Punnett Squares
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
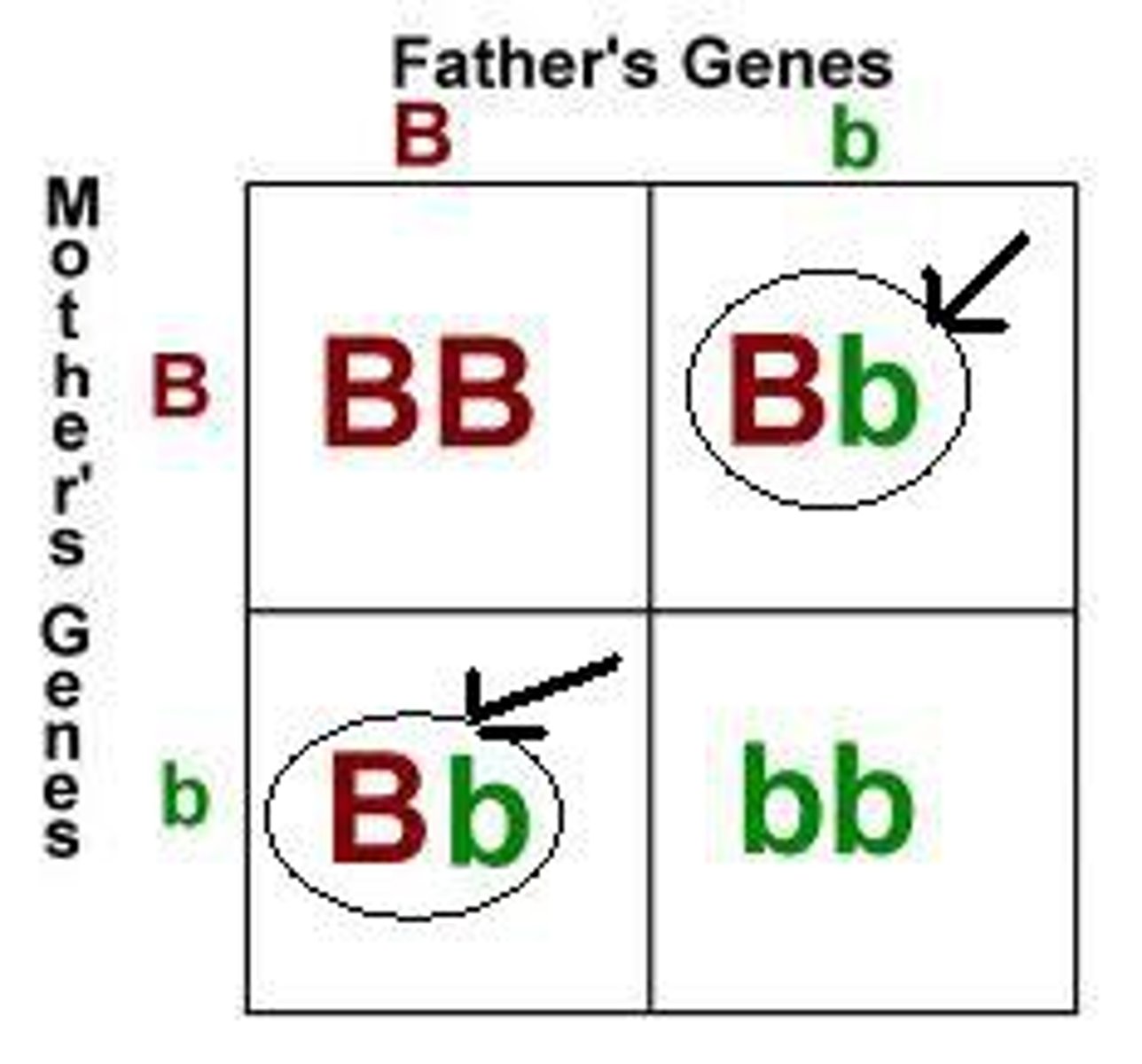
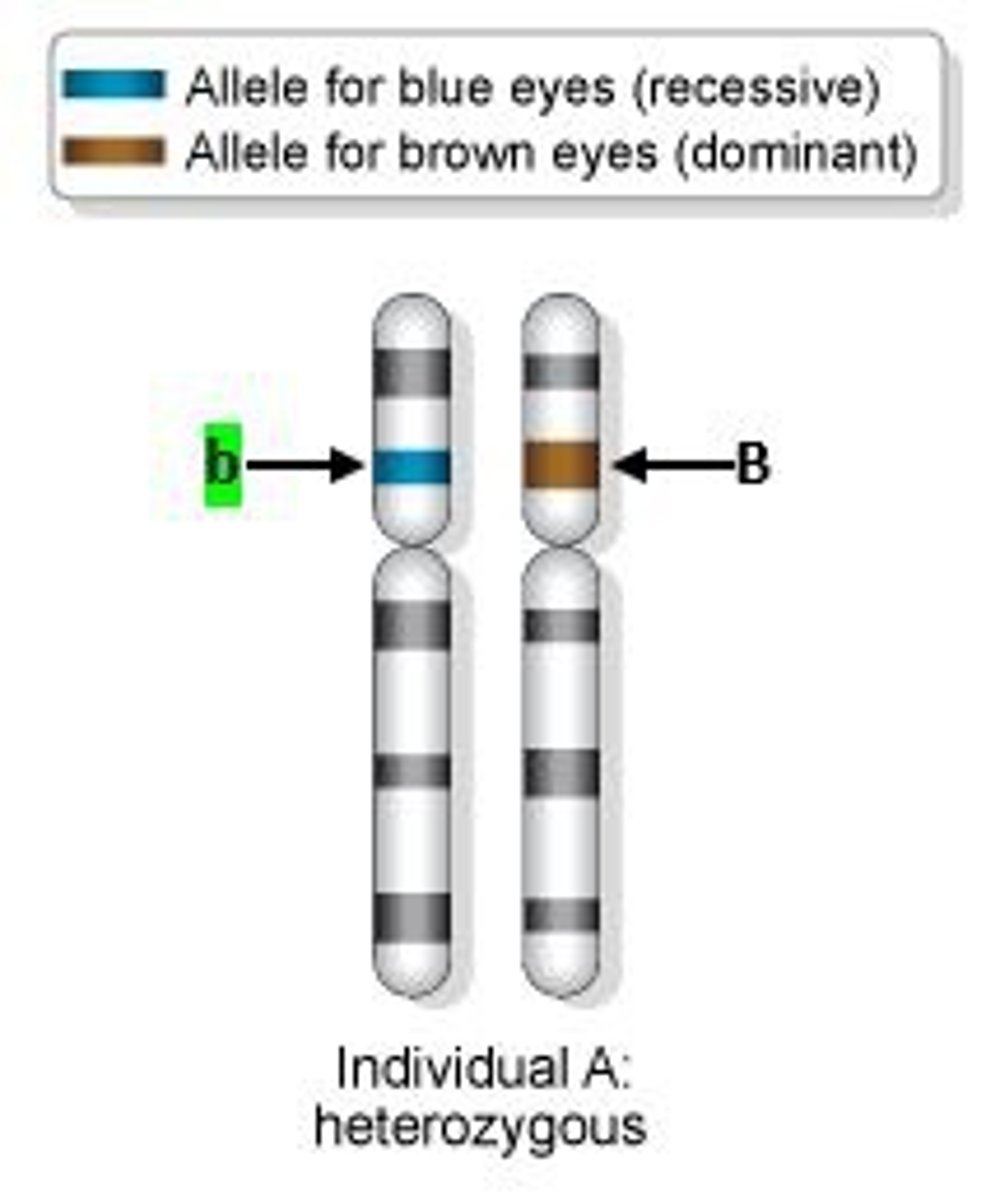
Heterozygous
A genotype with two different size letters. Ex. Bb
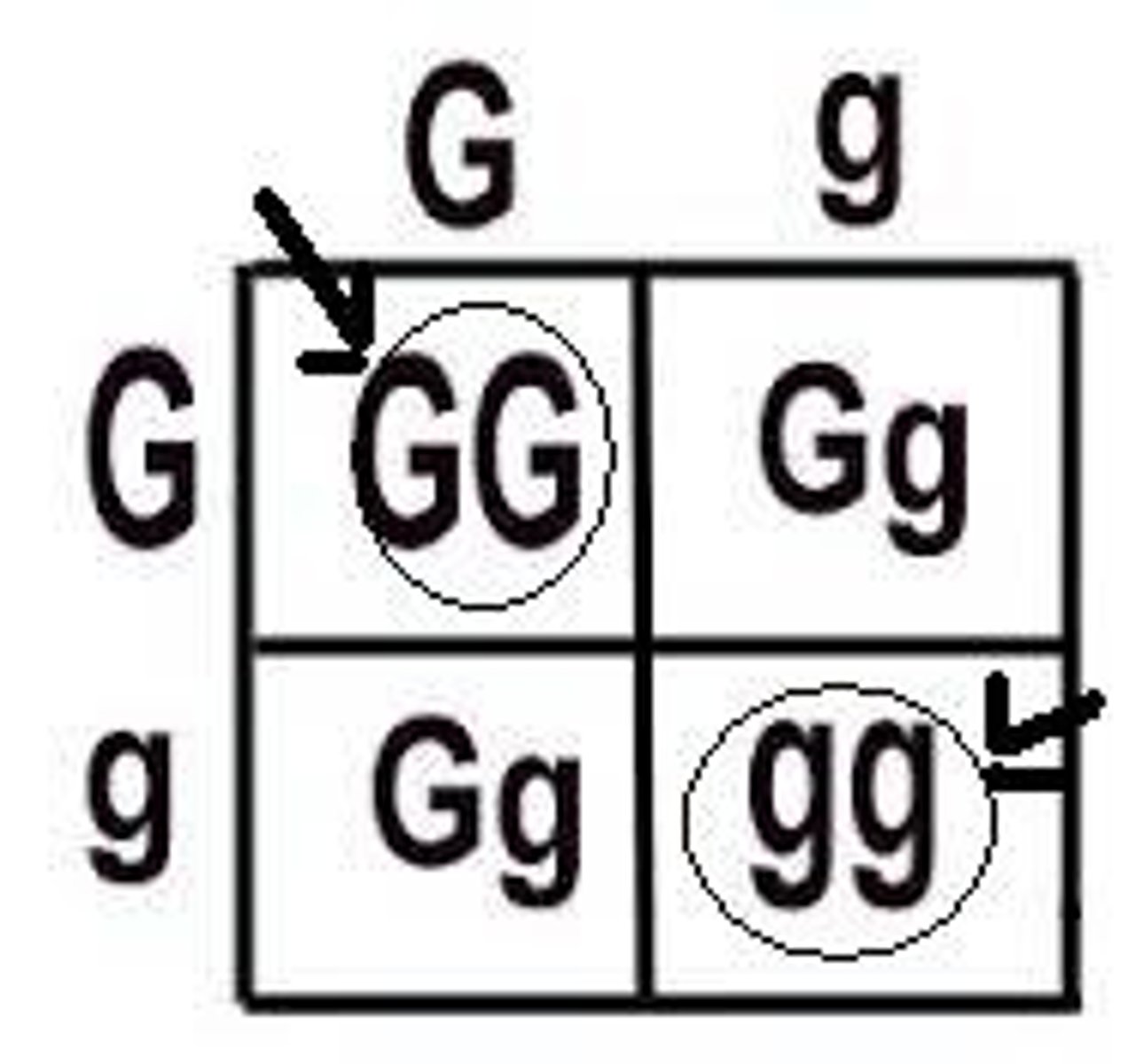
Homozygous
A genotype with two of the same size letters. Ex. gg, GG
Allele
A version of a gene represented by a letter. There are two of these in each genotype.
Genotype
The two letters that represent the genes of one parent. We need two of these to make a Punnett square.
