Computer Science Fundamentals
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
298 (decimal)
Convert 12A (hexa) to decimal
100 (decimal)
Convert 1100100 (binary) to decimal
0.29296875 (decimal)
Convert 0.4B (hexa) to decimal
0.34375 (decimal)
Convert 0.01011 (binary) to decimal
JPEG
Compression format for color still images, or the name of the joint organization of ISO and ITU-T establishing this standard
PCM
Converting analog signals (sound, etc.) into digital signals
MIDI
Interface to connect a musical instrument with a computer
Arithmetic Shift
This type of shifting is used when data is handled as numeric data with a positive or negative sign; it is an operation of shifting a bit string, except for the sign bit, representing a fixed-point number. inserts a “0” in the rightmost place that has been made empty by the shift.
Complement
the value obtained by subtracting the given number from a certain fixed number, which is a power of the radix or a power of the radix minus 1.
Register
It is low-capacity, high-speed memory placed in the CPU for temporary storage of data.
EBCDIC
Computer code defined by IBM for general purpose computers 8 bits represent one character.
ASCII
7-bit code established by ANSI (American National Standards Institute) Used in PCs, etc.
Unicode
An industry standard allowing computers to consistently represent characters used in most of the countries. Every character is represented with 2 bytes.
11110100 (-12 in decimal)
What is the arithmetic left shift of 11111010?
11111101(-3 in decimal)
What is the arithmetic right shift of 11111010?
Logical shifting
It shifts an entire bit string of data and inserts 0s in places
vacated by the shift.
11110100
What is the left logical shift of 01111010
01001100
What is the right logical shift of 10011001
Cancellation of significant digits
a phenomenon where the number of significant digits drops drastically when one number is subtracted from another number almost identical to it, or when two numbers, one positive and the other negative, with almost identical absolute values are added together
Rounding error
Since computers cannot handle an infinite (non-terminating) fraction, bits smaller than a certain bit are rounded off, rounded down, or rounded up to the value with the limited number of significant digits. The difference between the true value and the result of such rounding is called the _
Loss of trailing digits
a phenomenon where some information (or a part thereof) in the lower digits, which cannot be contained in the mantissa, can be lost due to the alignment of the numbers when a very large number and a very small number are added together, or when one is subtracted from the other
Arithmetic shift: 11111001
Logical shift: 00011001
Perform arithmetic right and logical right shifts by 3 bits on the 8-bit binary number 11001100.
Binary: 1100100
Octal: 144
Hexa: 64
Express the decimal number 100 in the binary, octal, and hexadecimal notations.
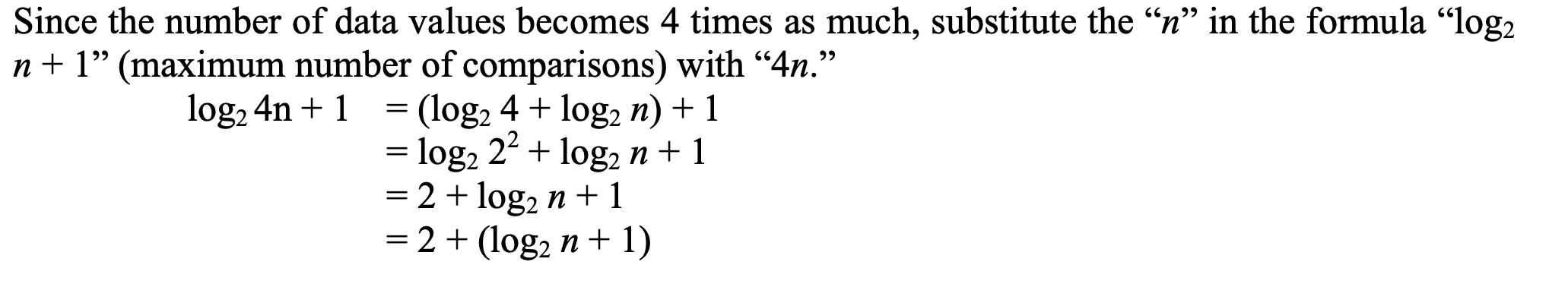
2 times
In binary search, when the number of sorted data values is quadrupled, how much does the maximum number of comparisons increase by?
