Introduction to Histology and Staining Techniques
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
How many steps are involved in studying histology with a microtome?
6: fixation, dehydration, clearing, infiltration, embedding and trimming
Fixation
Preserves tissue structure by using cross-linking proteins.
Dehydration
Removes water using increasing alcohol concentrations.
Clearing
Removes alcohol with miscible organic solvents. (both alcohol and parafin are miscible)
Infiltration
Tissue saturates with melted paraffin, until complete infiltration with the substance.
Embedding
Paraffin-infiltrated tissue is molded and hardened.
Trimming
Paraffin block is cut for microtome sectioning (slicing).
What does staining do?
Enhances visibility of tissue and cell structures.
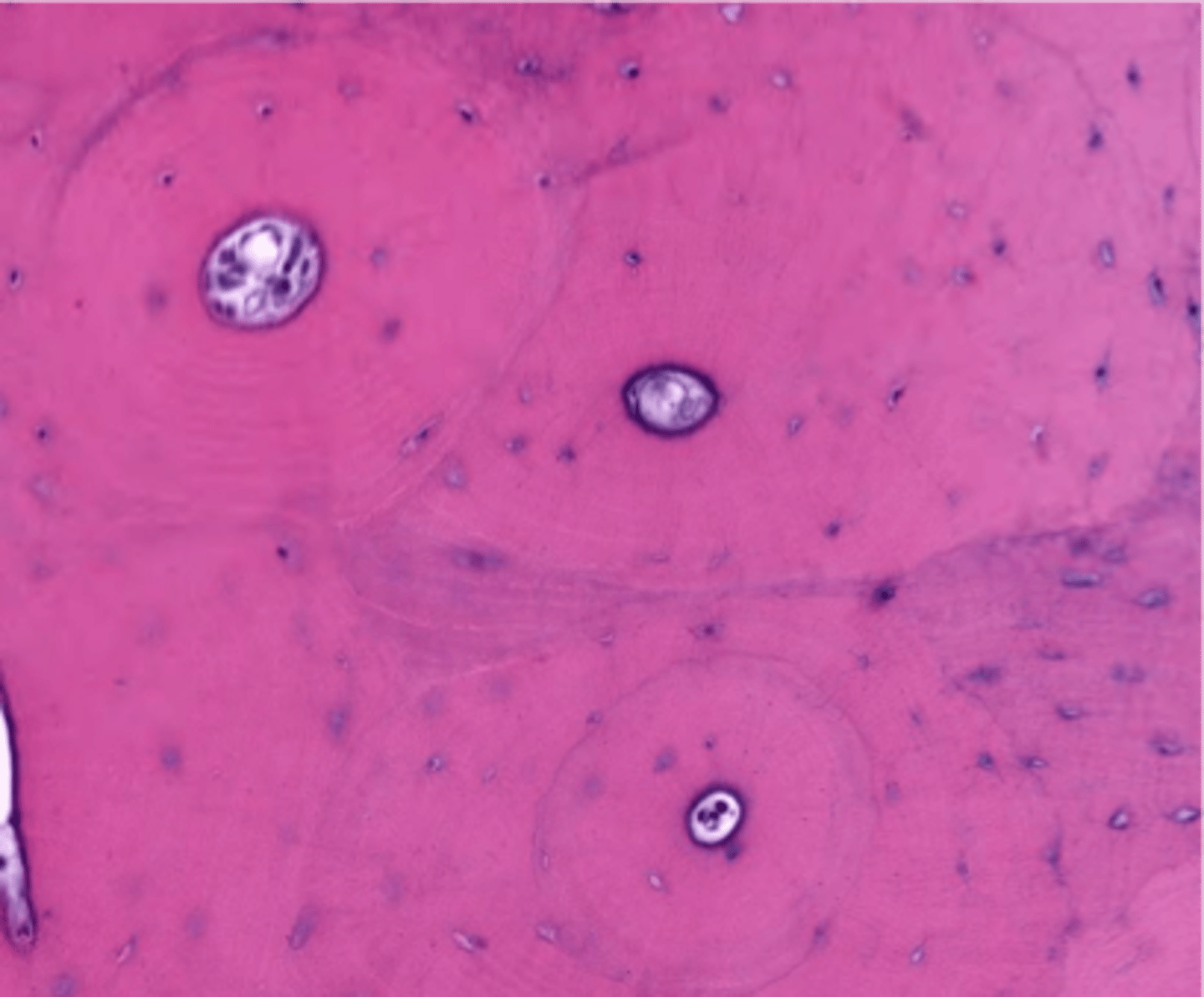
What happens withouts staninig?