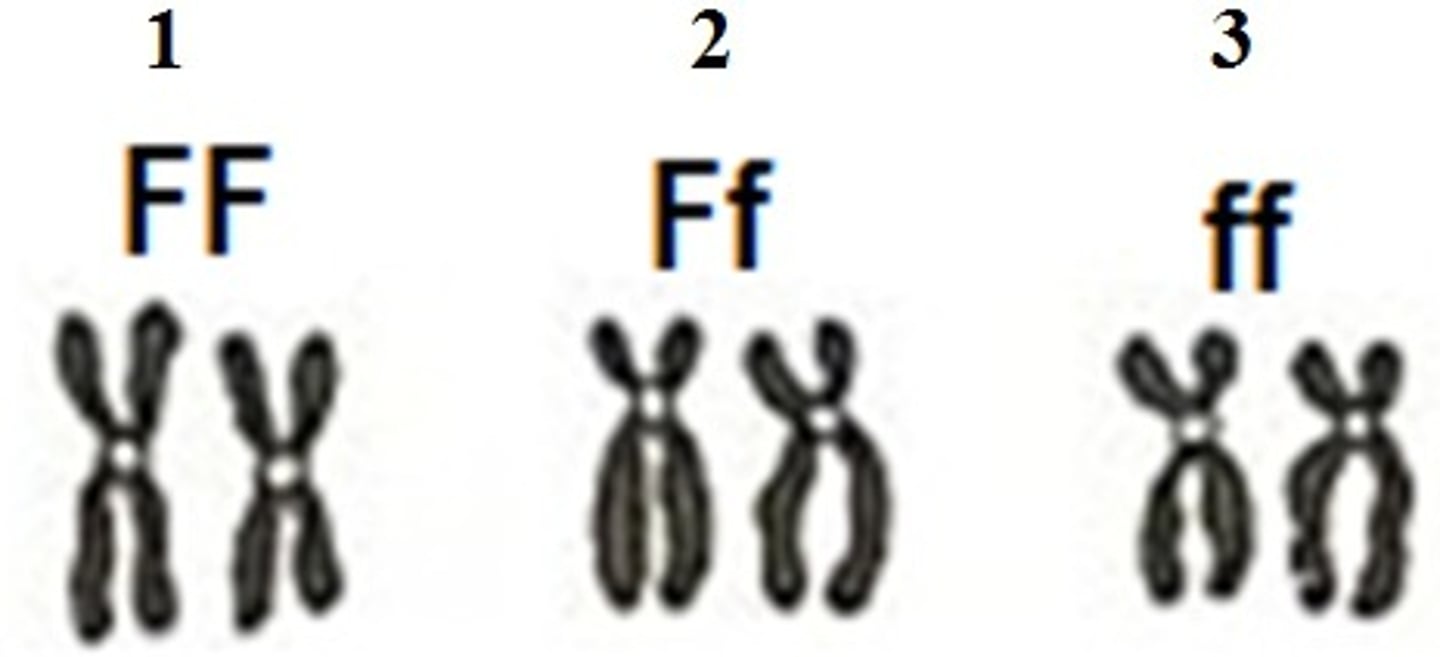
Phenotype
The trait or words explaining what a genotype means. Ex. Short pea plant
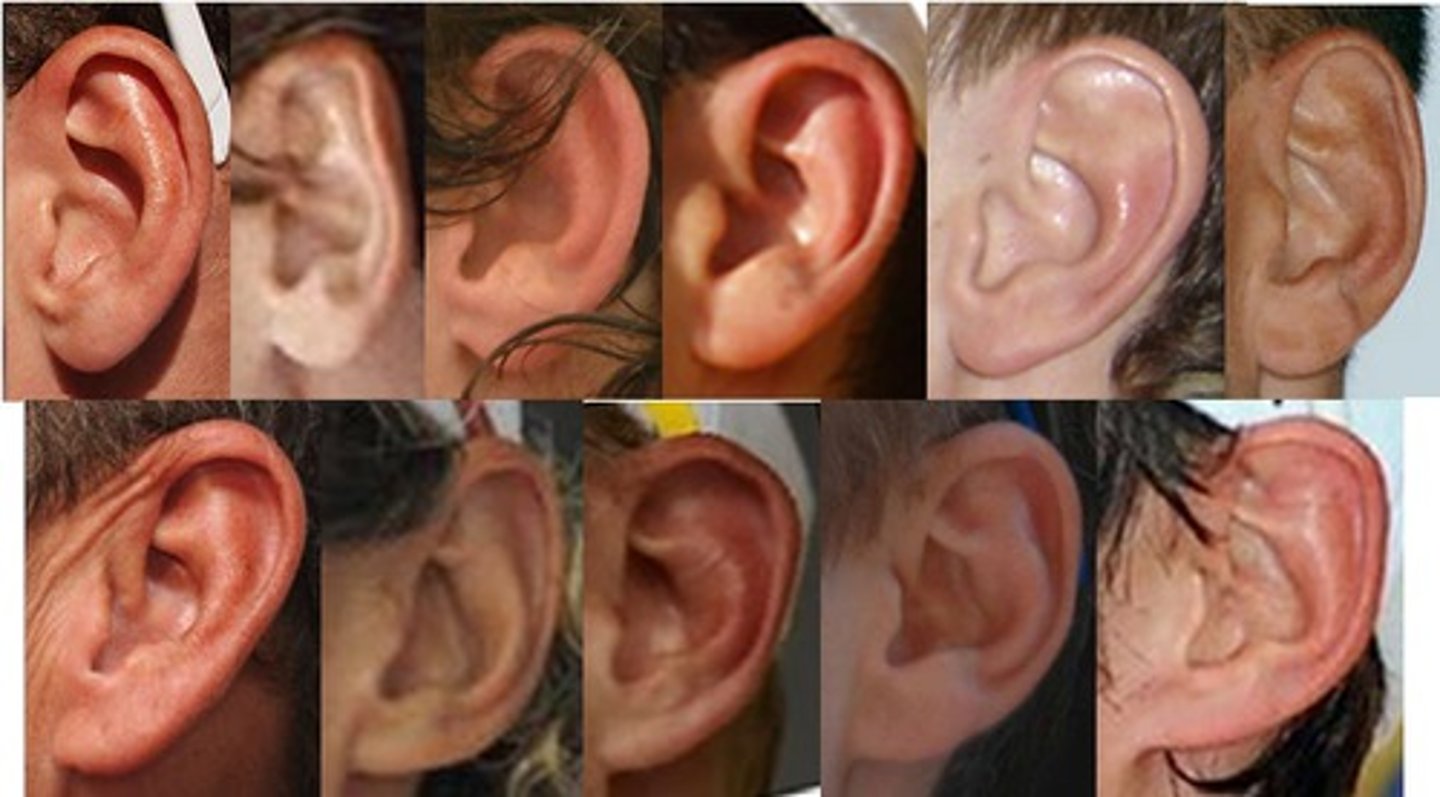
Probability
The likelihood that a particular trait will be passed on from parent to offspring.
Gregor Mendel
Monk who discovered the basics of how traits get passed on using Pea Plants.

Cross
The exchange of genetic material during reproduction.
