Untitled Flashcards Set
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
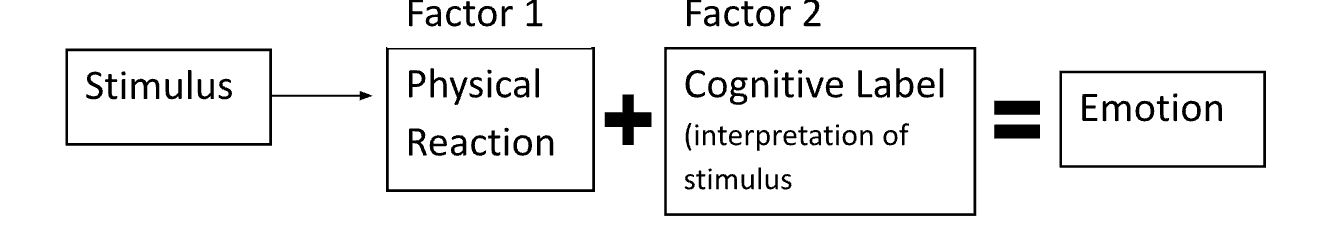
Theory suggesting that emotions result from our interpretations of bodily reactions.

Theory proposing that emotions and physiological responses occur simultaneously.
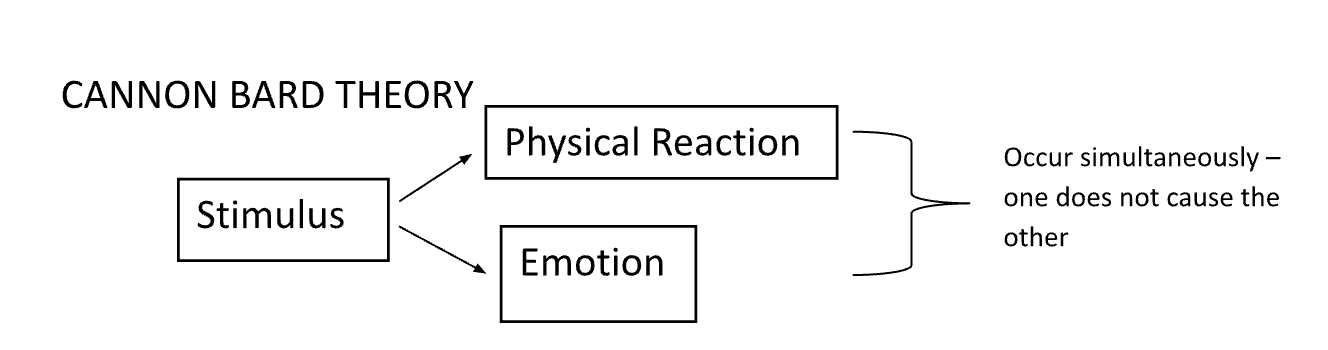
Theory stating that emotion is based on physiological arousal and cognitive labeling
The body's response to stress in three phases:
Alarm reaction Stage (sympathetic nervous system goes into fight or flight)
Resistance/adaptation stage (body tries to adapt to stress, endocrine system continues to secrete stress)
Exhaustion stage (body can no longer cope, resistance is depleted)
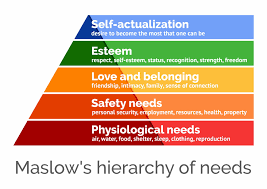
Maslows hierarchy of needs

Ancel Keys study
Investigated effects of semi-starvation. Men volunteerly starved selves, living off of smallest about of food they could. Men became obsessed with food and lost interest in sex and activities.