Intro to Medical Imaging - Lec
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What are the two divisions of medical imaging? What are they used for?
Therapeutic
Guide procedures such as surgery and rad therapy (Fluoroscopy, angiography, IR)
Diagnostic
Detect and diagnose disease (XR, CT, MRI, US, nuclear med)
What is the imaging technique with ionizing radiation and what is its principle/key concepts?
XR has a anatomical focus
Tissues absorb X rays different (attenuated)
Key concepts
radiodensity, superimposition, and contrast agents (barium/idoninated)
Clinical:
Skeletal - breaks, arthritis, dislocations
Chest (CXR) - pneumonia, HF, lung mass, pneumothorax
Abdomen (KUB) - bowel obs, free air (perforation)
Screening - mammography
Limits: Poor soft tissue, radiation dose (low),, only 2D
Now describe CT. Key concepts, clinical strengths, limits.
Creates cross sectional slides, computer reconstructs in 3D
Key concepts: Hounsfield units (HU), multiple images, IV contrast (asses vascularity, organ perfusion, inflam), CT angio(CTS) and venography (CTV)
Clinical: Emergency, oncology, vascular, abdomen/pelvis
Limits: sig rad dose, IV contrast (nephropathy allergy), metal artifacts
Now describe a technique that used real time imaging with sound waves.
Ultrasound - non ionizing, used high freq sound waves
Key concepts: Echogenicity (hyper/hypo/an-echoic), acoustic shadowing (gallstones) and enchantment, Doppler (direction/presence/velocity)
Clinical: Ob/Gyn (fetal asses, ovarian/uterine path), cardio (EKG{structure and function}), abdomen, vascular (DVT or carotid stenosis)
Point of care (POCUS): FAST exam (trauma), gunslinging procedures
Limits: Operator dep, bone and gas, obese patients
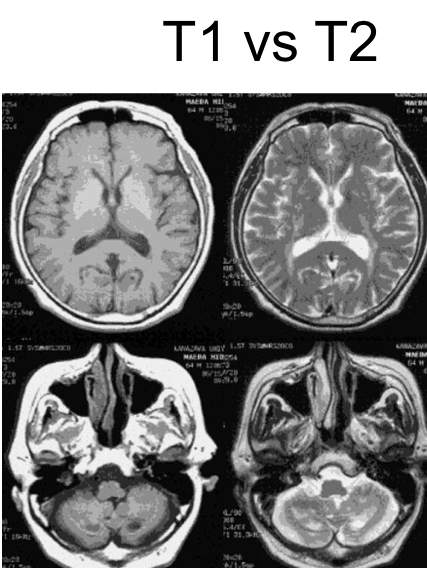
Now describe MRI. The principle/key concepts/clinical rel/limits.
Non ionizing, uses magnet and radio waves
Key concepts: T1 vs T2 weighting: Contract mechanism (T1: fat is bright, T2: water/pathology is bright), also can used fMRI to monitor blood flow
Clinical: Neurology, MSK, abdomen/pelvis
Limits: Slow, expensive, NSF risk with gadolinium
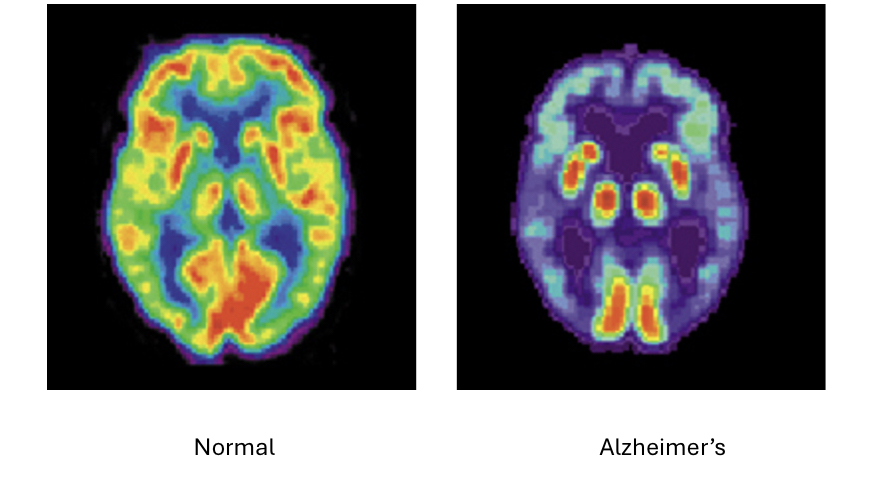
Describe nuclear medicine. They key concepts, clinical rel, limits and principle.