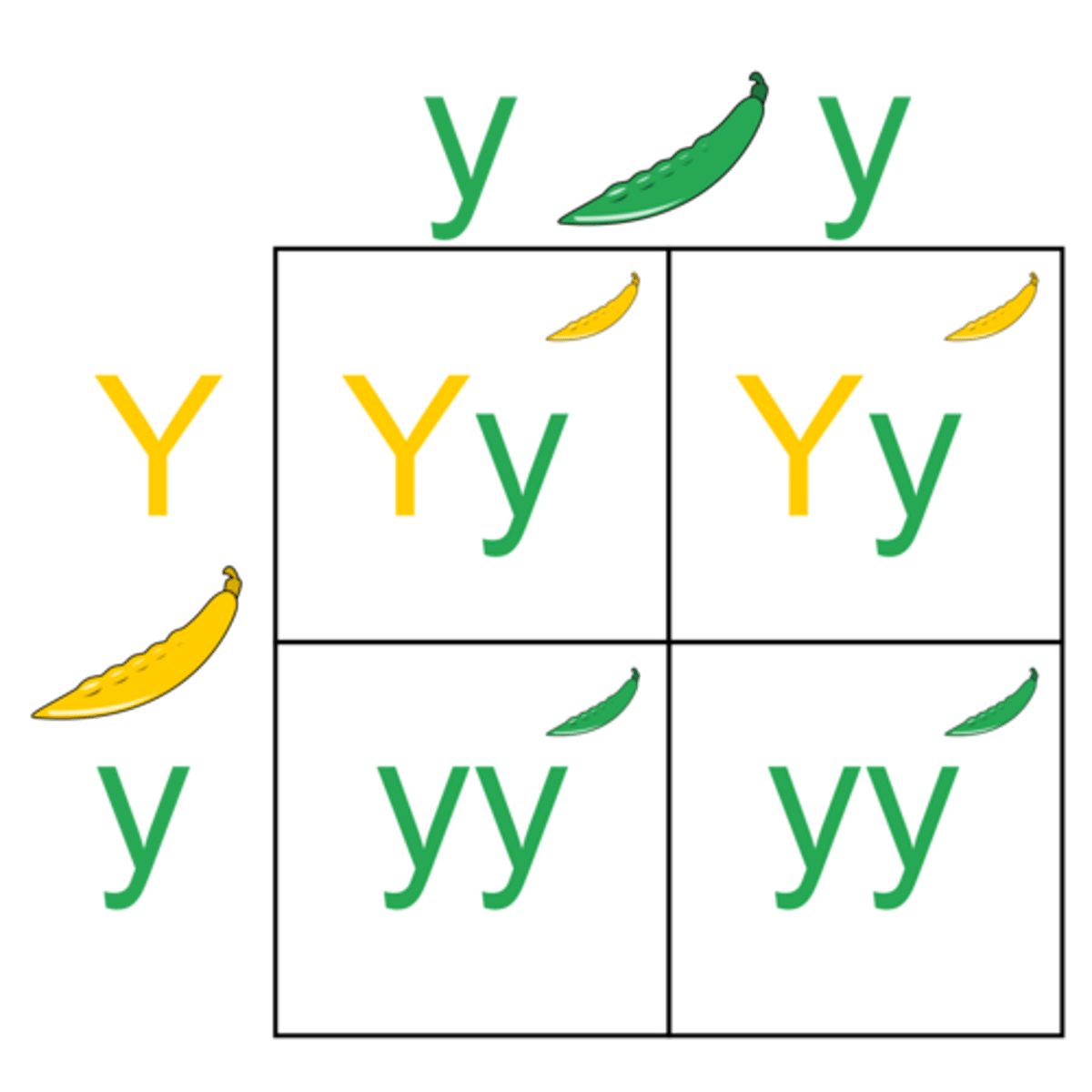
DNA
A molecule that contains the genetic instructions to make each organism.
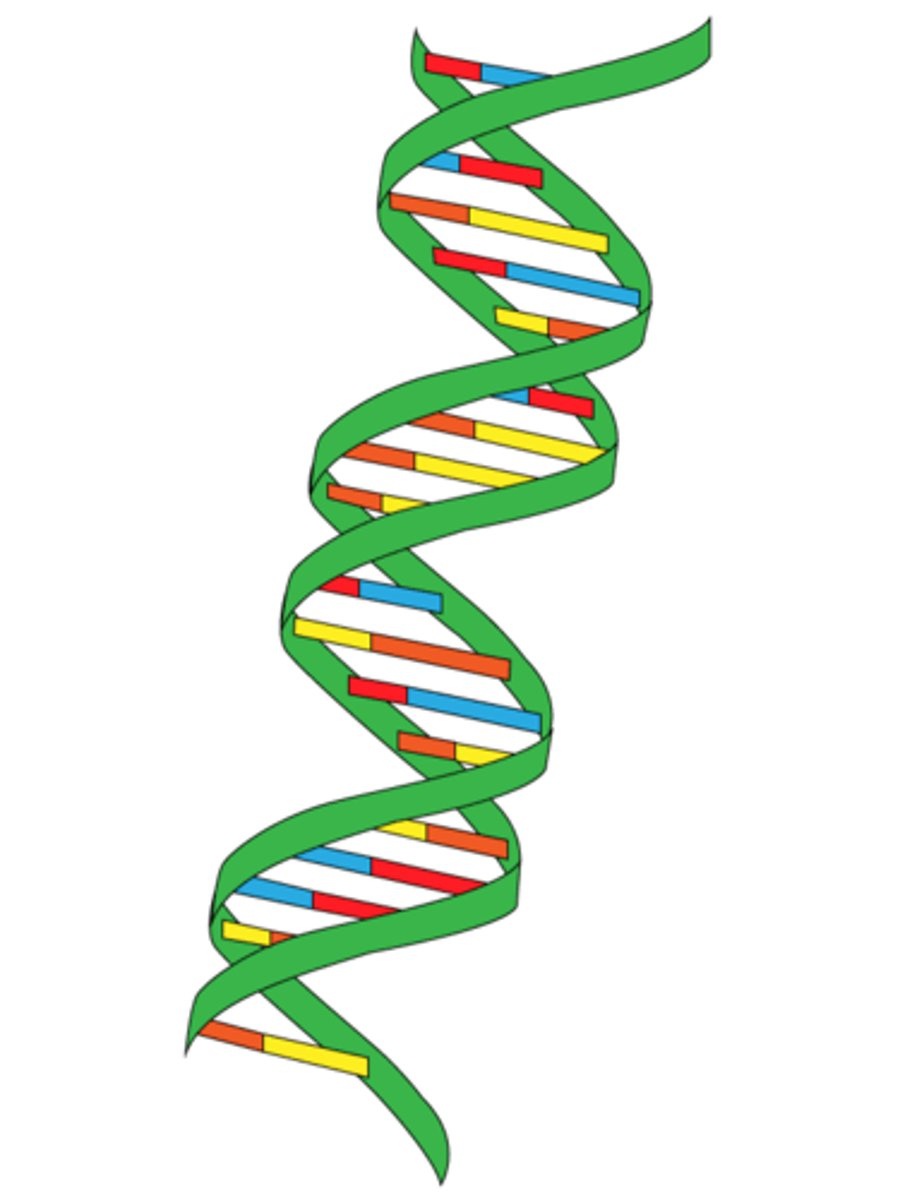
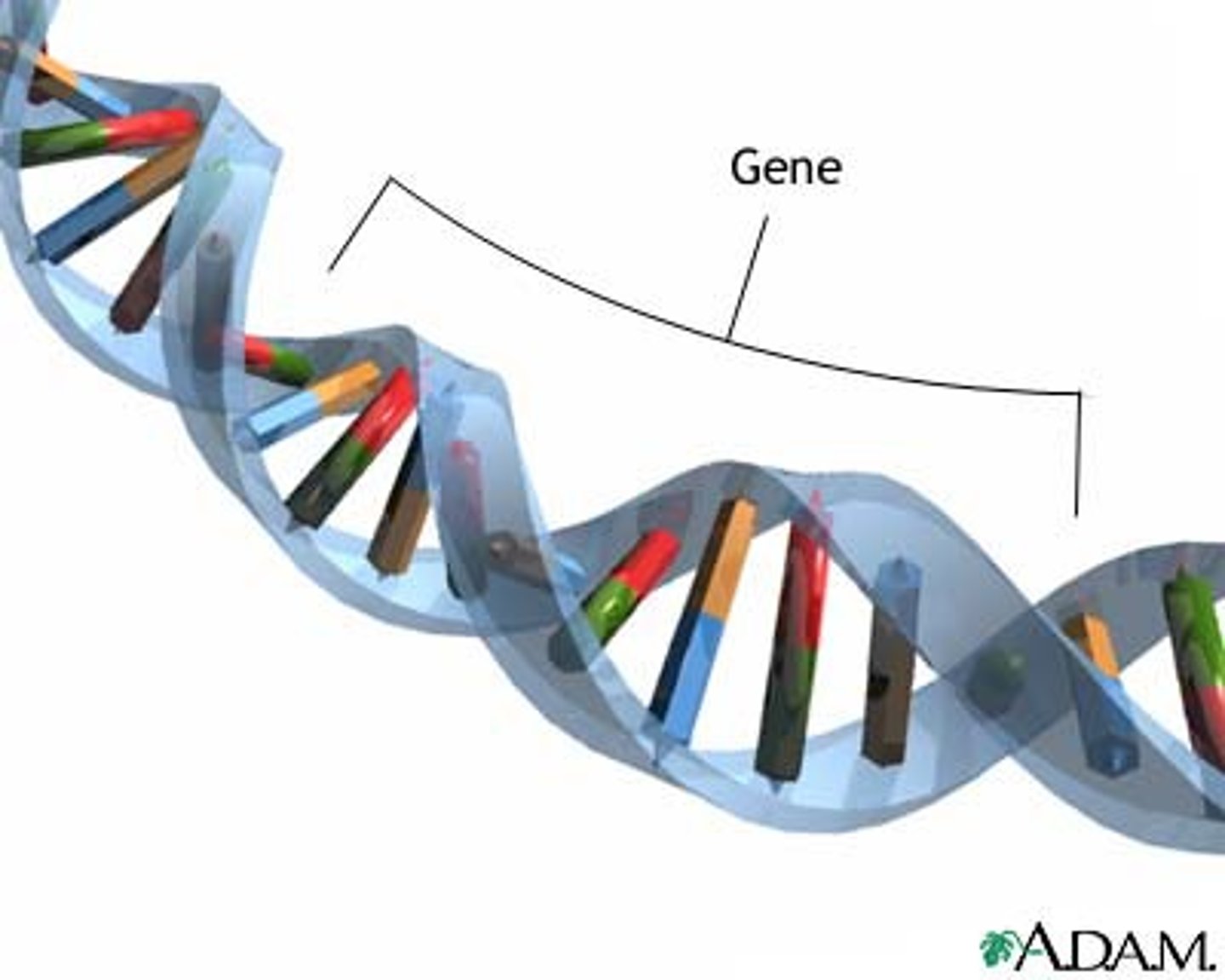
