Week 10: Caring for People with Biliary and Pancreatic Disorders
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Ursodeoxycholic acid (ursodiol)
long term therapy for cholelithiasis
dissolves cholesterol in gallstone, -oral bile duct dissolution therapy
-Must have a patent cystic duct, ultra sound q6 mo in first year to determine effectiveness
-report diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain (radiating to shoulders) IMMEDIATELY
-take with food and milk
Pancrelipase
pancreatic enzyme replacement for chronic pancreatitis
-administer with every meal or snack
-monitor for steatorrhea
-control diabetes w insulin if developed
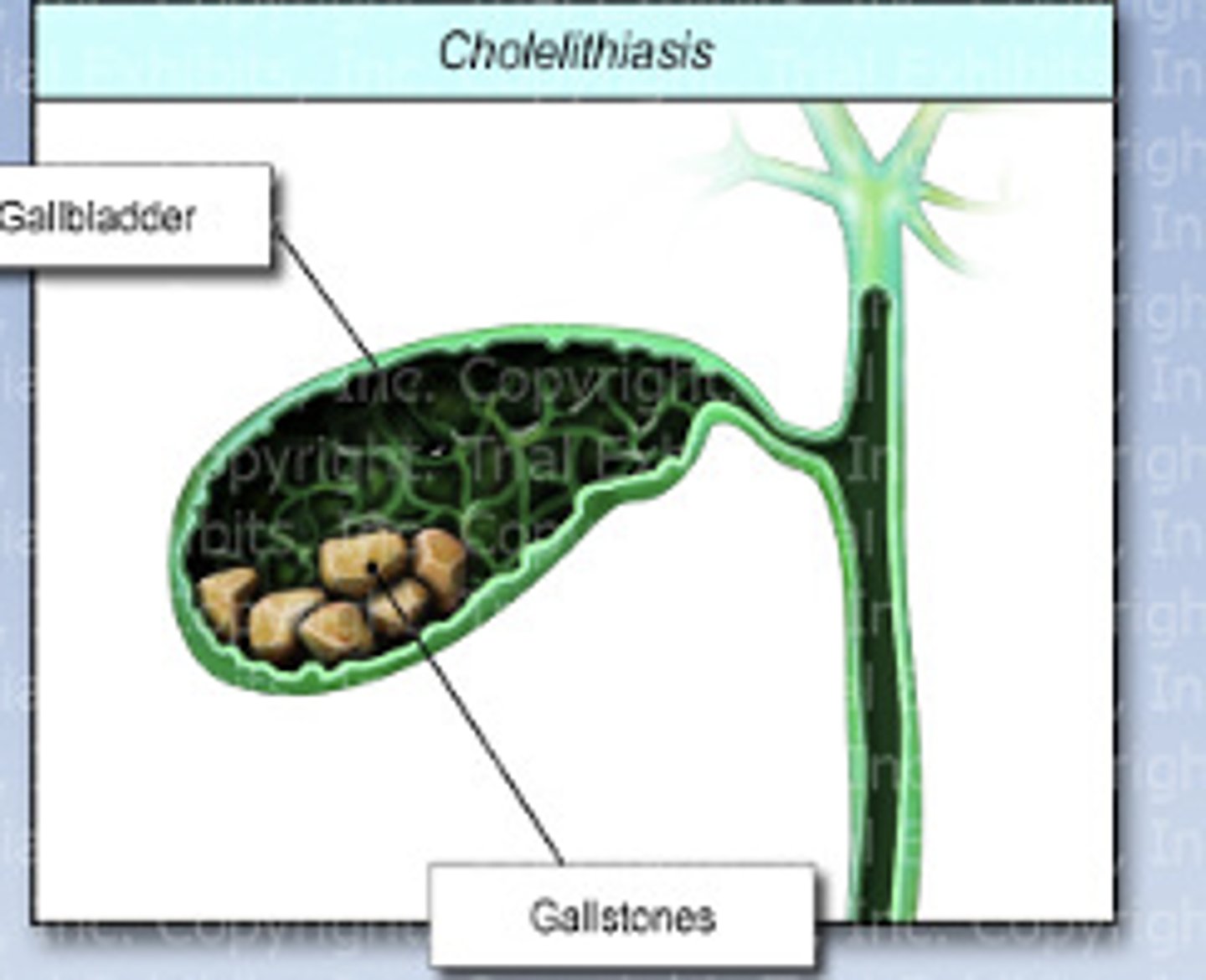
Gallstones
stones that develop when stored bile crystallizes
-mostly made of cholesterol
Hepatolothiasis
The presence of gallstone in the biliary ducts of the liver
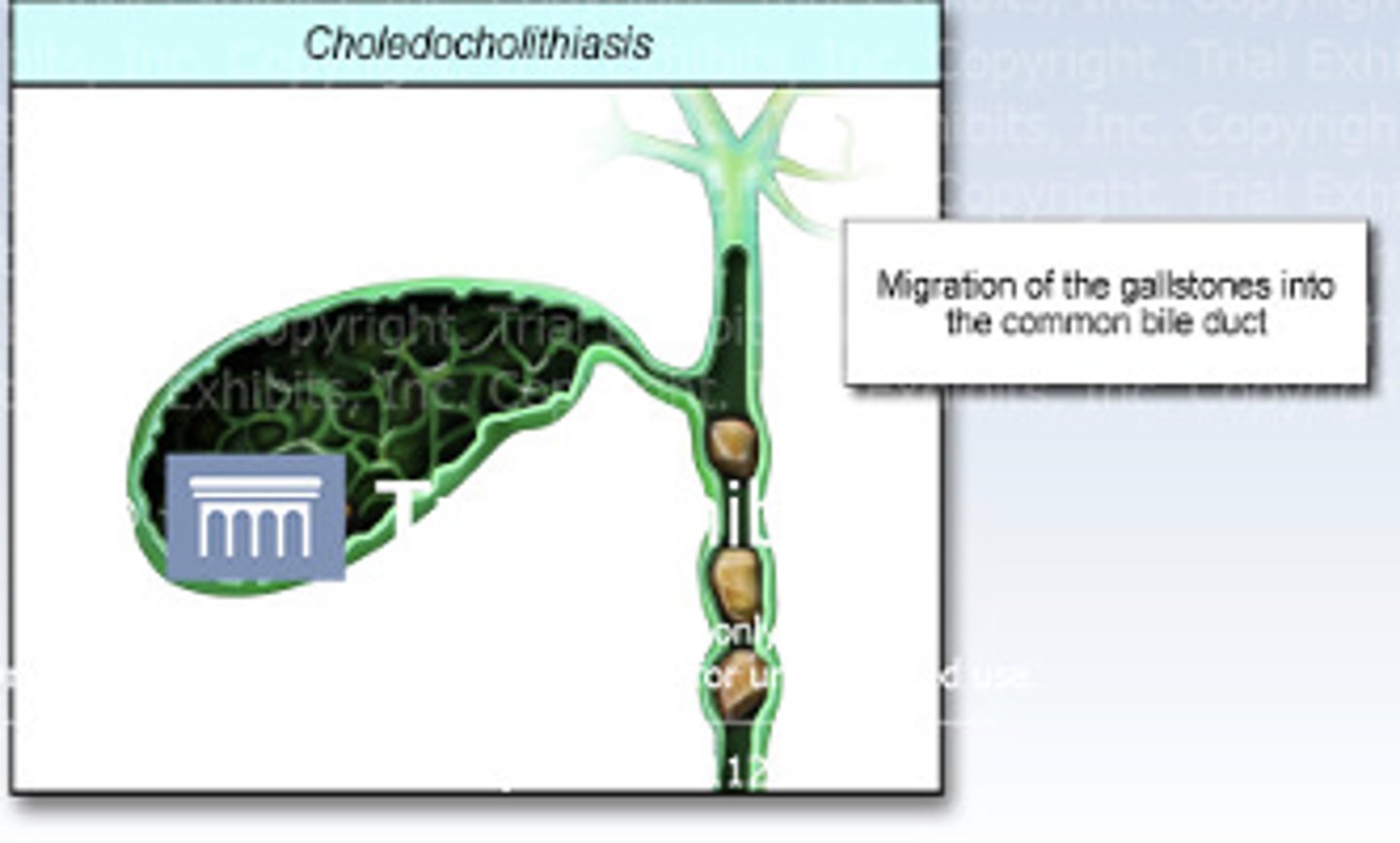