Pt given radioactive tracer —> emittion detected
radiopharm accumulates in target organ based on metabolic activity —>decays and emits gamma radiation —→ increased uptake in areas with increased metabolic activity
Key concept:
Clinical (How is it working): Onco(PET/CT), cardio(SPECT), endo, skeletal, neuro(PET)
Limits: High rad dose, low spacial resolution, exp
***”Hot spots” on imaging indicative of infection,, fracture, or malignancy
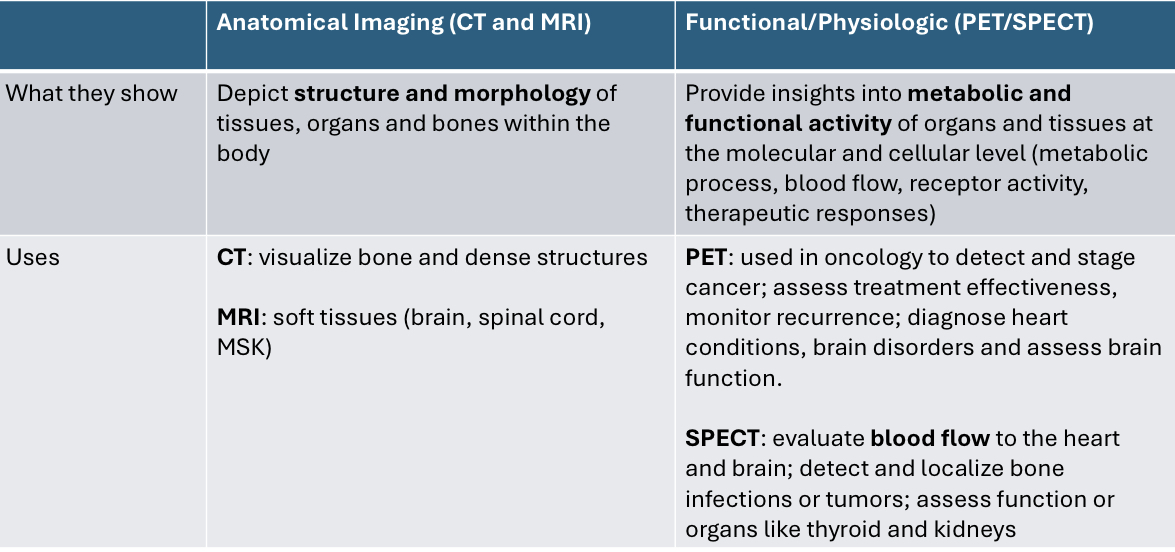
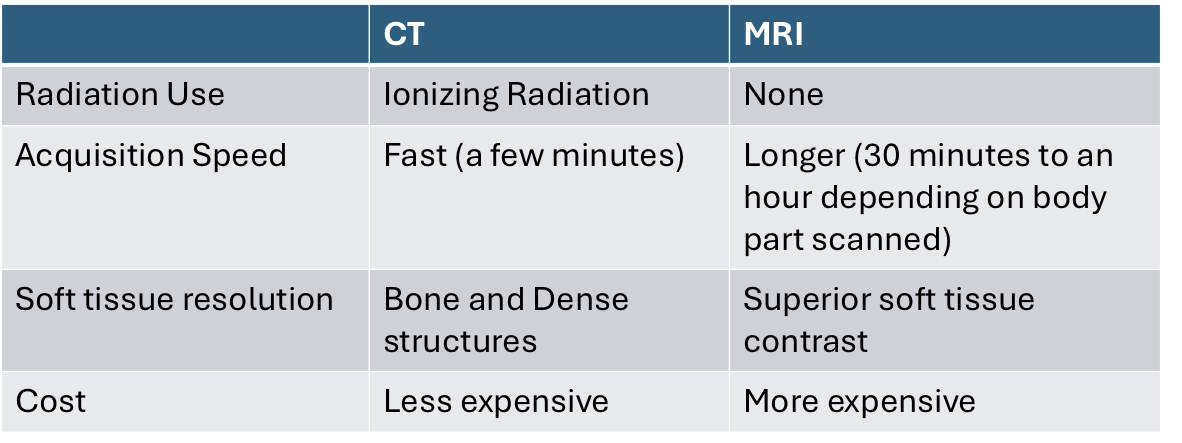
Compare and contrast MRI/CT/and PET/SPECT. Radiation use, type of tissues they examine, cost, and speed.
What is the principle we use when addressing a susceptible postulation ie pregnant or elderly?
We use the ALARA —> as low as reasonably possible principle
**8However for urgency —> FAST (US), CT or if outpatient MRI, PET/CT