Gene
A part of DNA that carries information that determines your traits.
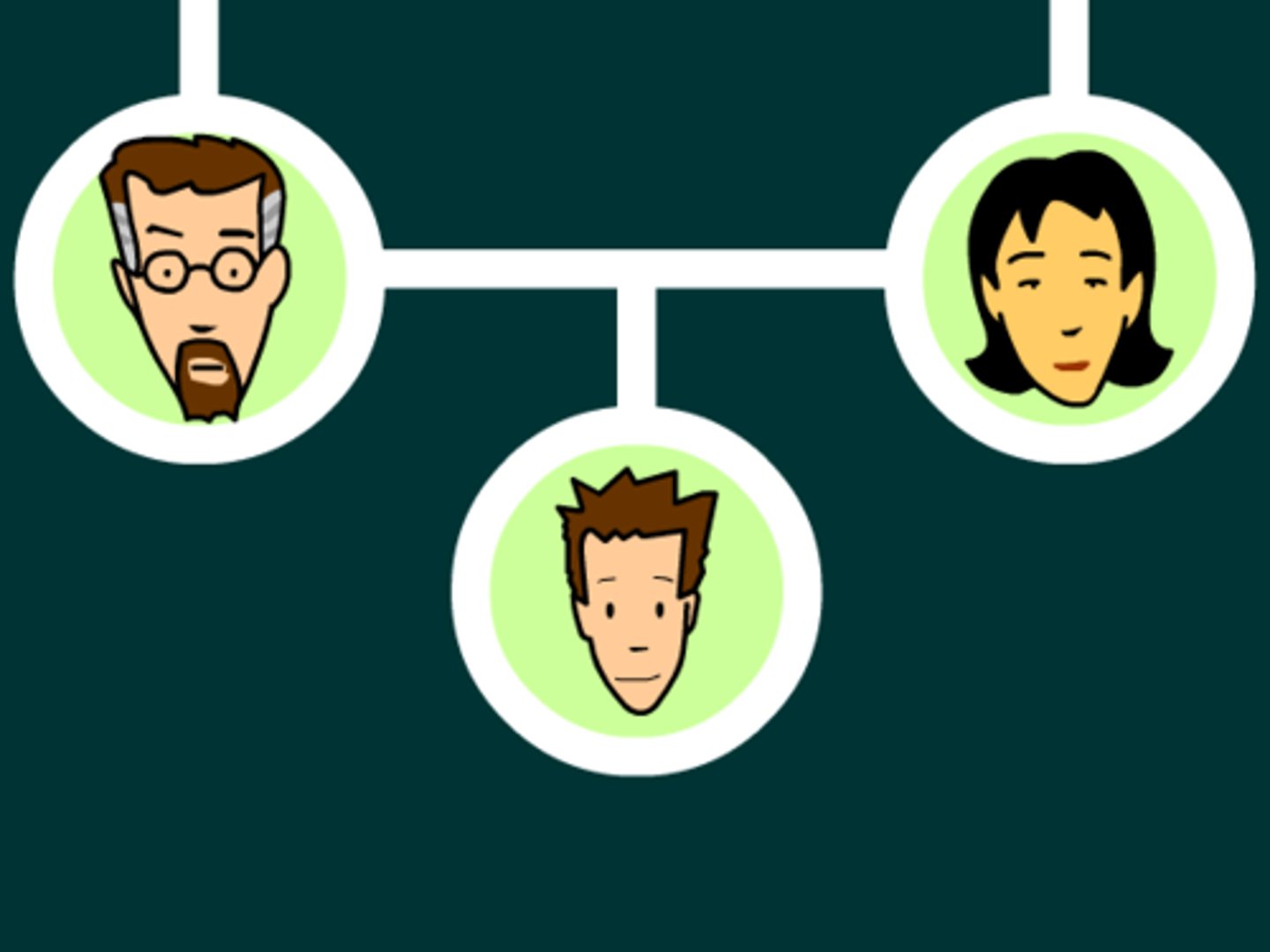
Heredity
The passing of traits from parents to offspring.