Unstaid tissue and cells are difficult to examine.
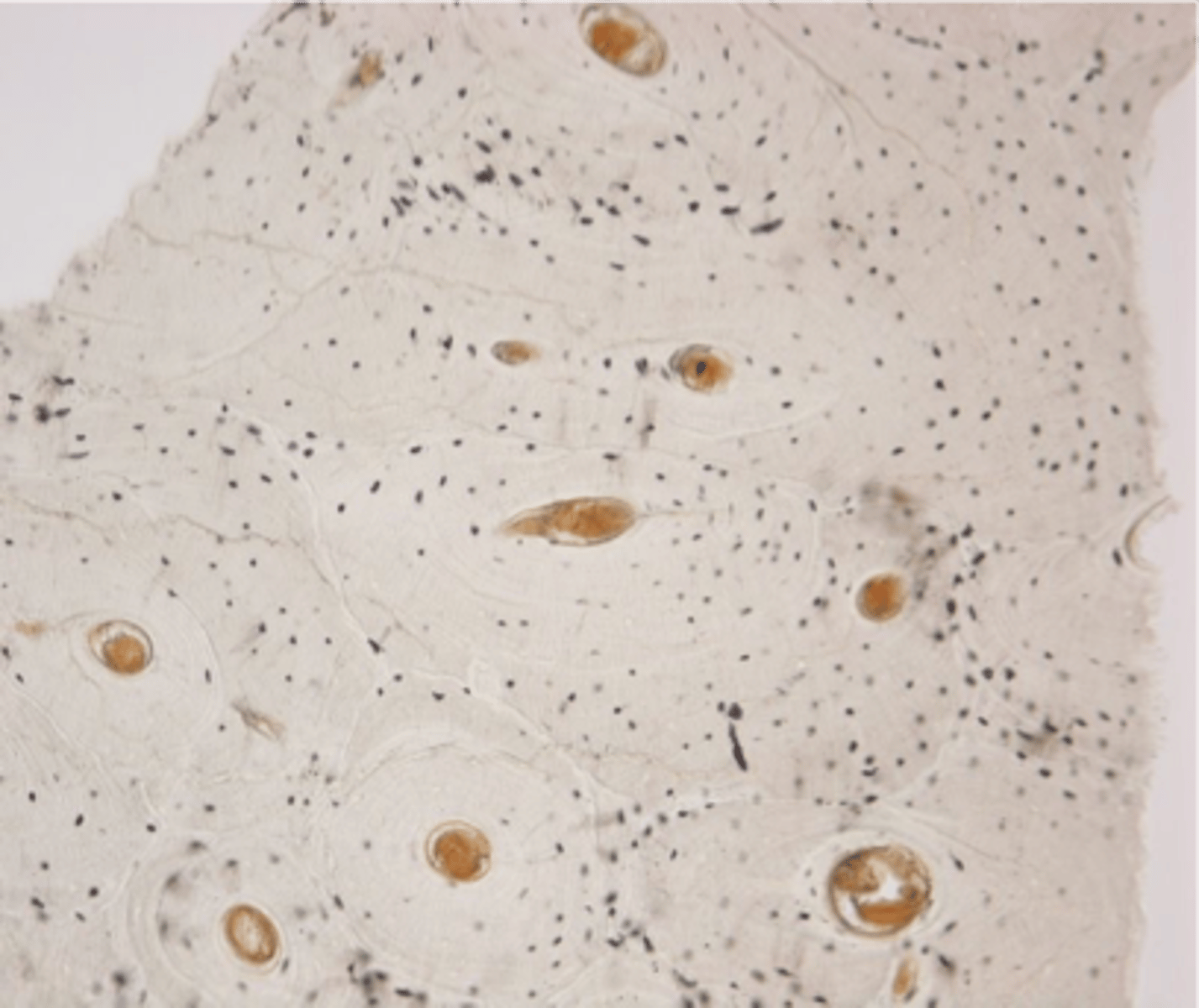
What are the two types of dies?
