Nutrition NDFS 100 BYU EXAM 2 BYU
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
What are the functions of fat in the body?
fuel storage, cushion, temperature regulation, cell membrane,transport and raw material, hormone synthesis, nerve impulse
What are the functions of fat in food?
concentrated calories, fat-soluble vitamins, aroma, flavor, texture,tenderness, satiety
True or False: Fat is the bodies major form of stored energy
true
T or F: Fat forms the major material of the cell membranes
true
T or F: Fat provides no nutrients
False; it provide essential fatty acids, fat-soluble vitamins, and other needed compounds.
What are the three types of lipids?
triglycerides, phospholipids, sterols
What is another name for triglycerides?
fatty acids
What is the structure of a triglyceride?
3 fatty acids + 1 glycerol molecule
In what two ways do fatty acids differ from one another?
chain length and degree of saturation
T or F: the shorter chain fatty acids or more unsaturated ones are harder
False; they are softer
What do fatty acids in food do?
Influence the composition of fats in the body
What does it mean when a fatty acid is saturated?
every available bond from the carbon chain is holding a hydrogen atom
What does it mean when a fatty acid is unsaturated?
the fatty acid carbon chain has a place where hydrogens are missing
What is it called on a carbon chain where a hydrogen is missing?
point of unsaturation
What is a monounsaturated fatty acid?
the carbon chain contains just one point of unsaturation
What is a polyunsaturated fatty acid?
the carbon chain contains two or more points of unsaturation
What is polyunsaturated often abbreviated as?
PUFA
T or F: The more carbon atoms in a fatty acid, the longer it is
True
T or F: The more hydrogen atoms attached to the carbons in a fatty acid, the more saturated the fatty acid is
True
What type of fatty acid is this?
saturated
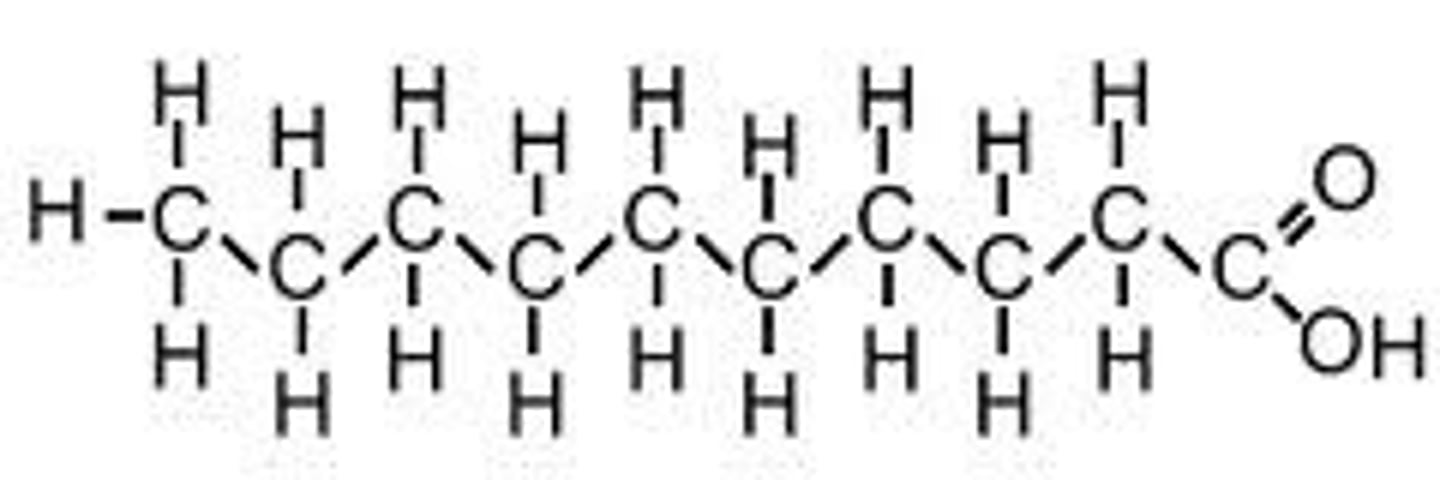
What type of fatty acid is this?