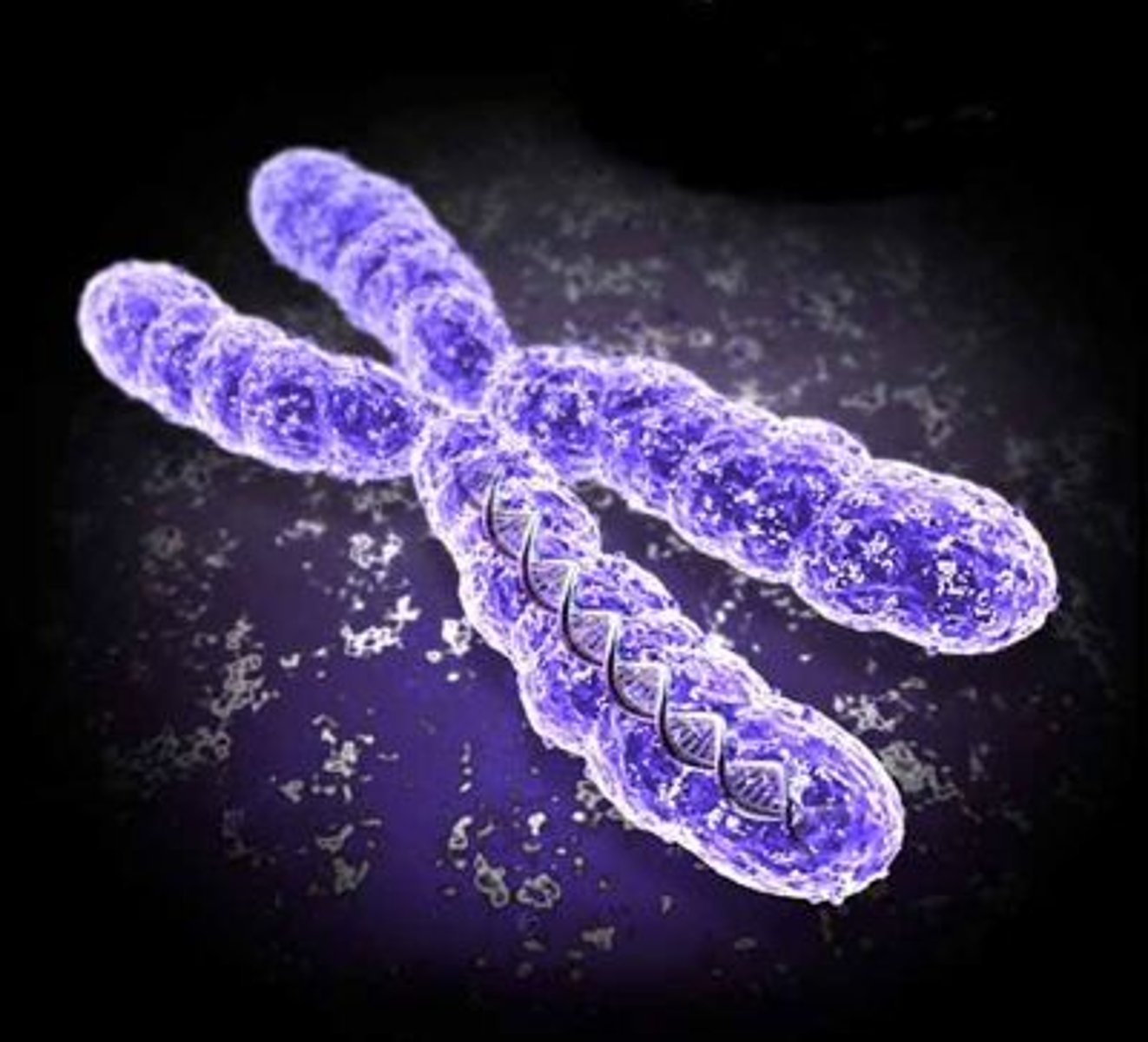
Chromosome
A structure located inside the nucleus of the cell that contain the DNA.
Dominant
The stronger version of a gene that will appear if it is present.
Recessive
The weaker version of a gene that will go into hiding if the dominant gene is present.