Basic (+) and Acidic (-)
Basic Dyes (+)
Stain anionic (-) components, like nucleic acids.
Acidic Dyes (-)
Stain cationic components, like ionized proteins.
Hematoxylin is what type of dye?
Basic dye staining anionic structures.

Eosin is what type of dye?
Acidic dye staining cationic structures.
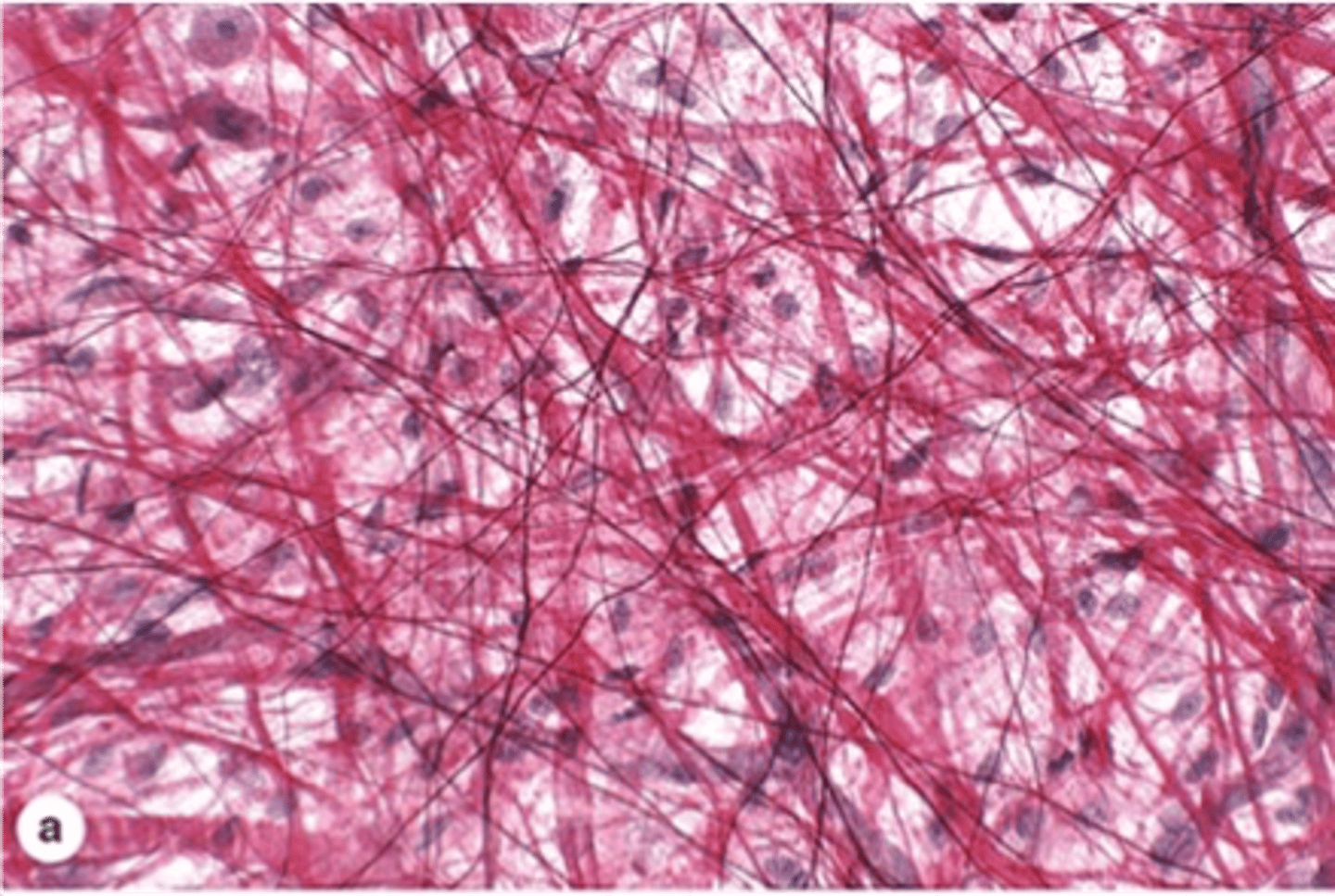
Hematoxylin stains what color?