Choledocholithiasis
the presence of gallstones within the common bile duct
Cholelithiasis
The presence of one or more gallstone in the gallbladder or biliary ducts
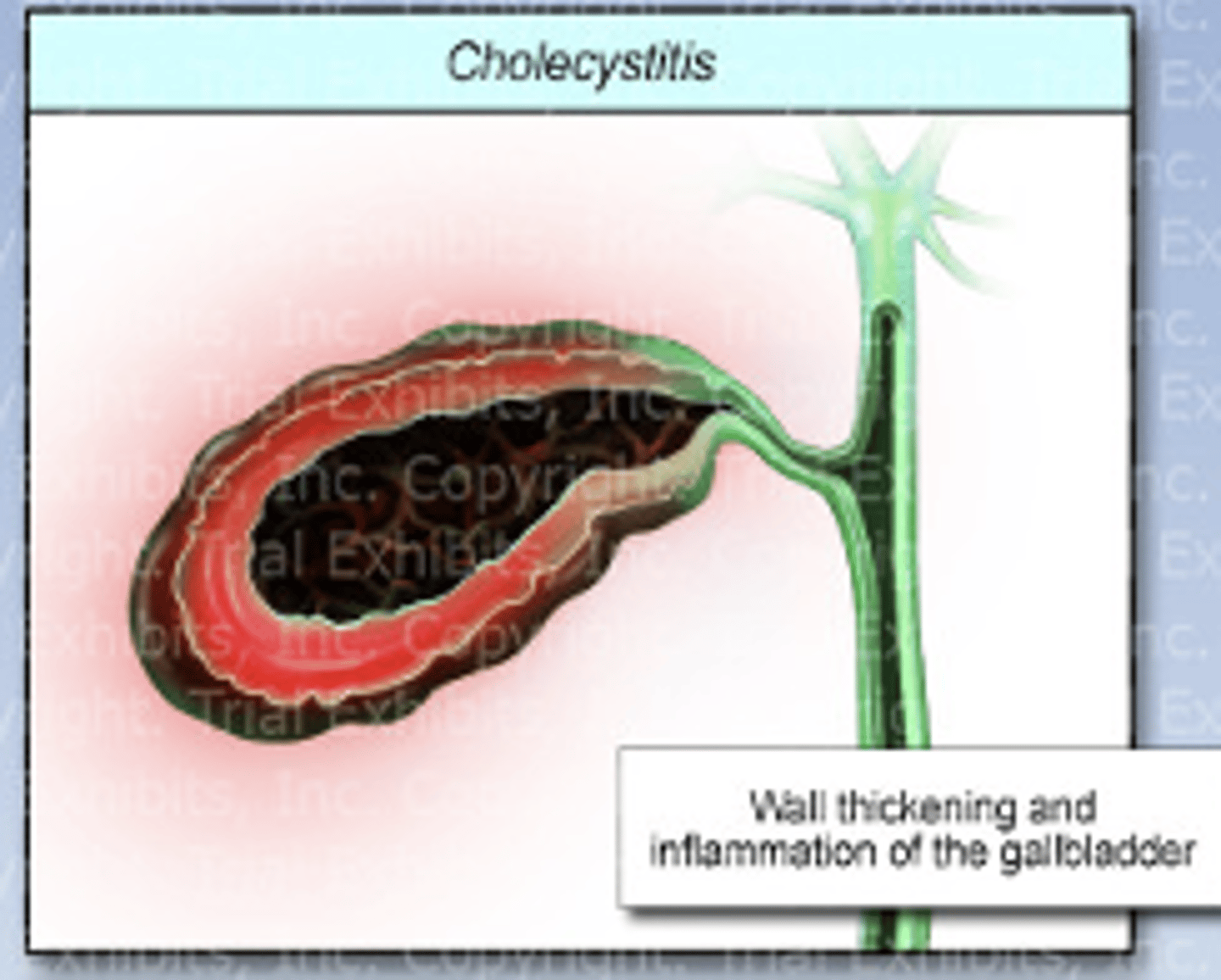
Cholecystitis
inflammation of the gallbladder
-caused by gallstone obstruction or stasis
Cholecystectomy
surgical removal of gallbladder
-indicated for cholelithiasis or cholecystitis
Lithogenic state of gallstone disease
conditions set to favor gallstone formation
-estrogen meds/female
-over age 40
-pregnancy
-overweight
-rapid weight loss
-having diabetes
4 stages of gallstone disease
Lithogenic state
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic
Complicated cholelithiasis
S/s of Cholelithiasis
-usually asymptomatic
-episodes of moderate to severe pain (biliary colic)
-RUQ epigastric pain may go to shoulder
-lasts LESS than 6 hrs
-occurs after fatty meal
-nausea, vomiting
