Alkanes
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
How does carbons bond energies compare to silicon’s?
Silicon’s bond energies are much lower than carbons
How are organic compounds classified?
They are classified in homologous series. A homologous series contains compounds with the same functional group which therefore have similar chemical properties
What is a homologous series
All share same general formula, formula of a homologue differs from its neighour by CH2. Contain the same functional group, have similar chemical properties. Show a gradual change in physical properties as molar mass increases. Can usually be prepared by similar methods.
Common functional group displayed formula
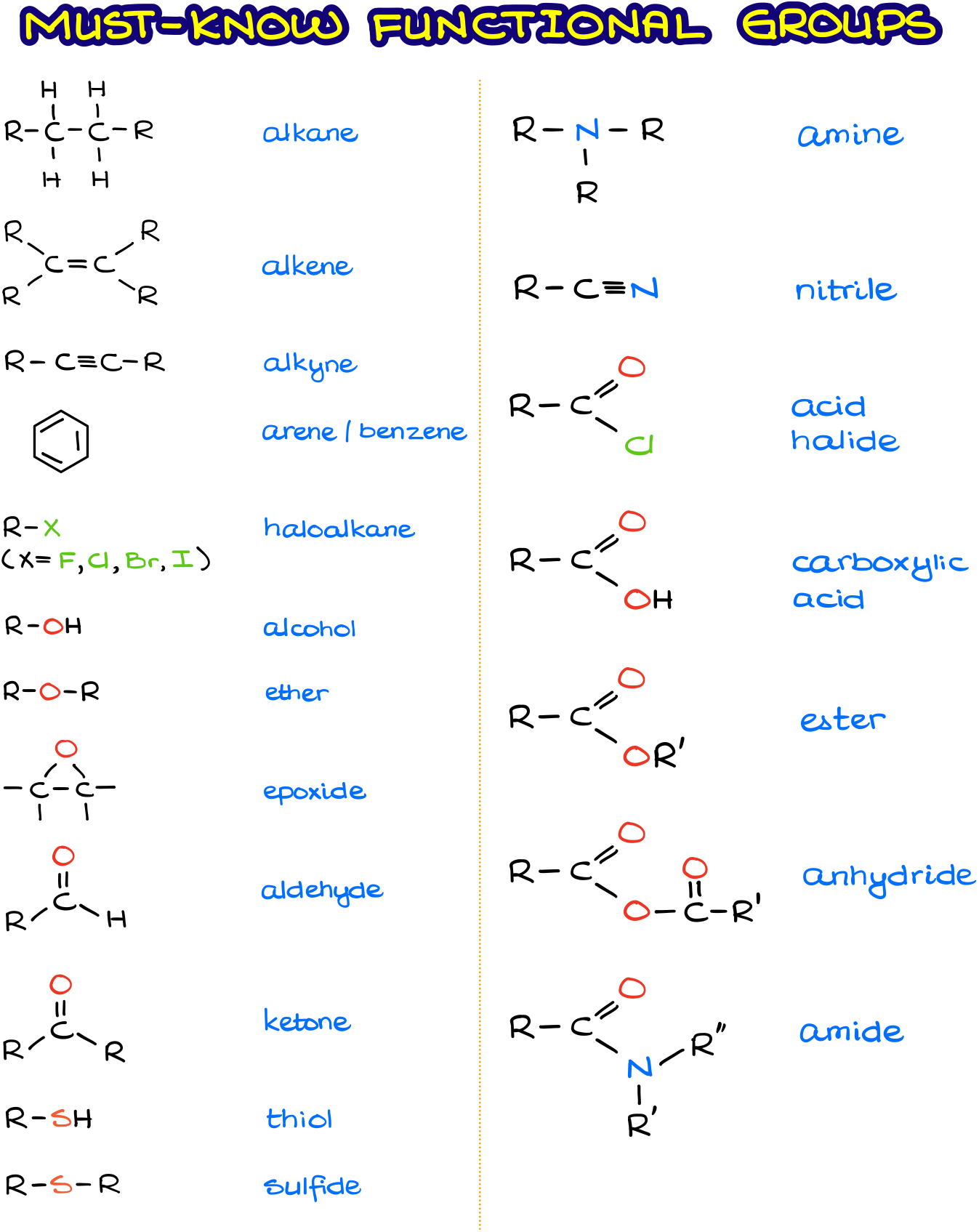
What are the 5 ways an organic compound is expressed
Empirical formula, displayed formula, structural formula, molecular formula and skeletal formula
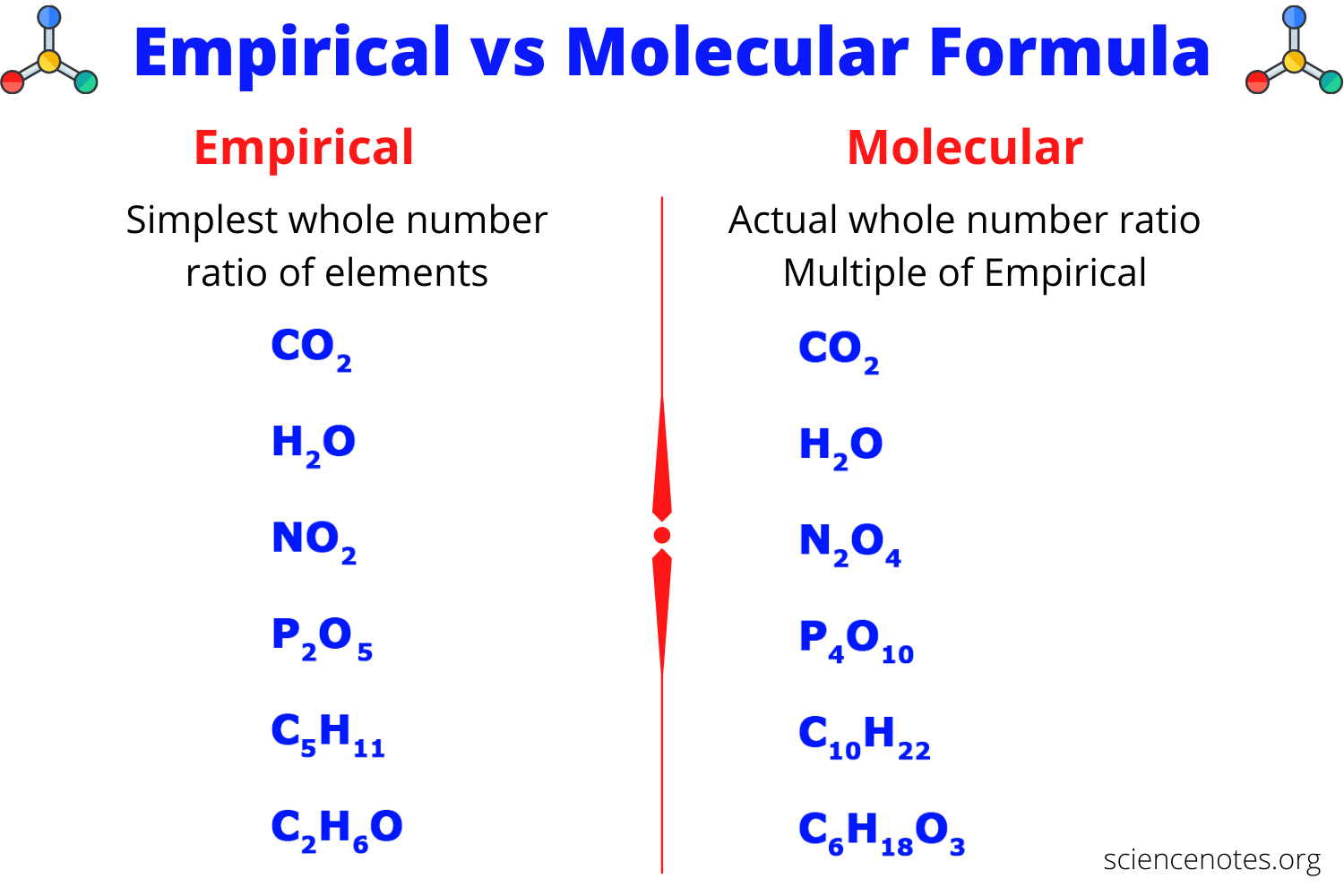
What is the empirical formula