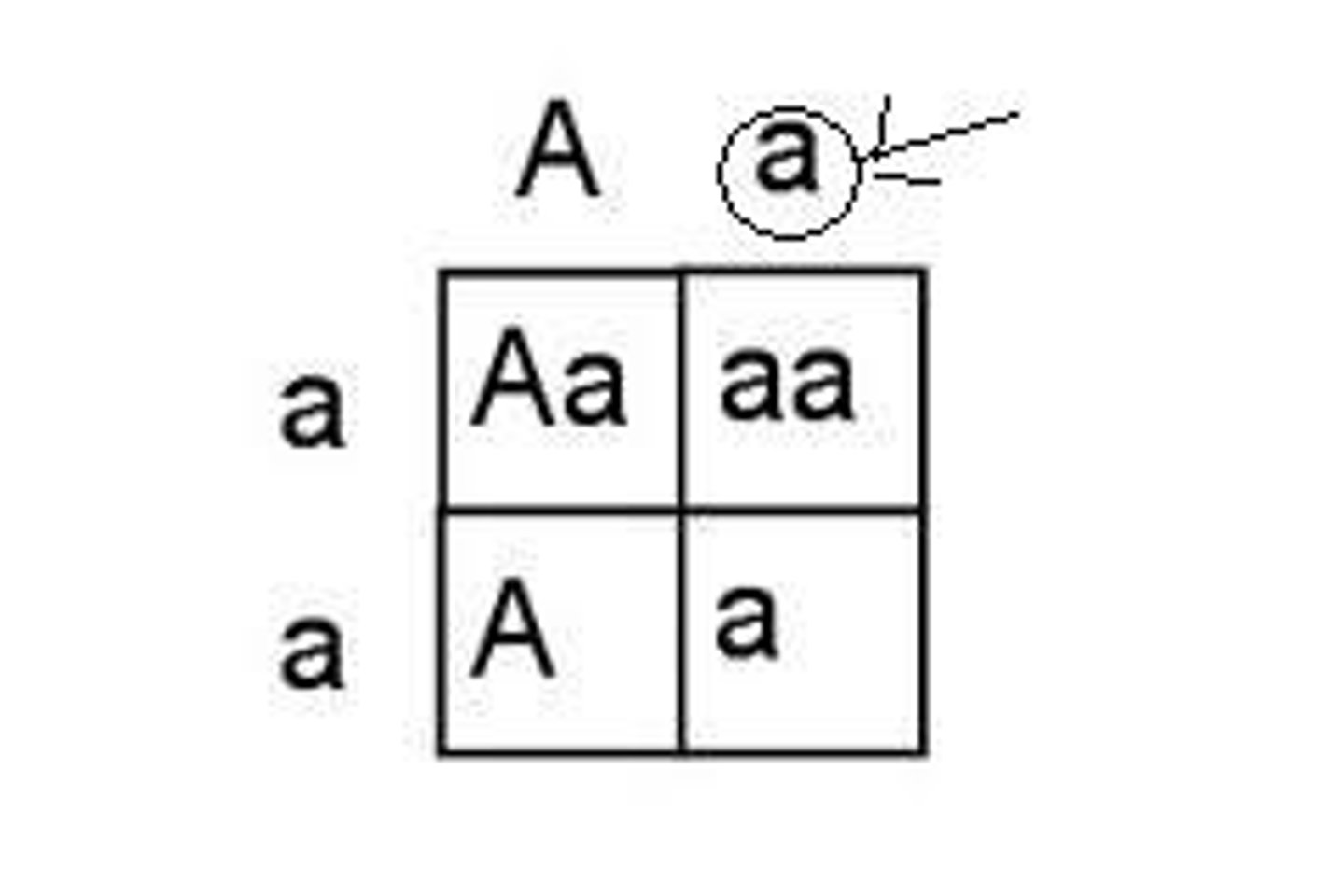
Offspring
Product of reproduction, a new organism produced by one or more parents

P Generation
the parental generation

F1 Generation
the first generation of offspring
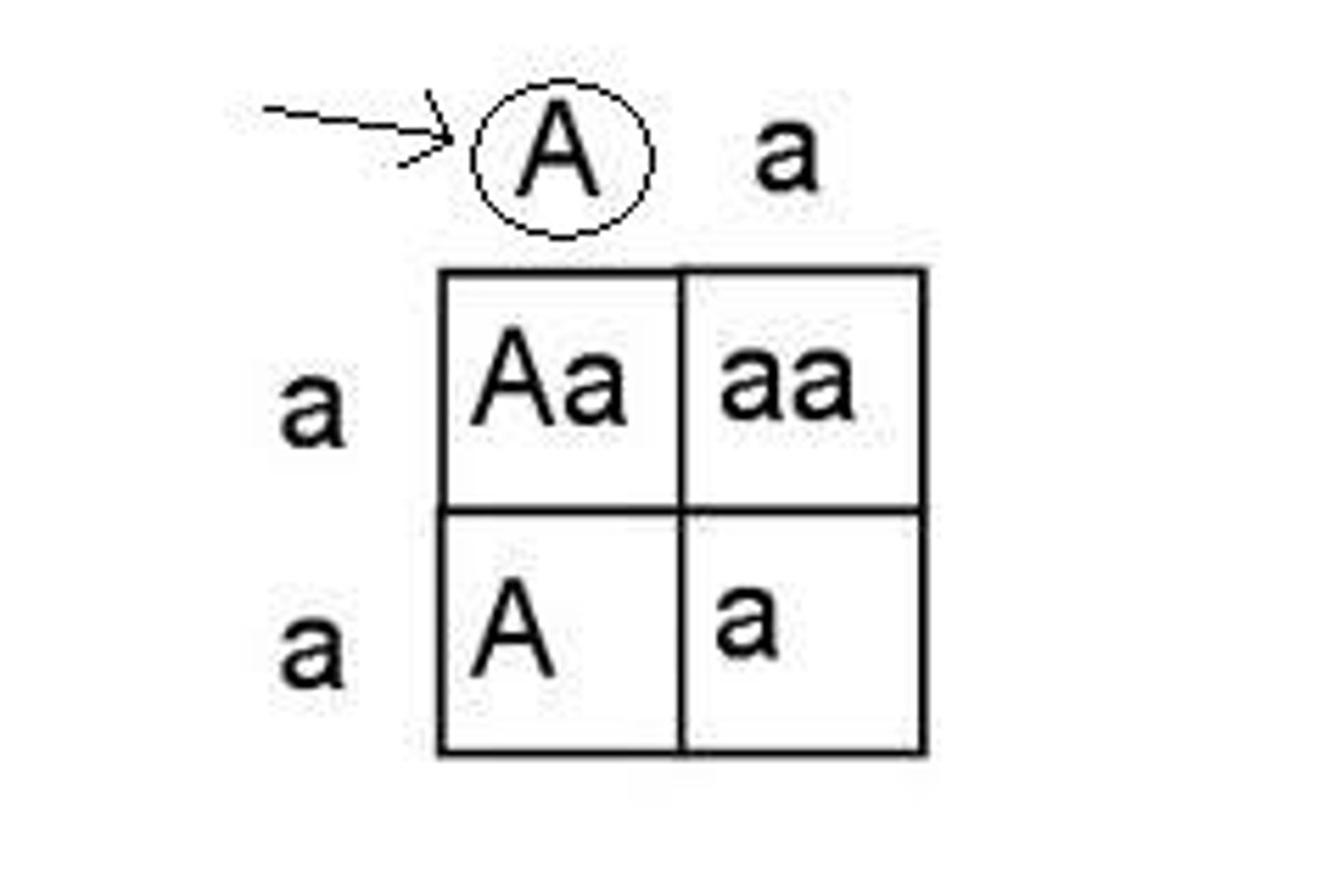
punnett square
a tool scientists use to investigate the possible combinations of genetic crosses

probability
A number that describes how likely it is that an event will occur

incomplete dominance
A pattern of inheritance in which two alleles, inherited from the parents, are neither dominant nor recessive. The resulting offspring have a phenotype that is a blending of the parental traits.

