BIO 150 Toxicology
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
List 1 branch other than post mortem toxicology
Clinical toxicology
What is the main focus of postmortem toxicology
Analysis of biological samples (ex blood, for drug, semen, etc.)
What is the main focus of seized drugs analysis
Physical evidence collection & characterization (ex things you can collect and seize for drug analysis)
What questions does toxicology help determine?
1. What was taken?
2. When was it taken?
3. How much was taken?
4. Did this substance contribute to the cause of death?
The questions work together to determine:
1. Manner of death (how did they die)
2. Mechanism of death (in what situation & what was happening in the body)
xenobiotic
Substances that are foreign to the body (any substance, not only poison)
drug
Compound that causes a physiological (or psychological) effect
poison
A substance that when ingested results in a toxic or damaging physiological response aka toxins
Who is Mary Anne Cotton, who did she poison and what did she use to kill?
England’s first serial killer, she poisoned her son (but many people surrounding her died of “gastric distress” which was actually her poison), she used arsenic trioxide to kill
What is "inheritance powder"?
Arsenic because people used it to kill wealthy family members
Arsenic was used to create what color?
Arsenic green/Scheele’s green
List 2 items that this particular arsenic generated color was used to make
1. Clothes
2. Candy
Who is Mathieu Orfila and why is he important to prosecuting poison cases in the 1800's?
Grandfather of toxicology, he studied poisons in general but focused specifically on arsenic (his work laid the groundwork for better understanding toxicology as a field of study)
What test did Mathieu Orfila use to identify the cause of death in the Marie Lafarge murder case?
The Marsh test: detection that was sensitive enough to detect small amounts of arsenic in food, tissue, or the stomach contents
What is the key indicator created as the product of the test used by Mathieu Orfila to determine the presence of arsenic in Marie Lafarge's dead husband?
Presence of the black mirror of arsenic (arsenic trioxide)
List 3 reasons why arsenic is an ideal poison to use in food
1. Colorless and tasteless — easily concealed in food.
2. Commonly available in household products.
3. Causes symptoms similar to illness, making it hard to detect.
What is an isotope? How many does Arsenic have?
An isotope is a variation of an element, arsenic has a few isotopes (33)
List 2 characteristics of covalent bonds
It creates stable molecules.
It allows bonding between nonmetals.
What is the difference between a polar bond and non-polar bond?
Nonpolar bond results from an even/equal sharing of electrons, polar means there is an unequal sharing
What are 2 other socially acceptable (without homicidal intent) uses of arsenic?
Cancer treatments & pesticides
List 3 modes of entry for a drug.
1. Inhalation (through nose)
2. Oral (through mouth)
3. Dermal Entry (through skin)
What is “the first pass” effect?
The first pass effect is when the liver metabolizes a drug before it reaches systemic circulation, reducing its potency
What organ is primarily involved in the first pass effect
The liver
List 2 contributing factors to toxicity in poisoning
1. Mode of ingestion
2. Body weight
What are opiates derived from; give an example
Poppy seed pods of the opium plant; heroin
What is the difference between an opiate and an opioid?
Opiates are a subset of opioids (opiates are naturally derived; opioids can be natural or synthetic)
What effect does the drug naloxone have on opioids?
It immediately reverses effects of opioids
ADME
Administration
Distribution
Metabolism
Excretion
Absorption phase
high is occurring; physiological changes/effects are actively happening
Postabsorption phase
beginning of decline of physiological response as body eliminates drug
Metabolite
Resulting waste as a product of breakdown of drugs in the body
What can metabolites tell us about a death caused by a drug?
The presence and type of metabolites help forensic toxicologists determine time since ingestion and whether the person died from an overdose or from delayed toxic effects.
Some drugs are metabolized very quickly, so identifying their metabolites may be the only way to confirm drug use before death.
Where in the body is the primary location for the metabolism of drugs?
The liver
List 3 places in the body that drug metabolites can be found.
1. Hair
2. Brain
3. Nails
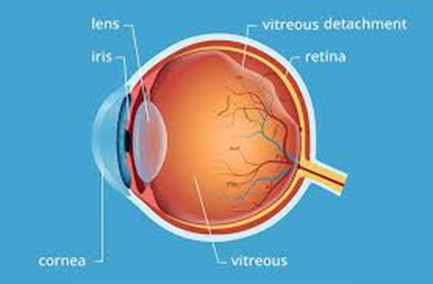
Where is vitreous humor located in the body?
In the eye
What is a key advantage of vitreous humor collection when testing for drug metabolites?
The eyeball is isolated anatomically, and drugs can get trapped in the vitreous humor, making it a reliable sample to collect (eye is one of the last things to deteriorate during decomposition)
Where is the vitreous humor?