5
There is a register which stores values in binary. After entering a positive integer x into this register, the operation “to shift the register value 2 bits to the left and to add x to the value” will be performed. How many times as large as x is the resulting register value? Here, assume that overflow due to shifting will not occur.
b) (NOT x) AND y
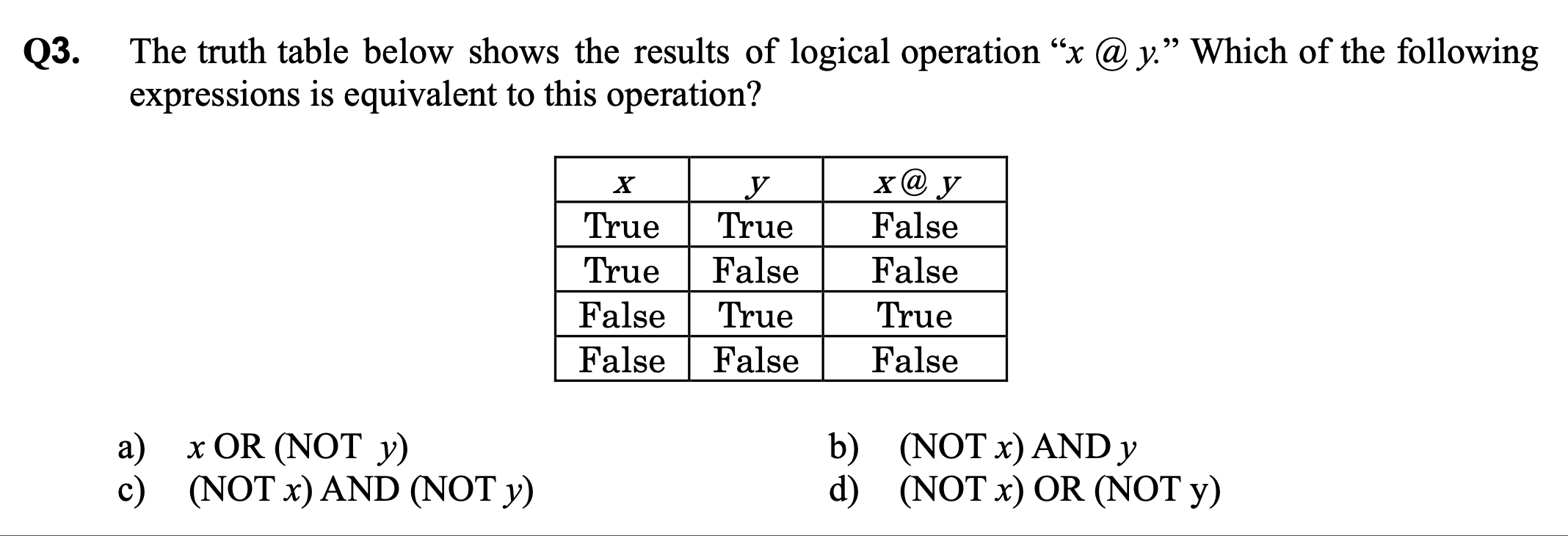
b.) FEB