Stains anionic tissues purple
Tissues that stain with basic dyes are said to be what?
Basophilic
What type of cell structures stain well with hematoxylin?
Those with acids:
Nucleic acids (nucleus contains DNA).
Glycosaminoglycans
Eosin stains what color?
Cationic structures, Pink
Tissues that stain with acidic dyes (eosin) are said to be what?
Acidophilic
What cell structures stain well with eosin?
Those with basic components:
Mitochondria
Secretory granules
Collagen
Hematoxylin & Eosin (H&E)
Common histology dye combination for tissue staining.
Are acidophilic tissues composed of acids?
NO
Basophilic
Structures that stain well with basic dyes.
Acidophilic
Structures that stain well with acidic dyes.
Periodic acid - Schiff (PAS) is what?
a special staining technique
What does Periodic acid - Schiff (PAS) stain?
Stains carbohydrates dark purple or magenta.
Example of a structure that stains with PAS?
Goblet cells: secretory granules rich in carbs are
PAS positive.
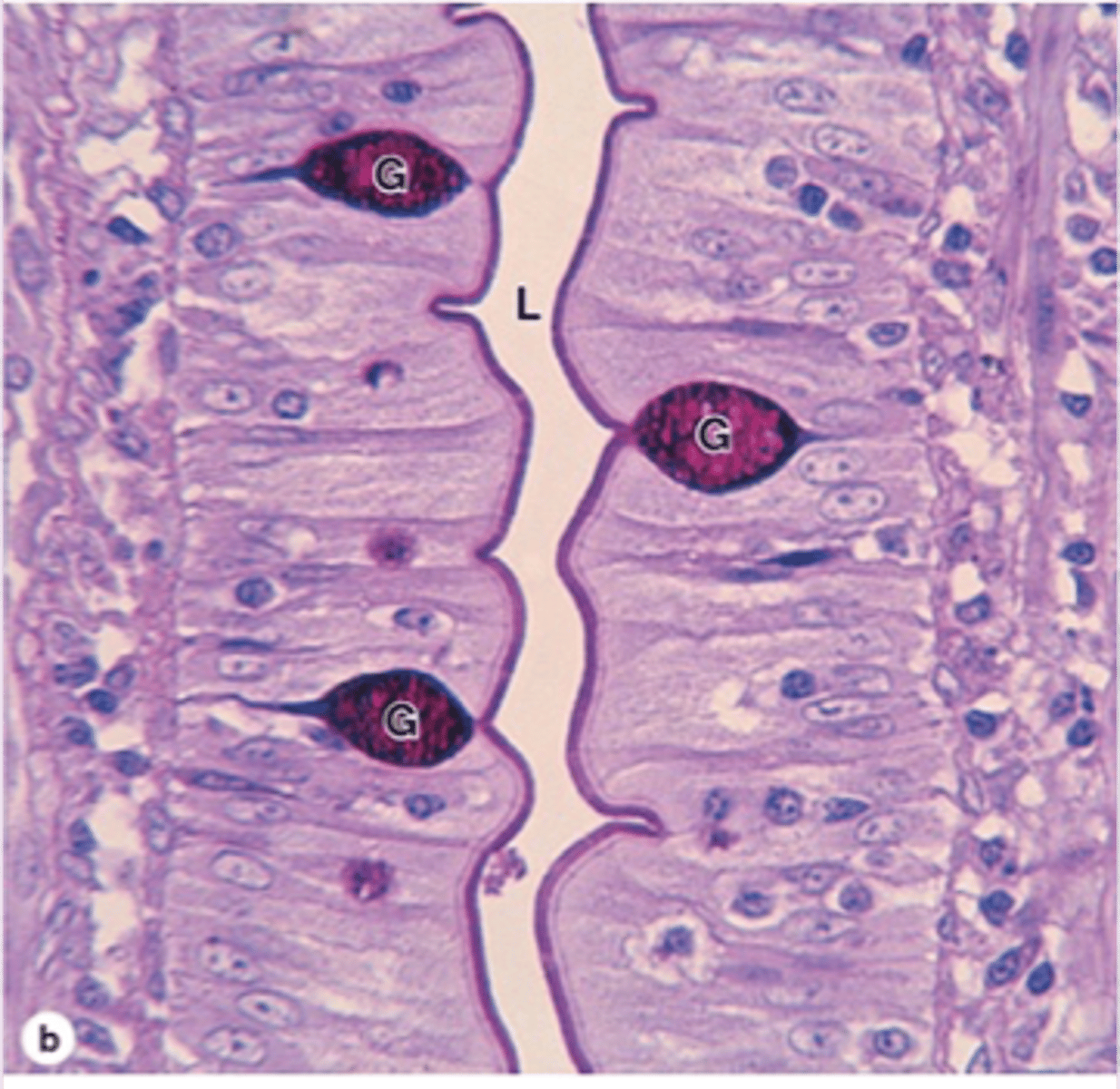
What is Sudan Black?
A lipid-soluble dye staining lipids black.
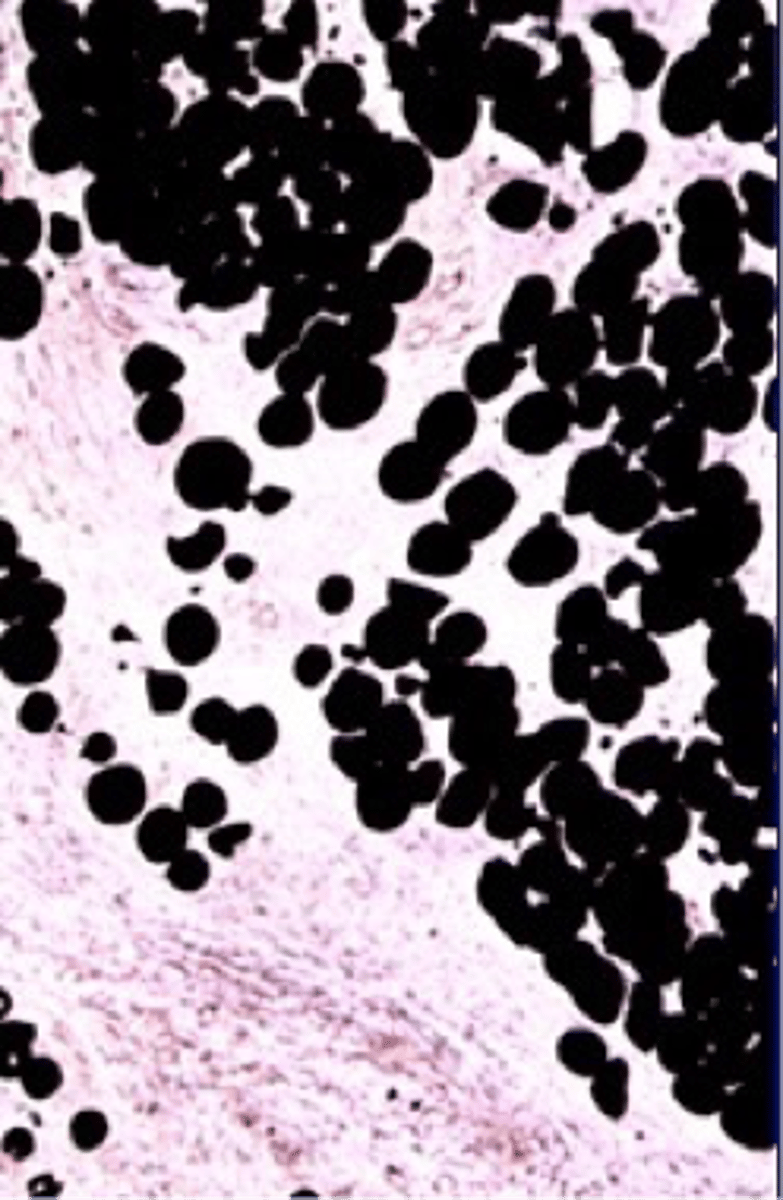
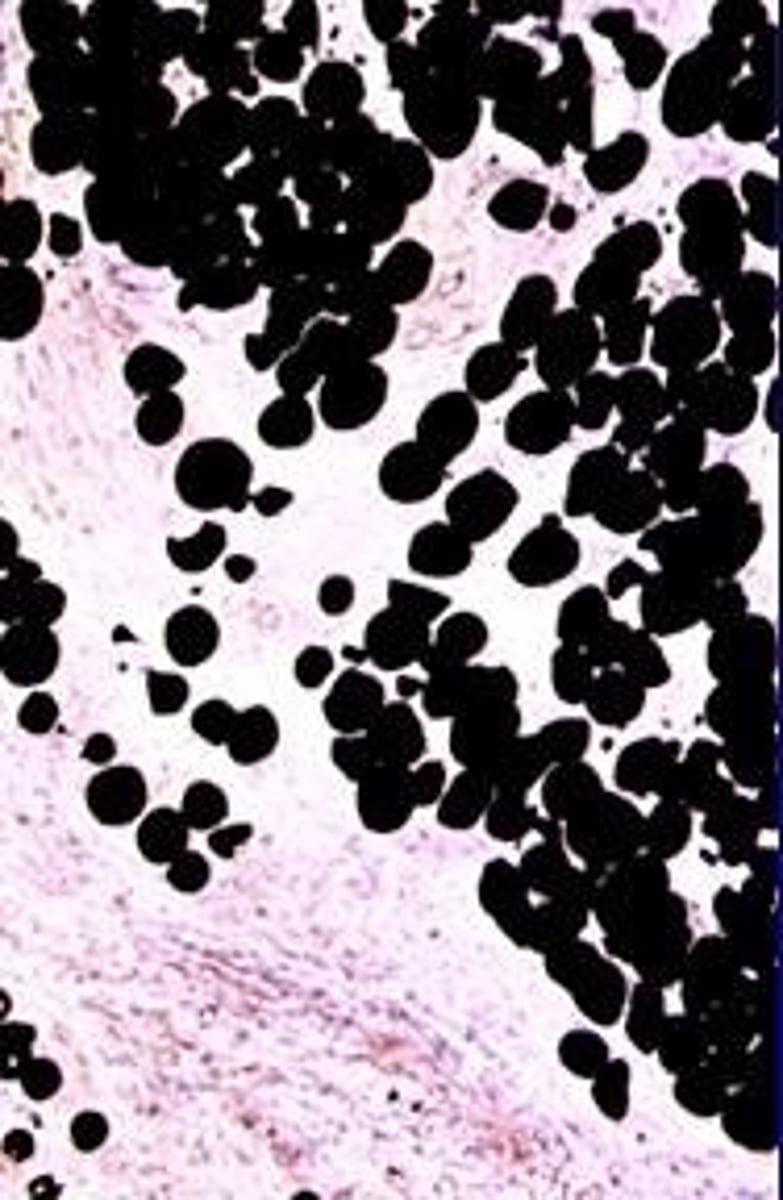
Adipose Cells
Cells rich in lipids, stained by Sudan black.
Light Microscope
Standard microscope with lower resolution and magnification.
Electron Microscope
High-resolution microscope, up to 400,000X magnification.