-unreliavable pain
-belching and bloating
S/s of Choledocholithiasis
-moderate to severe pain
-RUQ or epigastric pain may go to shoulder
-lasts LONGER than 6 hrs
-pain, belching, nausea, vomiting
S/s of Choledocholithiasis if gallstone completely blocks common bile duct:
-jaundice
-clay colored stool
-dark/brown amber urine
-fat in stool (steatorrhea)
S/s of cholecystitis
-moderate to severe pain
-RUQ or epigastric pain may go to shoulder
-lasts LONGER than 6 hrs
-pain, belching, nausea, vomiting
-possible jaundice
-fever
-tachycardia
-rebound tenderness
Laboratory Tests for Cholelithiasis
-Conjugated= ELEVATED
-Unconjugated= ELEVATED
-liver function= ELEVATED
-amylase= ELEVATED
Laboratory Tests for Cholecystitis
-WBC ELEVATED
-Conjugated= ELEVATED
-Unconjugated= ELEVATED
-liver function= ELEVATED
-amylase= ELEVATED
Treatment for Asymptomatic cholelithiasis:
no treatment needed
Treatment for Symptomatic cholelithiasis:
-cholecystectomy is recommended
-for patients no surgery:
-antibiotics
-opioids
-Urosdeoxycholic acid
-ERCP
What is Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP):
diagnosis and removal of gallstones
Nursing considerations for cholecystectomy:
-NPO
-IV antibiotics
-often same day surgery
-pain management
-antiemetic management (clear liquids once awake)
Open Cholecystectomy:
-hospital stay is longer
-avoid heavy lifting 4 to 6 weeks
-t tube placed for patency
Nursing considerations for life without gallbladder:
-liver will still make bile
-patients may experience chronic diarrhea
-gradually increase food from clear liquids to regular diet
-eat smaller more frequent meals
Pancreatitis
inflammation of the pancreas
-pancreas enzymes become activated while still in the pancreas causing digestion of the pancreas
How does pancreatitis occur?
