Chapter 1 - The foundations of economics
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
social sciences (3)
academic disciplines that study human society and social relationships
microeconomics (3)
examines the behaviour of individual decision-making units in the economy.
Two main groups are consumers/households and firms/businesses
macroeconomics (3)
examines the economy as a whole to obtain a broad overall picture of the economy
aggregates (3)
wholes or collections of many individual units, such as the sum of consumer behaviours and the sum of firm behaviours, and the total income and output of the entire economy
scarcity (4)
resources are insufficient to satisfy unlimited human needs and wants
choice (4)
since resources are scarce, it is not possible for all human needs and wants to be satisfied. This means that choices must be made about what will be produced and what will be foregone/sacrificed
efficiency (4)
making the best possible use of scarce resources to avoid resource waste
allocative efficiency (4)
when scarce resources are used to produce what people want and production is efficiency
equity (4)
the idea of being fair and just
economic well-being (4)
security with respect to income and wealth, having a job and housing
the ability to pursue one’s goals work productively and develop one’s potential
the ability to have a satisfactory quality of life, which includes numerous factors such as health, education, social connections, environmental quality, personal security
the ability to maintain all of the above over time
sustainability (4)
long-term maintenance or viability of any particular activity or policy
the ability of the present generation to satisfy its needs by the use of resources, and especially non-renewable resources, without limiting future generations’ ability to satisfy their own needs
interdependence (5)
economic decision-makers interact with and depend on each other
nobody is self-sufficient
occurs on many levels, individuals, communities, to nations and to groups of nations
consumers, workers, firms, governments, and all other individuals or groups of individuals depend on one another for the achievement of their economic goals
intervention (5)
govenrment getting involved with the workings of markets
economics (6)
the study of choices leading to the best possible use of scarce resources in order to best satisfy unlimited human needs and wants
4 FOPs (7/8)
land
labour
capital
entrepreneurship
opportunity cost (8)
the value of the next best alternative that must be given up or sacrificed in order to obtain something else
free good (9)
any good that ins’t scarce, and therefore has zero opportunity cost
basic economic questions (10)
what/how much to produce
how to produce
for whom to produce
rationing (13)
a method used to apportion or divide something up between its interested users
the method used to make resource allocation and output/income distribution decisions
two types: price and non-price rationing
free market economy (13)
uses price rationing to make resource allocation and output/income distribution decisions
planned economy (13)
uses non-price rationing to make resource allocation and output/income distribution decisions
production possibility curve (or frontier) — PPC (15-19)
represents all combinations of the maximum amounts of two goods that can be produced by an economy, given its resources and technology, when there is full employment of resources and efficiency in production
All points on the curve are known as production possibilities
why can’t an economy produce outside its PPC? (16)
because of scarcity
with its fixed quantity and quality of resources and technology, the economy cannot move to any point outside the PPC
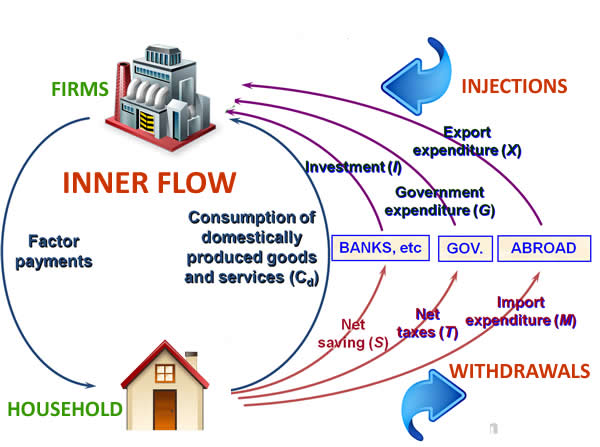
leakages in circular flow of income model (21)
household savings
taxes
imports
injections in circular flow of income model (21)
investment
government spending
exports
open economy (22)
economy has international trade with imports and exports
closed economy (22)
economy has no international trade with imports and exports
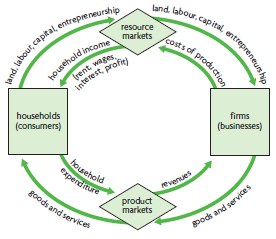
structure of circular flow of income model (no leakages and injections) (20)
Markets:
resource markets
product markets
Economic decision makers:
households (consumers)
firms (businesses)
structure of circular flow of income model (with leakages and injections) (21)
imports (21)
goods and services produced in other countries and purchased by domestic buyers
exports (21)
goods and services produced domestically and purchased by foreigners
positive economics (23)
based on positive statements, which are about something that is, was or will be.
“the unemployment rate is 5%”
“a higher price of apples results in fewer apples purchased”
“unemployment will increase next year”
normative economics (23)
based on beliefs and values.
“the unemployment rate should be lower”
“health care should be available free of charge”
refutation (27)
to contradict it, disprove it or show it to be false
Adam Smith (32/33)
wrote The Wealth of Nations 1776
father of economics
laissez faire - let it do / a free market without government intervention
Jeremy Bentham (33)
founder of utilitarianism
“it is the greatest happiness of the greatest number that is the measure of right and wrong”
Karl Marx (35)
wrote Das Kapital in 1867
Say’s Law (35)
supply creates its own demand, a theory that claims that the economy tends toward full employment in the absence of any government intervention
John Maynard Keynes (36/37)
wrote The General Theory in 1936
according to Keynes, wages are ‘sticky’, meaning that can’t change easily
circular economy (38)
goods should be produced in such a way that they can be repaired rather than thrown out. In addition, they would be made out of biological materials so that once discarded they can go back to the biosphere and prevent pollution of the planet