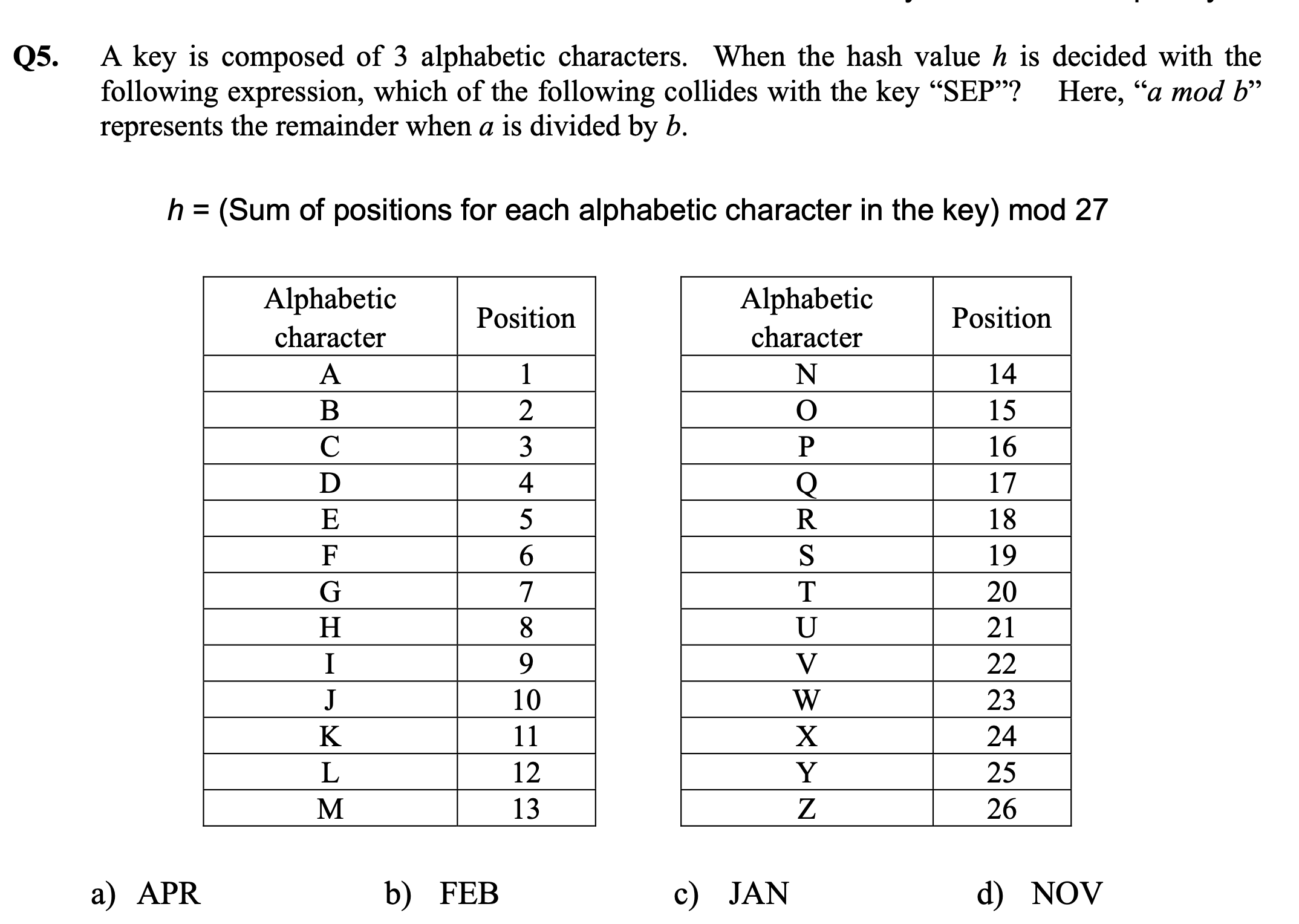
b.) 11
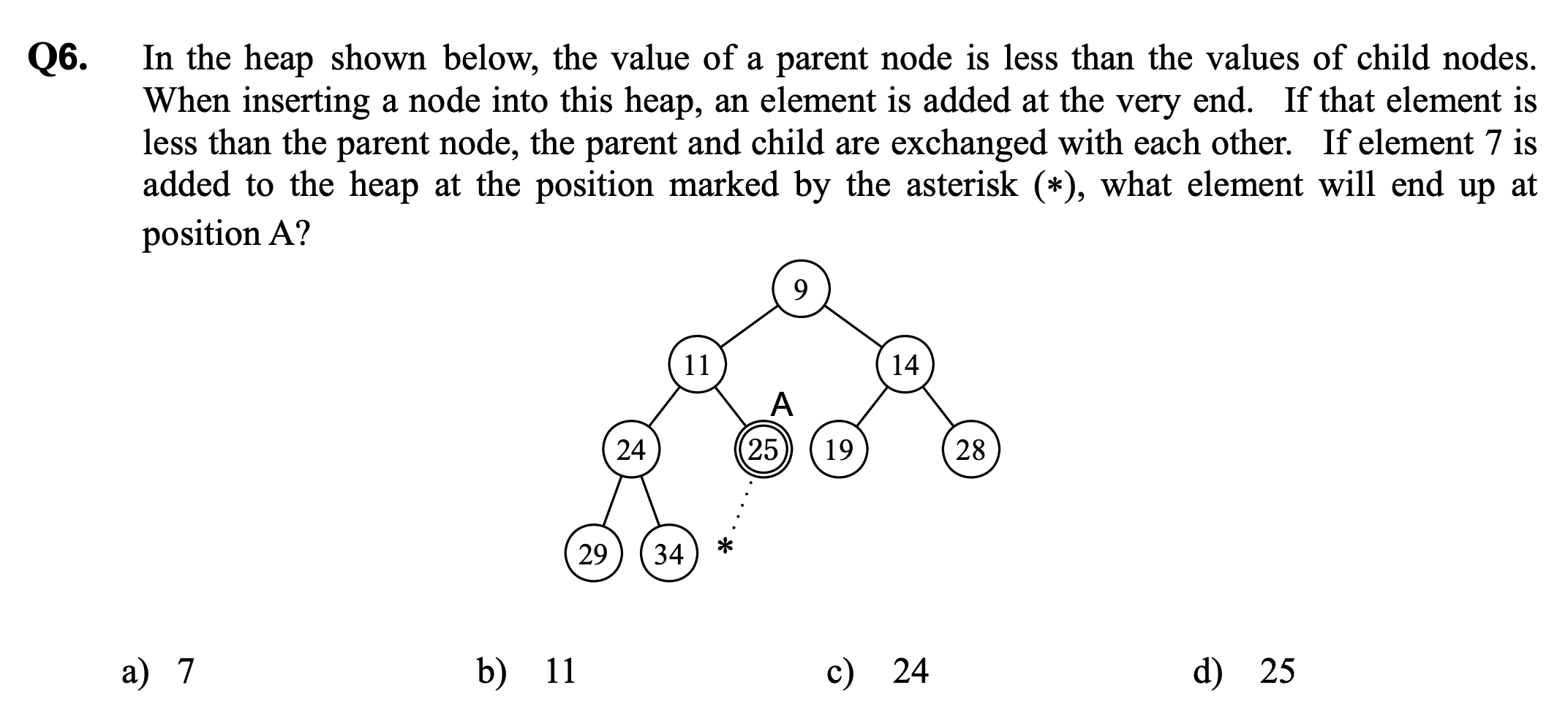
d) Persons included in Report 4 are not included in any of the other reports
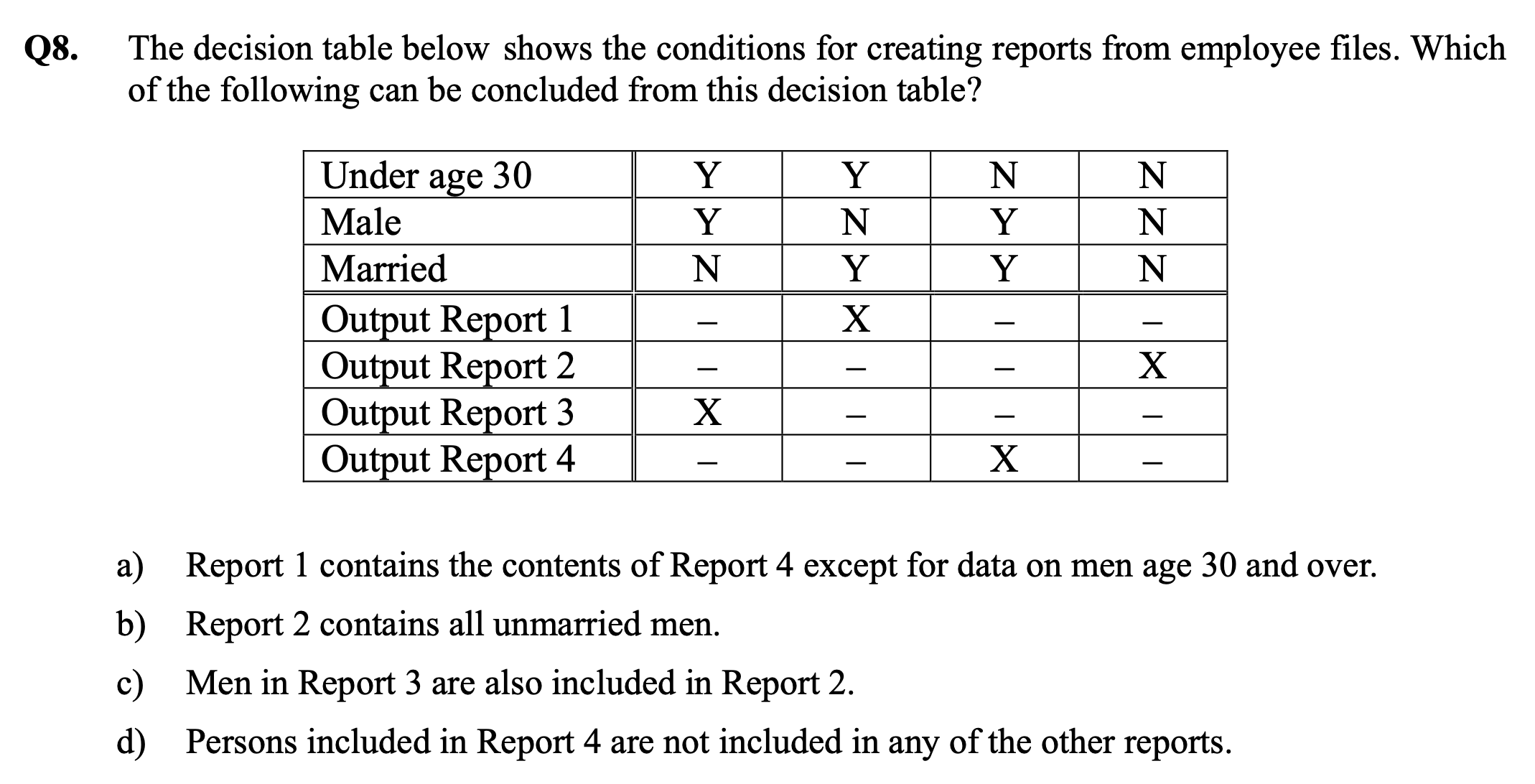
a) n > M