Simpliest whole number ratio of the elements in a compound
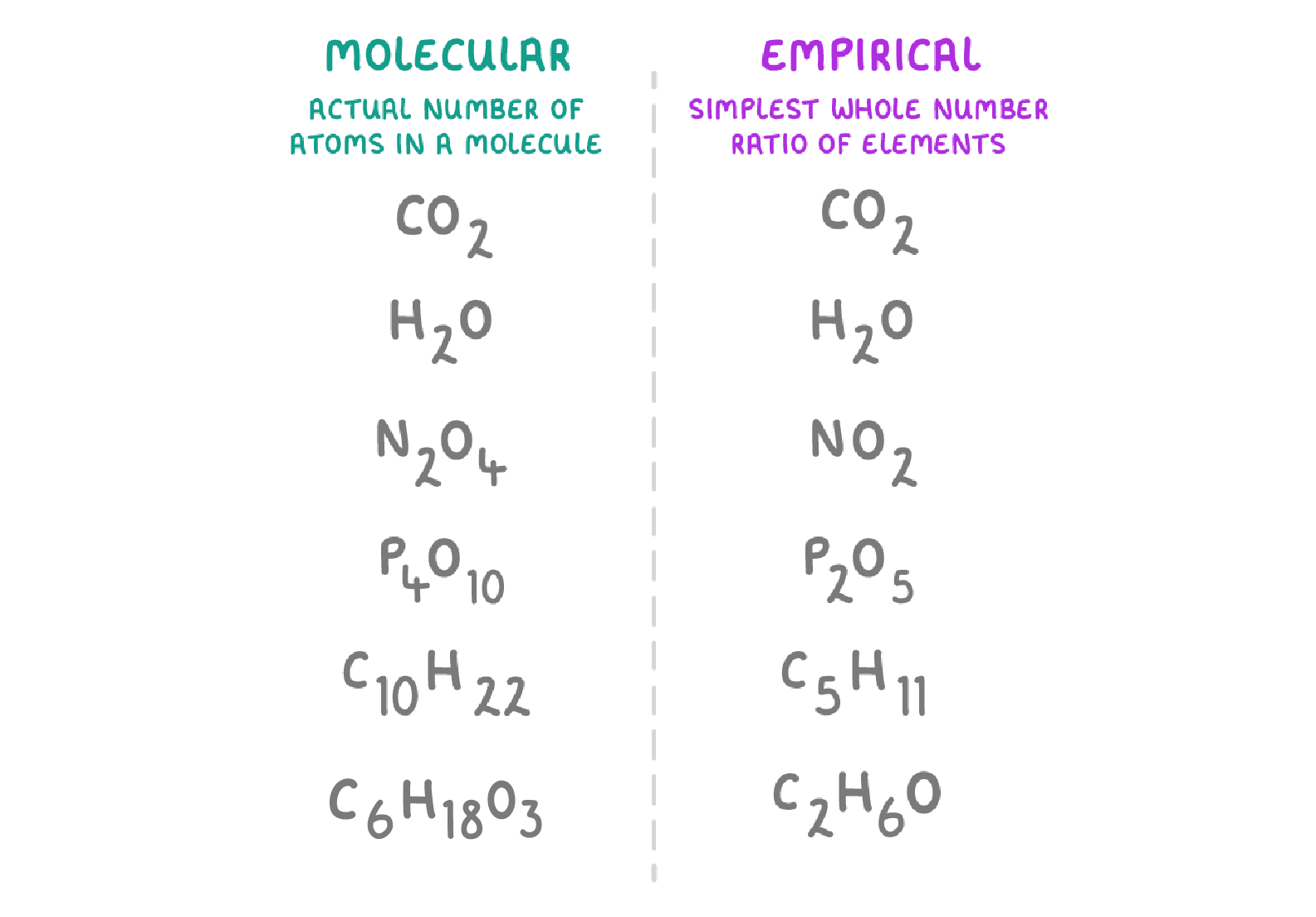
What is the molecular formula
The actual number of each element in a compound
What is the displayed formula
This shows how all the atoms are arranged and all the bonds between them
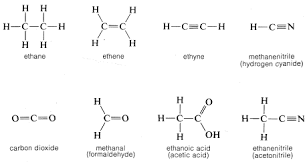
What is the structural formula
This illusrates how the atoms are arranged in a molecule
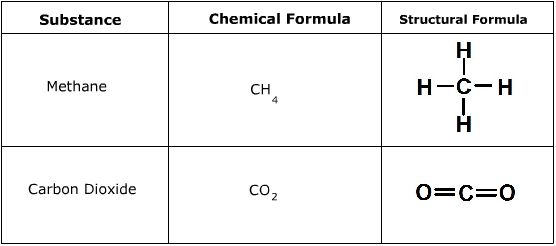
What is the skeletal formula?
This shows the bonds of the crabon skeleton only, with any functional groups. The hydrogen and carbon atoms that are part of the main chain ar enot shown. The carbon atoms are found at the each junction between bonds and at the end of bonds (unless a functional group is already there). Each carbona tom will have sufficient hydrogens bonded so the total number of bonds on each carbon is four
1st step in deciding the skeletal formula of a compound
The longest continuous straight chain of carbon atoms is selected and name according to the parent alkane.