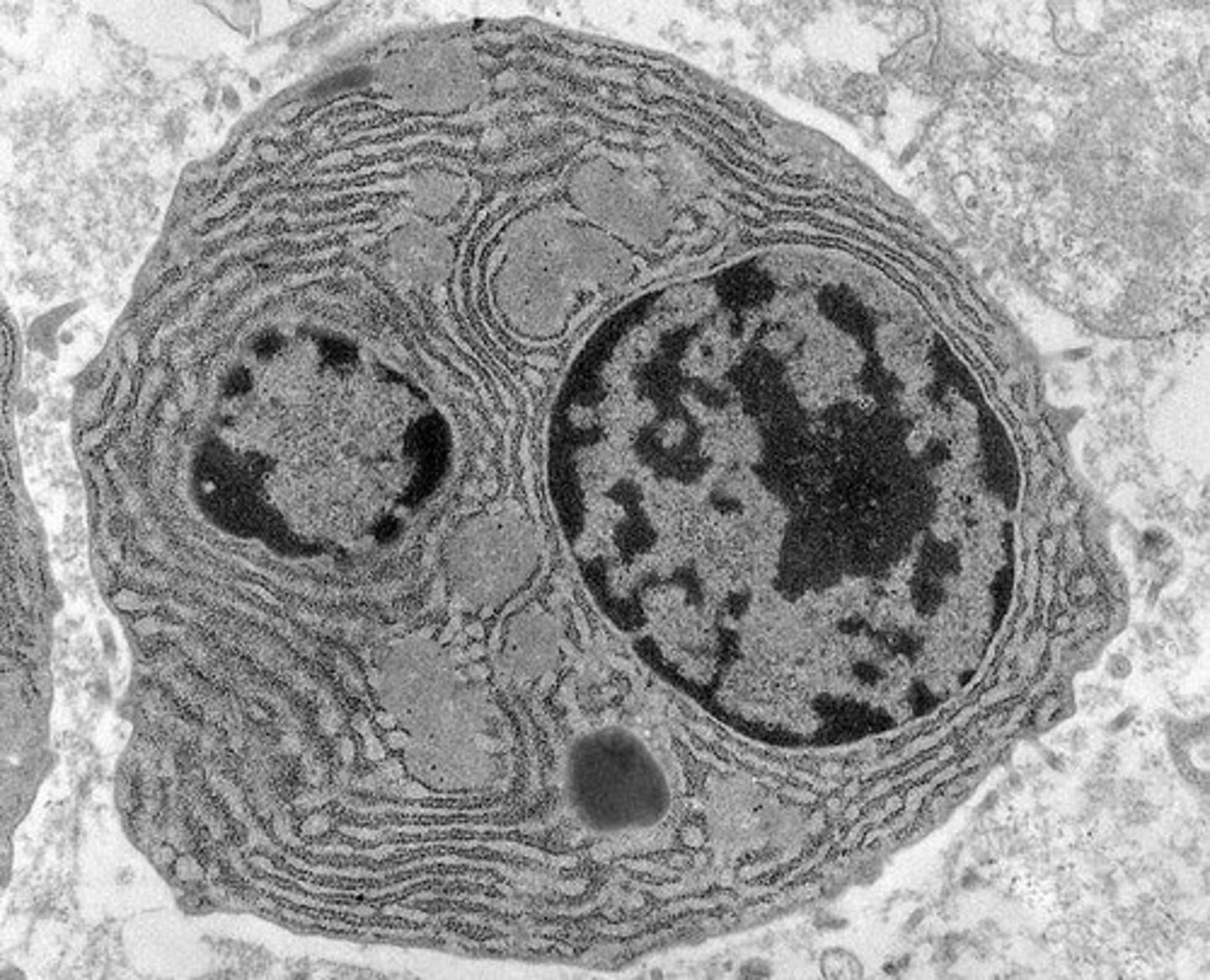
How does a light microscope compare to an electron microscope?
Electron microscopes provide more details and ultrastructure of the cells (organelles).
Ultrastructure
Detailed view of cellular organelles and structures.