co-dominance
Situation in which both alleles of a gene contribute to the phenotype of the organism
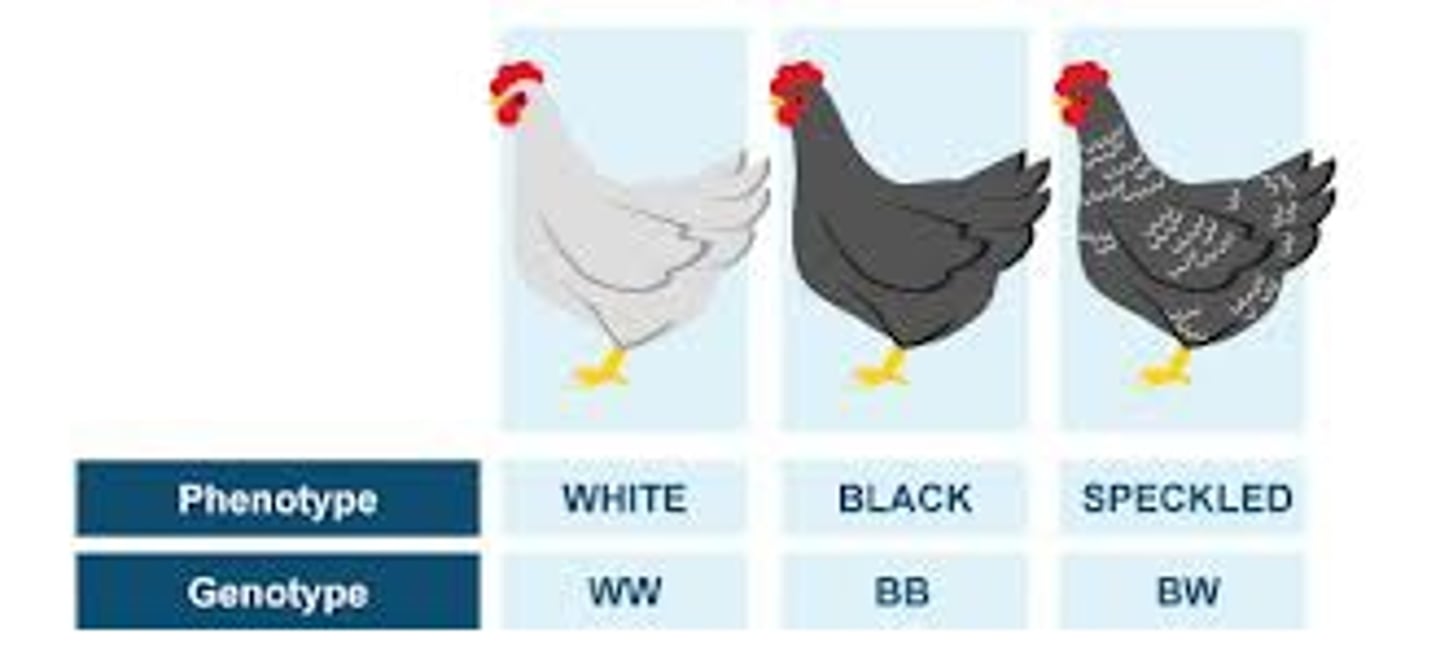
multiple alleles
A gene that has more than two alleles

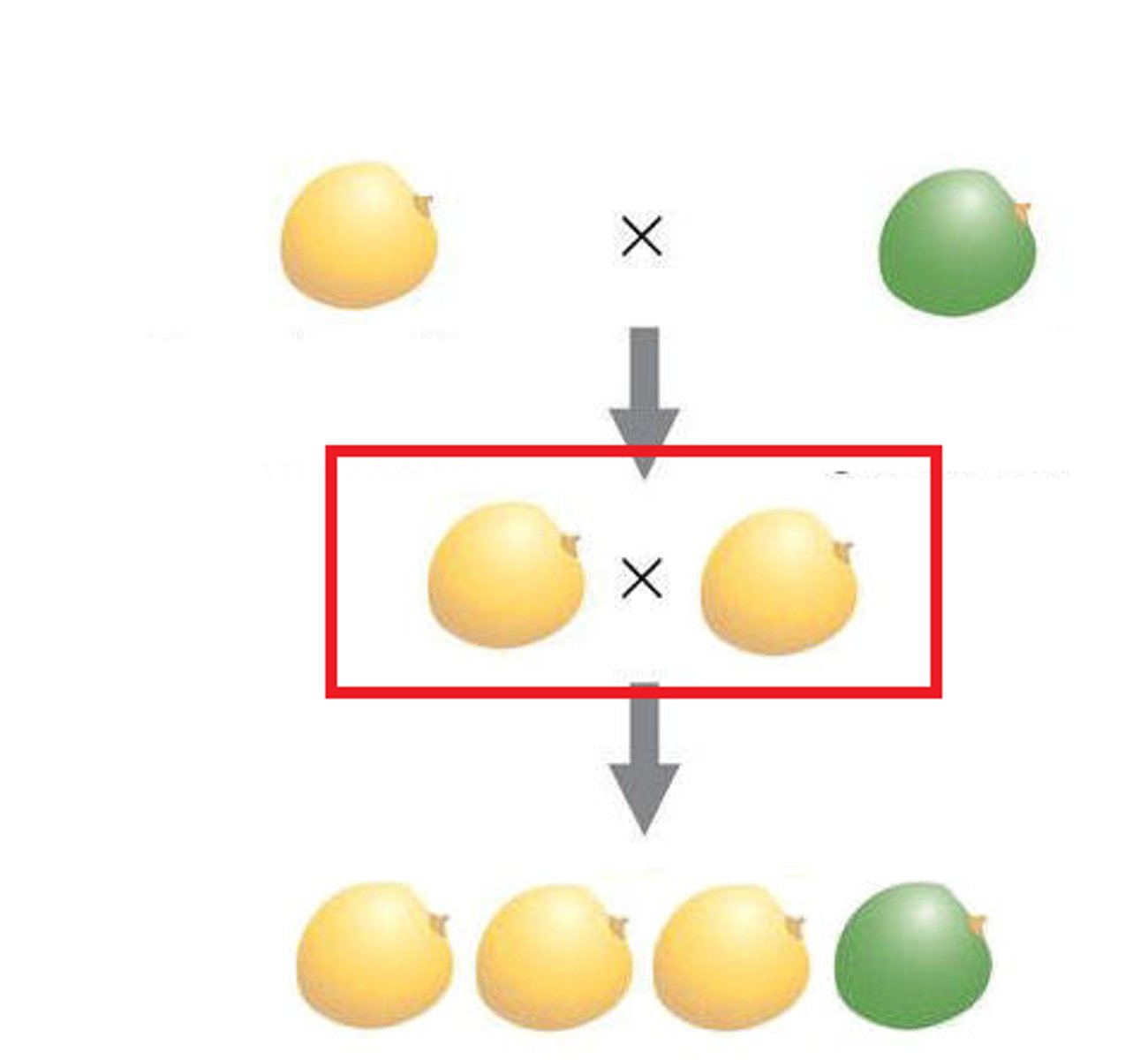
hybrid
Offspring of crosses between parents with different traits