polyunsaturated
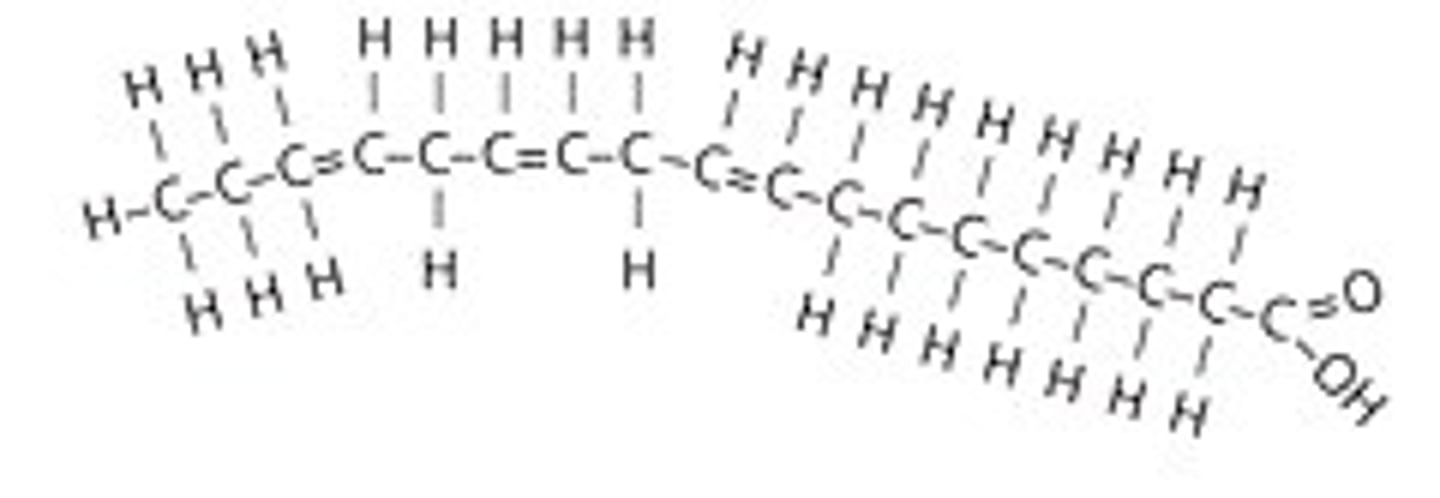
What does the degree of saturation in a fatty acid of a fat determine?
the fat's softness or hardness
What does it mean if a glyceride is solid at room temperature?
it contains more saturated fat
What does it mean if a glyceride is liquid at room temperature?
it contains less saturated fat
T or F: fluid milk is a solid fat
True
What is an essential Fatty Acid?
fatty acids that the body needs but cannot make
What are the four types of fatty acids?
saturated, monunsaturated, polyunsatured, trans
what are the properties of saturated fatty acids?
solid at room temp.
what are the health implications for saturated fats?
not good
What are sources of saturated fatty acids?
coconut oil, animal products
What are the properties of monounsaturated fatty acids?
liquid at room temp.
What are the health implications for monounsaturated fatty acids?
good:)
What are the sources of monounsaturated fatty acids?
canola olive peanut sesame oils
What are the properties of polyunsaturated fatty acids?
liquid at room temp
What are the health implications for polyunsaturated fatty acids?
good not great
What are the sources for polyunsaturated fatty acids?
Plant oils, flaxseed and fish oils
What polyunsaturated fatty acids do our body NOT make?
Omega 3 and Omega 6
What do saturated fats do to the HDL and LDL?
Decrease HDL and increase LDL
What do monounsaturated fats do to the LDL and HDL?
Decrease LDL... does nothing to the HDL
What do polyunsaturated fats do to the HDL and LDL?
Decrease both
What is bile?
an emulsifier
What is a phospholipid?
a type of lipid
What is a well-known sterol?
Cholesterol
Why is cholesterol important?
Fat digestion and cell structure
Are sterols an essential nutrient?
no
can sterols be made by the body?
yes
Do sterols provide energy?
no
What is a source of trans fat?
margarine and shortening
What is the AMDR for fats?
20-35%
How much of our fat calories should come from saturated fats?