2nd step in deciding the skeletal formula of a compound
The carbon atoms of the chain are numbered in order to indicate the position of any substituents on the chain ; the end of the chain from which the numbering starts is chosen so as to use the lowest values.
3rd step in deciding the skeletal formula of a compound
The name of any substituent prefixes the name of the parent alkane alphabetically
4th step in deciding the skeletal formula of a compound
If more than one group of the same kind is present, this is indicated in the name and all the position are given; in deciding the alphabetical order of the substituents, the prefixes di,tri , tetra are ignored
5th step in deciidng the skeletal formula of a compound
The number assigned to the functional groups are chpsem so as to be as small as possible ; the functional group number are given precedence over those asisgned to substituents
When does isomerism occur?
When2 or more compounds have the smae molecular formula but different structural formula
When does chain isomerism occur
This exists where compounds have the same molecular formula but different structure of the alkane chain
When does positional isomerism occur?
This type of isomerism is shown by molecules that have the same molecular formula and the same chain structure but different position of the functional group
How many structural isomers with a n unbranced carbon chain have the moleculra formula C4H8Br2?
6
How does fractional distillation work?
Fractional distillation separates components of a mixture based on differences in boiling points, using a fractionating column to enhance separation. The fractionating column has a temperature gradient set up inside of it, hot at the bottom cooler at the top. The hydrocarbons with longer carbon chains have stronger vdwfs and so condense lower in the column whilst the hydrocarbons with shorter carbon chains condense higher.