-choledocholithiasis
-alcohol use
Pain associated w/Pancreatitis:
-dull, boring, deep, piercing pain
-LUQ or epigastric pain may radiate for back
-severe 8 to 10
-sudden but persistent pain
S/s of pancreatitis:
-hypoactive bowel sounds
-LUQ epigastric pain
-nausea, vomiting
-abdominal distention
-mild jaundice
-hypocalcemia = hyperreflexia
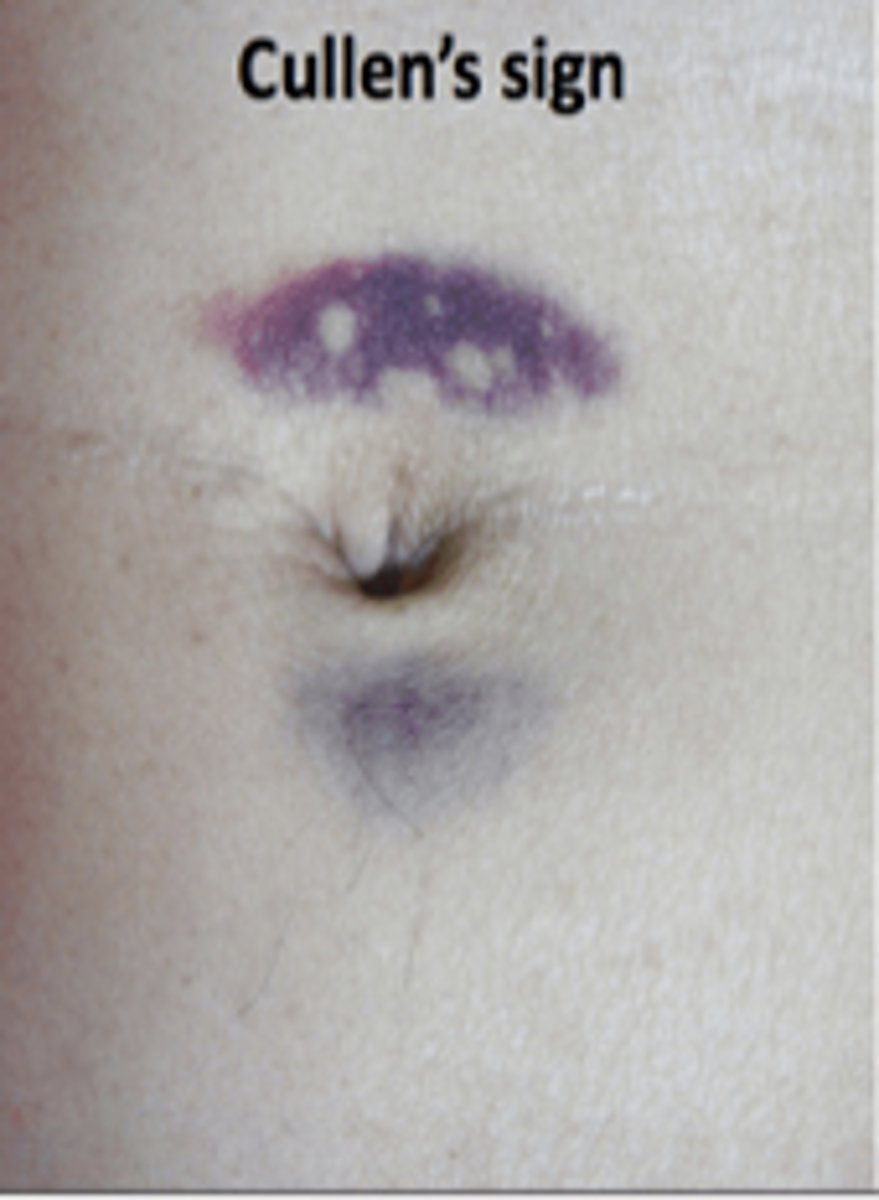
Cullen sign
Bluish peri umbilical discoloration from blood in the peritoneal cavity
PANCREATITIS SIGN
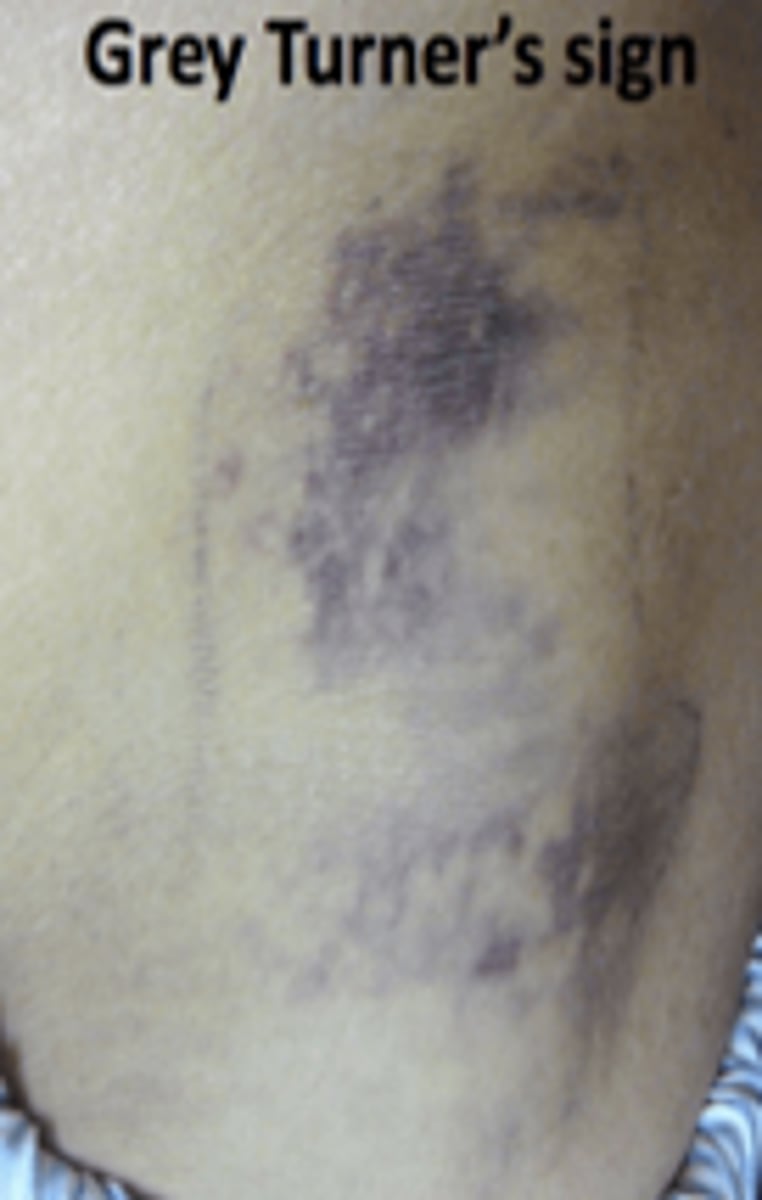
Grey turner sign
Bluish discoloration of the flanks from retroperitoneal hemorrhage
PANCREATITIS SIGN
Lab values for pancreatitis:
-WBC= ELEVATED
-Liver enzymes (AST/ALT)= ELEVATED
-ALP= ELEVATED
-Bilirubin= ELEVATED
-Amylase= ELEVATED
-Lipase= ELEVATED
Nursing considerations for pancreatitis:
-pain management
-balance electrolytes and volume due to vomiting
-anti nausea meds
-monitor for acute substance withdrawl syndrome
-place patient on NPO (surgery)
Psudocyst
an encapsulated collection of pancreatic secretions that forms in or around the pancreas
S/s of pseudocyst
-persistent abdominal pain
-nausea and vomiting
-elevated amylase
-low grade fever
ASSOCIATED WITH ACUTE PANCREATITIS
Chronic pancreatitis
-a long-standing inflammation of the pancreas that alters the normal structure and functions of the pancreas
-often associated with chronic alcohol abuse
S/s of chronic pancreatitis:
-chronic abdominal pain (upper abdomen or back pain)
-nausea and vomiting
-mild jaundice
-may develop diabetes
-fatty stools and weight loss
Nursing considerations for chronic pancreatitis:
-pain management
-no alcohol
-no smoking or caffeine
-bland low fat diet
-small frequent meals
-if diabetes: use insulin
Nursing considerations for t-tube:
-the drainage in the t-tube should be yellow/green
-t tube should be placed in common bile duct
-bag should be below or at patients waist level