>10%
What happens to fats in the mouth in the process of digestion?
nothing
What happens to fats in the process of digestion in the stomach?
no
What happens to fats in the process of digestion in the small intestine?
emulsification
What happens to fats in the process of digestion in the large intestine?
nothing
What are Lipoproteins?
any kind of fat transporter
What are chlyomicrons?
transports fatty acids from small intestine to the liver
What is VLDL?
transports triglycerides from liver to body tissues
What is the LDL?
transports cholesterol from liver to body tissues
What is HDL?
takes excess cholesterol from cells back to the liver
T or F: a high LDL is good to have
false
What are three parts of an amino acid?
amino group, side chain, acid group
How many amino acids are essential?
nine
What are the functions of protein?
growth, maintenance, antibodies, acid/base, transport, energy, fluid/electrolyte balance, blood clotting, building body compounds
What are essential amino acids?
amino acids that we need to ingest from foods
What are non-essential amino acids?
amino acids that we can make on our own
How do you measure nitrogen balance?
subtract protein intake from protein excretion
What is positive nitrogen balance?
growth (children, pregnant,bodybuilders)
What is nitrogen equilibrium?
healthy people (college students)
What is negative nitrogen balance?
sickly people
What is the RDA for Protein?
0.8 g/kg
What is the AMDR for Protein?
10-35%
Marisa weighs 135 lbs. She is currently eating 50 g of protein daily. Is protein intake low, adequate, or high?
adequate protein
Today, Marissa ate 150 g of protein, 200 g of carbohydrates and 50 g of fats. what percentage of her dietary intake is from protein?
32% from protein
What is the consequence of eating too much protein?
Weight gain
What is the consequence of eating too little protein?
protein energy malnutrition
What is celiac disease?
a reaction to the proteins in wheat, barley, and rye
What happens in your body if you have celiac disease when you eat the proteins from wheat, rye and barley?
the villi in the small intestine is damaged and nutrient absorption is limited
How is celiac disease diagnosed?
colonoscopy
What are the nutrients of concern for vegans and vegetarians?
B12, Vitamn D, Iron, and Zinc
How are fat soluble vitamins transported?
Protein
How are water soluble vitamins transported?
freely in fluids
How are fat soluble vitamins stored?
In the fatty tissues and liver
How are the water soluble vitamins stored?
They are not usually stored
Alex has started the Atkins diet and eats a lot of fat (approx. 120 g.) With the Atkin's diet he lost 10 lbs! He now weighs around 175 pounds and is on a 2800 kcal diet.
What percentage of his calories come from fat?
Is this within the AMDR?
39%, no
What are health benefits from Omega-3 fatty acids?
Omega 3 lowers blood pressure, prevent blood clot formation, protect against irregular heartbeat, reduce inflammation, essential for infant growth. HDL cholesterol lowers inflammation in arteries, lowers risk of heart disease
T or F: Hydrogenation of fats helps them stay fresh longer
True
What are complimentary proteins?
grains and legumes
Tom Werner weighs 265 lbs and eats 62g of protein a day. What is his DRI for protein?
Is he low, adequate, or high?
96.4 g, low
Tom Werner went on a two week vacation down south for a barbeque symposium and now weighs 300 lbs. and is eating 105 g of protein a day.
What is his DRI for protein?
Is he low, adequate, or high?
109 g, adequate
What is hydrogenation?
adding hydrogen- creates trans fats
Why do we hydrogenate?
longer shelf life, helps sensories, more stability
What is an example of a hydrogenated food?
Peanut butter
What are proteins made up of?
amino acids- carboxyl and nitrogen
What are the strengths of being vegetarian?
not eating a lot of saturated fats, eating lots of fruits and veggies
What are the weaknesses of being vegetarian?
lacks B12, dairy, calcium, and you have to be careful with proteins
What are EPH and DHA?
types of omega 3 fatty acids
What is better to have... a high HDL or high LDL?
high HDL
What makes protein different than amino acids?
NITROGEN.... this is important. remember it.
What is high quality protein?
more closely matched by what the body needs
Which would be the highest quality protein for a human?
A. Beef
B. wheat
C. Fish
D. Tree Bark
E. Live crickets
A. Beef