rheumatica Diagnosis
Mostly __________
Labs
CBC w/ diff → may see normocytic anemia
ESR/CRP → often elevated
CK → usually _______
Imaging
__ or ___ → often show bursitis and/or tenosynovitis
Treatment
Low dose _________ (10-20 mg/day)
Response usually ______
Most can taper off after 1-2 _______
fatigue, soft, female, stress, regulation
Fibromyalgia
Controversial, chronic MSK syndrome characterized by widespread joint and muscle pain, _________, and tender points
Considered _____ tissue rheum condition
Epidemiology
Majority are ________
Peak between 20-50 y/o
Pathogenesis/Etiology
Unknonw
Thought to be genetic susceptibility and environmental triggers altering gene expression
Alterations in neuroendocrine and _______ responses
Alterations in pain ___________
depressed, pain, fatigue, sleep, cognitive
Fibromyalgia Multi-system characters
___________ mood
Widespread chronic ____
Severe _________
_________ dysfunction
Decreased well-being
Stiffness
_________ impairment
Headaches
Depression, IBS, fatigue, localized
Fibromyalgia Concomitant Conditions
__________ (25-60%)
___ (50-80%)
Migraines (50%)
Chronic ____________ Syndrome (70%)
Myofascial pain (possible ____________ form of FM)
WPI, SSS, generalized, 3
Fibromyalgia Diagnosis
ACR 2016 Fibromyalgia Diagnostic Criteria
Wide-spread Pain Index (___) >7 and Symptom Severity Scale (___) >5 OR WPI 4-6 and SSS >9
______________ pain, defined as pain in at leas four of five regions, is present
Left upper, right upper, left lower, right lower, axial
Symptoms have been present at a similar level for at least _ months
A dx of FM is valid regardless of other diagnoses that the pt may have. A dx of FM does not exclude the presence of other clinically important illnesses
individualized, comorbidities, exercise, CBT, SNRI, anticonvulsant, tricyclic, analgesics
Fibromyalgia Treatment
___________ and multidisciplinary
Nonpharmacologic
Education
Address _____________
___________ → can be hard b/c pain and fatigue
Cognitive behavioral therapy (___)
Pharmacologic
____ (duloxetine, milnacipran)
Alpha-2-ligand ___________ (pregabalin)
____________ antidepressant (amitriptyline)
Other options → fluoxetine, gabapentin, naltrexone
____________ haven’t shown benefit