At what temepratures are specific hydrocarbons collected in a fractionating column (diagram)
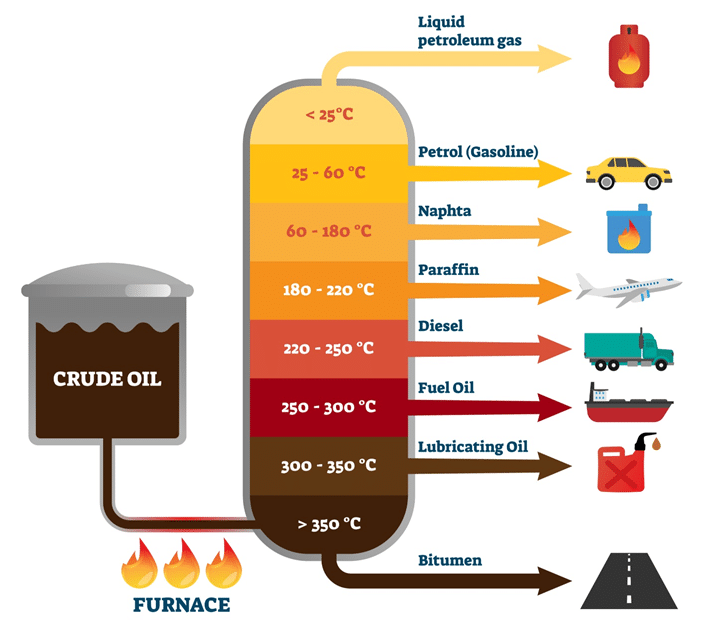
What is cracking?
The process of breaking down longer chained hydrocarbons into the higher demand shorter chained alkanes and alkenes using heat
What are the 2 types of cracking
Catalytic cracking and thermal cracking
What is thermal cracking
Thermal cracking takes place at high pressure and high temperature and produces a high percentage of alkenes (free radical mechanism) used to produce polymers such as poly (ethane)
What is a free radical?
A free radical is an atom or molecule that has an unpaired electron, making it highly reactive. In organic chemistry, free radicals play a key role in chain reactions, such as those involved in the process of thermal cracking.
What is the reactive intermediate in thermal cracking
free radical
What is catalytic cracking?
This cracking takes place at a slight pressure, high temperature and in the presence of a zeolite catalyst and is used mainly to produce motor fuels and aromatic hydrocarbons
What is the reactive intermediate in catalytic cracking
Carbocation
equation for complete combustion of hydrocarbon
The complete combustion of a hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy. The general equation is: Hydrocarbon + O2 → CO2 + H2O.
equation for incomplete combustion of a hydrocarbon
The incomplete combustion of a hydrocarbon reacts with limited oxygen to produce carbon monoxide, carbon, and water, releasing less energy. The general equation is: Hydrocarbon + O2 → CO + C + H2O.
What gases are released from vehicle exhausts
CO, NOx (oxides of nitrogen) and unburned hydrocarbons are all released from vehicle exhausts
What are catalysts sometimes spread over and why
An inert ceramic honey comb and this is because it increases surface area for the catalyst
What are the main catalysts for the removal of pollutatn gaases
Palladiun (Pd), Platinum (Pt), Rhodium(Rh) and Iridium (used for nitrogen)
How do catalytic converters work for nitrate oxides, carbon monoxides and unburned hydrocarbons
The exhaust gases are mixed with air and passed over the solid catalyst which converts the oxides of nitrogen into nitrogen whilst the unburned hydrocarbons and the carbon monoxide are oxidised into carbon dioxide and water. The relase of the harmful pollutants in the local area is reduced.
Equations for converting unburned hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide and water
2NO → N2 + O2
2NO +2CO → 2CO2 +N2
C8H18 + 2 SNO → 8CO2 +9H2O + 25/2 N2
How is sulfur dioxide made and what problems does it cause
Combustion of hydrocarbons containing sulfur leads to sulfur dioxide that causes air pollution. This is because the sulphur dioxide dissolves in rainwater and causes acid rain which kills fish and trees and damages limestone buildings.
Equation for making sulfur dioxide and sulfuric acid from sulfur dioxide
2S + O2 → SO2
SO2 + H2O + 1/2O2 → H2SO4
How can sulfur dioxide be removed and what is the balanced symbol equation to represent this?
Sulfur dioxide can be removed from flue gases using calcium chloride
SO2 +CaO → CaSO3
Acid-base reaction